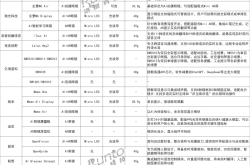
2025 Synopsys SNUG Silicon Valley Conference: AI Pioneers the Future of Chip Design
![]() 03/24 2025
03/24 2025
![]() 541
541
Produced by Zhineng Zhixin
The 2025 Synopsys SNUG Silicon Valley Conference offered a wealth of valuable insights.
Sassine Ghazi, President and CEO of Synopsys, engaged in a thought-provoking discussion with Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft, on the transformative impact of AI in silicon and system design. They highlighted AI's potential to revolutionize chip design innovation, optimize workflows, and accelerate product development, while acknowledging the challenge of managing escalating engineering complexity.
Synopsys showcased its latest AI advancements, including strategic partnerships with Microsoft, NVIDIA, and OpenAI, and the introduction of new platforms such as HAPS 200 and Zebu 200. The company unveiled a roadmap envisioning AI's evolution from a 'co-pilot' to an 'autonomous driver' in chip design, and foresaw the future application of 'Agent Engineers'.
These innovations aim to reimagine the engineering process, from silicon to systems, to meet the complexity and speed demands of the pervasive intelligence era.

Part 1: Synopsys Innovations and AI Collaborations
● The collaboration between Synopsys and Microsoft was a standout feature of the SNUG Silicon Valley 2025 Conference, marked by significant strides in optimizing EDA tools and accelerating chip design.
Synopsys optimized its EDA products for Microsoft's Azure cloud platform, leveraging Azure's robust computing capabilities to drastically reduce design time and cost. Sassine Ghazi emphasized in his speech that this optimization not only benefits Microsoft's datacenter chip design but also aids semiconductor customers using Azure, lowering their total cost of ownership (TCO).
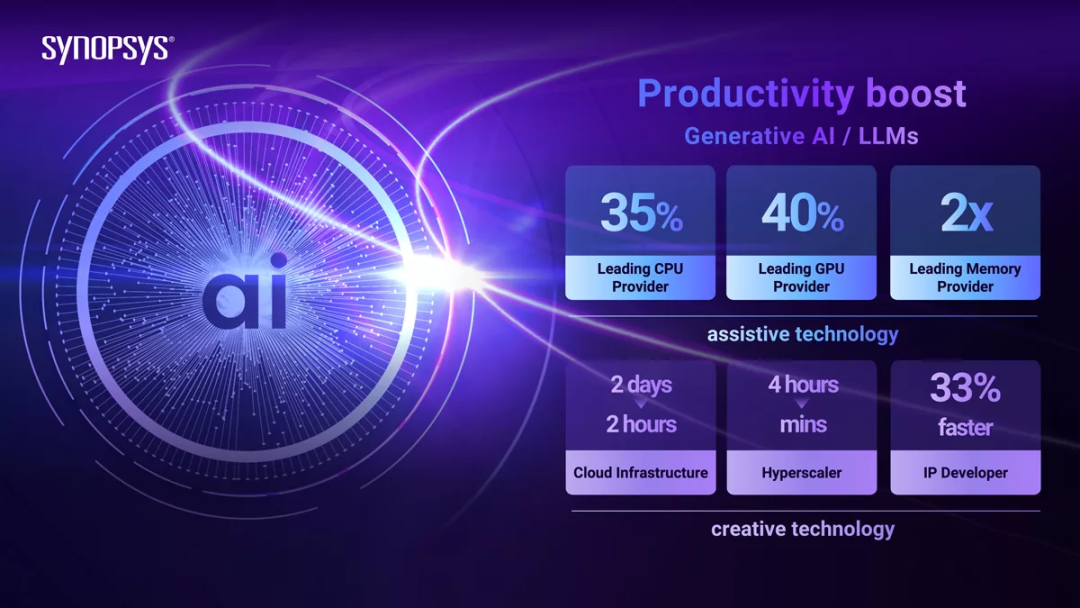
Synopsys and Microsoft collaborated to introduce Copilot technology into chip design, unveiling the Synopsys.ai Copilot knowledge assistant. This assistant has enhanced productivity by 35% to 40% for top customers, with one leading memory supplier experiencing a doubling of efficiency.
Synopsys.ai Copilot efficiently supports engineers by reducing hours-long tasks to minutes through natural language interaction and intelligent suggestions, maintaining high design quality standards.

● Synopsys' collaborations with NVIDIA and OpenAI further extend its footprint in AI.
◎ NVIDIA, a leader in AI computing, integrates its GPU technology with Synopsys' EDA tools, providing robust support for AI-driven design automation and optimization.
◎ OpenAI's large language models (LLMs) lay the groundwork for Synopsys to develop smarter design assistants.
Ghazi emphasized that these collaborations aim to create AI agents tailored to the semiconductor market, addressing the complexity of chip design. By combining NVIDIA's computing power with OpenAI's generative AI technology, Synopsys is developing tools capable of autonomously completing design tasks, catalyzing the transition from human-led to intelligent chip design.
These collaborations not only bolster Synopsys' technological prowess but also offer forward-thinking innovative solutions to its customers.
● Synopsys launched the HAPS 200 and Zebu 200 platforms to enhance verification efficiency in chip design and expedite time-to-market.
◎ HAPS 200 is an advanced hardware prototyping platform that aids customers like Arm and NVIDIA in early hardware and software co-verification, shortening the development cycle.
◎ Zebu 200 is a high-performance simulation platform designed for complex system-level verification, capable of managing verification needs for tens of billions of transistors.
The launch of these platforms underscores Synopsys' continuous innovation in verification technology, assisting customers in navigating the complexity and time pressures of modern chip design. Ghazi mentioned in his speech that Arm and NVIDIA have adopted these platforms, reporting significant improvements in verification efficiency, reducing verification cycles from months to weeks.
Synopsys' AI technology has demonstrated its value in numerous customer cases, with customers using Synopsys.ai experiencing notably enhanced productivity and shortened design cycles when tackling complex designs.
Ghazi shared a specific case: a leading semiconductor company utilized Synopsys.ai tools to reduce its AI chip design time by 30% while optimizing performance and energy efficiency.
This achievement is attributed to the deep integration of AI in the design process, encompassing automated RTL generation, testbench development, and performance optimization. Through these applications, AI not only enhances design efficiency but also assists engineers in managing complexity, setting a new benchmark for the chip design industry.
Part 2: AI's Application in Chip Design and Future Trends
The vision for AI's transformation from a 'co-pilot' to an 'autonomous driver' in chip design borrows from the development trajectory of autonomous vehicles.
In 'co-pilot' mode, AI assists engineers in design tasks such as code generation or parameter optimization. In 'autonomous driver' mode, AI will possess autonomous decision-making capabilities, capable of independently completing the entire design process. Synopsys is achieving this transformation through the development of 'Agent Engineers'.
● Ghazi delineated this transformation into five stages (L1 to L5):
◎ In L1 and L2 stages, AI provides basic assistance and support for specific tasks.
◎ In L3 stage, multiple AI agents collaborate to solve cross-domain problems.
◎ In L4 stage, AI initiates planning and adaptive learning.
◎ In L5 stage, AI achieves fully autonomous design. The roadmap envisages a profound shift from human-led to AI-driven chip design.

The innovative concept of Agent Engineers involves AI-driven assistants collaborating with human engineers to tackle increasingly complex challenges. Ghazi outlined the development roadmap for AI in semiconductor design, cleverly likening it to autonomous driving levels:
◎ Level 1: Co-pilot AI: AI primarily aids engineers in generating testbenches, debugging code, and effectively boosting workflow efficiency.
◎ Level 2: Action AI: AI gains the ability to autonomously execute specific tasks, such as rectifying signal integrity violations or optimizing power consumption.
◎ Level 3: Multi-agent AI: Different AI agents collaborate to optimize workflows across logic design, verification, and power analysis.
◎ Level 4: Autonomous AI: AI begins making independent design decisions, significantly reducing the need for human intervention.
◎ Level 5: Full Automation: AI-driven design automation reaches its ideal state, autonomously completing the entire chip design cycle from architecture planning to manufacturing.
'Agent Engineers' are a core innovation proposed by Synopsys, enhancing design efficiency and innovation through the collaboration of AI agents and human engineers. These AI agents focus on specific tasks such as RTL generation, testbench development, and assertion verification, thereby alleviating the workload on engineers.
For instance, in L1 and L2 stages, Agent Engineers can assist in generating documentation or rectifying design errors; in L3 and L4 stages, multiple agents collaborate to optimize signal integrity and timing convergence; in L5 stage, Agent Engineers will autonomously reason and execute complete design tasks.
Ghazi stressed that this model not only improves efficiency but also addresses the shortage of engineering talent. In the future, Agent Engineers will become 'super assistants' to human engineers, propelling chip design into an era of intelligence.
The complexity of chip design and the pressure of product cycles are escalating, rendering traditional workflows unsustainable.
AI assists engineers in addressing these challenges through automation and intelligence. For example, Synopsys.ai tools can swiftly explore design spaces, optimize performance, power, and area (PPA) trade-offs, and predict potential issues, minimizing late-stage iterations.
Furthermore, AI accelerates the verification process by shortening verification cycles through simulation and analysis.
Ghazi noted that AI is not merely an efficiency tool but also an innovation catalyst, enabling engineers to concentrate on high-value tasks such as architecture design, thereby driving industry progress.
AI's Application in Silicon Lifecycle Management (SLM) and Processor Optimization
SLM monitors chip health in real-time through embedded sensors, particularly in 3D ICs, predicting failures and enhancing reliability. For instance, in datacenters or automotive applications, SLM can monitor chip temperature and stress to prevent failures due to overheating. Synopsys plans to optimize CPUs, GPUs, and Quantum Processing Units (QPUs) to adapt to AI-driven workload demands.
Ghazi stated that future chip design will increasingly rely on AI optimization, achieving full lifecycle management from design to operation, pushing the industry towards higher performance and efficiency.
Conclusion
The 2025 Synopsys SNUG Silicon Valley Conference painted a compelling picture of AI-driven transformation in chip design. Through collaborations with industry giants such as Microsoft, NVIDIA, and OpenAI, Synopsys is spearheading the innovation wave in the EDA field.
AI not only aids engineers in managing complexity and enhancing efficiency but also presents possibilities for future design paradigms through 'Agent Engineers' and the 'autonomous driver' vision. AI will play an increasingly pivotal role in chip design, propelling the industry towards new heights of intelligence, efficiency, and sustainability.
With its forward-looking strategy and robust technological capabilities, Synopsys continues to provide exemplary solutions for customers, helping the semiconductor industry embrace the opportunities and challenges of the pervasive intelligence era.