Digital Banks: Innovative Drivers of Sustainable Development in the Financial System
![]() 08/06 2024
08/06 2024
![]() 688
688
Since the beginning of the industrial era, humanity has witnessed three industrial revolutions. Centered on mechanization, electrification, and informatization, respectively, these revolutions have had a revolutionary impact on the three major factors of production and their combinations, driving profound and comprehensive transformation and upgrading of social and economic structures and significantly enhancing total factor productivity.
The financial sector is also undergoing dynamic changes. Today, driven by the wave of digitization, the financial industry is undergoing transformation and upgrading, with digital banks emerging as a force that cannot be ignored.
Over the past decade, the number of digital banks has increased significantly, and their share in the financial system has gradually grown.
Recently, Oliver Wyman and WeBank jointly released the "Global Digital Banking Development and Innovation Trends Report" (hereinafter referred to as the Report). Based on a sample study of 235 digital banks worldwide, the Report reveals the development experience of digital banks over the past decade and explores their future development trends.
Innovators in the Financial System
Europe witnessed the establishment of the first batch of digital banks.
Between 2010 and 2015, driven by the development of fintech and regulatory support, Europe saw the emergence of a number of digital banks, including Monzo, OakNorth, Starling Bank, N26, and Revolut, which have collectively attracted hundreds of millions of customers since their establishment.
At the same time, similar new banks offering banking services through fintech companies emerged in markets such as North America, Asia, and South America. In China, digital banks represented by WeBank and MYbank also emerged.
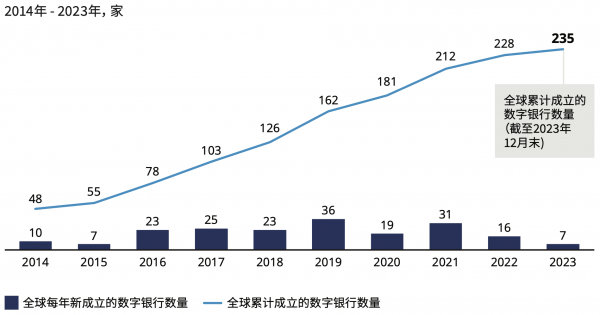
In recent years, the number of global digital banks has increased significantly. According to the Report, by 2023, there were a total of 235 licensed digital banks worldwide, while the number of institutions providing digital banking services more broadly exceeded 300. Asia has become the region with the most digital banks, with approximately 100 in 2023, followed by Europe with approximately 70.
Figure 1: Number of Licensed Digital Banks Worldwide
Digital banks can be classified into two types: native digital banks and derivative digital banks. Native digital banks, typically newly established banks or fintech companies, focus on online services and leverage fintech to provide online financial services to regions underserved by traditional banking and to customers not covered by traditional banking services, such as WeBank and Nubank. Derivative digital banks, on the other hand, are derived from traditional banks.
As digital technology continues to evolve, traditional financial institutions are also leveraging fintech to digitize their existing banking services and enhance their digital capabilities. Digital banks essentially play the role of an "industry catalyst," actively contributing to the digitalization of the financial industry.
Banks have widely adopted large language models and generative AI technology in scenarios such as smart office, code generation, and intelligent customer service. They are actively exploring the application of the metaverse and digital humans in the financial industry, advancing the integration of digital and physical realms, and pursuing ESG goals, thereby accelerating their digital transformation and enhancing support for the digital economy.
It can be said that digital banks have made invaluable contributions to the innovation and development of the financial system. By continuously promoting open-source technology and jointly establishing de facto technical standards, digital banks enhance the international influence of China's technology. Take WeBank as an example. In the process of improving China's open-source innovation ecosystem, WeBank has taken on the role of a pioneer, vigorously promoting the development of open-source technology. By the end of 2023, the bank had open-sourced 36 projects in areas such as AI, blockchain, cloud computing, and big data, attracting over 40,000 stars and over 15,000 forks. These projects not only provide effective technical solutions for various industries but also offer valuable insights for financial institutions engaging in open-source development.
Exploring Sustainable Development through Diversified Paths
Overall, digital banks have been validated and recognized in major markets worldwide. However, due to differences in market environments, inherent strengths, and business choices, global digital banks exhibit diversified development paths.
For example, Chinese digital banks rely on a large population base and a developed mobile internet to serve a leading number of customers globally in their industry. In contrast, some digital banks in Europe and the Americas focus on niche markets, serving fewer customers but achieving better profitability.
The Report concludes that in recent years, global digital banks have continuously explored sustainable business models, diversified business models, unique ecological resources, multi-market coverage, and technological and data infrastructure innovations. These efforts will be crucial in distinguishing leading global digital banks from their competitors.
Firstly, by combining market characteristics and user needs, digital banks can create sustainable business models and diversify their revenue streams. There are roughly two types of business models for digital banks: those relying on large population bases and retail customers as their primary source of income, leveraging economies of scale and technological advancements to improve operational efficiency and achieve profitability once a critical user base is reached; and those focusing on niche markets with smaller populations but higher profitability, specializing in specific customer segments (such as SME financing) or scenarios (such as automotive finance). These models help digital banks find suitable development paths in different market environments, enhancing customer experience and operational efficiency through innovation and technology.
Furthermore, many digital banks are exploring diversified revenue models, including Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS), technology capability exports, and non-financial services for SME customers, to improve profitability and secure higher valuations in the capital market.
Secondly, digital banks leverage their inherent strengths to tap into unique ecological resources and explore multi-market coverage. By integrating with other scenarios within the ecosystem, digital banks can offer seamless service experiences to customers and promote the common development of the ecosystem. In terms of data utilization, while ensuring personal information protection and data compliance, digital banks can leverage alternative data available within the ecosystem to achieve more precise customer acquisition, product pricing, and risk management through big data analysis.
For digital banks with different inherent strengths, approaches to leveraging ecosystems vary. Some European digital banks focus on financial services as an entry point, developing super apps to build ecosystems and provide one-stop solutions for customers. Meanwhile, digital banks derived from traditional banks strengthen their connections with external partners and share ecosystem resources by tapping into the resources accumulated by their parent traditional banks.
Thirdly, digital banks actively participate in the infrastructure construction of data element circulation, serving as innovators. Not only do digital banks play a crucial role in data element circulation, but they can also act as "data circulation facilitators" or "data circulation promoters," driving the sharing of data elements and fostering a healthy data ecosystem. By actively participating in the circulation and sharing of data elements, digital banks can further advance their own development and bring additional benefits to financial infrastructure construction and various application scenarios.
The Evolution of Digital Bank Models
The Report notes that leading digital banks on various continents have moved beyond their startup phases, with top digital banks achieving economies of scale and robust profitability. In the coming years, technical standards and risk management models of global leading digital banks may become industry standards, promoting standardization and unity within the industry and enhancing the overall development level of the digital banking sector.
Concurrently, with the continuous development of technologies and applications such as AI, Web 3.0, IoT, and the Metaverse, innovative applications, products, and services will continue to emerge in the digital banking industry. The Report suggests that the specific forms and business models of digital banks may further evolve with the advent of new technologies, driving further enhancement of industry value.
Figure 2: Outlook for Future Digital Bank Models

As their scale grows and their businesses diversify, leading digital banks are also adopting some traditional banking models. For instance, digital banks in Japan offer offline branch services and ATMs, while virtual banks in Hong Kong, such as WeLab Bank, have begun using relationship managers (RMs) to serve high-net-worth clients. Digital banks in Europe are actively seeking securities brokerage licenses to provide one-stop personal financial services to customers. These initiatives demonstrate the evolution of digital bank business models, as they seek to integrate online and offline services, human and automated services, and comprehensive financial services while maintaining the convenience and low fees that define digital banking.
On the other hand, after more than a decade of digital development and transformation, many leading traditional banks have developed strong technological and data capabilities, continuously exploring and experimenting with new business models. Traditional banks in many markets now offer fully online services, including remote account opening and online lending. These innovative services not only enhance customer experience but also strengthen the competitiveness of traditional banks in the digital era.
For Chinese digital banks, as global digital banks accelerate their pace of development, their leading edge will gradually narrow, and challenges will increase. Responding to the challenges posed by new technologies, standards, and models from digital banks in other regions, as well as serving broader markets, will become key development priorities for Chinese digital banks in the next stage.