Huixing Smart Manufacturing fails to meet performance targets for two years: major customers also serve as shareholders, asset-liability ratio far exceeds peers
![]() 09/19 2024
09/19 2024
![]() 586
586
"Harbor Business Observer" Yang Danni
On September 10, Guangdong Huixing Precision Smart Manufacturing Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as "Huixing Smart Manufacturing") responded to the review inquiry letter. This is the third time the company has received regulatory inquiries since submitting its listing application to Beijing Stock Exchange on October 30, 2023. Its sponsor is Kaiyuan Securities. Huixing Smart Manufacturing is an intelligent manufacturing enterprise engaged in computers, communications, and other electronic equipment. Its major customers include BYD, Guangdong Leyuanheng, TCL Vietnam, etc.
The company's main products are divided into three categories: the first is intelligent conveying logistics systems, the second is system modules, and the third is precision components.
Huixing Smart Manufacturing's transactions with its two major customers, BYD and Leyuanheng, are primarily focused on the first two product categories.
01
Weak solvency, asset-liability ratio higher than industry average
Huixing Smart Manufacturing's prospectus remains at the time of submission. From 2020 to 2022 and the first half of 2023 (the reporting period), the company achieved operating revenues of RMB 123 million, 207 million, 366 million, and 232 million, respectively, with main business revenues of RMB 107 million, 206 million, 363 million, and 232 million, accounting for 86.65%, 99.40%, 99.25%, and 99.94% of total operating revenues, respectively.
During the same period, the company's net profits attributable to shareholders were -RMB 8.5418 million, 5.2853 million, 29.827 million, and 11.8832 million, respectively, with gross margins of 21.19%, 20.42%, 21.82%, and 20.02%, respectively.
In 2023, Huixing Smart Manufacturing achieved operating revenues of RMB 485 million and net profits attributable to shareholders of RMB 34.967 million. While revenues and net profits have improved year after year, the company's top five customers and accounts receivable have also continued to rise. During the reporting period, the sales revenue from the company's top five customers accounted for 12.42%, 19.77%, 49.63%, and 66.31% of total sales revenue, respectively.
The company explained that in 2021 and 2022, with the optimization of routine epidemic control measures, the demand from downstream customers rebounded, and the demand for the lithium battery industry exploded. The company selectively prioritized orders from high-quality customers such as Leyuanheng, Jingshi Electromechanical, and BYD, resulting in an increasing concentration of sales revenue from the company's top five customers.
At the end of each reporting period, the company's accounts receivable balances were RMB 49.3682 million, 73.1441 million, 172 million, and 231 million, respectively.
In terms of aging, most of the balances are concentrated within one year and 1-2 years. The company stated that at the end of each reporting period, the aging of its accounts receivable and contract assets was generally within two years, accounting for 73.15%, 79.65%, 97.43%, and 94.86%, respectively. The aging structure is sound and continues to improve.
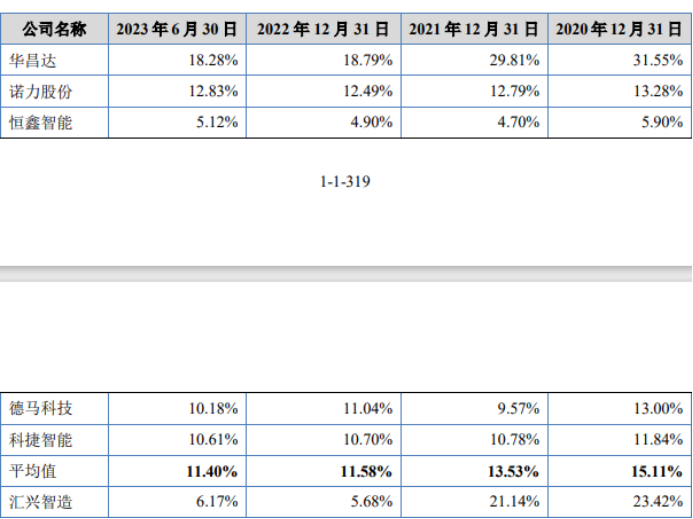
However, it is important to note that there are significant fluctuations in the actual provision ratio for bad debts in accounts receivable at the end of each period for Huixing Smart Manufacturing compared to comparable companies in the same industry. During the reporting period, the actual provision ratios for bad debts in accounts receivable were 23.42%, 21.14%, 5.68%, and 6.17%, respectively, while the average values for comparable companies in the same industry were 15.11%, 13.53%, 11.58%, and 11.40%, respectively.
From a trend perspective, it is evident that the actual provision ratio for bad debts in accounts receivable for the company was initially high and then decreased, while the industry average remained relatively stable within the range of 11%-15%.
Huixing Smart Manufacturing explained that the aging structure of accounts receivable has been optimized. Additionally, during the reporting period, the company discovered that some long-term customers were facing operational difficulties and bankruptcy reorganization during the collection process of accounts receivable. As a result, the company made full provisions for bad debts against their accounts receivable balances. In 2022, the management approved the write-off of RMB 9.7593 million in accounts receivable for which full bad debt provisions had been made, resulting in no large individual provisions for bad debts at the end of the period and an improvement in the quality of accounts receivable.
At the same time, the company's accounts receivable turnover ratio, which is weaker than that of its peers, was 2.11, 3.19, 2.70, and 2.08 for the reporting periods, respectively, while the industry average for comparable companies was 2.65, 3.23, 3.10, and 2.40, respectively.
The company believes that the increase in accounts receivable turnover ratio in 2021 compared to the previous period was due to the increase in downstream demand, leading to rising operating revenues. At the same time, the company maintained strict measures for managing accounts receivable, resulting in slower growth in accounts receivable compared to revenue growth. In 2022, the turnover ratio declined due to a significant increase in revenue from new energy battery industry customers, primarily from clients such as Leyuanheng and BYD, who paid through the Di Chain, prolonging the payment cycle for accounts receivable.
Of greater concern to outsiders is the pressure on Huixing Smart Manufacturing's solvency, particularly as its asset-liability ratio is significantly higher than that of its peers.
At the end of each reporting period, the company's consolidated asset-liability ratios were 68.91%, 77.31%, 77.73%, and 61.33%, respectively, while the industry average for comparable companies was 68.99%, 58.44%, 52.54%, and 53.70%, respectively. It is evident that the industry average asset-liability ratio has continued to decline, while that of Huixing Smart Manufacturing remains relatively high.
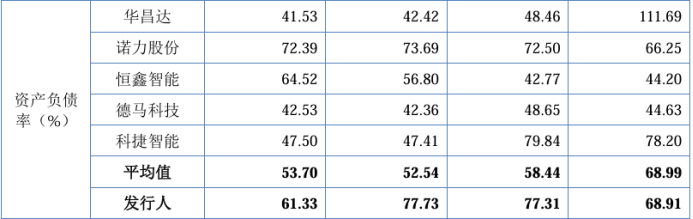
In terms of current and quick ratios, Huixing Smart Manufacturing also lags behind the industry average.
The company stated that during the reporting period, the current and quick ratios were lower than the industry average for comparable companies, and the asset-liability ratio was higher. This was primarily due to the company's business model, which involves staged payments according to contract terms, resulting in large contract liabilities at the end of each period. Additionally, the company prepares for project fulfillment, leading to significant payables. As a result, operating liabilities are relatively high at the end of each period. Furthermore, as a non-listed company, Huixing Smart Manufacturing relies primarily on loan financing, and as the scale of its orders expands rapidly, so does the scale of credit financing.
02
Leyuanheng's surprise investment and soaring revenues amid performance decline risks
Leyuanheng, both a major customer and a shareholder acquired shares just a year before the listing application, forming a unique business relationship with Huixing Smart Manufacturing. However, the third round of review inquiry letters indicates that regulators have concerns about whether Leyuanheng (688499.SH) and BYD (002594.SZ) affect the stability of Huixing Smart Manufacturing's performance.
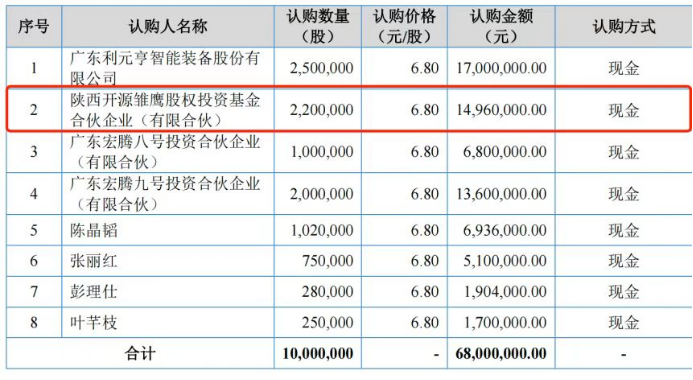
Records show that Leyuanheng began cooperating with the company in 2018 but did not appear in the top five customer list from 2018 to 2021. In 2022, it became the company's largest customer and subscribed for 2.5 million shares of Huixing Smart Manufacturing at a price of RMB 6.8 per share on November 21, 2022, totaling RMB 17 million with a fair value of RMB 18 million, representing a 3.67% stake.
Leyuanheng stated that this investment in Huixing Smart Manufacturing was an industrial investment aimed at acquiring technology, raw materials, or channels along the upstream and downstream of the industrial chain, aligning with its primary business development direction and not considered a financial investment.
Huixing Smart Manufacturing believes that Leyuanheng's procurement scale was approximately RMB 3.5 billion and RMB 3.4 billion in 2022 and 2023, respectively. The issuer obtained orders through full competition, with some orders won and some lost. The transaction behavior between the two parties did not deviate from market principles due to their shareholding relationship. The key contract terms, such as settlement methods, progress, and critical milestones for project execution, remained unchanged before and after Leyuanheng's investment, indicating that no special treatment was given to the issuer due to changes in shareholding.
The direct impact of being both a shareholder and a core major customer is a surge in sales revenue: During the reporting periods, the revenues from Leyuanheng to Huixing Smart Manufacturing were RMB 40,300, 1,762,600, 96,004,700, and 31,528,800, respectively, with a particularly notable jump from less than RMB 2 million in 2021 to nearly RMB 100 million in 2022.
The prospectus discloses discrepancies between the revenues from sales to Leyuanheng and the procurement payments disclosed in Leyuanheng's annual reports. The differences were -RMB 130,000, -RMB 24,628,900, RMB 25,157,400, and RMB 13,545,700, respectively.
Harbor Business Observer notes that Huixing Smart Manufacturing previously explained that the inconsistency in 2022 was due to Leyuanheng recognizing the "Qinghai Gallery Conveyor Line Project" valued at RMB 24.7016 million as a procurement in 2021. After recognizing revenue in December 2021 based on an abnormal equipment acceptance agreement, Huixing Smart Manufacturing made an accounting error correction and adjusted the revenue recognition to June 2022.
The second round of review inquiry letters also mentioned that during the reporting period, the issuer had 30 projects with cross-year adjustments to revenue recognition timelines, including 11 projects such as the Qinghai Gallery Conveyor Line, which were adjusted to 2022, involving a total contract value of RMB 42.4398 million. In the first-round inquiry response, the issuer failed to specify the initial and final inspection times for the intelligent conveying logistics system as required.
Huixing Smart Manufacturing emphasized that the reasons for cross-year adjustments in revenue recognition timelines were primarily due to shifting revenue recognition from based on delivery notes to based on acceptance document dates. Delays in the acceptance process were primarily due to customers adjusting project progress and product delivery and acceptance timelines based on actual needs during project execution. During the reporting period, the issuer strictly followed its revenue recognition policies and project execution according to contract terms and customer requirements, with no artificial adjustments to acceptance timelines or manipulation of performance.
It is worth noting that the third round of review inquiry letters mentioned significant changes in the company's major customers. Besides BYD and Leyuanheng, other top five customers changed in 2022 and 2023. From 2021 to 2023, the company's sales to BYD were RMB 14,058,400, 51,501,200, and 73,491,700, respectively, while sales to Leyuanheng were RMB 1,762,600, 96,004,700, and 50,654,400, respectively. The significant increase in sales to Leyuanheng in 2022 was due to increased orders from BYD, while the decrease in 2023 was due to changes in BYD's procurement model after 2022, primarily sourcing related equipment or production lines from suppliers.
In 2022 and 2023, the company's sales gross margins to Leyuanheng were 25.33% and 17.79%, respectively, while those to BYD were 17.04% and 12.79%, respectively. Due to a decline in gross margins for power lithium battery equipment business, large provisions for inventory impairment and credit losses, Leyuanheng's net profit attributable to shareholders after deducting non-recurring items was -RMB 195 million in 2023.
The review inquiry letters pointed out that considering changes in procurement models of major customers such as BYD and Leyuanheng, the company's market and industry chain position, market competition, customer stability, and new customer acquisition, as well as order backlog and post-period performance, the issuer should explain whether these factors pose significant adverse impacts on its sustainable operations and whether there are risks of significant declines in operating performance. Risk disclosures and material event notifications should be made as appropriate.
According to the company's responses, in addition to significant fluctuations in revenues from BYD and Leyuanheng, there were also notable impacts on gross margins.
From 2021 to 2023 and the first half of this year, Huixing Smart Manufacturing's sales gross margins to BYD were 29.22%, 17.04%, 12.79%, and 18.45%, respectively, while those to Leyuanheng were 11.79%, 25.33%, 17.79%, and 16.47%, respectively.
Regarding the risk of performance decline, Huixing Smart Manufacturing noted the following: 1) During cooperation with major customers BYD and Leyuanheng, some projects faced fierce competition, resulting in lower project gross margins due to lower quotes. The company anticipates continued cooperation with these customers at potentially lower prices, which may weaken the guarantee for sustainable growth and increase the risk of performance decline. 2) In 2023, intensified market competition and adjustments to product pricing strategies led to significant fluctuations in the operating performance of major integrator customers such as Leyuanheng, resulting in fewer orders and lower gross margins for the company. If these customers fail to effectively address these challenges, the company's sales volume and profits may further decline, adversely affecting its overall performance. 3) If market demand for new energy vehicle power batteries grows slower than expected, lithium battery manufacturers slow down capacity expansion, and the company fails to effectively respond to adverse factors such as maintaining advanced product development and technical capabilities, competing with major domestic and international competitors, achieving market expansion targets, or maintaining new order scales, the company may face significant operational pressures and risks of performance declines.
03
Gambling agreement remains in place, 2022 and 2023 performance targets unmet
The prospectus discloses that Huixing Smart Manufacturing's gambling agreement with Shaanxi Kaiyuan Chuying Equity Investment Fund Partnership (hereinafter referred to as "Kaiyuan Chuying") has not been terminated, and there is a risk of triggering repurchase clauses.
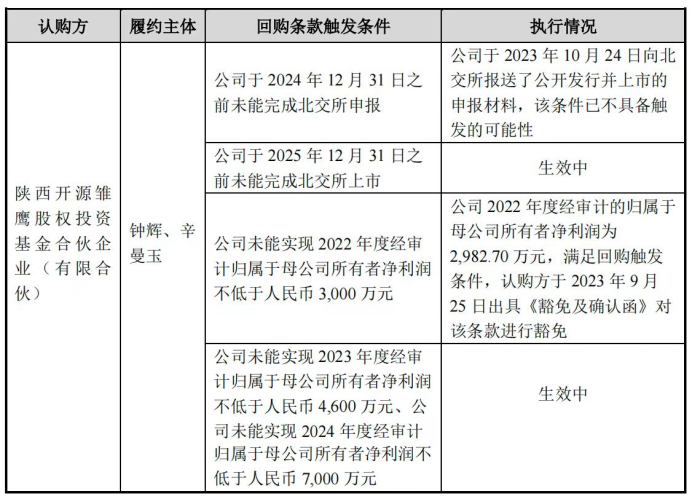
The specific trigger conditions and risks for the repurchase clauses mentioned in the table above are as follows: (1) The company fails to complete its listing on Beijing Stock Exchange by December 31, 2025, and (2) the company fails to achieve audited net profits attributable to shareholders of the parent company of at least RMB 46 million in 2023 and RMB 70 million in 2024. The company's responses to regulators indicate that it achieved operating revenues of RMB 485 million and net profits of RMB 36.1562 million in 2023, meeting the second repurchase clause trigger condition. If Kaiyuan Chuying's equity fund does not grant an exemption and exercises its repurchase right in the future, the company's actual controllers and their spouses will be required to repurchase the corresponding shares.
The prospectus shows that in November 2023, Shaanxi Kaiyuan Chuying Equity Investment Fund Partnership (Limited Partnership) (hereinafter referred to as "Kaiyuan Chuying") subscribed for 2.2 million shares of the company at a price of RMB 6.8 per share. As of the signing date of the prospectus, Kaiyuan Chuying held 3.23% of the pre-IPO shares.
According to the agreement on the repurchase amount in the special investment terms that have not yet been terminated by Zhong Hui, the actual controller of Huixing Smart, and his spouse Xin Manyu, the repurchase amount = Party B's (Kaiyuan Chuying) investment funds × (1 + 8% × investment years) - all cash dividends received by Party B from the company (if any), which means that in the absence of future dividends, the annualized investment return rate is 8% (simple interest). Based on the investment years, the investment return rate on the repurchase date is estimated to be 12%, with a stock premium rate of 32.35%.
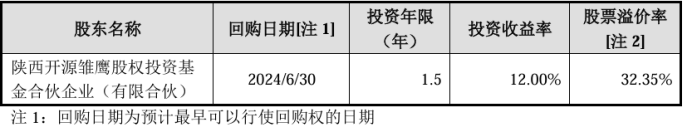
Upon calculation, the secondary market premium rate of the company's shares held by Kaiyuan Chuying Equity Fund exceeds the investment return rate of exercising its repurchase right, making it less likely that it will exercise this right in the future. In summary, there is a risk of triggering the repurchase clause that has not yet been terminated by Zhong Hui and Xin Manyu. If they fail to coordinate with Kaiyuan Chuying Equity Fund to exempt or terminate the relevant clauses in the future, they will be obligated to fulfill the corresponding repurchase obligations. Given that the secondary market premium rate of the company's shares held by Kaiyuan Chuying Equity Fund currently exceeds the investment return rate of exercising its repurchase right, the risk of the two individuals actually fulfilling their repurchase obligations is relatively low. In response to the review inquiry letter, Huixing Smart stated that according to the terms of the gambling clauses that have not yet been terminated, if the gambling clauses are triggered in the future, Zhong Hui and Xin Manyu will need to pay a repurchase amount of no more than 15.4587 million yuan. Considering their substantial personal and family assets and good financial status, they have the financial capability to fulfill the repurchase clause of the gambling agreement.
According to Tianyancha, the executive partner in charge of Kaiyuan Chuying is Shanghai Kaiyuan Sichuang Investment Co., Ltd., a wholly-owned subsidiary of Kaiyuan Securities, the sponsor of Huixing Smart. As early as February 9, 2021, the China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC) issued the "Guidance on the Application of Regulatory Rules - Disclosure of Shareholder Information for IPO Companies." The regulatory rules clearly state that when submitting application materials, issuers must provide a special commitment stating whether the following situations exist among their shareholders, and disclose this commitment publicly: (1) Entities prohibited by laws and regulations from holding shares directly or indirectly hold shares of the issuer; (2) Intermediaries involved in the current issuance or their responsible persons, senior management, or handling personnel directly or indirectly hold shares of the issuer; (3) Improper benefit transfers occur through the issuer's equity.
If new shareholders are added within 12 months before the issuer submits its application, the prospectus must fully disclose the basic information of the new shareholders, the reasons for their investment, the investment price and pricing basis, whether the new shareholders have any connections with other shareholders, directors, supervisors, or senior management of the issuer, whether they have any connections with intermediaries involved in the current issuance or their responsible persons, senior management, or handling personnel, and whether there is any shareholding on behalf of others by the new shareholders.
Regarding the impact of gambling clauses, industry insiders told The Harbor Business Observer that regulators are concerned about whether gambling clauses are truthfully disclosed. Gambling clauses themselves are not necessarily negative. The current key issue for Huixing Smart is that its performance does not meet expectations, leading to changes in its shareholding structure after the repurchase. This would require modifications to the IPO disclosure information, and changes in shareholding structure are considered significant events that may jeopardize the success of the IPO.
04
Three Self-regulatory Measures in Recent Years
From a compliance perspective, the prospectus reveals that Huixing Smart has been subject to three warnings during the reporting period. Specifically, on November 24, 2021, the National Equities Exchange and Quotations (NEEQ) served the company with a "Notice of Oral Warning to Guangdong Huixing Precision Smart Manufacturing Co., Ltd. and Related Responsible Entities." This warning addressed violations related to the actual controller's misuse of company funds, untimely review and disclosure of related-party transactions, and resulted in oral warnings for the issuer, then-Chairman Zhong Hui, Secretary to the Board Deng Gaoquan, and Chief Financial Officer Peng Lishi.
On June 28, 2023, the NEEQ imposed oral warnings as self-regulatory measures on the company and its actual controller Zhong Hui, as well as then-Chief Financial Officer Peng Lishi, for violations related to information disclosure.
On September 1, 2023, the NEEQ issued a written warning to the company and its actual controller Zhong Hui for failing to timely review and disclose agreements involving special investment clauses. This warning was also recorded in the securities and futures market integrity records.
Furthermore, during the reporting period, the company used personal bank accounts belonging to Zhong Hui, Zhong Jianhui, Deng Gaoquan, Huang Yan, and Yan Dafu for external payments and receipts. Additionally, the company exhibited irregularities in financial internal controls, such as accounting errors, cash transactions, and third-party payments.
While these warnings do not affect Huixing Smart's IPO, they do reflect the need for the company to strictly adhere to regulatory requirements and ensure compliance. (Produced by Harbor Finance)







