"$3.6 Trillion Spree to Form AI Superpower! OpenAI Unleashes Its Full Potential - Who Will Reign Supreme?"
![]() 01/23 2025
01/23 2025
![]() 437
437
Is OpenAI, the frontrunner in the AI sector, planning something monumental?
Despite its status as the world's most renowned AI company, OpenAI's journey in 2024 was far from smooth. The much-anticipated GPT-5 faced delays, Sora remained a concept in PPT form for a year, and OpenAI recently denied plans to launch AGI (Artificial General Intelligence) in February. Meanwhile, its competitors are surging ahead, with AI large models rapidly closing the gap with ChatGPT.
However, just over half a month into 2025, OpenAI couldn't contain its urgency, unveiling two groundbreaking announcements that promised to dispel the gloom. First, OpenAI severed ties with Microsoft, gaining the freedom to build its own computing clusters and leverage resources from other enterprises. Second, Trump announced that OpenAI would jointly establish a company named "Stargate" with SoftBank, Oracle, and MGX, with SoftBank managing finances, OpenAI handling operations, and Masayoshi Son serving as chairman.

(Image source: OpenAI)
"Stargate" will immediately invest $100 billion (approximately RMB 727.25 billion) in constructing AI infrastructure in the United States, with cumulative investments expected to reach $500 billion (approximately RMB 3.63625 trillion) over the next four years. Following this announcement, SoftBank's share price surged 10%, Oracle's share price jumped 7.17% on Tuesday local time, while Microsoft's stock performed poorly, likely impacted by its separation from OpenAI.
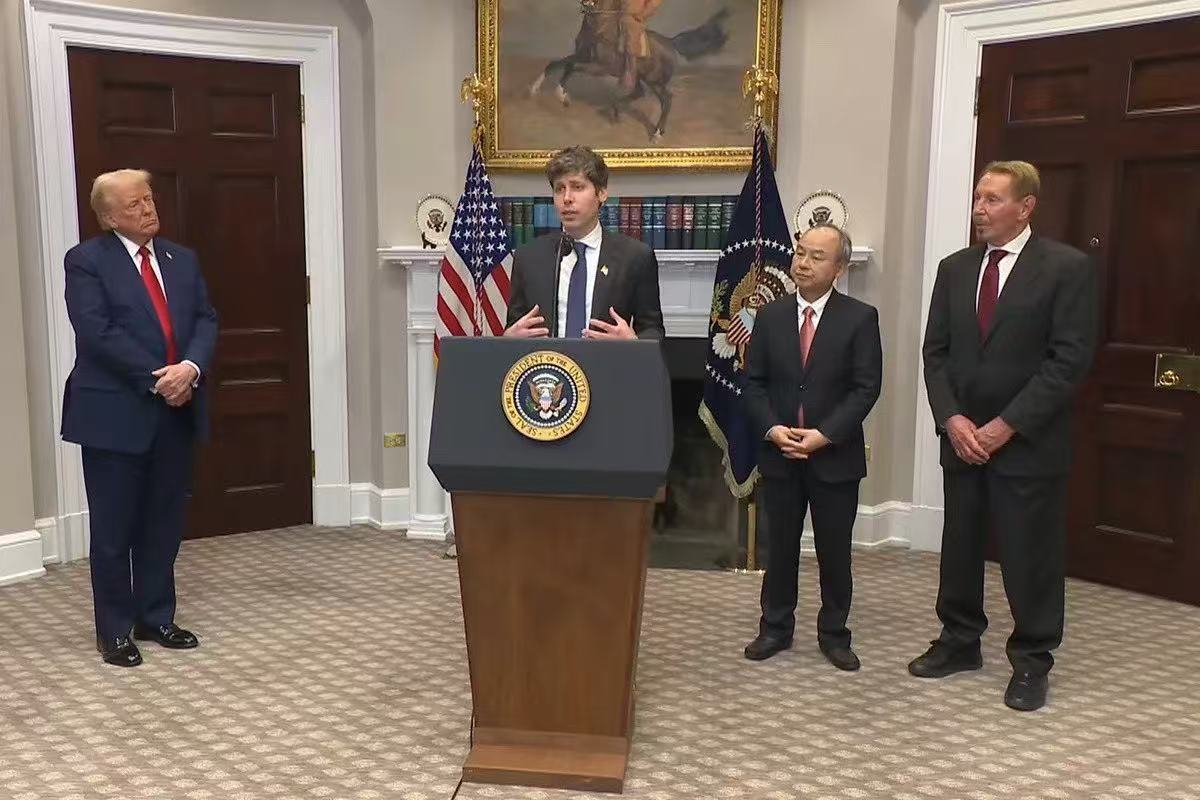
(From left to right: Trump, OpenAI CEO Sam Altman, SoftBank founder Masayoshi Son, and Oracle founder Larry Ellison)
In previous funding rounds, OpenAI has raised colossal sums that would be the envy of any ordinary entrepreneur. However, for OpenAI's ambitious AI plans, these funds were but a fraction of what was needed. Sam Altman, OpenAI's CEO, once proposed investing $7 trillion to reshape the semiconductor industry and lay the groundwork for the AI era. While a $7 trillion investment in AI is clearly unrealistic, OpenAI undeniably requires substantial resources. Breaking free from Microsoft and establishing Stargate could fill OpenAI's resource gap, fully unleashing the potential of large AI models.
Breaking Free, OpenAI Unleashes Its Full Potential
Before GPT-4, the computational power and data volume required to train large AI models were manageable, enabling OpenAI to experience a period of rapid growth. However, post-GPT-4, the computational demands and data requirements soared significantly.
In terms of data, OpenAI could purchase from other enterprises, hire staff to create original data, or utilize other large AI models to generate data. Theoretically, enhancing computational power, which seemed simpler, became a challenging issue for OpenAI. Around 2024, foreign media outlets like Analytics repeatedly reported that OpenAI was on the verge of bankruptcy.
In 2019, Microsoft invested $1 billion in OpenAI, in return for which OpenAI migrated all its service facilities to Microsoft's Azure cloud computing platform. As the computational demands for training large AI models grew, coupled with an expanding user base, the computational power needed for inference tasks also increased, gradually rendering Microsoft's computational resources insufficient for OpenAI's needs. OpenAI was also plagued by internal disputes over computational resources, with senior management expressing dissatisfaction towards Microsoft.

(Image source: Generated by Doubao AI)
After adjusting its agreement with Microsoft, Microsoft retained the right of first refusal (ROFR) and exclusive rights to use OpenAI technology in products like Copilot, maintaining the current revenue-sharing model until 2030 (currently, Microsoft receives 20% of OpenAI's revenue). Meanwhile, OpenAI gained autonomy over computational power. As early as June 2024, OpenAI forged a partnership with Oracle, leveraging computational resources from Oracle's cloud computing platform. With the adjusted agreement, OpenAI can now collaborate with other cloud computing platforms.
The issue is that the training and inference calculations for GPT-4 alone amount to approximately 2.15e25 FLOP (21.5 million ExaFLOP), equivalent to 20,000 A100 GPUs running for 90 to 100 days. The computational power required for future large AI models will exhibit exponential growth. Coupled with the computational demands for training Sora and AGI, OpenAI will require over 100,000 GPUs.
This is precisely why OpenAI needs to collaboratively build data centers with enterprises like SoftBank, Oracle, and MGX, investing approximately $100 billion annually to construct cloud computing infrastructure for OpenAI, satisfying the computational demands of future large model training and inference tasks.
Of course, other AI enterprises have also proposed low-cost large model training methods, such as the renowned DeepSeek in the open-source large model field. Leveraging data distillation technology, it trains student models using other large AI models as teacher models, having trained the DeepSeek-V3 large model at a cost of only $5.576 million. Through practical testing, DeepSeek-V3's daily performance is on par with mainstream domestic large AI models. Recently, DeepSeek launched the R1 large model, which did not lag behind OpenAI's GPT-4 model in both the AIME2024 and MATH-500 tests.

(Image source: DeepSeek)
However, training large models using data distillation technology also has its drawbacks, such as relying on the teacher model's capabilities and being unable to surpass them, potentially resulting in the loss of detailed features. In summary, while data distillation technology can significantly reduce the cost of training large AI models, it is destined to be a follower rather than a leader in driving AI industry development and progress.
OpenAI's ability to attract substantial investment lies in its technological leadership. Once it loses this leadership position, OpenAI will inevitably lose the support of numerous enterprises, especially since its goal is to lead the industry forward.
Spending is Easy, but Earning is Difficult: Accelerating the AI Startup Elimination Race
Unlike concepts like the metaverse and blockchain, the experience enhancements brought by AI are tangible. Financial professionals use AI to query laws, regulations, and industry information, media workers utilize AI to generate images and text, and office workers employ AI to summarize documents or PDFs. However, despite AI integrating into and facilitating our lives today, many netizens still believe it's no different from the metaverse and blockchain, merely a new financial bubble.
This viewpoint persists because no enterprise's AI business has achieved profitability to date, with the entire AI industry's biggest beneficiary being NVIDIA, which develops computational GPUs. Additionally, constructing computational clusters requires substantial costs, naturally leading to the gradual elimination of small enterprises unable to bear these burdens.
Unlike the booming new energy vehicle industry in recent years, which has high entry costs and requires substantial funds to participate, the AI industry has low entry costs. However, the subsequent costs of building top-tier large AI models may be even higher than those of developing new energy vehicles. Enterprises with strong capabilities can build low-cost large AI models based on data distillation technology without needing to collaborate with AI companies, further compressing AI enterprises' profit margins.

(Image source: Generated by Doubao AI)
OpenAI has already collaborated with numerous internet giants like Microsoft and Apple, but it still cannot achieve profitability in the short term. In 2024, OpenAI's expected loss was approximately $5 billion, and due to the need to construct computational clusters and data centers, its loss is likely to increase in 2025 and 2026.
The data research institution The Information predicts that OpenAI's loss will reach $14 billion in 2026, with profitability not expected until 2029. If this is the case for OpenAI, it goes without saying for other enterprises. Lei Jun believes that the elimination race in the AI industry has already begun, with over 80% of AI enterprises expected to be eliminated in the next three years.
However, OpenAI is, after all, the global leader in the AI industry and the most highly valued AI company. With AI being considered the fourth industrial revolution, the United States will not stand idly by. The joint establishment of the subsidiary Stargate by OpenAI with enterprises like SoftBank, Oracle, and MGX is clearly driven by the United States.

(Image source: Generated by Doubao AI)
The incomplete training of GPT-5 and the lesser-than-advertised functionality of Sora are both attributed to insufficient computational power. Collaborative investments totaling $500 billion can significantly alleviate OpenAI's financial pressure, aiding it in constructing a large-scale computational cluster. Freed from Microsoft's restrictions and empowered by Stargate, OpenAI will unleash its potential, enabling multiple projects to commence simultaneously without worrying about computational power, and the likelihood of internal project teams competing for computational resources will greatly diminish.
Based on the computational power provided by Oracle's cloud computing platform and Stargate, in 2025, we will have the opportunity to witness GPT-5 and a more powerful Sora, with OpenAI striving towards the ultimate form of large AI models—AGI.
Advancing to the Next Peak: The Era of AGI Has Arrived
While OpenAI is powerful, investors' money is not free. Prolonged capital burn without achieving profitability may lead investors to abandon OpenAI in a few years. For OpenAI, the establishment of Stargate and the severing of ties with Microsoft are most significant in helping it solve the computational power dilemma and funding challenges. Without these worries, OpenAI will be able to accelerate the development of GPT-5 and AGI, thereby achieving profitability as soon as possible.
OpenAI, Amazon Web Services, and other enterprises have recently announced news regarding AGI. On January 6, Sam Altman even stated in a blog post that he knows how to build AGI and is confident in launching it in 2025. In 2023, OpenAI's official mission statement also mentioned that its goal is to build AGI that benefits all humanity. Based on this news, netizens on the X platform speculated that OpenAI would launch AGI in February.

(Image source: Generated by Doubao AI)
AGI, capable of autonomous learning and reasoning like humans and handling any task, is considered the ultimate form of AI. OpenAI, the leader in the AI industry, is also regarded by many netizens as the enterprise with the greatest hope of being the first to launch AGI. However, as more and more internet giants enter the AI industry, the pressure on OpenAI is also increasing.
At the re:Invent conference in early December 2024, Amazon Web Services revealed plans to launch a universal large model capable of Any To Any by mid-2025, supporting the input and output of information in any modality.
The difference is that previously, OpenAI relied on investor funding, while enterprises like Amazon Web Services, xAI, Doubao, Tongyi, etc., are supported by internet giants and do not need to pursue profitability in the short term. In the past, OpenAI had an urgent need to achieve profitability, making it difficult to devote more energy to technological research and development. With Stargate as a backup, OpenAI will now go all out and move towards AGI.








