Revolutionizing the Robotics Industry: Why Auto Companies Are Embracing Humanoid Robots
![]() 12/24 2024
12/24 2024
![]() 761
761

Introduction
The surge in popularity of humanoid robots has sparked a wave of enthusiasm among automakers, prompting them to explore new frontiers in the robotics industry.
"In the future, only cars, drones, and humanoid robots will achieve large-scale mass production," stated NVIDIA founder Jen-Hsun Huang in late November.
Indeed, China's humanoid robot market is currently booming. Various companies, including tech giants like Boston Dynamics and Unitree Robotics, industrial automation firms such as Inovance and Topstar, and innovative robot enterprises like Senhan Technology and Figure.ai, are engaged in R&D and production. Notably, automakers are also diving into this new blue ocean.
Tesla, the pioneer, along with Huawei, Xiaomi, XPeng, BYD, GAC, SAIC, Toyota, Chery, and Changan, have all laid out plans for this emerging robotics landscape. With continuous technological advancements and a growing market, it's anticipated that more automakers will join the R&D and production of humanoid robots.

However, some question whether automakers are rushing into humanoid robots prematurely, given that their car manufacturing technology is not yet fully mature. While there's a connection between automotive manufacturing and humanoid robot technology, the technical thresholds and market demands are vastly different.
Some automakers, without fully mastering the core technology of automotive manufacturing, are eager to extend their business into the field of humanoid robots. These companies either invest in robot companies or develop their own humanoid robot technology, aiming to secure a place in this emerging field. So, what drives automakers to make such layouts?
The Demand for Robots is Ubiquitous
Robots encompass a broad spectrum, categorized by function to suit specific application scenarios and needs:
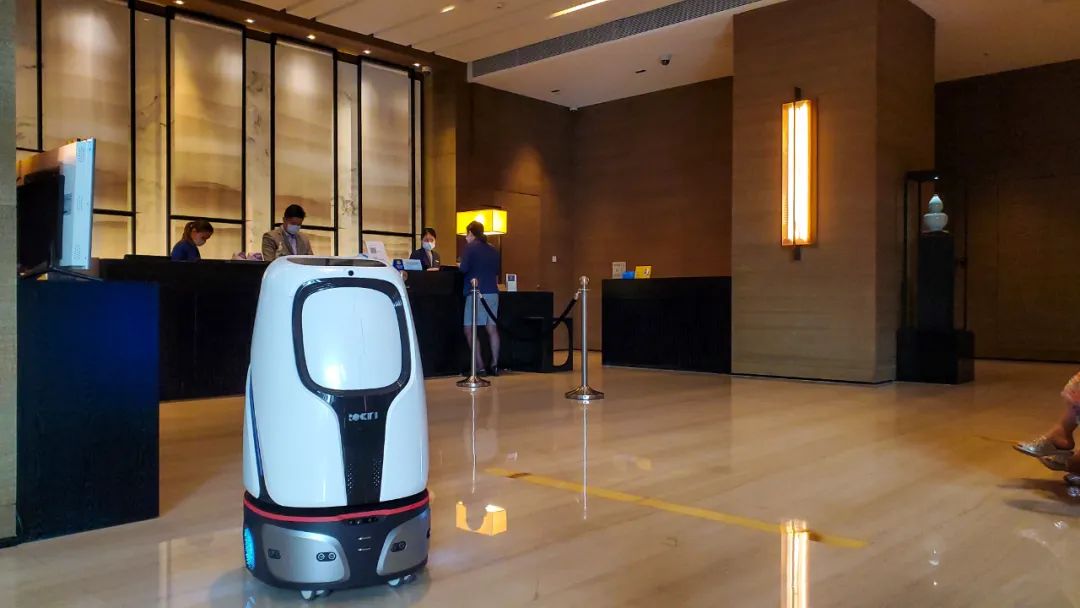
Public service robots are the most common in daily life, providing services such as reception, navigation, and security. For instance, reception robots greet passengers at airports and train stations, while tour guide robots offer navigation services to tourists, and security patrol robots ensure public safety.

Personal/household service robots are also becoming increasingly popular, offering services like cleaning, entertainment, and education at home. Sweeping robots automatically clean floors, and intelligent companion robots engage children in play and study, adding fun and convenience to family life.
Agricultural robots are a new favorite in modern agriculture, capable of precise planting, pesticide spraying, and other tasks. Military robots demonstrate their prowess in the military field, while specialized robots like search and rescue robots and underwater operation robots are designed for specific tasks.
Service robots are also widely used in industries like restaurants, hotels, and hospitals. Medical robots perform delicate surgeries, assist in rehabilitation therapy, and play a crucial role in nursing, providing strong support for medical staff.
Finally, industrial robots are invaluable assistants on factory production lines, responsible for automating processes such as precise assembly, efficient welding, and heavy lifting, significantly enhancing production efficiency.
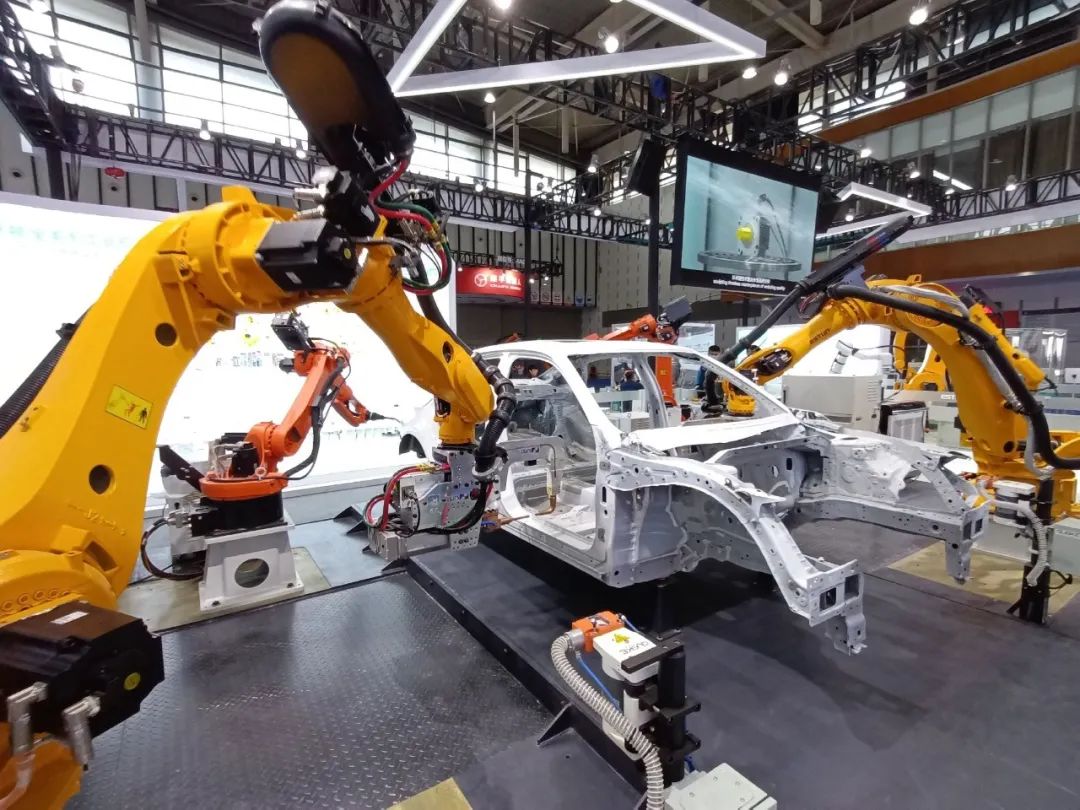

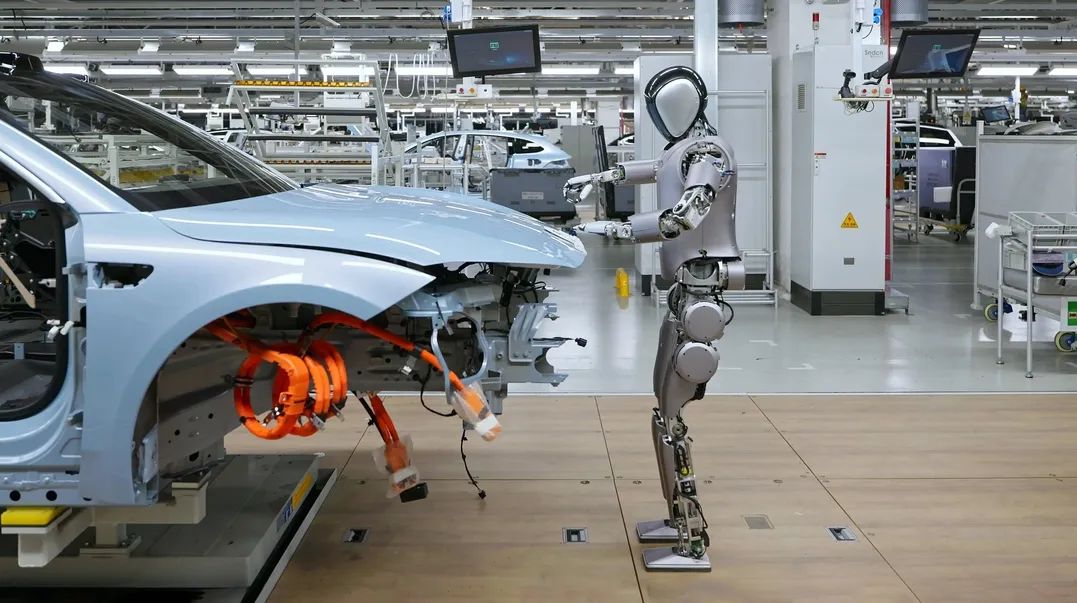
Automakers value the potential of industrial robots. As the backbone of the automotive manufacturing industry, automakers have stringent requirements for production efficiency, quality control, and cost optimization. In this context, the value of industrial robots becomes increasingly evident, making them highly sought-after.
Industrial robots, with their efficient, precise, and stable working characteristics, have revolutionized automaker production lines. In the assembly process, they quickly and accurately assemble components, significantly boosting production efficiency. Additionally, their tireless nature allows automakers to produce more cars in a shorter time.
Beyond assembly, industrial robots play a vital role in other production processes. In painting workshops, robots apply car paint evenly and precisely, enhancing both efficiency and the paint's aesthetics and durability. In logistics and handling, industrial robots effortlessly lift heavy objects, reducing labor costs and avoiding human error.
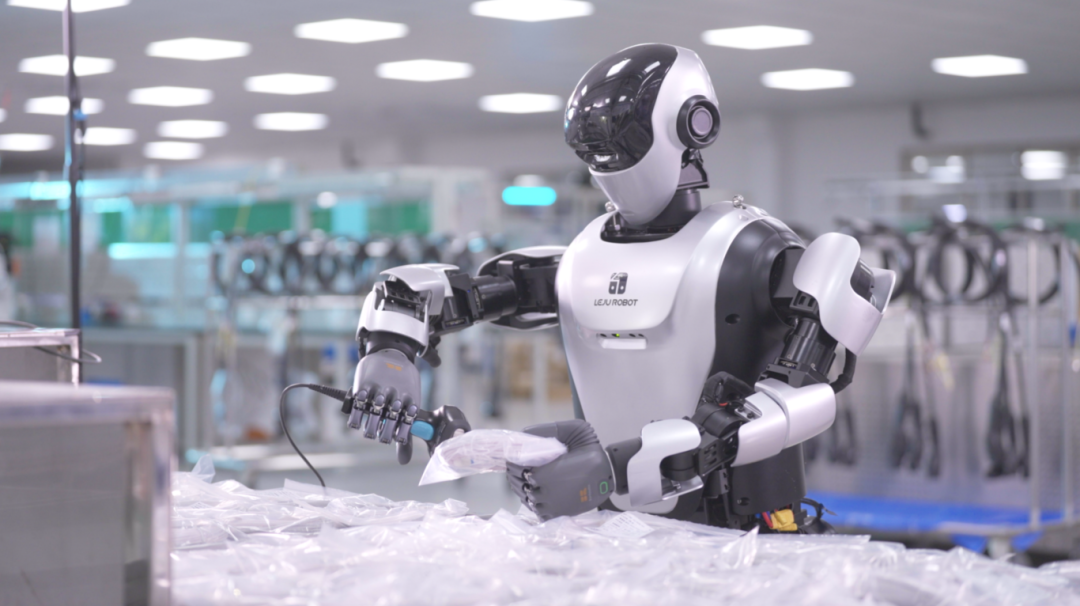
Those familiar with factories will recognize the aforementioned robotic equipment. However, this is only a fraction of what automakers can currently apply, and a small portion of the broader definition of robots. Today, the humanoid robots or embodied intelligence we are discussing offer even greater value in the vision of automakers.
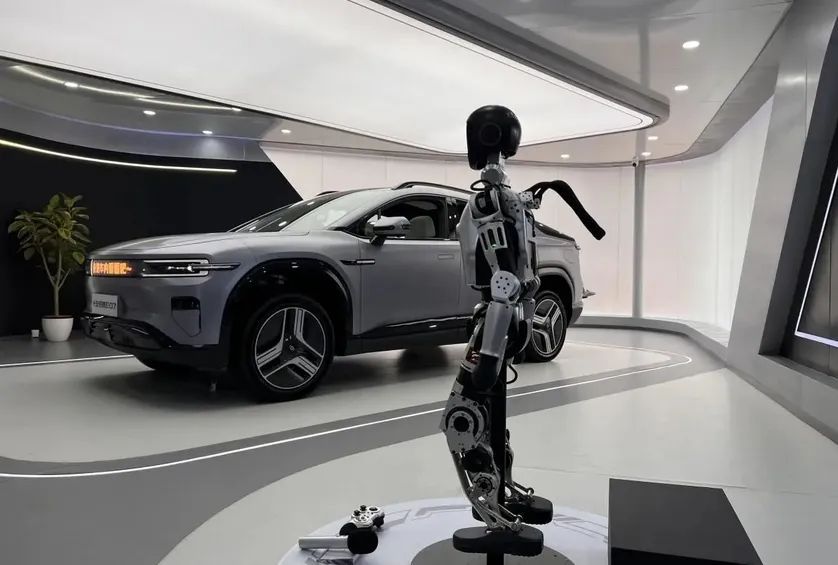

Besides excelling in the automotive manufacturing industry, humanoid robots are gradually expanding their application boundaries. With their biomimetic design, highly flexible interaction capabilities, and powerful built-in intelligent information processing systems, humanoid robots are quietly emerging as a new service force in some automotive brand experience stores.
In the more distant future, Tesla founder Elon Musk has high hopes for his Optimus humanoid robot, expecting it to perform multiple tasks and transform the way people work and live. For instance, it could replace humans in unsafe or tedious jobs, serve as a household assistant, enhance industrial production efficiency, and provide personalized services across various sectors.
Are Automakers a Good Fit for Humanoid Robots?
"The automotive and robotics industries share many synergies in the supply chain. At the technological level, technologies such as autonomous driving, chips, sensors, and LiDAR in automobiles can be mutually referenced. In production, robots can be utilized in automobile manufacturing to improve efficiency and quality. In the market, automakers' sales channels and brand influence can help promote robot products."
"If smart cars are the crown of intelligent manufacturing, then intelligent robots will be the crown of machine intelligence. I believe that in the future, manufacturers of smart cars will also be manufacturers of intelligent robots. I envision smart cars and intelligent robots eventually becoming a unified industry, capable of producing a synergistic effect greater than the sum of its parts."

Like smart cars, humanoid robots share similar driving principles: hardware, software, and software-hardware decoupling.
Currently, the automotive field has made significant progress in technological innovation and R&D, particularly in core areas such as autonomous driving, sensor technology, machine vision, and artificial intelligence. These technologies have not only driven the intelligent transformation of the automotive industry but also provided robust support for technological advancements in related fields.
Notably, the development of automobiles and humanoid robots exhibits high similarity in many aspects, such as perception and understanding of complex environments, autonomous decision-making, and action capabilities. This similarity offers ample opportunities and possibilities for technology transfer between the two at the hardware and software levels.
For example, the Optimus humanoid robot not only inherits Tesla's technological advantages accumulated in the automotive field but also innovates and breaks through on this foundation, aiming to create an intelligent robot that fully understands its environment, efficiently performs tasks, and coexists harmoniously with humans. This provides other automakers with inspiration and motivates them to join in.

More importantly, compared to foreign enterprises, Chinese enterprises or Chinese automakers have a natural advantage in venturing into the field of humanoid robots: policy support. Recently, cities like Nanjing, Chongqing, and Hangzhou have successively announced support policies for the robotics industry, seizing this opportunity. Some argue that these policies have shifted the industry from a stage of technological showmanship to deeper R&D waters.
Additionally, AI technology is the core driver of intelligent interaction. With the rapid development of AI technology, its application in automakers has become increasingly widespread. Major automakers have increased their investment in AI technology R&D. It can be said that AI technology provides robust support for the development of embodied intelligence, and the application of embodied intelligence, in turn, promotes the intelligent transformation of automakers.
Therefore, automakers can transfer their technological and resource advantages in automotive manufacturing to the R&D of humanoid robots, realizing technology sharing and application expansion. By venturing into the field of humanoid robots, automakers can tap into new market demand, diversify revenue sources, and provide strong support for future strategic transformation.

Relevant institutions predict that the size of the Chinese humanoid robot market will reach 2.158 billion yuan in 2024 and is expected to hit 38 billion yuan by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate exceeding 61%. Musk predicts that by 2040, there will be at least 10 billion humanoid robots in use worldwide, with prices ranging from $20,000 to $25,000.
However, some believe that other types of robots, such as industrial robots and service robots, are more likely to achieve mass production. The current optimism regarding the mass production prospects of humanoid robots in the consumer market may be misplaced, as humanoid robots still face challenges such as technological difficulties, high costs, and uncertain market demand.
Looking back, car manufacturing itself is a complex and massive systematic project involving technologies and resource integration from multiple fields. If a company's technology and experience in car manufacturing are not yet mature, rushing to expand into the robotics field may pose numerous risks and challenges.