Does Trump's Tariff Increase Make Apple's Biggest Rival a "Free Winner"?
![]() 04/27 2025
04/27 2025
![]() 487
487

Can Samsung Truly Benefit from the Sino-US Tariff War?
In the midst of the tariff war, technology enterprises have undeniably emerged as one of the most affected industries amidst these trade shocks. Amidst daily updates of tariff figures by Trump, data released by South Korean media on April 22 revealed that global sales of Samsung mobile phones reached 19.03 million units, surpassing Apple and ranking first in sales for the second consecutive year.

This is not the first time Samsung mobile phones have topped global smartphone sales. A report from the renowned research institution Canalys in October 2024 showed that Samsung led Apple with a global market share of 18%, becoming the market leader. The sales volume of the Samsung Galaxy S25 series reached 4.56 million units in one month.
While Trump announced on April 11th that chips, notebooks, smartphones, and other goods would be exempt from "reciprocal tariffs," many American media outlets have pointed out that, in the face of high tariff barriers, price increases for Apple are inevitable, and its long-standing rival Samsung may seize this opportunity for development. Several data reports in 2024 indicated that Samsung mobile phones held a market share of approximately 25%-31% in the United States, second only to Apple's 49%.

Under the pressure of high tariffs, why is Apple more reliant on the Chinese supply chain than Samsung? Why can Samsung mobile phones, which perform poorly in China, continue to dominate the world market? In the context of high tariffs, is Samsung mobile phone truly more advantageous than Apple?
Apple is More Dependent on the Chinese Supply Chain Than Samsung
At the outset of the tariff war, many third-party agencies discovered that 90% of iPhone production and assembly in the United States is currently located in China. According to Wedbush's analysis, after the adjustment of the industrial chain, only 5% of iPhones are manufactured in Vietnam and India, while the remaining 5% are produced in other countries.
UBS analysts estimate that the basic model price of the $1,199 iPhone 16 Pro Max assembled in China will increase by $800, representing a 67% hike.
Despite Trump's exemption of smartphone components on April 11th, the US technology industry generally believes that the Semiconductor 232 Investigation being promoted by the US Department of Commerce may lead to new tariff policies for the semiconductor and other technology fields. In the future, the United States is likely to impose a special chip tax, which will inevitably affect the relevant smartphone and personal computer markets.
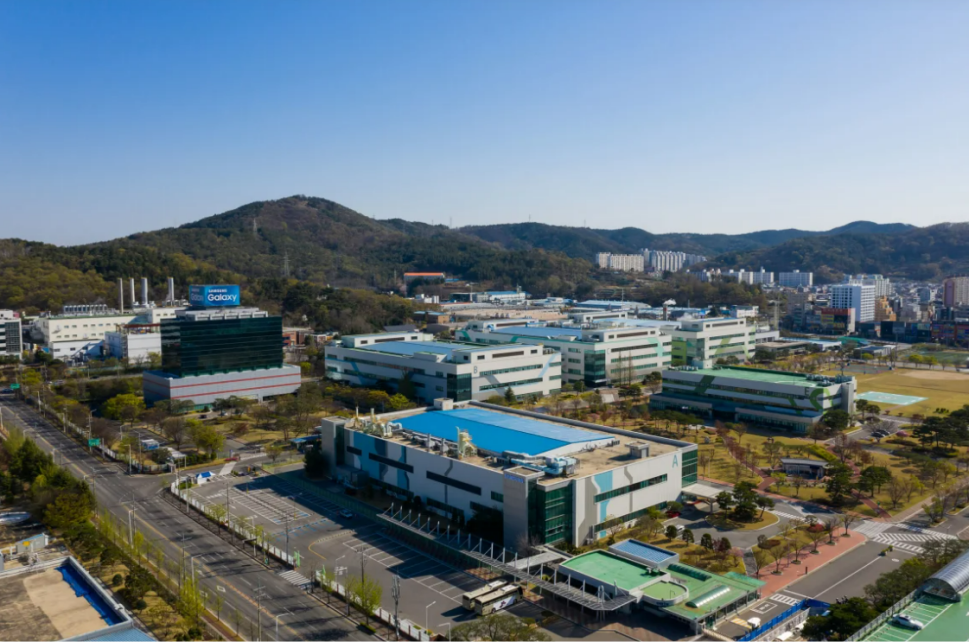

Samsung's Mobile Phone Manufacturing Plant in South Korea
A CNN commentary argues that compared to Apple, Samsung's advantage lies in its smartphone business not being reliant on China. According to some Wall Street analysts, as the largest smartphone manufacturer in terms of global market share, Samsung cannot escape tariffs or their potential economic impact. However, it won't significantly alter its mobile device business due to tariff issues.
Due to China's powerful manufacturing industry, the US technology industry still needs to rely on China's extensive network of component suppliers and assembly facilities to mass-produce 3C products such as smartphones, laptops, and monitors at this stage. Of course, these supply chains benefit from the tariff reciprocity of the above products.
Unlike Apple, which closed its last mobile phone factory in China in 2019, Samsung has ceded a significant share of the Android market to Huawei. Although Samsung still maintains other electronic product businesses in China. According to Samsung insiders, most of Samsung's smartphone industry chains are now located in South Korea, Vietnam, India, and Brazil. Furthermore, a survey by technology industry research company Counterpoint Research showed that 90% of Samsung's smartphone production takes place in Vietnam, with India being the second largest mobile phone production center.

Reports indicate that in 2018, Samsung Electronics established the "world's largest mobile phone factory" in Noida, a suburb of New Delhi, India. The annual mobile phone production capacity of the factory reached 120 million units. By 2024, Samsung had become India's largest smartphone exporter.
Samsung Does Not Rely on Selling Mobile Phones in China, But Still Makes Money from Mobile Phones
Samsung officially launched its mobile phone business in China in 2002. Just three years later, Samsung surpassed Nokia and became the best-selling mobile phone brand in China at that time. In 2013, Samsung reached its peak in the Chinese market, firmly occupying the first position. However, by 2016, multiple Samsung mobile phones successively experienced explosions and caught fire. In October 2017, a replaced Note7 safety version caught fire on a Southwest Airlines flight, directly instilling fear in Chinese consumers regarding Samsung mobile phones.
With the precipitous decline in the reputation of Samsung mobile phones, by 2018, Samsung's market share had plummeted to 0.3%. Since then, Samsung mobile phones have continued to be sold in China, but sales have been dismal. Data shows that in 2023, Samsung's shipments in the Chinese market were only 2 million units, performing worse than some domestic second-tier mobile phone brands.
However, on a global scale, Samsung mobile phones have long been the sales champion of smartphones. Data from research company Canalys shows that in 2024, Samsung mobile phones ranked first in smartphones in all of Europe (excluding Russia) with shipments of 46.4 million units and a market share of 34%. Europe is also the largest market for Samsung mobile phones. Additionally, Samsung mobile phones have a stable market share of over 40% in Latin American countries such as Brazil and Chile, and are the top-selling mobile phone brands in the local market. In the United States, Samsung mobile phone sales in 2024 were approximately 45 million units, consistently ranking second after Apple. Samsung's Galaxy S series holds a significant share in the high-end European and American markets.
Behind Samsung's impressive mobile phone sales lies a comprehensive full industry chain layout. Most components can be independently researched, designed, and even produced, from mobile phone screens to chips to flash memory. This comprehensive supply chain layout enables Samsung to precisely control costs in the mobile phone manufacturing process.
Moreover, due to Samsung's comprehensive chip industry chain, it holds an absolute market share in the field of memory and flash memory chips. Currently, Samsung's mobile storage chip industry ranks first in the world, accounting for about 40% of the global storage chip market. China's mobile phone and PC industries rely on its chip products. Zhuosheng Micro, the largest domestic manufacturer of mobile phone RF front-end chips, purchases most of its chip raw materials from Samsung. Huawei, Xiaomi, vivo, and other mobile phone brands use Zhuosheng Micro's chips.

According to authoritative agency data, the market share of domestic products in the storage chip field of China's mobile phone market is only 4%. Each year, the market needs to import storage chips worth about $100 billion, of which Samsung, as the main supplier, obviously benefits from this demand. According to industry analysis, Chinese mobile phone enterprises have contributed approximately 260 billion yuan in revenue to Samsung. It is noteworthy that over 60% of Samsung's profits stem from its semiconductor business, and a significant portion of this business revenue comes from the Chinese market. Although Samsung mobile phones have minimal sales in the Chinese market, they still obtain considerable profits from Chinese mobile phone manufacturers due to their robust industrial chain advantages.
Is South Korea's Samsung Not Afraid of US Tariffs?
Some media view the success of Samsung mobile phones as a different kind of victory for American technology enterprises. Relevant reports indicate that foreign investors led by the United States hold 55% of the common stock of the Samsung Group, with major shareholders and related companies accounting for 21%, and South Korean investors holding only 19% of the shares. In terms of equity structure, American capital dominates the common and preferred shares of Samsung Electronics. Consequently, some people cannot help but ask, is Samsung an American company or a South Korean company?

The answer to this question is actually quite clear. Samsung's major operational voting rights and decision-making powers are controlled by the "Lee family" in South Korea. Although the United States holds most of the capital, it only participates in dividends and does not involve operations. Samsung's dominant position in the mobile phone chip field can be traced back to the US industrial adjustment in the 1990s, when the United States took action to check and balance the Japanese chip industry. In 1997, when the Asian financial crisis erupted, Samsung's main business, DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory), suffered huge losses in the market. The United States took this opportunity to purchase a large number of Samsung shares at low prices, forming the current high proportion of foreign capital in Samsung's equity structure.
Since most of Samsung's equity and dividends belong to the United States, the United States has spared no effort to support Samsung and provided it with numerous low-cost technology transfer and R&D cooperation opportunities that are difficult for other countries to obtain. In the global market layout, with the help of American capital, Samsung Electronics can obtain various technologies at a low cost. This advantage aids Samsung in jointly developing with Silicon Valley and American university laboratories, subsequently surpassing Japan in the field of DRAM and rapidly rising. After Trump announced the imposition of a 25% tariff on South Korea, the South Korean government did not take countermeasures. This indicates that there is obviously some tacit understanding between South Korea and the United States at the trade level.
While it is inevitable that Apple will raise prices, most media are not optimistic about Samsung mobile phones expanding their share in the US market. Many analysts stated that at this stage, Apple mobile phone users have high loyalty, and there is no evidence suggesting they will switch to other mobile phone brands due to price increases.
In the US market, Apple and Samsung users belong to different types of smartphone user groups, and there seems to be no substitution relationship between the two groups. Some analysis agencies believe that Samsung is probably not strong enough to shake Apple's leading position in the mid-to-high-end market in the United States.

Whether Samsung can completely avoid Trump's current tariff offensive remains uncertain. The Trump administration aims to promote the return of manufacturing to the United States. In this context, countries such as Vietnam and India are also included in tariff considerations. Although the current tariff rate is not high, Samsung is still inevitably affected.
In response to the US tariff strategy, the China Semiconductor Industry Association promptly issued the "Emergency Notice on the Rules for Determining the 'Origin' of Semiconductor Products" on April 11th, which stipulates that the core basis for defining the origin is the "tape-out place" of the chip. This move clarifies that regardless of where the chip manufacturer originates, as long as its tape-out process is not completed in the United States, it can be exempted from tariff impacts.
For domestic mobile phone manufacturers, Samsung, as the main supplier of storage chips, primarily performs wafer tape-outs in South Korea. According to the new rules of origin, the cost of mobile phone core components is expected to remain stable and will not be affected by tariff increases.
Reference Materials
1. Can Apple's Biggest Rival Gain an Advantage in Trump's Tariff War? CNN Business
2. Here is the Price of the "Made in the USA" iPhone, CNBC
3. Leaving the World's Largest Mobile Phone Market, Samsung is Still the World's Number One, Anti-Short Selling Frontline