Tesla Enters Robotaxi, Also Needs to 'Pass Three Levels'
![]() 06/30 2025
06/30 2025
![]() 797
797

On June 22, Tesla officially entered the Robotaxi field, reigniting the entire race.
Although Tesla's Robotaxi model unveiled this time is a 'modified' Model Y, not the CyberCab specifically developed for Robotaxi as claimed last year. A few days after its launch, the riding experience of Tesla's Robotaxi was only 'satisfactory'.
But obviously, the entire Robotaxi industry still regards Tesla as an important competitor.
On June 23, Hello officially announced that it had officially entered the Robotaxi field through investments from Hello, Ant Group, and CATL. The collaborative model of Internet + manufacturing has endowed Hello Robotaxi with the imagination of scale since its inception.
On the same day as Hello, WeRide spread the news that it had secretly submitted an application for listing on the Hong Kong stock exchange. Planning a secondary listing less than a year after its initial listing means that WeRide has also reached a critical point for a new round of scale expansion.
In May this year, Pony.ai signed a strategic cooperation agreement with Uber. This is another important third-party platform partner following RQI, Gaode Maps, and Alipay. From independently operating Robotaxi to launching third-party operating platforms, Uber has obviously recognized Pony.ai's technology and operational capabilities. Robotaxi services can be selected at any time on the aggregated car-hailing platform. In addition to express cars and private cars, consumers now have the sci-fi option of 'virtual drivers'.
Tesla's entry has also triggered the entire industry's thinking about Robotaxi operations.
Even if it is always in the first tier of global intelligent driving players, Tesla entering the L4 field also needs to start with equipped safety officers. There is no shortcut for the implementation of Robotaxi.
In contrast, the global Robotaxi first-tier players such as Waymo, Pony.ai, and Luobo Kuaipao have an operating 'generation gap' of more than two years over new players.
On the other hand, the modified Model Y used for Robotaxi has a single-vehicle cost as low as US$40,000, which is already close to mass-consumer passenger cars.
In the trend of continuously declining costs, the Robotaxi industry has finally reached a new node of scale.
There is no doubt that the first year of mass production of Robotaxi has arrived.
Tesla struggles after entering, Robotaxi has long been dominated by many players
With excitement mixed with mediocrity, this was Tesla's Robotaxi performance within a few days of its launch.
The most responsive was the performance of the capital market. On June 22, Tesla launched a limited-edition Robotaxi service in Austin, USA, available only to invited users. Upon the announcement, Tesla's market value surged by 8%. In the following days, Tesla's market value retreated to the level before the announcement.
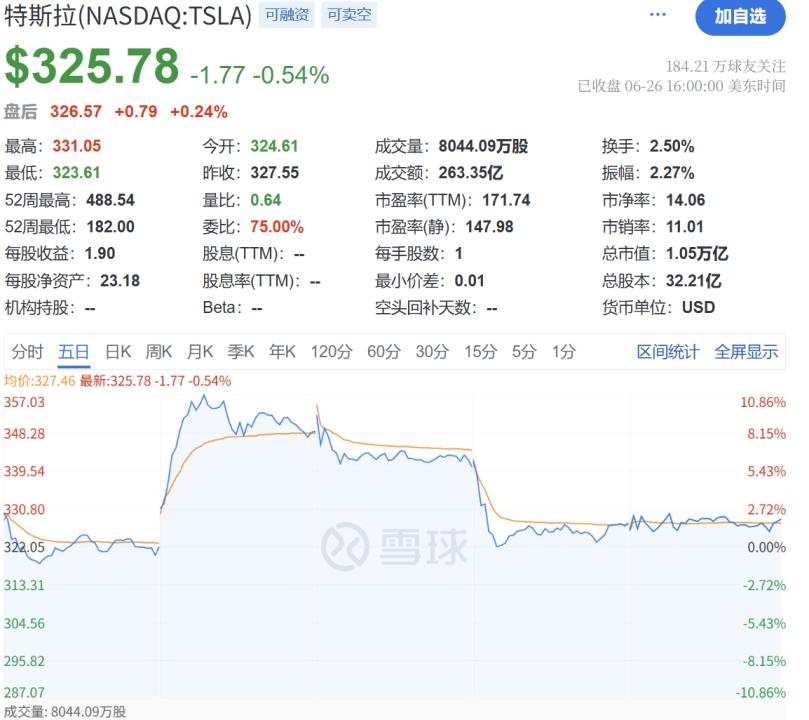
Within two days, investors' attitude towards Tesla 'flipped'. This mainly came from the fact that Tesla's Robotaxi performance was unsatisfactory. This leading player in the field of intelligent driving did not demonstrate any advanced performance that is currently ahead of the Robotaxi industry.
'Musk operates Robotaxi within a limited scope, from an invitation system to open operations. This approach instead confirms that Waymo's approach is correct. Austin is the first place where Waymo operates unmanned services. It is a place with little rain, and there are basically no pedestrians on the road.'
As summarized by Lou Tiancheng, co-founder and CTO of Pony.ai, Tesla's Robotaxi is retracing Waymo's path. Like Waymo, Pony.ai, Luobo Kuaipao, and other players who are currently industry leaders, Tesla also needs to start from the stage of having safety officers on board and operating in small areas.
Tesla's entry into the field for a week has proven that the Robotaxi industry 'has no shortcuts'.
From 'manned to unmanned', from limited areas to open operations, Robotaxi must experience a several-fold increase in safety under the same scenario at each stage before moving on to the next stage.
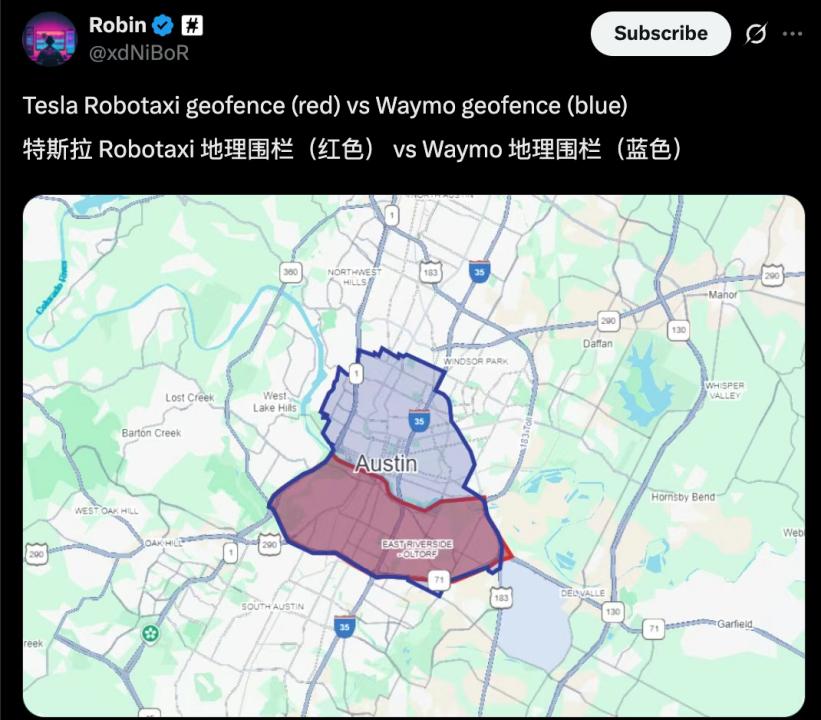
As early as 2021, Pony.ai obtained a Robotaxi unmanned testing license and commenced commercial charging for the first time in the same year. At the initial stage, Pony.ai also started from a small area (Yizhuang Development Zone) and gradually progressed from having a safety officer in the driver's seat, no one in the driver's seat but a safety officer in the front passenger seat, no one in the entire vehicle but a 1:1 remote safety officer, and finally arrived at the current stage of only equipping 1:N remote assistance personnel.
Therefore, even if Tesla comes, it also needs to 'pass three levels'.
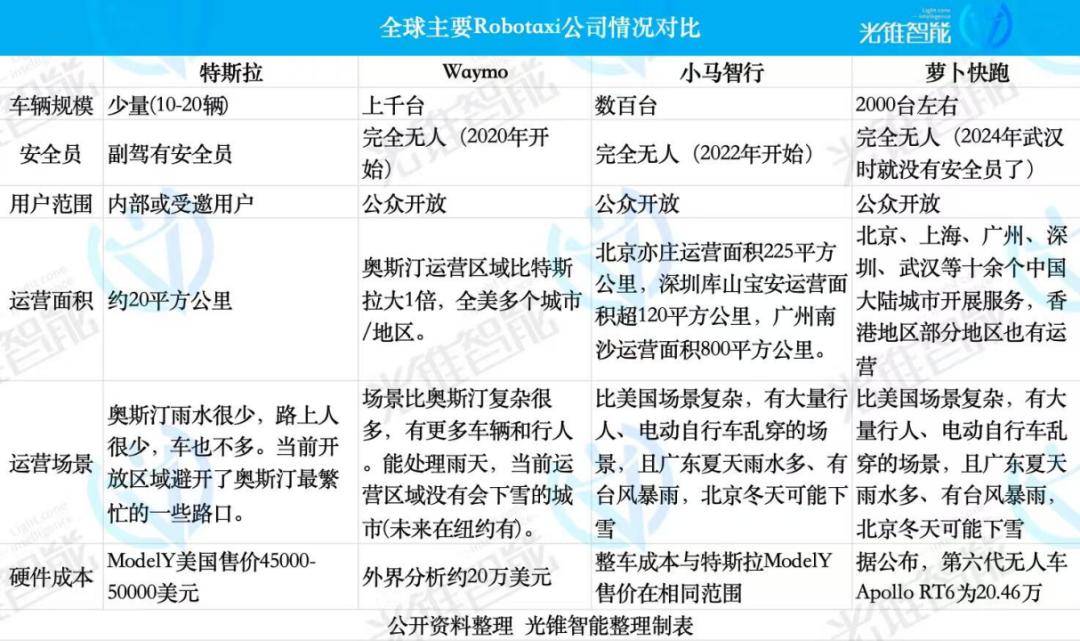
Gradually expanding the operating scope, reducing human intervention, and increasing the operating scale, Robotaxi companies are verifying step by step. The top players have established fleets of hundreds or thousands of vehicles, capable of providing uninterrupted operations in Guangzhou during rainy weather and Beijing during snowy weather.
From this perspective, Tesla, with only 20 Robotaxis, obviously has not yet officially entered the 'poker table' of the Robotaxi industry. But from the perspective of mass production, Tesla is also an important 'disrupter' in the Robotaxi industry.
Because the Robotaxi model launched this time by Tesla is a 'modified' Model Y, not a vehicle specifically re-developed and designed for the Robotaxi business. Tesla wants to use L2+ intelligent driving hardware capabilities combined with the cost of mass-consumer cars to achieve Robotaxi, and it still needs to prove itself through unmanned and large-scale operations.
Only after extreme cost reduction can Robotaxi talk about scale
Autonomous driving technology is already mature enough. In the past year, players have focused their efforts on 'cost reduction'.
For a long time, there has been a route dispute between the 'pure vision vs. lidar' solutions in the Robotaxi industry. In order to promote the cost reduction of Robotaxi, players on different routes have different technical path preferences.
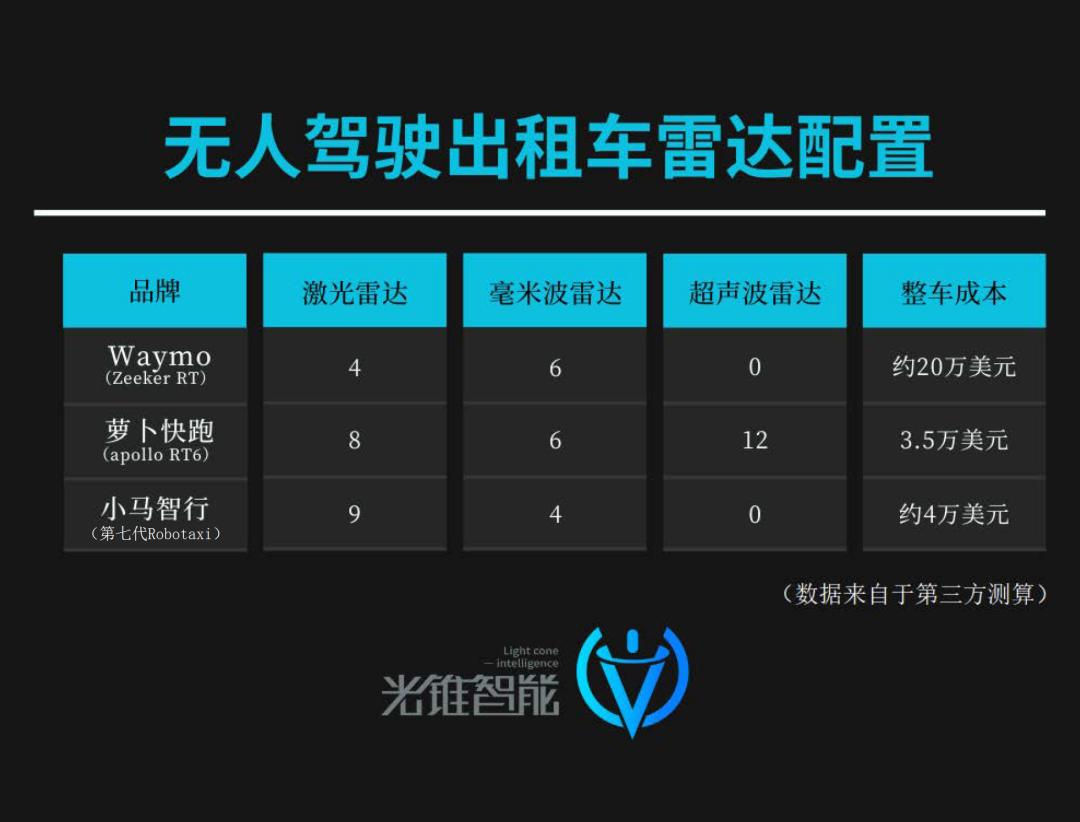
Starting from first principles, the pure vision solution represented by Tesla follows the principle of extreme cost reduction – achieving the same level of autonomous driving with the lowest possible hardware cost. The level of autonomous driving is mainly driven by algorithms. The cost from algorithms will continue to be diluted as cars are sold.
But players who use lidar believe that 'safety is 1, and everything else is the 0s that follow'.
Installing lidar can meet the 'diversity and redundancy' of data for high safety standards. Along with the wave of electrification + intelligence of Chinese automobiles, the lidar industry chain is no longer what it used to be. In recent years, the cost of lidar has dropped very quickly. Currently, the cost of a lidar can be achieved at the level of one thousand yuan. When the cost of lidar as a percentage of the entire vehicle cost is acceptable, the dispute between the 'pure vision' and 'fusion perception' routes no longer has commercial significance.
In addition to lidar, many Robotaxi players are also using technology to drive cost reduction at more levels. For example, Pony.ai's newly launched seventh-generation Robotaxi has a 70% reduction in the cost of its autonomous driving suite compared to the sixth generation. Among the hardware costs, lidar costs have decreased by 68%, and domain controller costs have decreased by 80%.
According to the calculations of a securities trader, compared to the costs of peers, Pony.ai's costs are significantly lower than the approximately US$200,000 calculated by the outside world for Waymo. Compared with domestic peers, it is slightly higher than Baidu's sixth-generation driverless vehicle Apollo RT6 at RMB 204,600.
But overall, the costs of China's top Robotaxi players and Tesla's Model Y solution are at the same level.
However, to achieve sustained cost leadership, it will ultimately be determined by the technical depth of Robotaxi players in the long run. At this year's Shanghai Auto Show, Light Cone Intelligence saw that many intelligent driving suppliers are actively trying to use domestic substitution and technology optimization to continue to reduce the cost of computing hardware.
Only after extreme cost reduction can Robotaxi truly talk about scale.
So how many Robotaxis can achieve profitability?
Zhang Ning, Vice President of Pony.ai and head of the L4 Robotaxi business, introduced to Light Cone Intelligence that 'in cities like Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen, when the number of Robotaxis deployed reaches 1,000, operations will reach the break-even point.' In May 2024, when Baidu disclosed its profit timeline, it also mentioned plans to deploy 1,000 units in Wuhan within the year, achieve a break-even point by the end of 2024, and achieve full profitability in 2025.
Everyone holds the simple ideal of 'the more invested, the easier it is to make money', and the Robotaxi industry has entered the stage of attacking cities.
2025, Towards Profitability
Various indications show that the Robotaxi industry will become profitable in 2025.
On the Pony.ai side, the company's unaudited first-quarter report for 2025 shows that total revenue was RMB 102 million, a year-on-year increase of 12%. Among them, Robotaxi business revenue was RMB 12.3 million, a year-on-year increase of 200%. The Robotaxi business has become the main factor driving Pony.ai's revenue growth in the first quarter.
Why can the Robotaxi business significantly increase the company's performance? The main reason is that ordinary people are using it more and more.
It is understood that Pony.ai's Robotaxi business revenue mainly comes from two categories: passenger fare revenue and technical solution project revenue. Pony.ai's passenger fare revenue increased significantly in the first quarter, with a year-on-year increase of 800%.
This is also the case with Luobo Kuaipao. According to Baidu's first-quarter report, Luobo Kuaipao provided over 1.4 million trips worldwide in the first quarter of this year, a year-on-year increase of 75%. As of May 2025, Luobo Kuaipao has provided over 11 million trips worldwide.

With the maturity of technology and the increase in user volume, the government is also continuously promoting the implementation of Robotaxi.
Currently, autonomous driving technology has been included in the '14th Five-Year Plan' for the development of the digital economy, and multiple departments jointly promote the marketization and road access of autonomous vehicles. At the specific operational level, Shenzhen, Shanghai, Beijing, and other places are actively providing policy support in terms of liability determination, road testing, and commercial operation. Shanghai also proposed that when an accident involving a driverless car occurs, the vehicle owner or manager should first advance the compensation, and then may seek compensation from the responsible party.
With the introduction of detailed policies, Robotaxi has also eliminated users' original safety concerns, adding another layer of protection to commercial operations.
As it accelerates its landing, the entire Robotaxi industry is undergoing a fierce 'land grab'.

In 2024, Baidu conducted large-scale verification in Wuhan, attracting widespread attention from society. In 2025, Pony.ai and other industry players are continuously expanding their testing scope.
Baidu's Luobo Kuaipao is 'aggressively' promoting its overseas layout. On March 28, Luobo Kuaipao announced that it would deploy over 1,000 fully driverless vehicles in downtown Dubai to carry out large-scale testing and operational services. On June 18, it was approved to conduct tests on designated road sections and during specified time periods in Tung Chung, Hong Kong. The scope of Luobo Kuaipao's business plan currently also includes countries and regions such as Switzerland, Turkey, and Benin.
On the Pony.ai side, it is about 'internal and external cultivation'. Currently, Pony.ai's Robotaxi covers a total service area of over 2,000 square kilometers in Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen, covering key transportation hubs such as central urban areas, airports, and high-speed rail stations. In addition, Pony.ai is also rapidly promoting the commercial landing of the global market. It has not only deployed autonomous driving businesses in countries and regions such as South Korea, Luxembourg, and the Middle East, but has also established strategic partnerships with Uber, Singapore's ComfortDelGro Group, and Luxembourg's travel company Emile Weber.
In terms of operation quality, Pony.ai also implements refined operation strategies for different user groups. On Pony.ai's own APP, the number of registered users in the first quarter of this year increased by over 20% month-on-month. On third-party platforms with a wider reach to consumers, Pony.ai CEO Peng Jun introduced that 'in the past year, 80% of orders came from Pony.ai's own App, and 20% came from third parties'.
In addition, automakers are also actively deploying. For example, RQI, a subsidiary of GAC, has expanded the business operation scope of Robotaxi from Guangzhou to Shenzhen. Mobility service platforms such as E-Share Technology under Dongfeng, Cao Cao Mobility under Geely, and Enjoy Mobility under SAIC have also successively launched Robotaxi businesses, and have obtained demonstration operation licenses in cities such as Wuhan, Wuxi, and Suzhou.
2016 was the year when Robotaxi just started. In that year, Waymo operated independently, and General Motors acquired Cruise. Nine years have passed, and Robotaxi enterprises have experienced both highs and lows. In 2025, the great era of Robotaxi has arrived.