AI+ Evolution Continues! A Premier Prefecture-Level City Takes Center Stage
![]() 02/27 2025
02/27 2025
![]() 869
869
By | Bai Jiajia
Reflecting on his return to China from Cambridge, UK, to start a business in 2008, Yu Kai was profoundly impressed by the Suzhou Industrial Park investment promotion team's passion for attracting talent.
"Their eagerness wasn't driven by annual output value requirements but rather by humbly introducing the context of industrial upgrading and asking, 'Can you share your insights with us?'" Yu Kai recalled.
At that time, Yu Kai had just founded AISpeech, a company focused on speech recognition technology and dialogue systems. Today, this field is recognized as a cornerstone for AI development, but over a decade ago, Suzhou's global talent search was more instinctive—
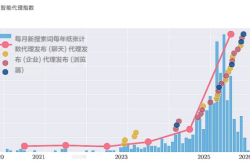
In 2007, Suzhou launched the Gusu Innovative and Entrepreneurial Leading Talent Program to attract and nurture potential "saplings" from around the world.
Recently, the fruits of these saplings have come into full bloom.
On February 14th, Suzhou hosted a high-level "AI+" Innovation and Development Promotion Conference. Wu Qingwen, Deputy Secretary of the Suzhou Municipal Party Committee and Mayor, stated that as a major economic and industrial hub, Suzhou is seizing the transformative opportunities presented by AI, leveraging its vast industrial scale, numerous application scenarios, and robust innovation drive to empower AI across industries and into everyday life.

To attract more companies like AISpeech to settle in Suzhou early on, the local government also announced a maximum project funding of 100 million yuan and a maximum housing subsidy of 10 million yuan for AI talent.
Amidst the global AI wave, many cities are seeking differentiated paths, and Suzhou has clearly provided a unique response.
What sets this response apart? Can other cities draw inspiration from it?
1. Weaving AI into the Fabric of Industry
The growth trajectory of AISpeech is a microcosm of Suzhou's AI industry development.
In 2008, the domestic voice market was virtually uncharted territory. "We arrived too early," admitted AISpeech CEO Gao Shixing.
At that time, the internet was not yet widespread, and the concept of smart terminals was even more elusive. The team once found themselves in a dilemma of "advanced technology, lagging market" and could only struggle to survive in the English education market.
The turning point came with the burgeoning IoT industry in Suzhou.
In 2009, Suzhou's IoT output value surpassed 10 billion yuan, and an industrial chain encompassing sensor research and development, chip manufacturing, and system integration began to take shape.
The government keenly captured this trend and hosted the China (East China) International IoT Technology Expo in 2011, the only international expo in China primarily showcasing IoT core technologies.
This exhibition was exceptionally popular, with over 800,000 printed invitations. Gao Shixing also foresaw the explosion of mobile IoT amidst the crowds and thus vigorously promoted the company's business transformation towards smart terminals that same year.
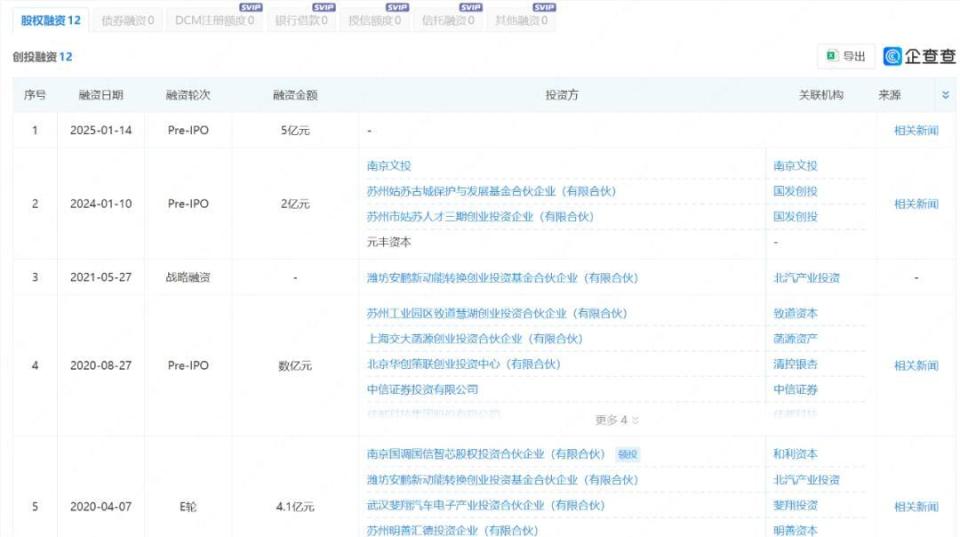
In harmony with Suzhou's IoT industry, AISpeech surged ahead. From 2012 to 2025, AISpeech successively received 12 rounds of funding, with the latest round amounting to 500 million yuan.
AISpeech's vertical large model DFM-2 and full-link dialogue technology have been adopted by over 200 IoT and related enterprises, spanning sub-sectors such as black and white electronics, kitchen appliances, small appliances, and consumer electronics, creating over 450 benchmark cases. Additionally, it has performed impressively in the fields of chips, smart cars, and conference offices.
After more than a decade, AISpeech has emerged as a leading player in domestic AI and has been designated as the "National New Generation AI Open Innovation Platform for Language Computing".
AISpeech is but one facet of Suzhou's AI landscape.
Currently, over 2,100 AI-related enterprises are scattered across Suzhou, encompassing core areas such as robotics and autonomous driving.
By integrating these areas, Suzhou has established 15 "arteries" for the deep integration of AI and industry, known as the "1+15" AI industry promotion system. Within this system, there are 140 approved provincial-level AI fusion innovation products and application solutions.
Judging from the data, the "1+15" system has already yielded initial results.
In terms of the city's GDP, Suzhou's total GDP reached 2.67 trillion yuan in 2024, with a year-on-year growth rate of 6%, higher than the national average, and the driving force of AI technology cannot be overlooked.
Even focusing solely on the AI industry, last year's revenue scale exceeded 230 billion yuan, with a year-on-year growth rate of over 20% and an average growth rate of 30% in the past five years, firmly positioning Suzhou as a national frontrunner.
2. Industrial Upgrading Fuels AI Development
The inevitability of Suzhou's AI industry—deeply intertwined with the real economy—is rooted in Suzhou's industrial endowment and forward-looking vision.
Looking back, the inception of Suzhou Industrial Park was a pioneering experiment.
The renowned Suzhou Industrial Park was established in the 1990s through cooperation between the Chinese and Singaporean governments. By 2001, it had cumulatively introduced 764 foreign-invested projects, including 39 Fortune 500 companies such as General Motors, Emerson, and L'Oréal.
International leading enterprises brought output value but also pressure. Simply engaging in "contract manufacturing" was insufficient to promptly or proactively address buyers' needs, and for these multinational giants, upgrading products or enhancing efficiency was crucial for maintaining their competitiveness.
Thus, Suzhou anticipated the need for industrial upgrading earlier than other cities.
To some extent, the park's 2002 proposal to benchmark "Silicon Valley" and create a "high-tech industrial cluster" was a manifestation of upgrading pressure forcing innovation.
The demand for industrial upgrading fostered a strong desire for high-tech, so it's no surprise that Suzhou's AI technology is deeply integrated with industry; it was born here.
But what is more crucial is the "early start".
Although each generation of AI technology brings new breakthroughs, at the system and industrial application levels, it necessitates long-term in-depth technological research and development. Therefore, the earlier the participation, the richer the experience and data, and the more pronounced the iterative advantages of industrial applications.
This advantage is directly reflected in the quantitative relationship between talent and innovative enterprises.
According to data from the Suzhou Science and Technology Bureau, three-quarters of Suzhou's unicorn cultivation enterprises and science and technology innovation board listed companies today originate from the entrepreneurial enterprises introduced by the 2007 Gusu Innovative and Entrepreneurial Leading Talent Program, the same program that brought AISpeech back to China.
Because Suzhou established the "demand-technology-talent" closed loop early on, each round of industrial upgrading has become an opportunity for Suzhou to further deepen the integration of new technologies and industries.
For instance, around 2015, several hundred-billion-yuan industrial clusters in Suzhou collectively encountered a "transformation zero point", among which the pressure on the biomedical industry primarily stemmed from shortening the R&D cycle.
As a result, iDiscovery, a drug development system based on AI and other technologies developed by Qiguang Dejian, emerged at the right time, not only shortening the screening and discovery cycle of traditional ADC drugs by 70% but also reducing R&D costs by 90%.
Validating algorithms beside lathes and iterating models on assembly lines allows each technical decision to find a value anchor in financial statements. It can be said that the inevitability of Suzhou's AI stems from an unbreakable truth:
The integration of any innovation with the real economy is essentially a precise match between technology supply and industrial demand.
3. The Triad of Policy, Collaboration, and Enterprise
The uniqueness of Suzhou's AI stems from its industrial endowment and forward-looking layout, but what is more valuable for reference are its three strategies for promoting the AI industry.
Strategy 1: Leverage Endowment to Craft Policy, Convert Advantages into Victories
Long before the current AI boom, Suzhou had proactively applied to establish a "National New Generation AI Innovation and Development Pilot Zone".
In the Ministry of Science and Technology's reply in March 2021, special emphasis was placed on "fully leveraging the advantages of manufacturing to promote the deep integration of AI and the real economy."
This precisely aligns with Suzhou's endowment, which is clearly not luck but the result of Suzhou's proactive efforts.
Suzhou has always been adept at striving for and creating a development environment conducive to itself.
To date, Suzhou has issued a comprehensive set of plans to boost AI development, the policy foundation for three key elements, and several application supports for subdivisions. Including international and national standards, 14 standards in the "AI+" field have been issued.
In the past year, the "AI+" special working group, composed of personnel dispatched from multiple departments such as the Suzhou Municipal Party Committee's Financial Office and the Municipal Development and Reform Commission, has repeatedly traveled to national ministries and commissions such as the National Development and Reform Commission, Ministry of Science and Technology, Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, People's Bank of China, and State Administration of Taxation to understand and strive for relevant policies. Obviously, they will continue to spend 2025 on the road.
Strategy 2: Regional Collaboration, Comprehensive Perfection
"A notable feature of Suzhou's AI industry development is the clear pattern of regional collaborative development." Suzhou has ten counties and districts under its jurisdiction, forming a development pattern named "Comprehensive Perfection", with each district responsible for AI closely aligned with its own industry.
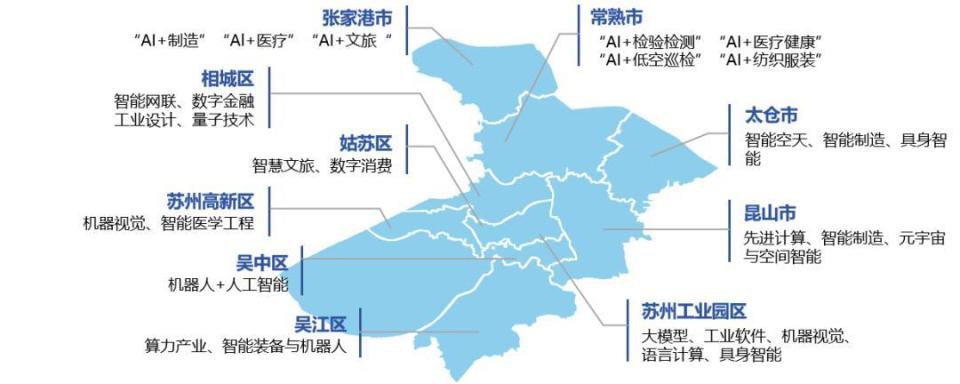
Taking Wuzhong District, which is primarily responsible for "AI+Robotics", as an example.
Wuzhong District has gathered over 1,000 robotics enterprises, forming a complete industrial system encompassing upstream robot core components, midstream robot body manufacturing, and downstream integrated applications. In 2024, the scale of the "AI+Robotics" industry in the district exceeded 160 billion yuan.
Strategy 3: Enterprise Leadership, Government Support
The vast potential of AI is undeniable, but market demand is constantly evolving. To avoid detours, AI enterprises at the forefront of the industry, who are "hearing the cannons", can provide the most precise direction.
"Taking AI enterprises as the starting point, strengthen all links of the AI industrial chain," the Suzhou government emphasized in the external documents of this AI+ conference, "cultivate a comprehensive industrial ecosystem encompassing public laboratories, alliance associations, financial capital, and standard systems to provide favorable development conditions for Suzhou's 'AI+' applications."
Enterprises discern linear trends in industrial upgrading from spot demands in the market, while the government uses these clues to chart a course towards the AI era. Suzhou's AI development confirms a pragmatic path:
When the innovation ecosystem and industrial upgrading drive each other, AI technology and industry form an inseparable double helix.
When top-level policies, regional collaboration, and enterprise breakthroughs converge into a triad, and innovation is deeply integrated with the real economy, a city will have the confidence to face challenges in any era.