What stage has humanoid robot development reached?
![]() 10/10 2024
10/10 2024
![]() 612
612
In recent years, humanoid robots, as outstanding representatives of artificial intelligence technology in the physical world, have gradually demonstrated their enormous potential and value. With the rapid development of general large models, humanoid robots have gained unprecedented generalization capabilities, propelling the entire industry into the initial stage of commercialization. The vast potential of this field has attracted the attention of many technology giants, including Tesla, OpenAI, NVIDIA, Samsung, and others, who have deployed strategies to gain a leading position in this emerging market.
Taking Tesla as an example, its founder Elon Musk introduced the concept of a humanoid robot, Tesla Bot, in 2021, followed by the launch of the prototype Optimus in 2022. By December 2023, Tesla unveiled the upgraded version of Optimus, Gen2, which significantly improved upon its predecessor in terms of perception, brain processing, and motor control capabilities. With the gradual implementation of Tesla's Optimus, the industry generally predicts that 2025 will mark the advent of the era of mass production for humanoid robots. Their application scenarios will evolve through three stages: initial adoption in automotive factories, comprehensive penetration into manufacturing, and ultimately maturing to enter households.
According to calculations by AVIC Securities, by 2030, the global demand for humanoid robots is expected to reach 2 million units, corresponding to a market space exceeding 570 billion yuan. This immense market potential undoubtedly paints an exciting blueprint for the future development of humanoid robots. So, where does the development of humanoid robots stand today?
01. Continuous Capital Injection
Since 2022, the humanoid robot industry has seen frequent financing activities, with a total of 42 financing rounds raising nearly 9 billion yuan, averaging over 100 million yuan per round. In 2023, investment enthusiasm intensified, with 23 investment events recorded throughout the year, raising over 5 billion yuan. In the first two months of 2024, the average amount per financing round surpassed 200 million yuan, doubling compared to 2022, demonstrating strong capital confidence in the future prospects of the humanoid robot industry.
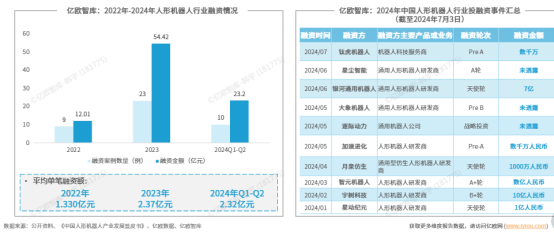
Specifically, from January to February 2024, the humanoid robot industry saw 10 investment rounds, with disclosed financing amounting to approximately 2.32 billion yuan. Among them, Unitree Robotics secured 1 billion yuan in its B+ round, while Galaxy General Robotics raised 700 million yuan, setting a new record for the highest angel round funding in 2024. These financing achievements underscore the continuous optimism of capital towards the humanoid robot industry and inject strong momentum into its future development.
According to statistics from the International Federation of Robotics (IFR), China accounted for 52.5% of global industrial robot sales in 2023, establishing itself as the world's largest robot application market. Currently, China's robot industry is undergoing rapid development, with the intelligentization process accelerating in downstream applications such as industrial manufacturing and retail consumption. As a carrier of cutting-edge technology, humanoid robots, with improved technology maturity and reduced costs, will be capable of undertaking more flexible tasks, thus holding immense market potential.
From a macro perspective, favorable policies and rapid advancements in large model technology are driving the rapid development of the domestic humanoid robot industry. Currently, humanoid robot manufacturers have begun small-batch commercial deliveries. According to research data from iResearch, shipments of humanoid robots are expected to reach approximately 2,000 units in 2024. Overall, the market presents numerous favorable factors, and the entire industry is at an initial stage of development, poised to unleash significant potential in the future.
02. Which key components deserve attention?
The composition of a humanoid robot can be broadly divided into the execution system, perception system, and control system.
In the execution system, the achievement of flexible joints relies on key components such as lead screws, motors, and reducers, which collectively determine the robot's motion flexibility. Tesla's Optimus robot joints consist of 40 actuators, with the costs of rotary joints, linear joints, and dexterous hands accounting for over 50% of the total, highlighting the importance of cost reduction. In this context, the domestic industrial chain exhibits significant advantages. Specifically:
Lead screws, as the core components of linear joints, are primarily categorized into trapezoidal lead screws and ball screws, with manufacturing processes including turning, milling, and grinding. Grinding machines play a vital role in both rough and finish machining. Currently, lead screws account for up to 23.4% of costs, making cost reduction an urgent need.
In terms of motors, frameless torque motors are widely used in rotary and linear joints, while coreless motors or brushless slotted motors are employed in dexterous hands. Together, motors account for approximately 8.9% of costs, making them another significant cost contributor in the execution system.
Reducers are primarily used in rotary joints, with harmonic reducers being the mainstream solution and planetary reducers suitable for some joints with lower precision requirements. Currently, reducers account for about 4.1% of costs.
The perception system serves as the medium for humanoid robots to interact with the environment, relying on a combination of various sensors. Sensors convert the physical quantities perceived by the robot about its internal and external environments into electrical outputs, categorized into internal and external sensors. The core sensors for humanoid robots include torque sensors, visual sensors, and tactile sensors, which collectively form the foundation of the robot's perception system. Currently, sensors account for approximately 24.7% of costs. Specifically:
Torque sensors are used in rotary and linear joints, while six-axis torque sensors can be employed in wrists and ankles to enhance compliance control. However, six-axis force/torque sensors are significantly more costly and difficult to manufacture than single-axis torque sensors, resulting in their early adoption primarily in space robotic arms for aerospace applications.
Regarding visual sensors, Tesla's Optimus utilizes a pure vision solution, while companies like Xiaomi and Unitree mostly employ multi-sensor fusion schemes to enhance the robot's perception capabilities and adaptability.
Tactile sensors represent one of the most significant marginal changes in Tesla's Optimus-Gen2 compared to its predecessor, with tactile sensors integrated into its hands potentially leading industry trends.
The control system serves as the intelligent 'cerebellum' of humanoid robots, responsible for real-time control of the position, speed, and direction of mechanical moving parts, ensuring they move according to expected trajectories and specified motion parameters. Due to the diversity of application scenarios and varying computational requirements among humanoid robots, controllers are typically developed in-house to meet demands for low power consumption, high computational power, and high integration.
Based on the above analysis, AVIC Securities recommends that investors focus on the following investment directions:
In the execution system, pay attention to Tier 1 suppliers such as Sanhua Intelligent Controls and Top Group, as well as lead screw suppliers like Beite Technology, Best Group, and Wuzhou Xinchun. In the perception system, focus on sensor suppliers like Kele Sensor, Donghua Test, and Hanwei Technology. In the control system and key components arena, consider reducer suppliers such as Leadshine Technology, Zhongdalide, and Shuanghuan Transmission, along with motor suppliers like Mozon and Buchang Electric. Additionally, domestic OEM manufacturer Boxlight is also worthy of close attention.
Overall, the trend in the humanoid robot industry is clear, currently at a crucial breakthrough stage from 0 to 1. 2024 is a pivotal year for achieving mass production. Moving forward, close attention should be paid to investment opportunities arising from technological iterations, designations, and new product launches.