Tested Mainstream AI College Application Tools: Enhanced Content and Elevated Auxiliary Significance
![]() 06/30 2025
06/30 2025
![]() 646
646


For most candidates navigating the college application process, leveraging AI capabilities can indeed yield twice the results with half the effort.

Original Tech News, AI New Tech Team
While using AI to aid in college application filling is not a novel concept, this year, bolstered by large models and the new college entrance examination reform, the market is abuzz with highlights. The reform replaces the traditional liberal arts and science divisions with the "3+3" and "3+2+1" self-selected subject models. Notably, this year, not only has the number of parallel volunteers increased to 45, but within each college major group, candidates can now list up to 6 major preferences, directly complicating college admission and application policies. The application guide, often spanning over 300 pages, heightens the risk of erroneous choices for candidates and their parents. However, the essence of application filling remains a logical exercise in screening and matching data: typically, based on college entrance exam scores, a subset of universities that meet or exceed the threshold is filtered from numerous nationwide options, and then the most suitable one or several options are matched as first and alternative choices based on the candidates' needs. No matter how intricate the data, systems, and decisions involved, they are manageable and straightforward for large AI models. A host of players, both established and emerging, including Baidu, Quark, and QQ Browser, have made "AI college application" their primary summer project.
Thus, the reliability of AI college application tools supported by large models has become a subject of ongoing debate. What distinguishes these AI application tools, and which one is most dependable? Will artificial intelligence streamline the application process? To uncover the answers, "Tech News" personally tested the three most popular applications on the market: Baidu, Quark, and QQ Browser (Tencent), evaluating their volunteer recommendation capabilities, complex demand resolution, recommendation explanation, and other aspects under identical conditions. To ensure fairness, the unpaid public versions of each AI were utilized to ascertain the suggestions AI can offer in a "zero-fee" scenario.
01 Rich Information Becomes a Fundamental Requirement
Filling out applications is inherently an information battle. Whoever possesses more accurate information gains the upper hand in the application process. Previously, candidates had to consult application books, relying on a single information channel, which was inefficient and might lead to missed opportunities due to misinformation. AI college application products, aided by algorithms and big data, achieve scientific information collection and integration, presenting multiple application schemes to candidates intuitively. Hence, the significance of accurate information cannot be overstated. First, let's examine Quark. The Quark APP has specifically launched a college entrance examination channel to aid candidates and parents in screening options. Notably, Quark recently unveiled its first large model for college application volunteers, simultaneously introducing three functions: "Deep Search for College Entrance Examination", "Volunteer Report", and "Intelligent Volunteer Selection", complete with a comprehensive college entrance examination knowledge base. The core "Volunteer Report" function operates via an Agent, generating intelligent entities with comprehensive volunteer schemes. Candidates simply need to input their scores and then select or specify their personal interests and preferences. In just 5 to 10 minutes, Quark mimics the analysis path of volunteer experts, focusing on multiple dimensions such as score ranking, interest areas, and future employment trends, to devise a 15-20 page "challenge-stability-guarantee" volunteer application scheme with varying gradients for candidates, culminating in a professional volunteer report. Here, we selected Henan as the college entrance examination province, subjects as physics, chemistry, and biology, and a score of 555. Interest preferences like target colleges, regional preferences, and major preferences were left unconstrained, with supplementary information filled in as "good employment is needed".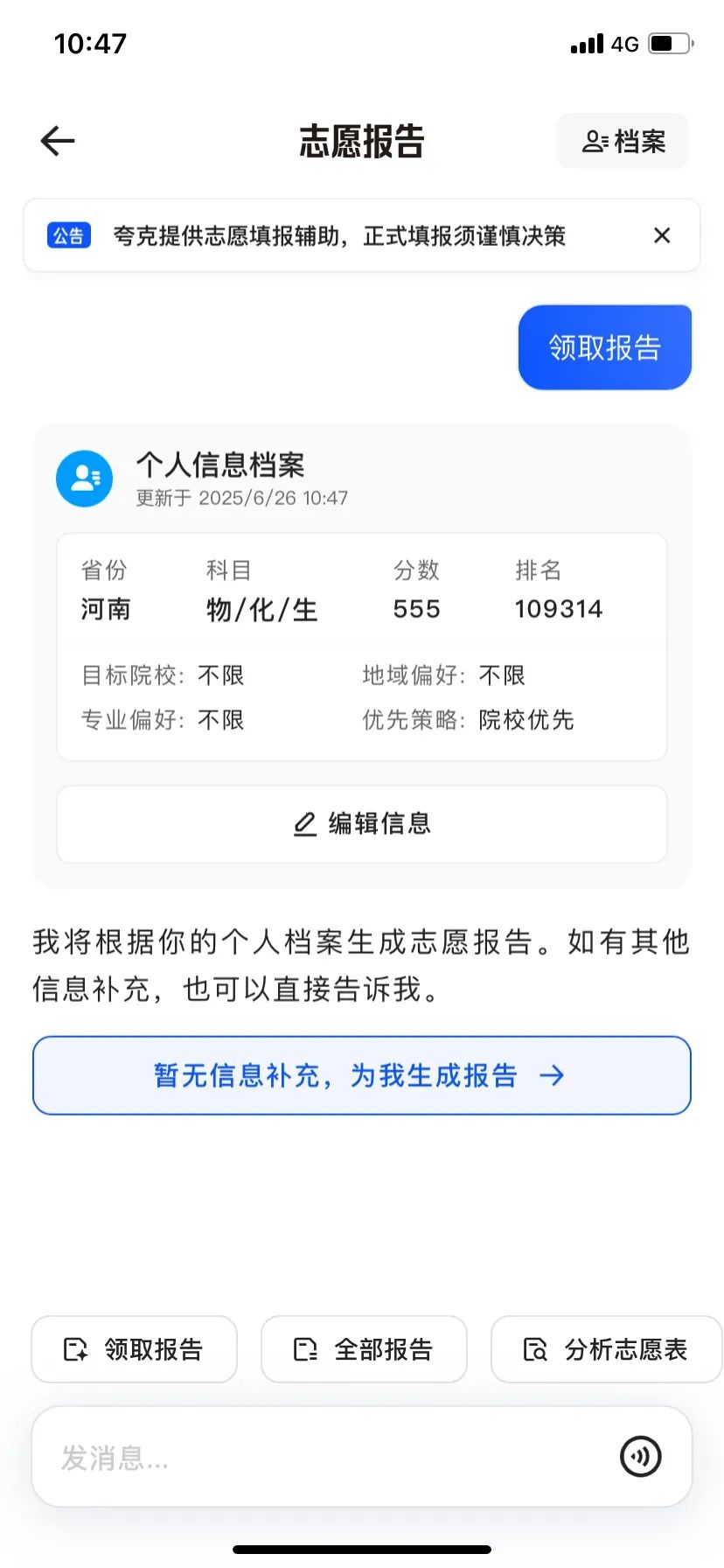
Source: Quark College Entrance Examination
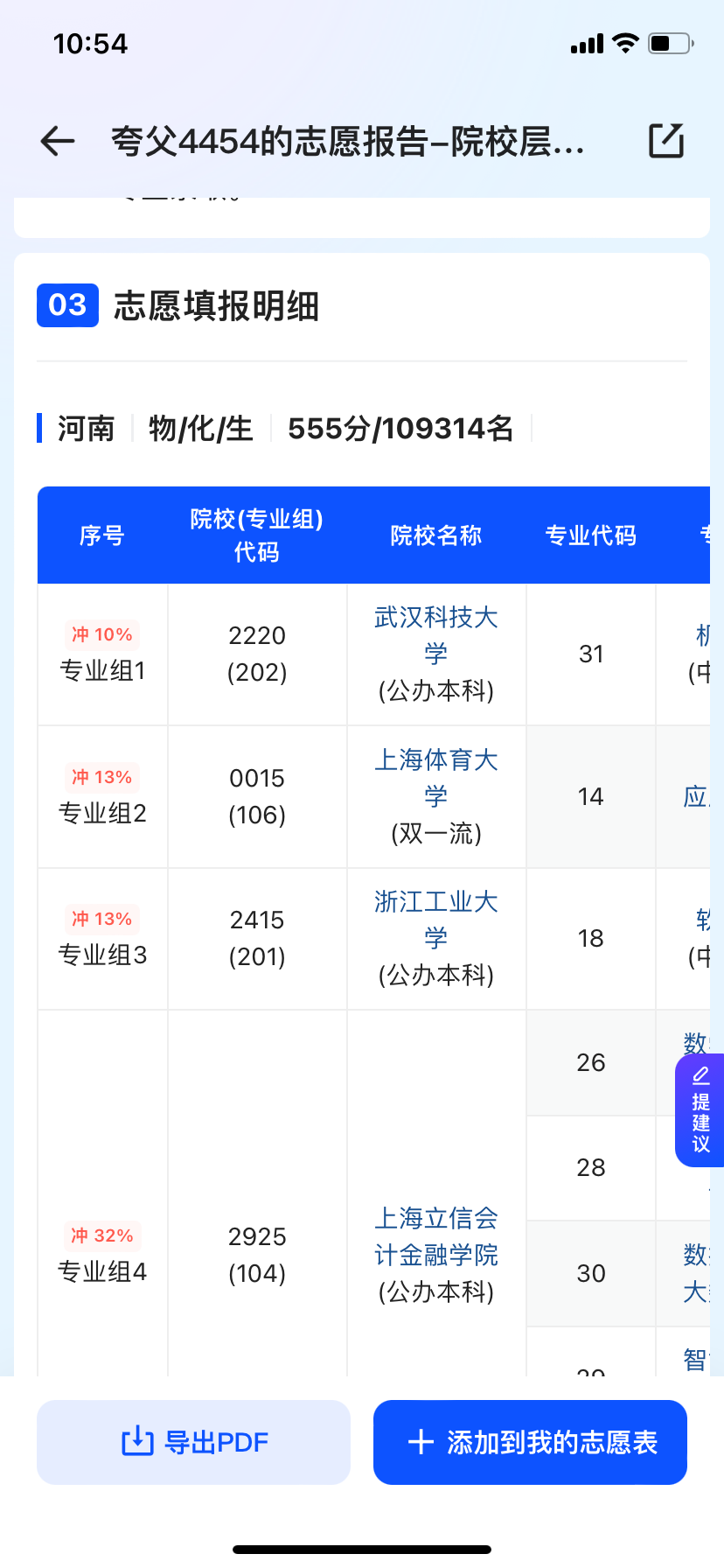
Ultimately, Quark's results were relatively comprehensive, providing five sections: candidate basic information, volunteer application strategy design, volunteer application details, volunteer form interpretation, and risk warning. The overall content was detailed and highly informative.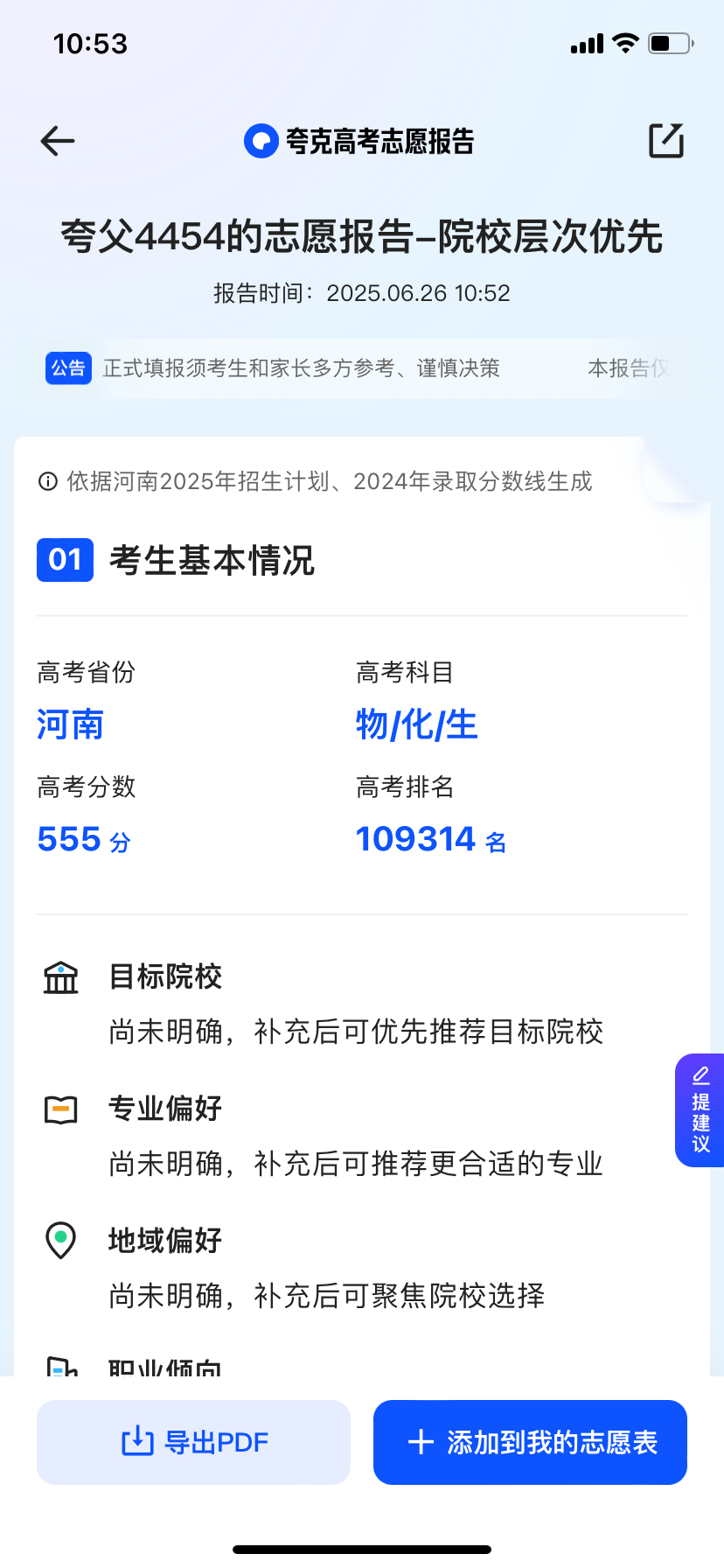



Similarly, we entered the same conditions into QQ Browser and requested a college application report. QQ Browser provided information across six sections: candidate information, strategy description, volunteer form details, volunteer form analysis, key college interpretation, and risk warning. While it featured an additional section on key college interpretation compared to Quark, the overall content was less detailed.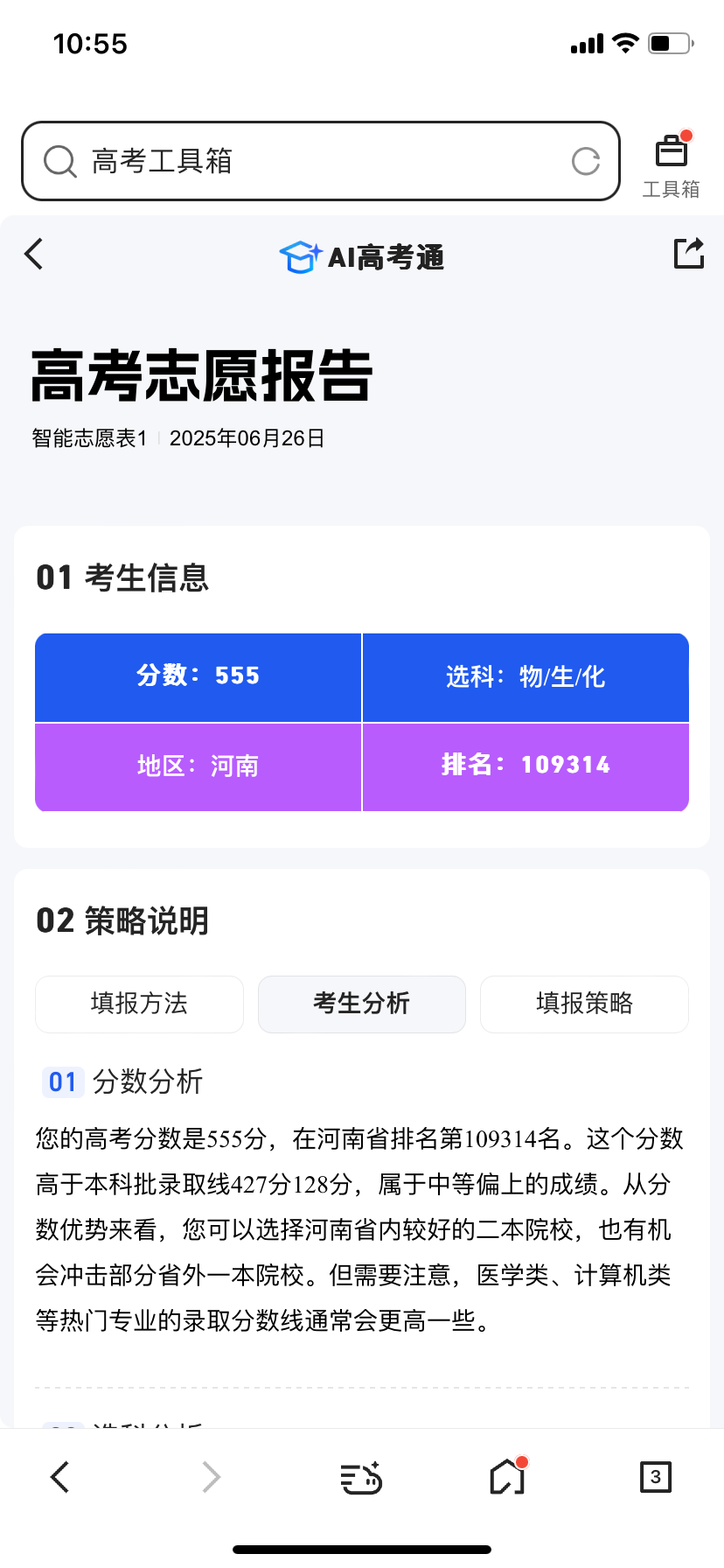
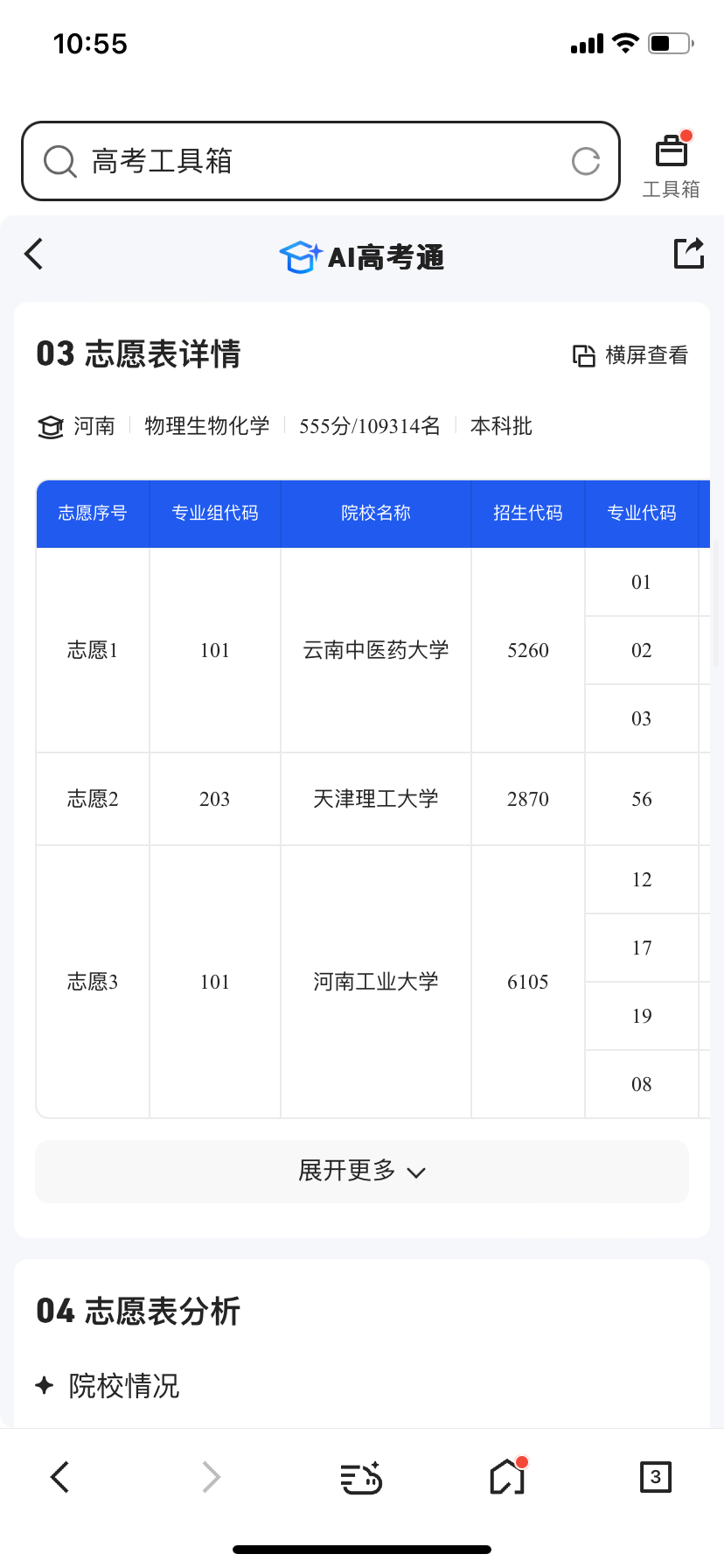
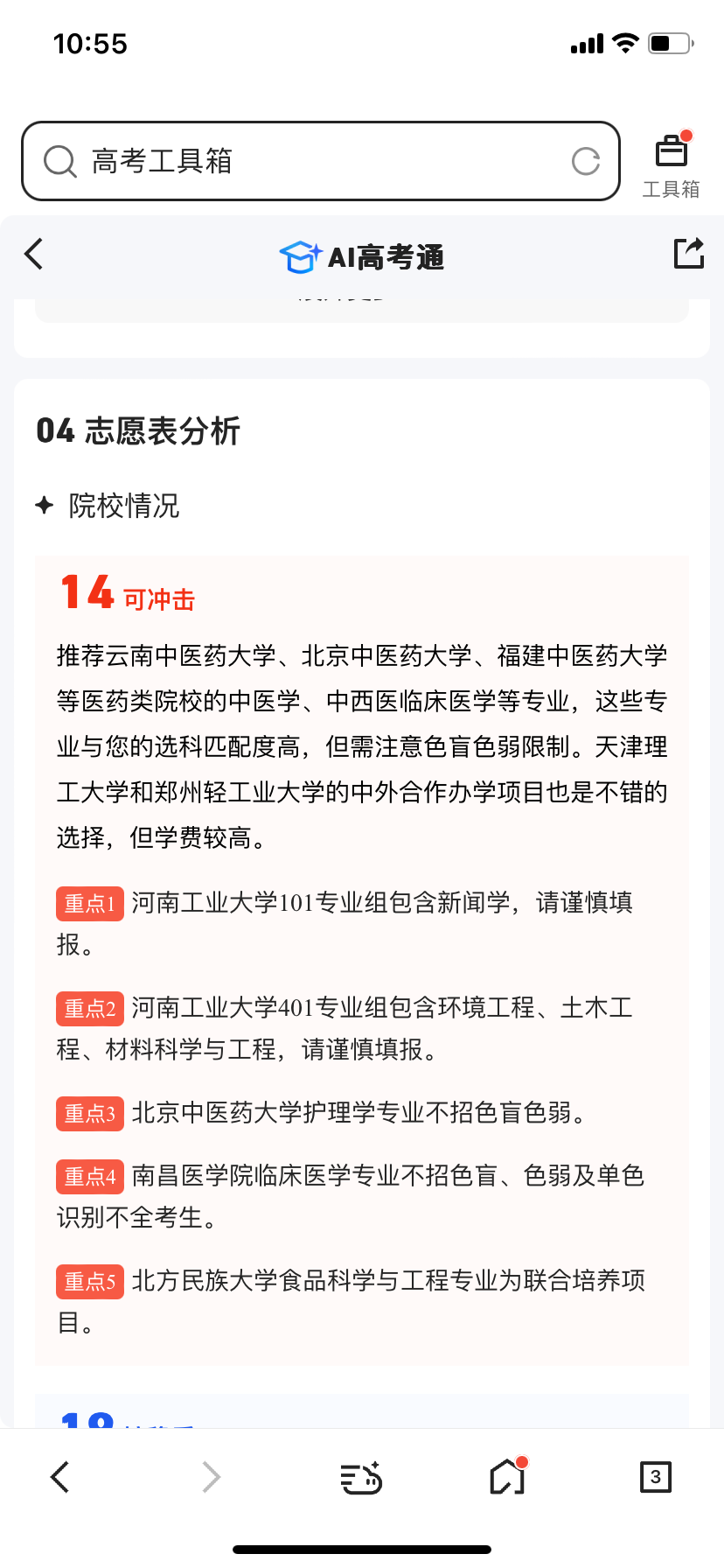


This year, Baidu launched a special college entrance examination section, integrating common content related to college applications. Besides its own AI volunteer assistant, it also introduced AI chat for volunteers and big data on the college entrance examination. However, despite the plethora of functions, they are largely result-oriented and lack proactive analysis content, requiring users to actively input information. Furthermore, the AI chat for volunteers report seems somewhat sparse compared to Quark and QQ Browser's reports.
Regarding in-depth college selection analysis and other aspects, the three products essentially continue last year's strategy of "challenge, stability, guarantee, AI three axes". In terms of the number of college recommendations, Quark offers 1,242, QQ Browser provides 642, and Baidu presents 320. Additionally, if candidates prioritize majors, Quark also includes a major priority option. Although there's a significant quantitative difference, each platform performs comprehensively and meticulously at the data level, offering references ranging from reportable major groups to historical scores, enrollment plans, and even tuition fees and subdivisions.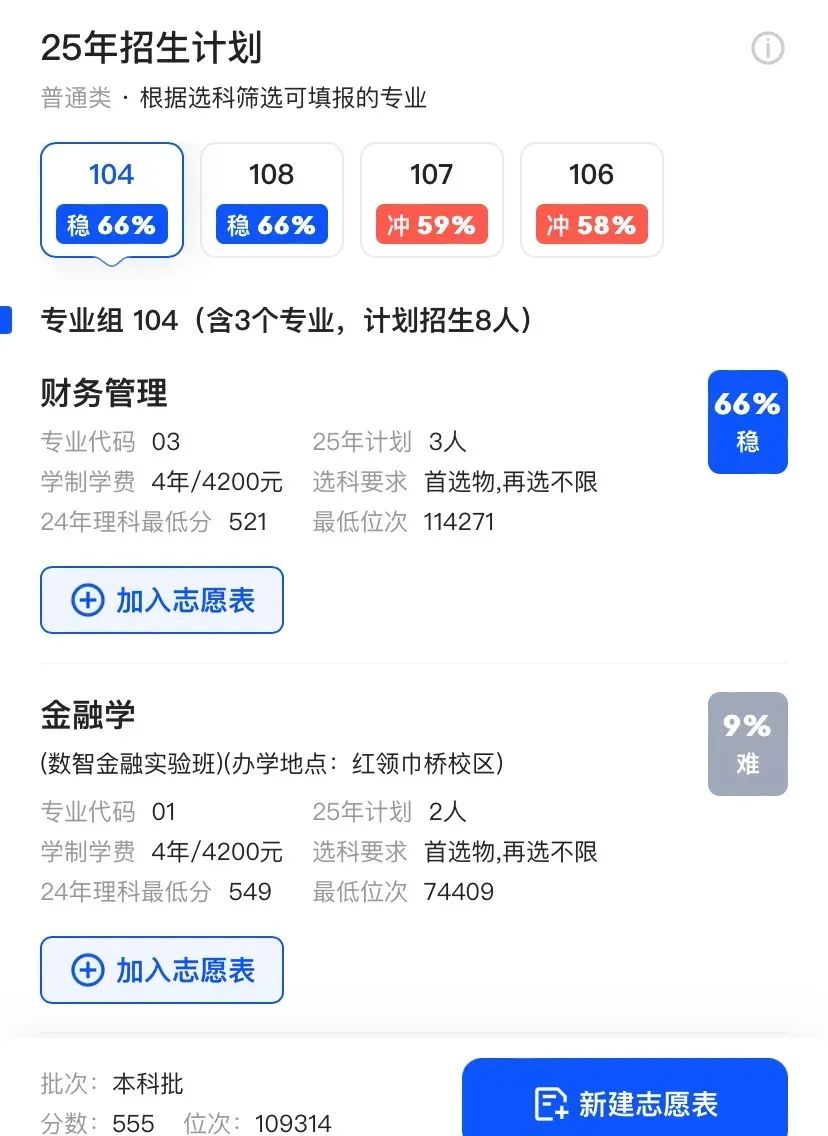
Source: Quark College Entrance Examination
However, in the crucial function of admission probability, each platform yields slightly different analysis results and calculation methods, accompanied by dazzling big data, which might confuse even parents, let alone recently graduated high school students. Based on "Tech News"'s inference from the information provided by each platform, this content stems from authoritative official websites, enrollment brochures, professional books, and videos from renowned teachers. Ultimately, AI integrates information from the entire network for collation and summary, outputting it through each platform's algorithm. It can be fundamentally understood as simply screening data and providing suggestions. In terms of overall information richness, Quark and QQ Browser proactively offer more information, which is beneficial for candidates without clear ideas. Conversely, Baidu integrates more information that needs to be passively obtained, suitable for candidates who already have their own preferences. In terms of core college recommendations, besides the quantitative difference, all three can satisfy candidates and their parents' needs. Of course, filling out applications is not merely a score-matching exercise but a profound decision-making process grounded in personal traits and career planning. Therefore, to utilize AI more accurately in the application process, input your thoughts and preferences as detailed as possible to obtain a more precise response. This is also a vital criterion for testing each platform's AI level.
02 Personalization Reaches New Heights
Under the traditional volunteer application model, candidates often rely solely on previous years' admission lines based on score ranges, resulting in a narrow selection scope and a lack of precise analysis of personal interests and abilities, easily leading to the dilemma of "high scores with low placement" or "majors not matching". Relying on big data and algorithm models, AI application tools can achieve multi-dimensional analysis from scores to personal traits, presenting candidates with rich and diverse college and major options. Thus, we also conducted more in-depth customized tests on the three platforms. Let's start with Quark. As mentioned earlier, Quark supports filling in personal information profiles, encompassing target colleges, regional preferences, major preferences, priority strategies, graduation plans, career inclinations, tuition preferences, and other personal hobbies and family backgrounds that can be specified.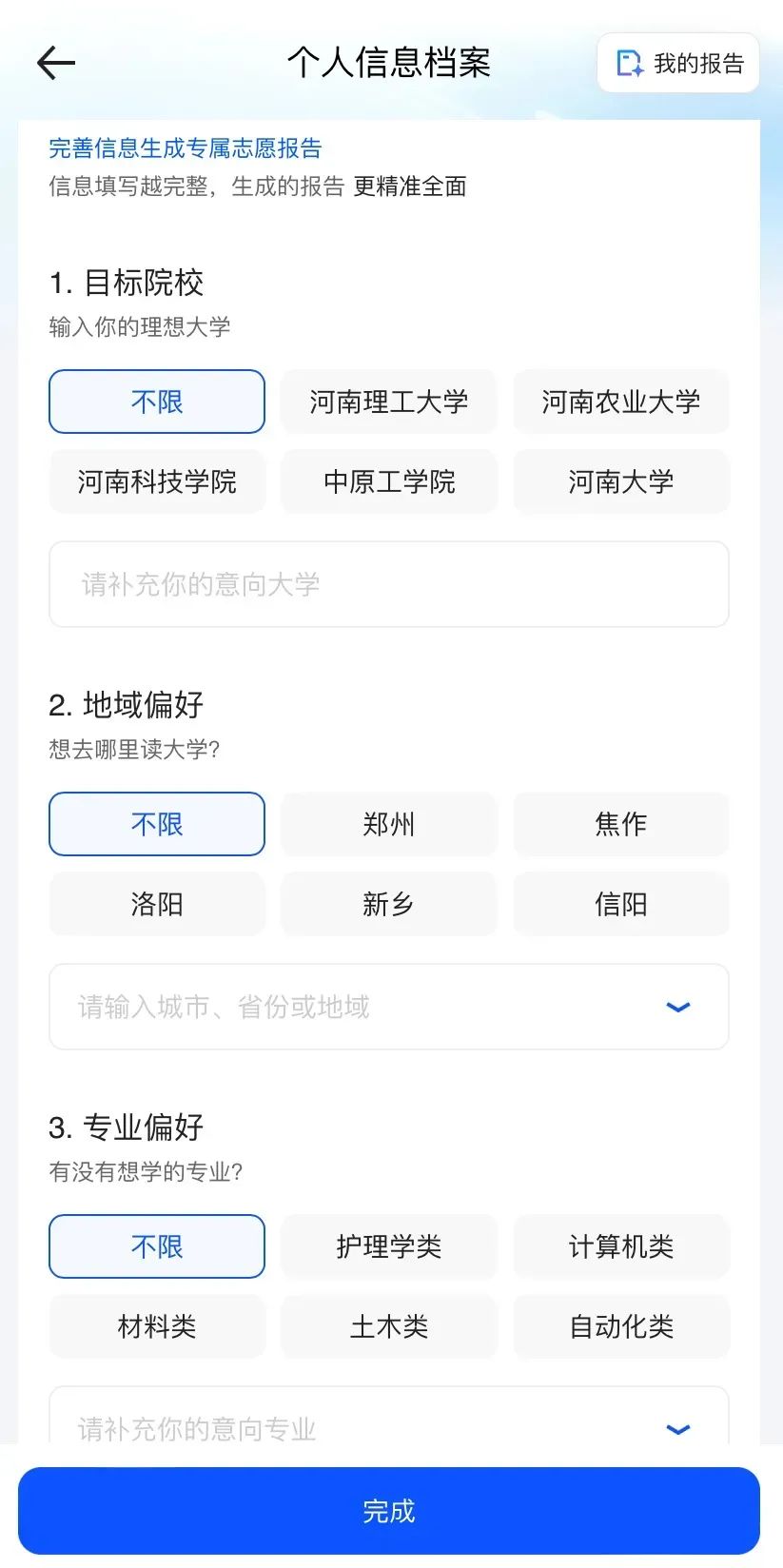
Source: Quark College Entrance Examination
This function focuses on personalized scenarios. When candidates have preferences or a general direction for their choices, Quark can analyze from multiple angles to further assist in the application process, akin to a privately customized volunteer application form, providing a more comprehensive experience and tailored recommendations for candidates. For instance, when a candidate wishes to pursue a literature major and subsequently plans to take the civil service exam, they might grapple with whether to choose a prestigious school or a favored major. For such questions without definitive answers, traditional search engines can hardly provide solutions, but with the assistance of AI and large models, relatively appropriate suggestions can be found. Furthermore, if candidates have numerous queries, Quark's "Deep Search for College Entrance Examination" function comes in handy. This function is essentially more like a chat-based AI tool for the college entrance examination. To enhance the accuracy and professionalism of answers, it refines the actual needs of candidates, with each type of need corresponding to a customized answer paradigm and key points to ensure the reply is both targeted and in-depth. Next is QQ Browser, whose information collection process is similar to Quark's. It also offers a user-friendly basic information template, requiring only ticking like multiple-choice questions. However, there are limitations, such as 10 regions for regional selection and a maximum of 8 majors for major selection, based on which searches are conducted.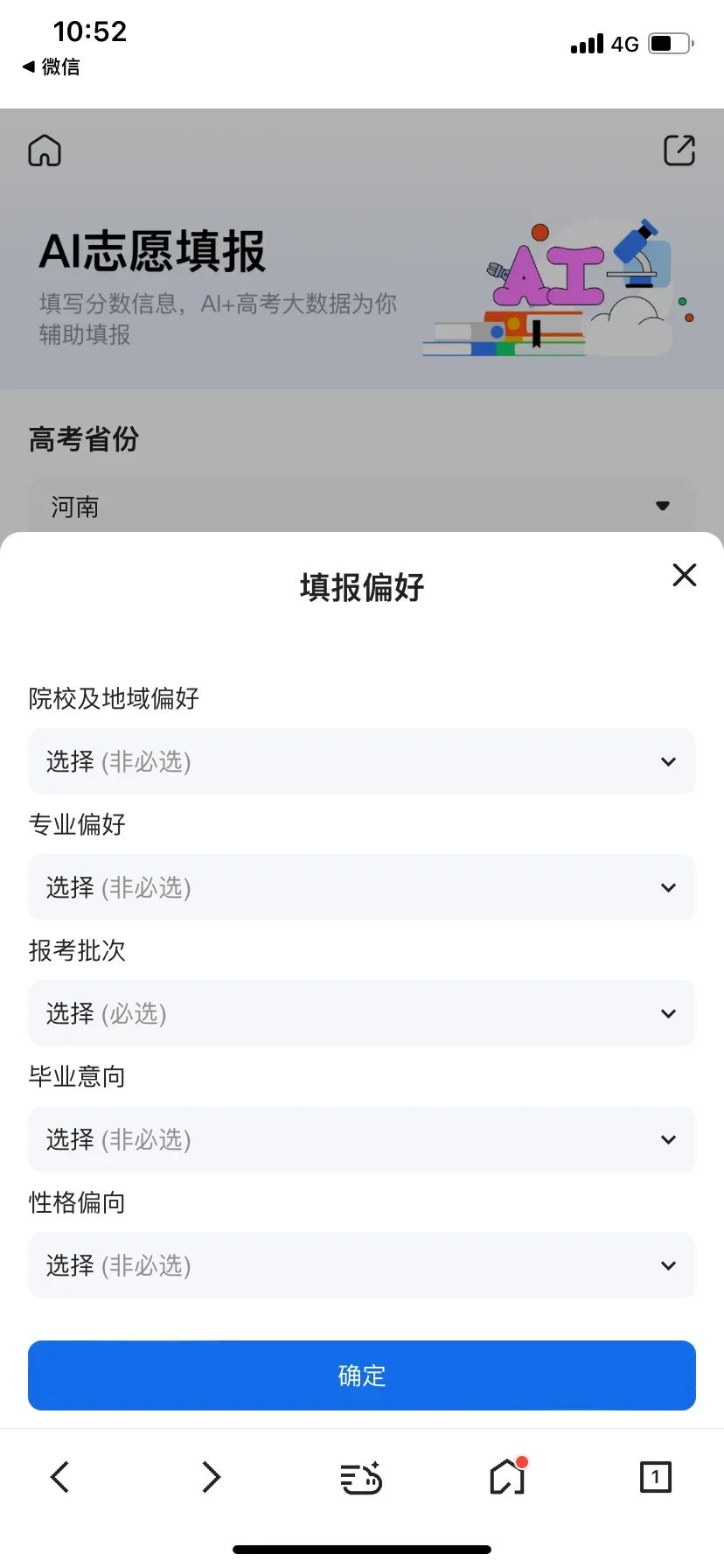
Source: QQ Browser
AI College Entrance Examination. Additionally, QQ Browser allows for basic information inquiries through dialogue. For example, inquiring about scores (query time and channels for college entrance examination scores in different provinces, one-point-one-segment curve charts, etc.); enrollment plans of various provinces and colleges; major subdivisions and employment situations, etc., akin to having a dedicated college entrance examination consultant. Baidu resembles a dialogue-based AI chat, but a closer look reveals notable differences. For instance, Baidu can create multiple volunteer forms. In cases of score changes or multiple candidates in a family, it avoids the hassle of repeated information alterations.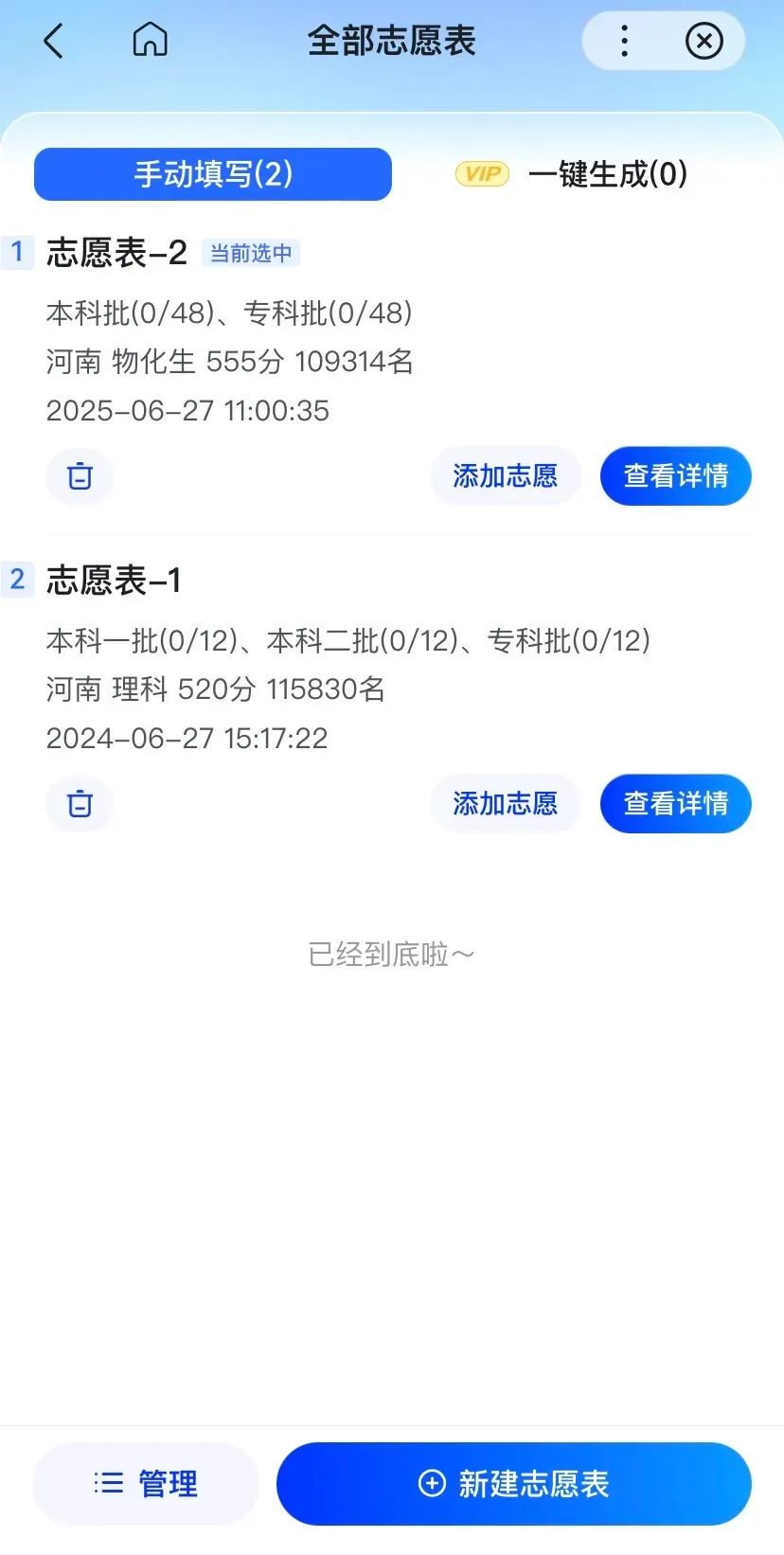 Source: Baidu College Entrance Examination Column
Source: Baidu College Entrance Examination Column