Xiaomi Thrives with 40% Sales Surge, Leveraging National Subsidies Amid Apple's Struggles
![]() 04/26 2025
04/26 2025
![]() 682
682
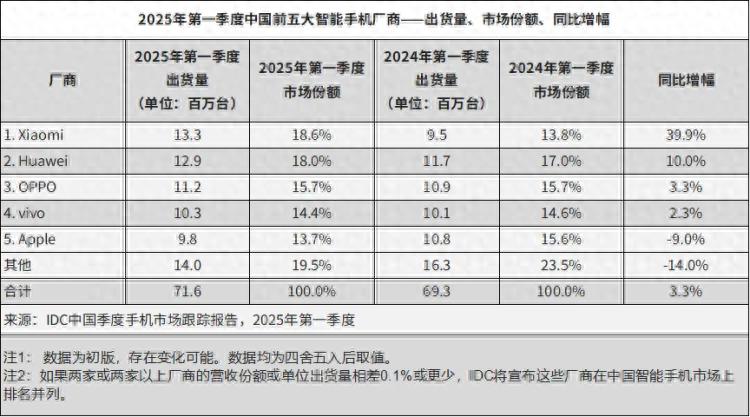
In the first quarter of 2025, China's smartphone market painted a fascinating picture: amidst a modest 3.3% year-on-year increase in overall shipments, Xiaomi emerged as the frontrunner with 13.3 million units sold, marking an astonishing 39.9% growth rate.
This performance not only outpaced established players like Huawei, OPPO, and vivo but also overshadowed Apple, the only brand to witness a decline in sales. Behind Xiaomi's countertrend surge lies the national subsidy policy (hereinafter referred to as the "National Subsidy"), a pivotal factor reshaping the market landscape. Xiaomi, with its strategic acumen, has emerged as the prime beneficiary of this policy dividend.
New National Subsidy Policy: Targeted Stimulus for the Mid-range Market
Earlier this year, the country expanded its subsidy scope to include consumer electronics such as mobile phones, tablets, and smartwatches. It offers a 15% purchase subsidy for products priced below 6,000 yuan, with a maximum subsidy of 500 yuan per unit. This design is both strategic and effective: it targets the mid-to-high-end market, avoiding the concentration of subsidies on high-end flagship models, while the 15% subsidy ratio significantly reduces consumer replacement costs without disrupting manufacturers' pricing structures.
Data reveals the National Subsidy's immediate impact on the market. China's smartphone shipments rose by 3.3% year-on-year in the first quarter, outpacing the global market's 1.5% growth rate, underscoring the policy's effectiveness in stimulating domestic demand. However, a deeper structural shift is underway as the National Subsidy redefines brand competition, favoring manufacturers adept at leveraging policy dividends to boost sales.

Data Insights: Xiaomi's "Volume and Price Growth" Strategy
Post-implementation of the National Subsidy policy, Xiaomi delivered a stellar performance in the first quarter:
- Double Champion: With 13.3 million shipments and a 39.9% year-on-year growth rate, Xiaomi led in both metrics, boasting a growth rate 12 times the industry average.
- Market Share Rebound: According to IDC data, Xiaomi's domestic market share surged from 13.8% in the same period last year to 18.6%.
- Premium Market Breakthrough: Amid rising average prices, Xiaomi's mid-to-high-end models, like the Xiaomi 15 series, saw a significant sales increase, proving that its growth wasn't solely driven by low-end models but achieved both volume and price growth.
In contrast, while Huawei made a strong comeback with its Mate and P series, it was hampered by production capacity constraints, achieving only a 10% growth rate. OPPO and vivo's growth rates aligned with the industry average, while Apple, due to its iPhone 16 Pro series' pricing strategy misaligning with the National Subsidy, became the only top-five manufacturer to experience negative growth.

Three Core Advantages: Xiaomi's "Full Benefit" from National Subsidies
- Cost-effectiveness Meets Policy Dividends: Since its inception, Xiaomi has been synonymous with "cost-effectiveness," and its pricing strategy aligns perfectly with the National Subsidy. For instance, the Redmi K80 series, starting at 2,499 yuan, becomes even more affordable at 2,124 yuan after a 15% subsidy, offering consumers quasi-flagship features at a mid-range price. This "policy amplifier" effect allows Xiaomi to dominate the 2,000-4,000 yuan price range.
- Comprehensive Product Matrix: Over 90% of Xiaomi's current models are priced below 6,000 yuan, fully encompassing the National Subsidy scope from entry-level Redmi models to flagship digital series. In contrast, high-end models like Huawei's Mate/P series and Apple's iPhone 16 Pro exceed the subsidy cap, unable to benefit from policy dividends, thereby weakening their competitiveness in the mainstream price range.
- Brand Premium from Ecological Synergy: Xiaomi's SUV7 launch unexpectedly bolstered its mobile phone business. In the first quarter, Xiaomi's smart ecological device activations surged by 28% year-on-year, with vehicle-mobile interconnection driving mobile phone replacement demand. Consumer surveys reveal that 15% of Xiaomi mobile phone buyers cited "enhanced brand preference due to Xiaomi's cars," translating ecological synergy into tangible market share gains.

Future Perspectives: Xiaomi's Global Ambitions
Based on its first-quarter growth rate, Xiaomi's domestic shipments for the full year are projected to exceed 50 million units. If it maintains its global market growth rate, annual shipments could reach 200 million units, positioning it as the world's second-largest smartphone vendor. However, challenges persist, particularly in the high-end market where Xiaomi faces stiff competition from Huawei, Apple, and Samsung.
Conclusion: The Long-term Test of Policy Dividends
The new National Subsidy policy has been a "timely rain" for Xiaomi, unlocking the key to breaking the smartphone market stalemate. However, the real test lies in transforming policy dividends into enduring brand assets, evolving from a "cost-effectiveness" label to a "technology leader."