Huawei Yang Ping: Rooting Smart Manufacturing with an Open Ecosystem
![]() 12/09 2024
12/09 2024
![]() 454
454
As an important pillar of the national economy, industrial manufacturing is facing unprecedented challenges and opportunities amid rapid changes in the global economy and technology. Major economies and emerging market countries are actively planning reindustrialization strategies, hoping to find new drivers of economic growth through technological revolutions. The rapid development of digital and intelligent technologies has promoted the cross-integration and deep penetration of technologies, making smart manufacturing the main theme of reindustrialization.
Against this backdrop, Huawei, as a global leading ICT (Information and Communication Technology) infrastructure provider, has not only demonstrated its technological prowess through its practices in the field of smart manufacturing but also provided valuable experience for the digital and intelligent transformation of the entire manufacturing industry.
On December 3, Huawei's China Enterprise Business Group held a media briefing on smart manufacturing in Chongqing with the theme of "Digital and Intelligent Manufacturing at Your Fingertips." Yang Ping, General Manager of Huawei China Enterprise Business Group's Smart Manufacturing System Department, shared Huawei's experience and gains in practicing digital and intelligent transformation in manufacturing and helping client companies achieve the same. This is of great reference value to many enterprises that are hesitant or unable to embark on digital and intelligent transformation due to various reasons.
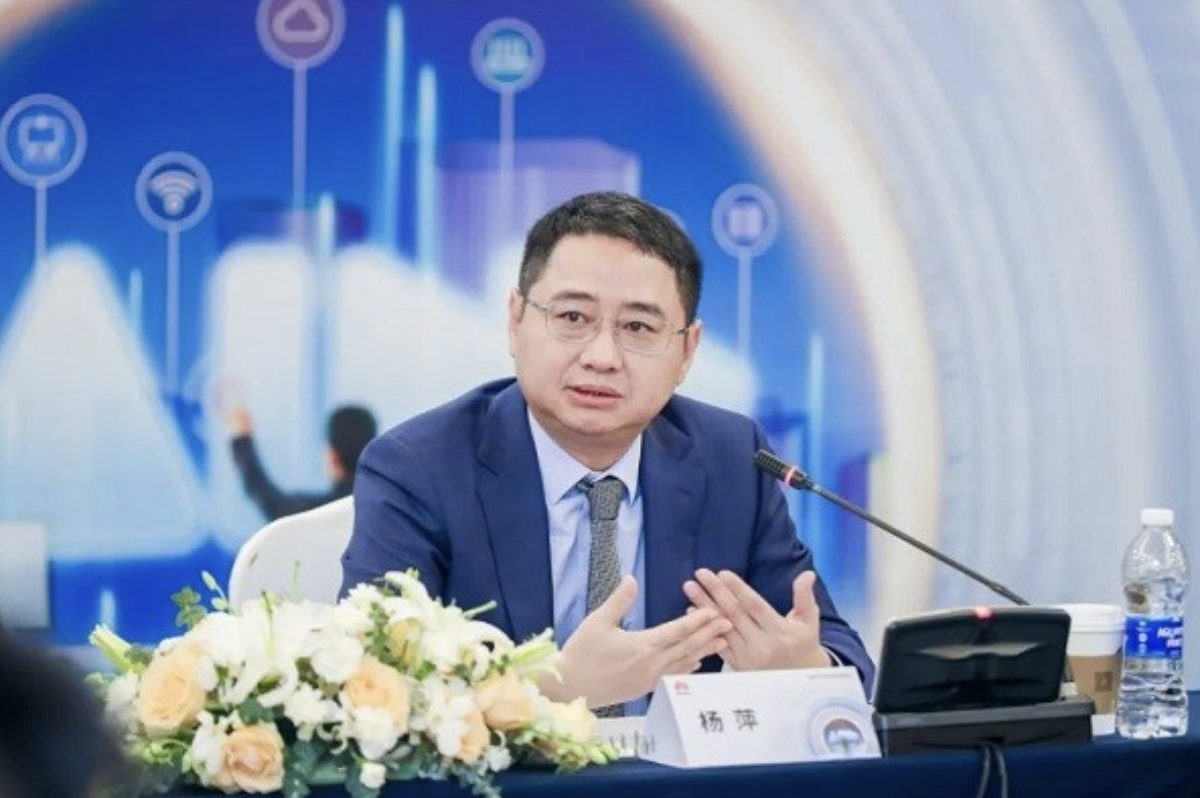

Yang Ping, General Manager of Huawei China Enterprise Business Group's Smart Manufacturing System Department
Intelligent Upgrade: A Necessary Task for Manufacturing Enterprises
Since the beginning of this century, significant adjustments in the global economic landscape have forced countries to seek innovative economic development strategies. Especially against the backdrop of slow economic growth, the transformation and upgrading of the manufacturing industry, which is the mainstay of the real economy, has been one of the most important topics of global concern. Exploring the path of transformation and upgrading of the manufacturing industry has also been a long-standing issue in industrial policies around the world.
At this stage, China's manufacturing industry is under double pressure from both domestic and foreign sources. On the one hand, relying on their original accumulation, developed countries' manufacturing industries have taken the lead in digital transformation and upgrading, continuously reducing production costs and increasing technological content, which has resulted in relatively weak international competitiveness for China's manufacturing industry and the risk of being "low-end locked" in the global value chain. On the other hand, with the decline in domestic labor and raw material cost advantages and the arrival of the "Lewis Turning Point," the original extensive development model of the manufacturing industry has been strongly impacted.
In addition, China has shifted to a stage of high-quality development and is in a critical period of transforming its development mode, optimizing its economic structure, and shifting its growth drivers. However, issues such as the low compatibility between manufacturing supply and market demand, challenges to the stability of industrial and supply chains, and tightening constraints on resource and environmental factors have become prominent.
Against this backdrop, the development level of smart manufacturing is directly related to the quality of China's manufacturing industry and is the main focus of building a manufacturing power. The development of smart manufacturing plays an important role in consolidating the foundation of the real economy, building a modern industrial system, and realizing new-type industrialization.
The research team of the "Research on China's Digital Economy Development and Policy" at the Development Research Center of the State Council pointed out: "The development stages of China's manufacturing enterprises vary greatly. Their digital transformation includes not only improving the informatization level of enterprises at a lower development stage but also realizing digitization, networking, and intelligence for enterprises at a higher development stage... Issues such as the lack of authoritative data standards, data security problems that need to be resolved, the need to improve data openness and sharing levels, relatively weak technological foundations and information infrastructure, and severe challenges to employment still exist, hindering the further advancement of digital and intelligent transformation in manufacturing."
One of the effective ways to solve the above problems is to promote the concept of "the wise leading the less wise." Pioneers in digital and intelligent transformation, represented by Huawei, have already summed up a set of effective methodologies for digital and intelligent transformation through practice, which can provide a favorable reference for other enterprises on how to effectively "avoid pitfalls" and "speed up" the path of digital and intelligent transformation.
Huawei: Why Deepen Involvement in Manufacturing?
Huawei's China Enterprise Business Group proposed the slogan "Deepen Involvement in Manufacturing, Root Smart Manufacturing" early on. Yang Ping mentioned that this decision was backed by a strong sense of responsibility and mission.
As a global leading ICT (Information and Communication Technology) infrastructure and intelligent terminal provider, Huawei itself is a manufacturing enterprise with strong R&D attributes.
Huawei's business scope covers to B businesses such as 5G, cloud services, computing, and storage, as well as to C businesses such as terminals and automotive BU. The company's extensive business scope forms a complex business network in sales, supply chains, and services. Without actively introducing new technologies and tools, it would be unimaginable to coordinate such a huge industrial chain.
Yang Ping introduced that Huawei began a business management transformation focused on informatization in the 1990s, building information systems such as IPD R&D process management and ISC supply chain management.
Huawei's true digital transformation started in 2014.
In this year, Huawei decided to implement a "breakthrough" action based on its existing connectivity business, entering the computing field, incorporating servers, storage, and other IT equipment into its product line, and setting two "100 billion" goals: to achieve 10 billion yuan in revenue in both the ICT and terminal business areas. To better achieve this goal and prevent the company from experiencing "entropy increase" issues due to business expansion, the need for comprehensive digital transformation emerged.
Huawei first established a full-scale, full-factor connectivity and real-time feedback system throughout the company, fully connecting over 6 million pieces of equipment from hundreds of brands in the production field, as well as dozens of communications between these equipment, laying the foundation for the subsequent interconnection of production data between factories.
On this basis, Huawei initiated data governance-related work and established a top-level data governance architecture. This architecture defines in detail the business object model (BOM) for each piece of data, clarifies the scope of responsibility for BOM-corresponding data, and stipulates the circulation methods of data between different departments. This system ensures that various industries, different groups, and functional departments can effectively communicate through a unified data platform.
Finally, Huawei also built a comprehensive security system. To ensure data security, the company implemented a multi-layer protection strategy to prevent outside attacks and threats from penetrating, being visible, being taken away, being defeated, being destroyed, and being untraceable.
Thus, Huawei created its first "T," namely, the capability of data governance and data platforms.
With the development and breakthroughs in artificial intelligence technology, especially generative AI technology, Huawei initiated an AI upgrade strategy across the entire group in 2018. It proposed upgrading the AI data governance system, deeply integrating AI models with data toolchains, and building on traditional data governance and data platforms by adding a layer of AI security governance and AI data toolchains. Based on Huawei Cloud's new AI computing platform, it constructed new enterprise AI data services, creating Huawei's second "T," namely, AI model and platform services, as well as AI governance and security capabilities.
In the process of carrying out its own digital and intelligent transformation with new technologies and tools, Huawei actively summed up experiences, refined methodologies for digital and intelligent transformation, and gradually expanded into a new business. While achieving its own iteration and evolution, Huawei also looks forward to contributing its experience and technological accumulation to China's journey from a manufacturing giant to a manufacturing power.
By providing traditional manufacturing enterprises with the computing, artificial intelligence, operating systems, databases, cloud, large models, and other technologies and resources required for digital and intelligent transformation, Huawei enables domestic traditional manufacturing enterprises to be independent in terms of basic software and hardware and possess globally advanced technological infrastructure. This is the fundamental reason for Huawei's deep involvement in manufacturing.
Huawei: How to Root Smart Manufacturing?
Yang Ping believes that digital and intelligent transformation is an ongoing process with no end. Relevant enterprises must adhere to the general principles of strategy as the foundation, data as the basis, and intelligence as the direction, and keep moving forward in practice.
To better promote the digital and intelligent transformation of manufacturing enterprises, Huawei has been actively exploring the application of digital and intelligent technologies in various aspects and scenarios of enterprises. It has also actively expanded its ecosystem, collaborating and empowering enterprises in various fields such as R&D, production, supply, sales, and services, and has already served over 7,500 manufacturing customers in China.
Yang Ping shared Huawei's cooperative practices in the automotive, pharmaceutical, and robotics industries.
At the Changan Automobile Smart Factory in Yubei District, Chongqing, Huawei, relying on its own experience in digital and intelligent transformation, assisted Changan Automobile in connecting the "three flows" of engineering data flow, production process flow, and commercial information flow based on the advanced architecture of the "one cloud, one network, one platform" smart factory solution, empowering the smart factory to build new capabilities for smart manufacturing. This accelerates the customer's achievement of industry-leading flexible manufacturing capabilities, enabling the production of high-quality smart cars while adapting to rapid market changes and building the company's core competitiveness.
In pharmaceutical research and development, Huawei has created a Pangu large pharmaceutical molecule model for pharmaceutical companies in drug molecule structure discovery, clinical trials, and genetic sign analysis. This model has been trained on over 1.7 billion pharmaceutical molecule data points, making it the largest pharmaceutical molecule model. It can effectively help pharmaceutical enterprise customers solve chronic problems such as long R&D cycles and high costs in traditional pharmaceutical research and development.
Based on Huawei's own IPD process experience, Huawei has effectively helped leading robotics enterprises reshape their structured R&D processes, achieving collaborative management of R&D quality and production quality. This allows customers to reduce R&D costs while significantly improving R&D effectiveness.
Yang Ping mentioned that in the future, Huawei will continue to deepen its ecosystem, focus on its strengths in complex hardware infrastructure and software infrastructure, and work together with thousands of manufacturing-oriented partners to complete the construction of an overall solution from the bottom layer to application development.
To root smart manufacturing, Huawei is also actively promoting the cultivation of digital and intelligent talents. It strives to accumulate sufficient talent reserves for the digital and intelligent transformation of the manufacturing industry by being application-driven and technology-supported. It has created three talent development systems for digital and intelligent management, applications, and technologies, targeting eight types of people in the manufacturing industry, including managers, architects, developers, operation and maintenance personnel, and ecological partners, and addressing the three different stages of enterprise digital and intelligent transformation (planning, construction, and operation). Over the past three years, it has trained over 20,000 digital and intelligent talents for manufacturing enterprises and universities.
Conclusion
With the in-depth development of a new round of technological revolution and industrial transformation, smart manufacturing has become the commanding heights of technological innovation in the global manufacturing industry, and its development has become an inevitable trend in the transformation of the global manufacturing industry. For traditional manufacturing enterprises, this is no longer a choice but a necessary task. Although the transformation process faces many issues, domestic traditional manufacturing enterprises still operate in a relatively favorable environment, with support and guidance from various national policies as well as digital and intelligent transformation solution providers such as Huawei, which can help enterprises embark on the path of digital and intelligent transformation better, faster, and more cost-effectively.
It is believed that as digital and intelligent technologies empower the transformation and upgrading of traditional manufacturing industries, smart manufacturing will effectively promote the deep integration of industries and resource elements, promote the formation of new-quality productivity led by science and technology, strongly support the high-quality development of China's new-type industrialization, promote the deep integration of the digital economy and the real economy, as well as the real economy and resource elements, continuously strengthen the foundation of the real economy, and support and lead the construction of China's modern industrial system.