Has China Once Again Rescued Tesla? China Contributed 40% of Production Capacity and 37% of Sales
![]() 01/06 2025
01/06 2025
![]() 621
621
For Tesla, China has undeniably been a fortunate land.
In 2018, Tesla made the bold decision to establish a factory in Shanghai. They signed an agreement with the Shanghai government in July of that year and secured the land in October.
Following the land acquisition, construction commenced on January 7, 2019, embodying the remarkable 'China Speed' – a feat of beginning construction, completion, production, and listing all within the same year. By December's end, the China-made Model 3 was officially delivered. This astonishing pace in China even astonished Elon Musk himself.

Thanks to the swift development of the Shanghai Gigafactory, Tesla was able to swiftly introduce the Model 3, subsequently boosting Musk's production capacity and delivery volumes.
Coupled with China's low manufacturing costs, the Tesla Model 3 became even more competitive. In the global market, Tesla continued to excel, emerging as the world's leading new energy vehicle company with a soaring market value. It's fair to say that initially, it was indeed China that rescued Tesla.
However, with the relentless advancement of China's new energy vehicles and the price wars waged by foreign automakers, Tesla now faces tremendous pressure.

Data reveals that in 2024, Tesla's global sales totaled only 1.7892 million vehicles, a decrease of approximately 20,000 units compared to the 1.808 million sold in 2023, marking a 1.1% decline.
Don't underestimate this 1.1% drop; it's the first time since 2015 that Tesla has experienced a year-on-year decline in annual sales. This sign is quite alarming, especially given the increasing trend and penetration of new energy vehicles. The former market leader is now declining, which is quite concerning.
But honestly, the 2024 figures still owe much to China's rescue of Tesla. Without the Chinese market's support, Tesla's decline would have been even steeper, potentially eroding confidence in the entire capital market.
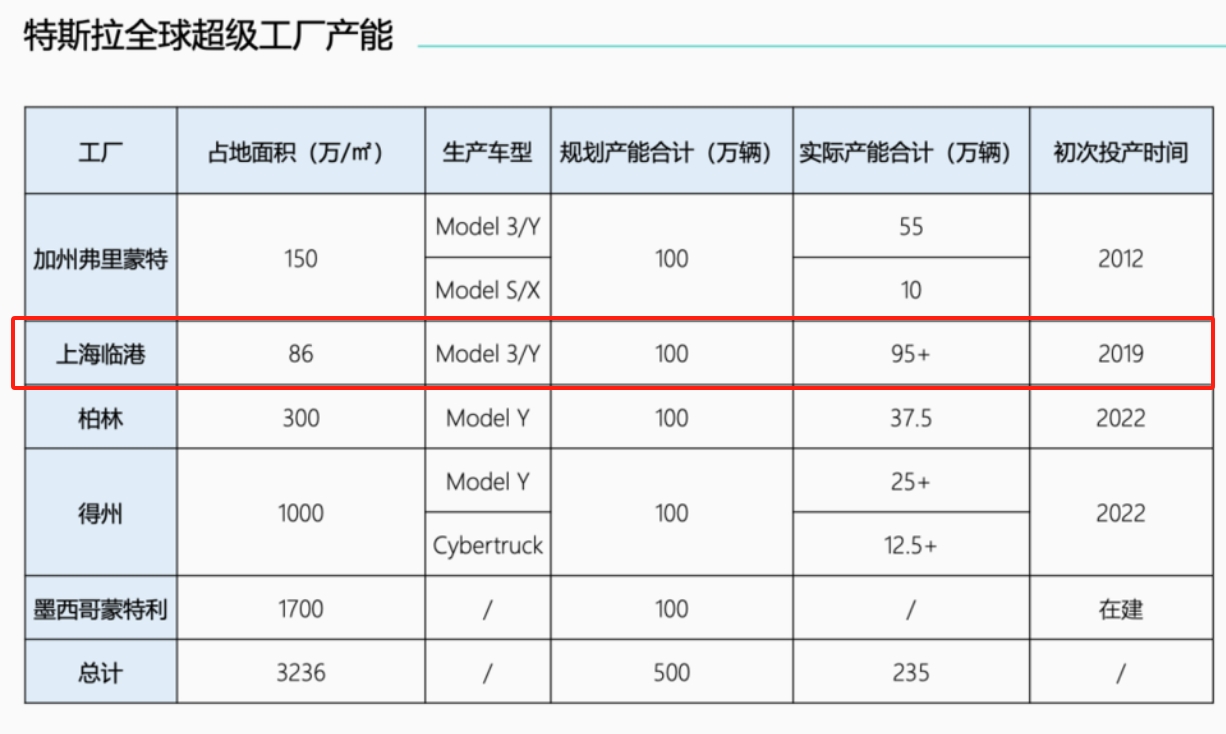
On one hand, the production capacity of the China factory accounts for 40% of Tesla's total production. Tesla had initially planned a global annual production capacity of 5 million vehicles across factories in the United States, Germany, Mexico, and China.
However, to date, the only factory that has truly met its planned production capacity is the Shanghai Gigafactory in China, with a planned and actual capacity of 1 million units, comprising approximately 40% of Tesla's 2024 production capacity.

Secondly, sales in the Chinese market contributed roughly 37% of Tesla's sales in 2024.
In 2024, Tesla sold 657,000 vehicles in the Chinese market, an 8.8% year-on-year increase from the 603,700 vehicles sold in 2023, setting a new record. These 657,000 vehicles accounted for 37% of Tesla's global total sales of 1.7892 million vehicles.
Imagine if China's contribution to production capacity wasn't so significant and performed poorly like Tesla's other factories. How could Tesla have guaranteed its production capacity?
If the Chinese market hadn't grown by 8.8% and sold over 50,000 additional vehicles, would Tesla's global market have suffered an even steeper decline? It's precisely the sales and production capacity in the Chinese market that have upheld Tesla's total production and sales in 2024.



