“Beijing Autonomous Vehicle Regulations” to be Implemented, Ushering in the Era of Widespread Smart Driving?
![]() 01/03 2025
01/03 2025
![]() 618
618
In recent years, the rapid development of autonomous driving technology has spurred a profound transformation in the global automotive industry. This technology not only significantly enhances traffic safety and operational efficiency but also holds immense potential for improving energy utilization and optimizing urban traffic management. As an international metropolis, Beijing leads the nation in smart city construction and bears a significant responsibility for promoting technological innovation and application in autonomous driving. Since Beijing issued its management policy for autonomous vehicle road tests in 2018, the city has emerged as a core region for domestic autonomous driving companies to conduct tests and demonstration applications, achieving remarkable technological advancements.
The implementation of autonomous driving technology, however, has not been without challenges, facing issues such as road safety, data privacy, technical standards, and legal liability. Resolving these issues necessitates legal and regulatory support to guide industry development and provide a clear framework for corporate research and development (R&D) and public application. Against this backdrop, the "Beijing Regulations on Autonomous Vehicles" (hereinafter referred to as the "Regulations") were introduced.
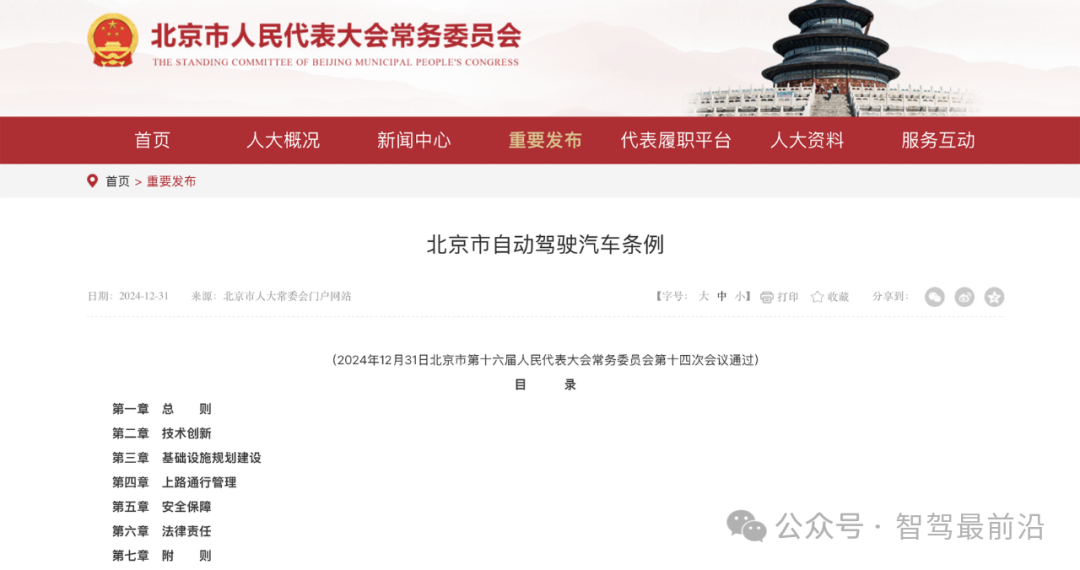
As a local regulation targeting the autonomous driving sector in China, the promulgation of these regulations marks a significant step forward for Beijing in exploring the integration of technology and regulation. The Regulations were passed by the Fourteenth Session of the Standing Committee of the Sixteenth Beijing Municipal People's Congress on December 31, 2024, and will officially come into effect on April 1, 2025. Comprising seven chapters and forty-eight articles, the Regulations cover general provisions, technological innovation, infrastructure planning and construction, road management, safety assurance, legal liability, and supplementary provisions. From clarifying the direction of technological R&D to regulating vehicle road applications and ensuring data and network security, the Regulations establish a comprehensive legal framework aimed at promoting technological innovation in autonomous driving, fostering smart transportation development, and safeguarding public interests and rights.
The commercialization and large-scale application of autonomous driving technology cannot be separated from the guidance and assurance provided by regulations. The promulgation of the Regulations not only offers clear policy guidance for enterprises but also lays the foundation for public acceptance and trust in autonomous driving technology. By regulating technological R&D, managing application scenarios, and strengthening safety assurance, it creates an inclusive and orderly environment for industry development. Simultaneously, the Regulations promote coordinated development and technological standardization in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, providing policy support for cross-scenario and cross-regional autonomous driving applications within the region.
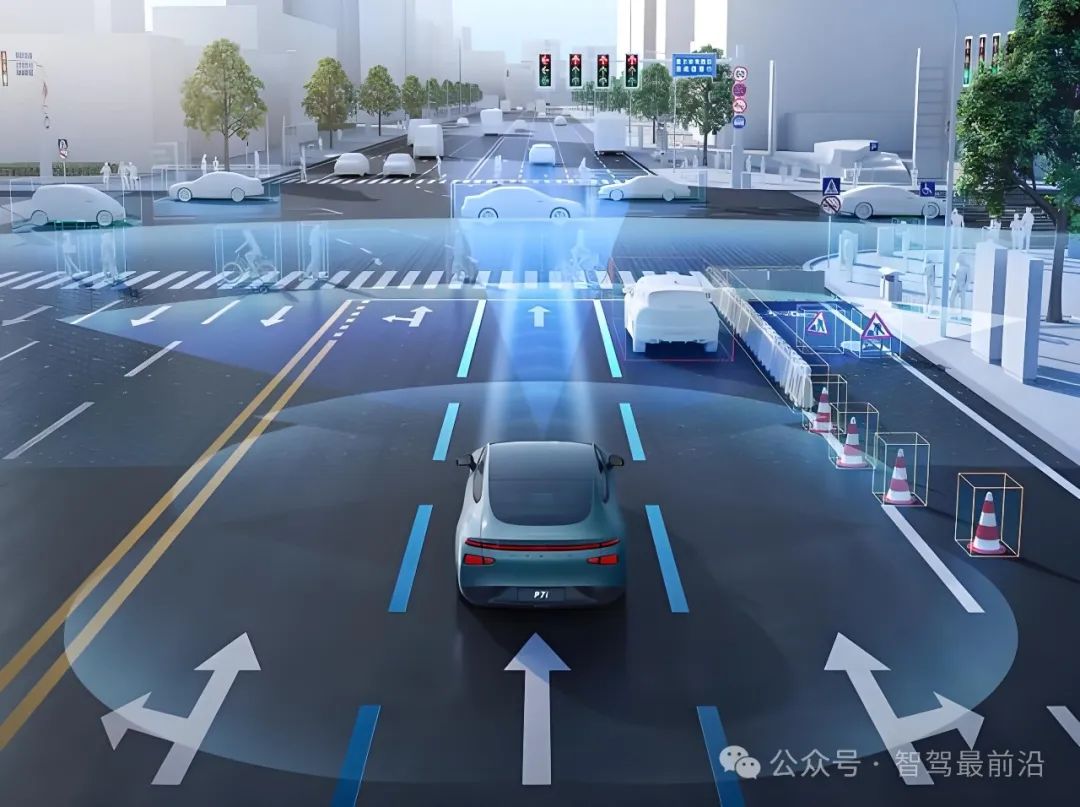
Technical Focus of the Regulations
With a focus on promoting technological development, the Regulations provide comprehensive legal support and technical guidance for the autonomous driving industry by fostering technological innovation, planning infrastructure construction, regulating road management, and strengthening safety assurance.

1.1 Technological Innovation in Autonomous Driving
Chapter Two of the Regulations explicitly states that Beijing will propel continuous innovation and application of autonomous driving technology by refining technology and industrial chains. Its core content includes key technology R&D, innovation platform construction, and standardization promotion.
The Regulations propose supporting the R&D of pivotal technologies such as perception, decision-making, and execution, which could propel the development of perception technologies like LiDAR, millimeter-wave radar, and high-precision cameras, thereby enhancing vehicles' environmental recognition capabilities. Simultaneously, the Regulations encourage enterprises to establish cooperative mechanisms for data development and utilization, fostering data service products and offering market-oriented and socialized applications and services. For instance, by developing efficient path planning and behavior prediction algorithms, real-time decision-making challenges in complex traffic scenarios can be addressed, and execution systems like wire-controlled chassis and intelligent braking technology can be optimized to boost vehicle reliability and execution capabilities.
The Regulations endorse the construction of technological innovation platforms, such as key laboratories, technological innovation centers, innovation consortia, and common technological R&D platforms. These platforms will amalgamate resources from enterprises, universities, and research institutions to expedite technological breakthroughs through collaborative research and expedite the rapid transformation of R&D results.
The Regulations also advocate standardization in autonomous driving technology. By formulating local standards encompassing infrastructure, safety evaluation, and autonomous driving maps, the Regulations furnish clear norms for technological R&D and application. Enterprises are urged to participate in the formulation of international, national, and local standards to bolster Beijing's technological discourse power in the global autonomous driving arena.
1.2 Infrastructure Planning and Construction
Infrastructure construction is a pivotal aspect of autonomous driving technology implementation. Chapter Three of the Regulations specifies intelligent roadside facilities, management platforms, and high-precision map technology support, aiming to provide a solid foundational support for autonomous driving technology.
The Regulations elucidate that Beijing will support multiple autonomous driving technology routes by retrofitting existing facilities or constructing new intelligent roadside infrastructure. For instance, by deploying V2X communication equipment, high-precision sensors, and intelligent traffic lights, real-time interaction between vehicles and roads can be achieved. Infrastructure planning and implementation will be closely aligned with the city's smart transportation development plan to ensure that traffic areas and road ranges meet both technical requirements and management convenience.
The Regulations propose constructing a unified autonomous driving service management platform tasked with collecting and managing vehicle operation data. This platform can conduct real-time monitoring and analysis of vehicle trajectories and anomalies, offering vital references for technological optimization and policy adjustment. Additionally, the Regulations mandate enterprises to upload data in compliance with national and Beijing-related regulations to ensure data standardization and security.
Regarding high-precision map support, the Regulations emphasize that Beijing encourages map surveying and mapping enterprises to explore real-time updates and secure applications of high-precision maps in accordance with relevant national regulations. The provisions of the Regulations will furnish legal support for the surveying, use, and uploading of high-precision maps in Beijing, enhancing the usage requirements for autonomous driving high-precision maps.
1.3 Road Management
The road application of autonomous vehicles is a crucial aspect of technology implementation. Chapter Four of the Regulations provides detailed regulations on traffic management, encompassing testing, demonstration applications, to pilot qualifications, ensuring the safe adaptation of technology to the road environment.
According to the Regulations, enterprises must complete road tests to verify vehicles' perception, decision-making, and execution capabilities and pass safety assessments before applying for demonstration applications. During the demonstration application phase, enterprises must validate vehicles' stability and adaptability in real traffic scenarios before applying for road application pilots.
For pilot activities, the Regulations require enterprises to possess robust operational capabilities and safety assurance measures. For instance, enterprises must possess network and data security assurance capabilities, formulate operation plans, and clarify vehicle operation areas, routes, and emergency response measures. Simultaneously, the Regulations endorse innovative applications of autonomous driving technology in various scenarios, such as personal passenger vehicles, urban public transportation, cargo transportation, and urban operation support. By progressively opening application scenarios in stages and by region, the Regulations propel technology to serve social needs, realizing the practical application of autonomous driving.
1.4 Safety Assurance
Safety is the cornerstone of autonomous driving technology development. Chapter Five of the Regulations puts forth comprehensive requirements for safety assurance from the dimensions of functional safety, network security, and data security.
The Regulations clarify that autonomous vehicle manufacturers are accountable for product functional safety and production consistency. Vehicles must pass functional safety verification and third-party testing to ensure their operational reliability in complex traffic scenarios. Enterprises must also rigorously manage functional changes and software upgrades to the autonomous driving system to ensure the vehicle's continued safety.
In terms of network and data security, the Regulations require enterprises to establish network security level protection mechanisms and fend off external attacks through data encryption and communication isolation. Regarding data security, the Regulations stipulate that enterprises must classify and protect collected data and strictly adhere to the Personal Information Protection Law for data involving personal privacy. For cross-border data transmission, enterprises must conduct risk assessments in accordance with national regulations to ensure data security and compliance.
Furthermore, the Regulations mandate enterprises to formulate emergency response plans for incidents and conduct regular emergency drills. Safety personnel and platform monitoring personnel must be proficient in handling emergency situations to ensure rapid vehicle control takeover in emergencies and prevent accident escalation. For traffic accidents, enterprises must collaborate with public security organs to provide operation data and accident analysis reports for liability determination and issue rectification.
By fostering technological R&D, planning infrastructure, regulating vehicle management, and strengthening safety assurance, the Regulations establish a comprehensive framework for the development of autonomous driving technology in Beijing. This not only offers a clear direction for technological development but also lays a solid foundation for smart transportation construction in Beijing. The implementation of the Regulations will effectively elevate the application level of autonomous driving technology while providing valuable experience for industry norms nationwide.
Impact and Significance of the Regulations
As a local regulation specifically targeting the autonomous driving sector in China, the promulgation of the Regulations not only regulates the technological R&D, infrastructure construction, and practical application of autonomous vehicles but also profoundly influences smart city construction, industrial coordinated development, and social governance.

2.1 Regulatory Role in Autonomous Driving Technology Development
The Regulations furnish a clear legal framework for the R&D, testing, application, and supervision of autonomous driving technology, guiding the direction of technological innovation and actively steering industrial development.
2.1.1 Clarifying Compliance in Technological R&D and Testing
The Regulations provide detailed regulations for the technology path from R&D to testing to application scenario implementation. Through rigorous safety assessments and road testing requirements, they ensure the usability and reliability of autonomous driving technology.
- Support for Technological Innovation: Chapter Two of the Regulations proposes fostering the R&D of perception technology, decision-making algorithms, and high-precision maps, which will directly elevate the overall performance of autonomous vehicles.
- Testing and Certification Standards: The Regulations clearly delineate the testing areas, methods, and safety requirements for vehicles, ensuring technology safety and legality in practical scenarios.
2.1.2 Promoting Standardization and Technological Iteration
The Regulations fill industry standard gaps by formulating local technical standards, providing unified guidance for all participants in the industry chain. Simultaneously, they encourage enterprises to participate in formulating national and international standards, propelling technology globalization.
- Formulation of Local Standards: Standards such as intelligent roadside facility construction and data security management furnish clear implementation guidelines for the industry.
- Promotion of Technological Iteration: Through innovation support policies and the opening of testing scenarios, the Regulations provide enterprises with opportunities to test and optimize technology, accelerating the application of new technologies.
2.1.3 Driving the Integration of Technology and Business Models
The Regulations establish a legal framework for deploying autonomous driving technology in logistics, sanitation, patrol, and other sectors, enabling enterprises to effectively convert technological advancements into commercial value. Pilot projects for Robotaxi and autonomous cargo vehicles not only advance related technologies but also diversify business models for smart transportation and logistics services.
2.2 Advancement of Smart Transportation and Urban Management
Autonomous driving technology is pivotal to smart transportation and smart cities. The Regulations foster the multifaceted integration of autonomous driving technology into urban governance.
2.2.1 Enhancing Traffic Efficiency and Travel Convenience
The Regulations endorse the use of autonomous vehicles in urban operations, public transportation, and cargo hauling, significantly boosting traffic efficiency and convenience.
Personal Travel: The Regulations permit autonomous functionality in personal vehicles, offering users safer and more efficient travel options.
Public Transportation: In taxi and bus services, the Regulations support autonomous driving, effectively alleviating urban congestion.
2.2.2 Elevating Urban Management Standards
The Regulations introduce autonomous driving into urban operations like sanitation and security patrols, markedly enhancing urban management intelligence.
Urban Sanitation: Autonomous sweeping vehicles efficiently cover major urban roads, improving cleaning efficiency.
Security Patrols: Unmanned security vehicles conduct real-time monitoring of key urban areas, promptly identifying and reporting potential hazards.
2.2.3 Supporting Smart City Development
Through the planning and development of intelligent roadside infrastructure, the Regulations provide hardware support for vehicle-to-everything (V2X) technology, enhancing the smart transportation system. The deployment of V2X communication equipment and high-precision sensors optimizes autonomous vehicle operations and provides real-time data for the overall transportation system, boosting road efficiency.
2.3 Safeguarding Public Safety and Rights
As a technology impacting public interests, autonomous driving must prioritize social safety and public rights. The Regulations comprehensively safeguard the public by regulating functional safety, network security, and data security.
2.3.1 Ensuring Functional Safety
The Regulations mandate that autonomous vehicle manufacturers bear primary responsibility for vehicle safety and pass rigorous functional safety tests.
Safety Assessment: A multi-tiered safety assessment system, including expert demonstrations, third-party testing, and platform monitoring, ensures vehicle safety in complex road conditions.
Emergency Management: Stringent requirements for safety personnel and platform security monitors enhance manual takeover and incident handling capabilities.
2.3.2 Protecting Network and Data Security
Network and data security pose significant challenges for autonomous driving, and the Regulations propose detailed protection mechanisms.
Data Classification and Hierarchical Protection: The Regulations require enterprises to classify and manage collected data, safeguarding personal information and sensitive data.
Cross-border Data Transmission: For autonomous driving data potentially involving national security, the Regulations mandate adherence to relevant national regulations to prevent data leakage.
2.3.3 Boosting Public Acceptance
Through media outreach and industry association engagement, the Regulations encourage public understanding of autonomous driving safety and potential, fostering social acceptance of new technologies.
2.4. Promoting Economic and Industrial Collaboration
The Regulations significantly contribute to the coordinated development of the autonomous driving industry chain and regional collaboration and international competition.
2.4.1 Stimulating Regional Economic Collaboration
The Regulations clarify Beijing's commitment to regional collaboration with Tianjin and Hebei, fostering technological and industrial chain synergy through policy recognition, standard compatibility, and scenario connectivity.
Cross-regional Testing: The Regulations support foreign enterprises in testing and applying technologies in Beijing, reducing cross-regional operational barriers.
Regional Collaborative Development: For instance, Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei smart transportation cooperation promotes the industrialization and large-scale deployment of autonomous driving technology.
2.4.2 Advancing Industrial Chain Optimization and Upgrading
The Regulations encourage collaborative innovation across autonomous driving industrial chain segments, from core component manufacturing to vehicle assembly and data services, driving industrial chain optimization and upgrading.
Industrial Integration: Deep collaboration between vehicle manufacturers and technology providers accelerates key technology commercialization.
Financial Support: Insurance institutions are encouraged to develop autonomous vehicle-specific insurance products, sharing risks with industry participants.
2.4.3 Enhancing International Competitiveness
By encouraging enterprises to participate in international standard-setting and technological exchanges, the Regulations support Beijing and China's greater global autonomous driving market influence.
The Regulations, with comprehensive technical specifications and institutional guarantees, propel the autonomous driving industry's rapid development. They foster technological research and development, industrial chain collaboration, and inject new vitality into smart transportation and smart city construction by enhancing social benefits and regional economic collaboration. Future implementations must dynamically adjust the Regulations to align with technological iterations, ensuring policy and technology synchronization.
Challenges and Opportunities in Technology-Regulation Convergence
The Regulations provide comprehensive policy support and legal protection for the autonomous driving industry but face implementation challenges due to rapid technological evolution. These challenges also present new industry development opportunities.
3.1 Challenges and Opportunities in Technology-Regulation Synchronization
3.1.1 Challenges: Technological Advancements Outpacing Regulations
Autonomous driving technology evolves swiftly, while regulation formulation and adjustment often require more time. This lag can hinder regulations from fully addressing technological innovation needs.
Expanding Technological Scenarios: Autonomous driving has expanded from closed-area testing to open roads and multi-scenario applications, while current regulations may not fully meet these varied needs.
Incomplete Regulatory Coverage: Detailed specifications for specific technological routes (e.g., pure vision solutions or vehicle-road coordination) require supplementation.
3.1.2 Opportunities: Exploring Dynamic Adjustment Mechanisms
The Regulations propose an annual evaluation and reporting mechanism, enabling continuous regulatory optimization.
Real-time Adjustments: Periodic evaluations and optimizations of autonomous driving access areas and applications align regulations with technological progress and industry needs.
Pilot Programs: Through demonstration projects and pilot activities, Beijing can verify technology-regulation compatibility and accumulate national regulatory formulation experience.
3.1.3 Suggestion: Establishing a Dynamic Regulatory System
Future reductions in the regulatory-technological development lag can be achieved through: utilizing AI to intelligentize regulation formulation and enhance efficiency; introducing a regulatory "sandbox" to test new technologies in specific areas, providing data for regulatory revisions.
3.2 Challenges and Opportunities in Network and Data Security
3.2.1 Challenges: Network and Data Security Threats in Complex Environments
Widespread autonomous driving adoption significantly increases vehicle networking and data use, posing severe network and data security challenges.
Network Attack Risks: Autonomous vehicles relying on V2X communication systems may become hacker targets, affecting traffic safety. Data Misuse and Privacy Breaches: Poor management of the vast data generated by autonomous vehicles, including user travel information and sensitive privacy, can have severe consequences.
Regulatory Challenges in Cross-border Data Flow: Balancing national security with data openness in international cooperation.
3.2.2 Opportunities: Driving Network and Data Security Technology Innovation
The Regulations' requirements for network security level protection and data classification management spur related technology development.
Data Encryption and Isolation: Promote data transmission encryption and high-strength network firewall deployment.
Privacy Computing Technology: Achieve data sharing and privacy protection balance through federated learning and multi-party secure computation.
Dynamic Security Management: Develop intelligent network security systems with real-time threat detection and defense capabilities to ensure vehicle operational security.
3.2.3 Suggestion: Facilitating Data Security Standardization through Collaboration
Future internationalization of data security standards and cross-border transmission rules can be promoted through enterprise, government, and research institution collaboration, enhancing China's voice in global autonomous driving data governance.
3.3 Challenges and Opportunities in Balancing Standardization and Internationalization
3.3.1 Challenges: Discrepancies Between Local, National, and International Standards
Autonomous driving industry standard formulation often involves multi-level coordination, with standard discrepancies potentially limiting industry development:
Local-National Standard Coordination Challenges: Beijing's local standards may surpass national standards in refinement and technical compatibility, but inconsistencies can lead to resource waste and industry barriers.
Lack of International Standard Discourse Power: Europe and the U.S. lead in autonomous driving international standard formulation, while Chinese standards' global influence is limited.
3.3.2 Opportunities: Demonstrating Local Standard Leadership
The Regulations establish detailed local laws and standards for autonomous driving, serving as a pilot and reference for national and international standard formulation.
Technology Verification Platform: Beijing's local standards can be validated through pilot projects, promoting national standard improvements.
International Cooperation Opportunities: By participating in international standard formulation and technological exchanges, Beijing can enhance its global autonomous driving influence.
3.3.3 Suggestion: Accelerating Standard Internationalization
Beijing can enhance its standard international competitiveness through:
Strengthening cooperation with international standards organizations to internationalize local standards.
Encouraging local enterprises to participate in international technology conferences and industry alliances, amplifying Chinese enterprises' global market technological discourse power.
3.4 Challenges and Opportunities in Business Model Innovation
3.4.1 Challenges: Commercialization Path Uncertainty
Despite the Regulations' policy support for various autonomous driving applications, commercialization faces challenges.
High Operational Costs: Autonomous vehicle R&D, testing, and operation involve significant investments, hindering short-term profitability.
Low User Acceptance: Public doubts about autonomous driving safety may slow commercial model adoption.
In a fiercely competitive market environment, enterprises are confronted with domestic and foreign competitors, necessitating rapid advancements in both technological prowess and commercialization strategies.
3.4.2 Opportunities: Fostering Exploration of New Business Models
The regulations explicitly endorse a variety of business models, including Robotaxi, unmanned delivery, and autonomous driving freight, creating a conducive testing ground for corporate innovation:
Shared Travel: The Robotaxi model can dramatically reduce per-trip costs and enhance urban transportation efficiency.
Intelligent Logistics: Unmanned cargo and delivery vehicles play a pivotal role in the logistics chain, cutting labor costs and boosting delivery efficiency.
Value-added Services: Autonomous driving-based in-cabin entertainment and advertising delivery services are poised to emerge as new revenue streams.
3.4.3 Recommendation: Diversified Development of Business Models
When pursuing business model innovation, enterprises can adopt the following strategies:
Phased Implementation: Gradually expand from controlled environments to open scenarios to mitigate initial investment risks.
Scenario Customization: Develop tailored solutions for diverse scenarios, including urban operations support, public transportation, and logistics.
User Education and Experience: Enhance public awareness and acceptance of autonomous driving technology through demonstration projects and test rides.
The "Beijing Regulations on Autonomous Vehicles" mark a significant milestone in harmonizing technology with regulation but also confront challenges like rapid technological evolution, cybersecurity risks, and commercialization hurdles. These challenges, however, also open up new avenues for industry growth, encouraging enterprises to explore more efficient and diversified approaches in technology R&D, data security, and business model innovation. Looking ahead, Beijing should continue refining its regulatory framework, deepening international collaboration, and further elevating China's autonomous driving technology to a global stage of competitiveness and influence.