Three Missed Opportunities! Former OpenAI Employee Returns to AI Programming Race, With Old Employer's Golden Support
![]() 09/24 2024
09/24 2024
![]() 523
523

Author | XuuShan, Editor | Evan“
After years of wandering, the prodigy returns to AI once again.
Open AI is emerging as the new 'Huangpu Military Academy' of AI, following in the footsteps of Google.
Jacob Jackson, a former OpenAI employee, founded AI programming company Supermaven in February 2024 and recently announced the completion of a $12 million Series A funding round led by Bessemer Venture Partners, with participation from OpenAI co-founder John Schulman and Perplexity co-founder Denis Yarats. Jackson is one of many OpenAI employees who have ventured out to start their own businesses.

The current team consists of five members. This is Jackson's second AI programming venture; previously, he was a two-time gold medalist at the IOI (International Olympiad in Informatics) and founded AI programming platform Tabnine during his college years. Tabnine was acquired by AI coding company Codata at the end of 2019.
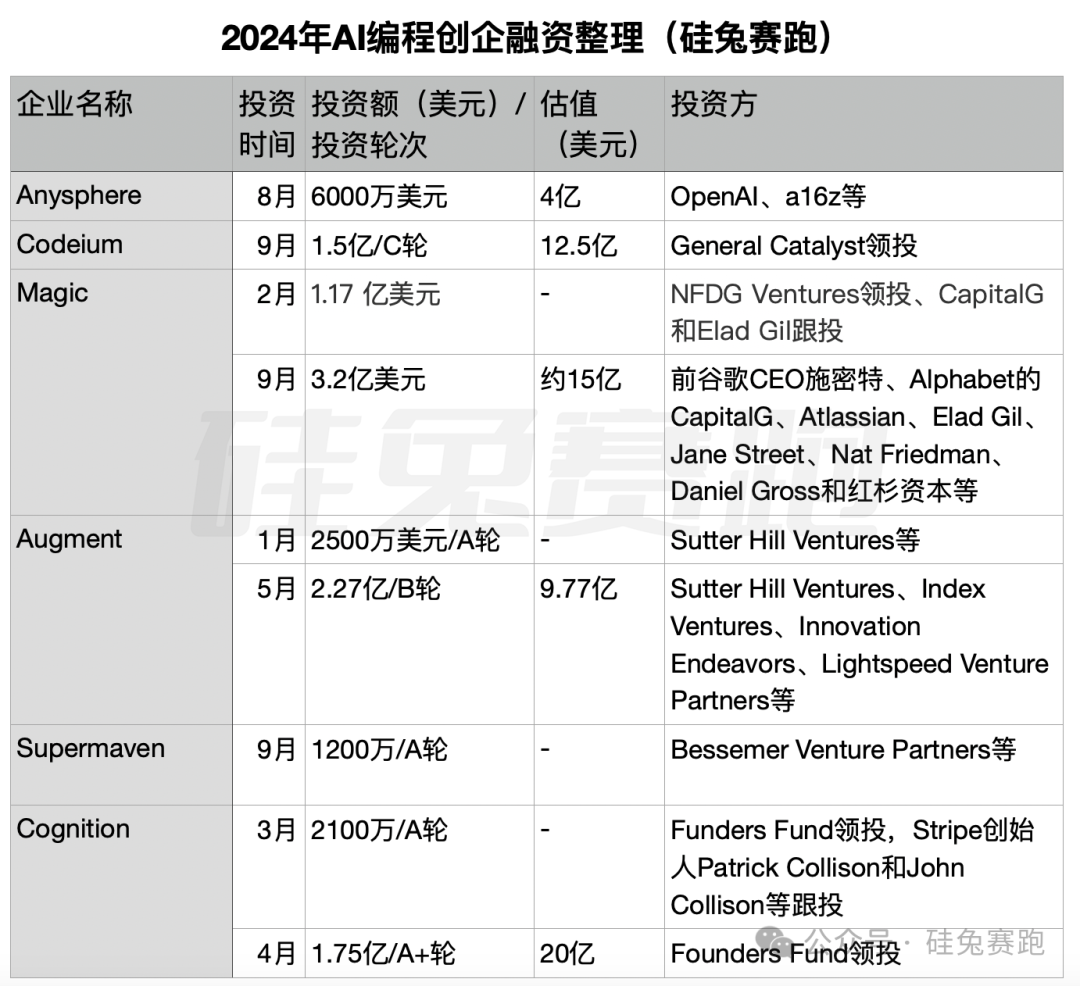
As Supermaven announced its funding, Silicon Valley was experiencing an investment boom in AI programming, seen as the fastest-growing commercialization track in AI applications. According to incomplete statistics, six AI programming startups have raised a total of $11.07 million in funding so far in 2024. Cognition, Augment, and Magic have each received two funding rounds this year, with valuations around $1 billion.
Supermaven's appeal in Silicon Valley lies in its speed and powerful functionality. Its eponymous AI programming platform, Supermaven, supports a 1 million token context window, enabling it to understand vast amounts of code while maintaining long-term responsiveness.
To date, Supermaven boasts over 35,000 developer users, with its code editor, Supermaven VS Code, exceeding 100,000 downloads and achieving an annual recurring revenue (ARR) of $1 million.
As a seasoned player in the AI programming space, Jackson re-enters the fray. How does he view this rapidly evolving landscape? What advantages does Supermaven bring to compete with players like Magic and Replit?
01
Exiting OpenAI, AI Programming Veteran Starts Anew, Earning First Fortune with GPT-2
Jacob Jackson was among the first in Silicon Valley to recognize GPT models' potential to transform code writing. He witnessed the AI programming sector's transformation from obscurity to prominence. Jackson's first fortune was made through GPT.
In 2018, OpenAI's 'predict the next word' Transformer architecture had yet to demonstrate true intelligence. As a senior computer science student at the University of Waterloo, Jackson foresaw the immense potential of OpenAI's GPT-2 model for code completion. In just nine months, he and his team leveraged GPT-2's Transformer architecture to create their first code completion tool, Deep TabNine.
Programmers could install Deep TabNine as a plugin in their code editors. As they wrote code, TabNine would suggest the next line. Upon launch, Deep TabNine stunned the industry with its support for 23 mainstream programming languages, compatibility with five editors, and high-quality code suggestions.
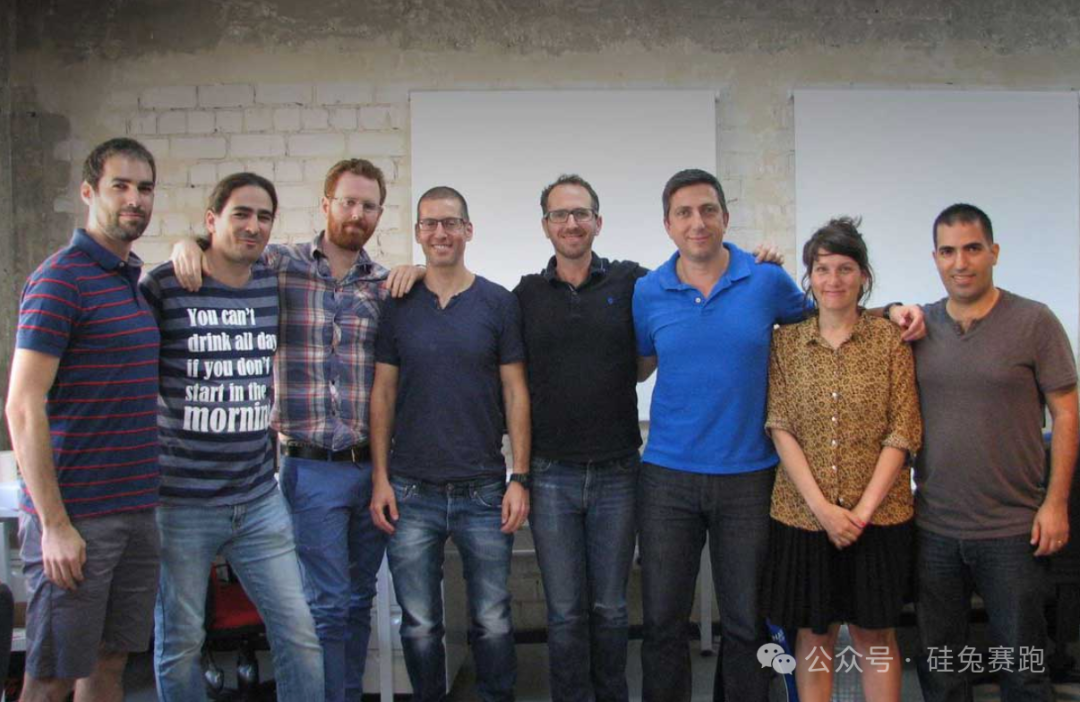

Group photo of the TabNine founding team, with Jacob Jackson fourth from the left. Many netizens hailed TabNine as the best code completion tool they had ever used, dubbing it a 'killer app' for programmers. Within months, it amassed 300,000 downloads on the VS Code extension marketplace, performing well among new code type plugins.
TabNine showed early signs of commercial success – users were required to pay if their code hints exceeded 400KB, with personal plans costing $49 and business plans $99. TabNine also thoughtfully provided TabNine Cloud server functionality for PC users. By the time of its acquisition, TabNine had secured nearly $60 million in venture capital funding.
TabNine's success paved the way for Jackson's second foray into AI programming. In 2019, during his final exams, Jackson sold Tabnine to Israeli AI software company Codata and joined OpenAI as an intern. He worked at OpenAI until 2020, becoming one of its early researchers.
While at OpenAI, Jackson focused on distributed training of large language models. Around 2020, he recognized generative AI's potential in search and left OpenAI to develop Same Energy, a visual search engine.
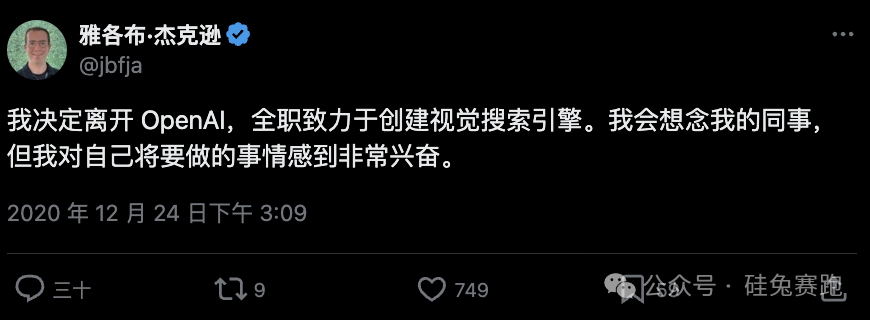
Same Energy supports both text-to-text and image-to-image search. For instance, users can input a joke and select Twitter as the source, and the engine will return similar jokes from Twitter. Similarly, entering an image will yield similar images.
'By integrating richer visual understanding, Same Energy captures the artistic style and emotion of images. We hope it can help users discover new styles and inspire creativity,' said Jackson in an interview.
Same Energy Search Engine
Looking back from 2024, it's clear that Jackson accurately predicted two significant directions for generative AI: AI code completion tools and AI search engines. Unfortunately, he didn't persist in either. Same Energy remained in beta and failed to commercialize, with its website no longer operational.
In recent years, Jackson has seen tools like ChatGPT and GitHub Copilot transform how developers work. 'Today's AI programming tools are exhilarating. Since founding Tabnine, underlying technologies for large models have significantly improved, and more developers are using AI tools to accelerate their workflows,' he said. Inspired by this shift, Jackson founded Supermaven, creating an AI coding platform similar to Tabnine but with enhanced code quality and underlying technologies.
'As AI systems become smarter, we'll create new applications to drive technological progress. I believe AI will generate immense economic value,' said Jackson, explaining his return to AI programming. Rather than fearing AI replacing software developers, he advocates leveraging AI to boost productivity while preserving humans' decision-making authority over critical issues.
02
Supermaven Chat Adapts o1 Model; New Funding Boosts Text Editor Development
In today's rapidly evolving landscape of large models, startups that adapt quickly reap early rewards.
On September 13, OpenAI unveiled its new o1 model, showcasing enhanced complex reasoning capabilities.
Supermaven promptly integrated o1 series models into its editor chat tool, Supermaven Chat. Developers can use Supermaven Chat to invoke models like o1-preview, o1-mini, and Claude 3.5 Sonnet for code writing.
Supermaven maintains sustained responsiveness when handling large codebases. With low latency and fast response times, it's beloved by engineers.
'Supermaven only takes 10-20 seconds to access a developer's code repository,' said Jackson. The platform's foundation is its proprietary AI model, Babble, based on a new neural network architecture that comprehends vast amounts of code simultaneously. 'Supermaven is the fastest and most powerful AI coding assistant on the market,' he added.
Regarding the new funding, Jackson said it will be used to develop Supermaven's text editor, currently in beta. It accelerates daily tasks and helps experienced developers navigate large codebases. Developers can use Supermaven for end-to-end building, testing, and delivery.
Supermaven employs Babble, a proprietary language model optimized for inline code completion. 'Our in-house model and service infrastructure offer the fastest completion speeds and the longest context window among all AI code assistants like Copilot,' said Jackson.
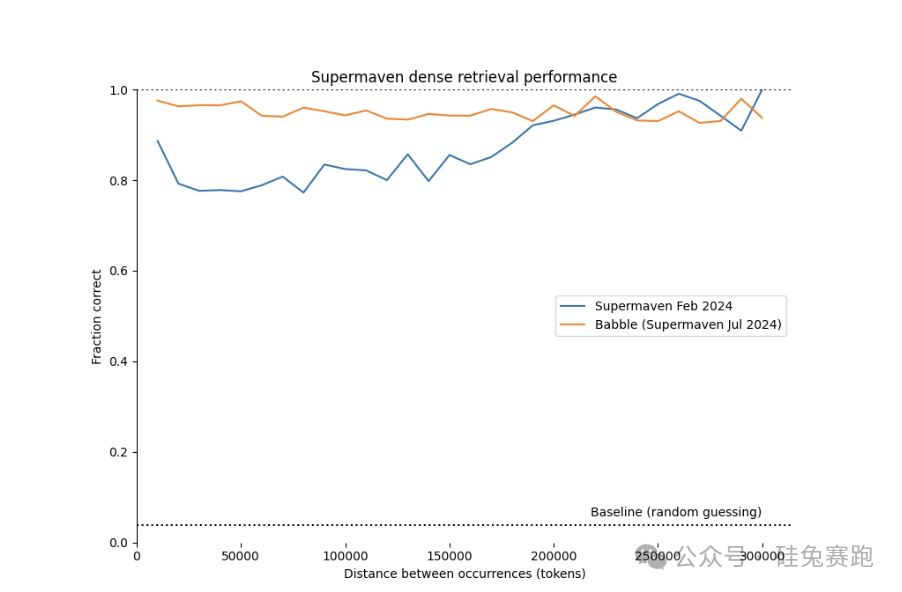
Supermaven's Babble model enhances performance in dense retrieval tasks.
Supermaven is the first AI programming startup to offer 'next location prediction' code completion. It jumps to code locations and suggests changes based on context, supporting all IDEs (IntelliJ, PyCharm, WebStorm, etc.).
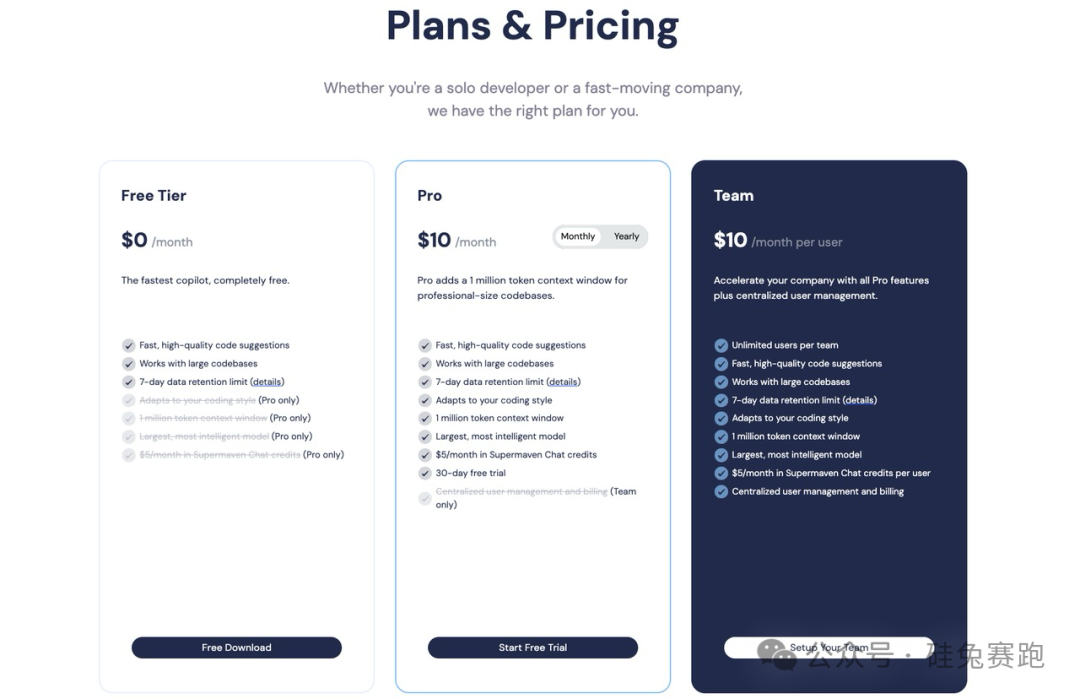
Currently, Supermaven offers three business models: free, premium Pro subscriptions, and enterprise Team plans. Jackson noted that Supermaven's annual recurring revenue (ARR) reached $1 million this year. 'We aim for significant growth by year-end,' he added. 'Despite industry headwinds, the AI coding market is growing rapidly.'
03
AI Entrepreneurs Flood Programming Race: Opportunities and Risks Coexist
The AI programming landscape has evolved since Jackson's initial foray.
Polaris Research predicts the AI programming market will reach $27.17 billion by 2032. Latest surveys show 1.8 million users and 77,000 companies use GitHub Copilot, with an ARR of $100 million. Increasingly, engineers integrate AI programming into their workflows.
'With AI advancements, programming is no longer a must-have skill for everyone. AI's magic lies in empowering everyone to become a programmer,' said NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang.
To democratize programming, AI pioneers like Google, OpenAI, Microsoft, Cognition, Anysphere, and Poolside are vying in the AI programming space.
AI programming tools can be broadly categorized into two types: AI code completion tools like Supermaven and AI agents that autonomously program based on requirements, such as Replit Agent.

Source: Medium
However, some users have mentioned that the code quality provided by existing AI programming assistants/tools is not high. At the same time, many large companies remain cautious about AI programming, fearing that AI programming tools may leak their confidential data. Some AI programming tools provide relatively poor code quality, which can easily lead to errors and system vulnerabilities. Apple has banned AI code assistants such as Copilot, fearing that it may affect system stability. Jackson mentioned that Supermaven will not use customer data to train its models. However, he also mentioned that the company will retain data for a week to "enable the system to respond quickly."
On the other hand, according to the analysis of Silicon Rabbit, programmers are currently choosing their AI programming partners on different platforms such as Replit Agent, Cognition, Cursor, etc., but the overall proportion of paying users to total users is still relatively low, and the cost of user migration is also relatively low. At the same time, different underlying models will also widen the gap in code programming capabilities among players. According to observations, most code tools are fine-tuned based on large models from OpenAI, Microsoft, and Google. These code tools can quickly understand various language structures and patterns, provide more general solutions, and as the large models are upgraded, there is a significant improvement in performance. However, for some specific scenarios or requirements, code tools often struggle to respond in a timely manner.
A few code tools, like Supermaven, which build models from the ground up, can provide faster innovation speeds and more flexible improvement strategies in specific scenarios, offering a higher degree of customization to adapt to specific programming environments and developer workflows.
To date, no startup in the AI programming sector has a dominant advantage, and competition among players continues.







