Is Intel's Automotive-Grade SoC Platform Still Favored by Automakers?
![]() 03/11 2025
03/11 2025
![]() 509
509
Produced by Zhineng Zhixin
Intel's automotive-grade SoC platform, known as Malibou Lake, aims to establish itself as a key player in the automotive industry by integrating its hybrid architecture, AI acceleration, open ecosystem, and robust security features. This platform consolidates cutting-edge technologies such as high-performance computing, hardware virtualization, and edge-to-cloud connectivity, offering automakers a comprehensive solution ranging from smart cockpits to autonomous driving.
However, the central question remains: Are automakers actually utilizing this platform?
Part 1: Features, Advantages, and Disadvantages of Intel's SoC Platform
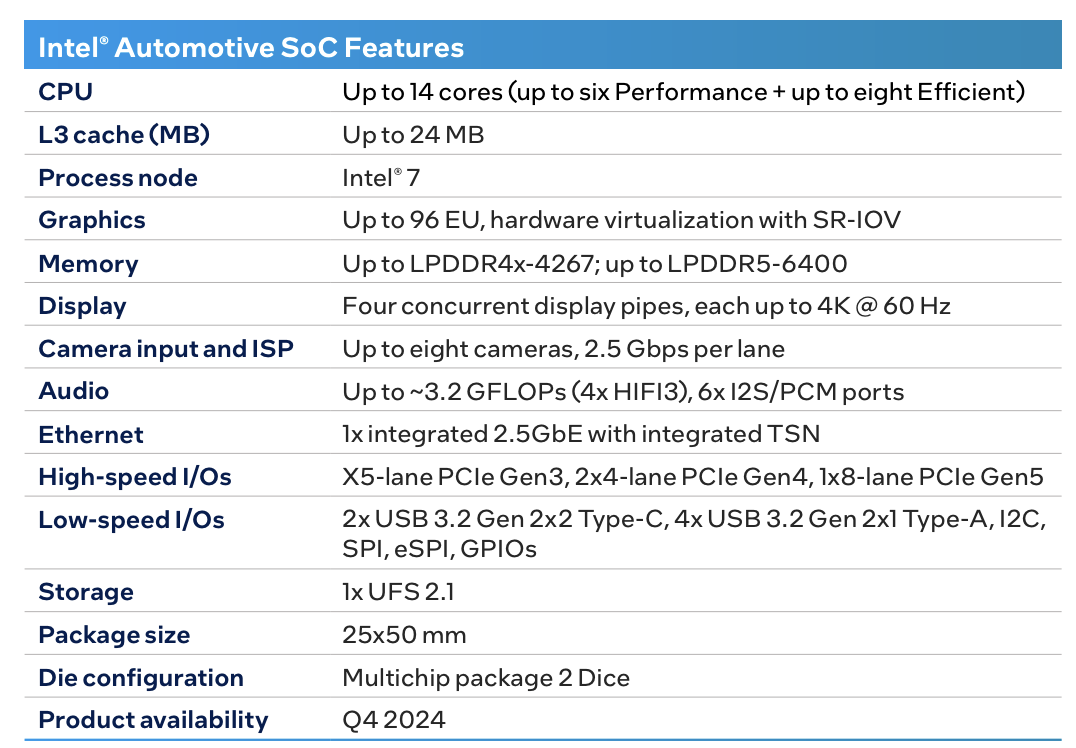
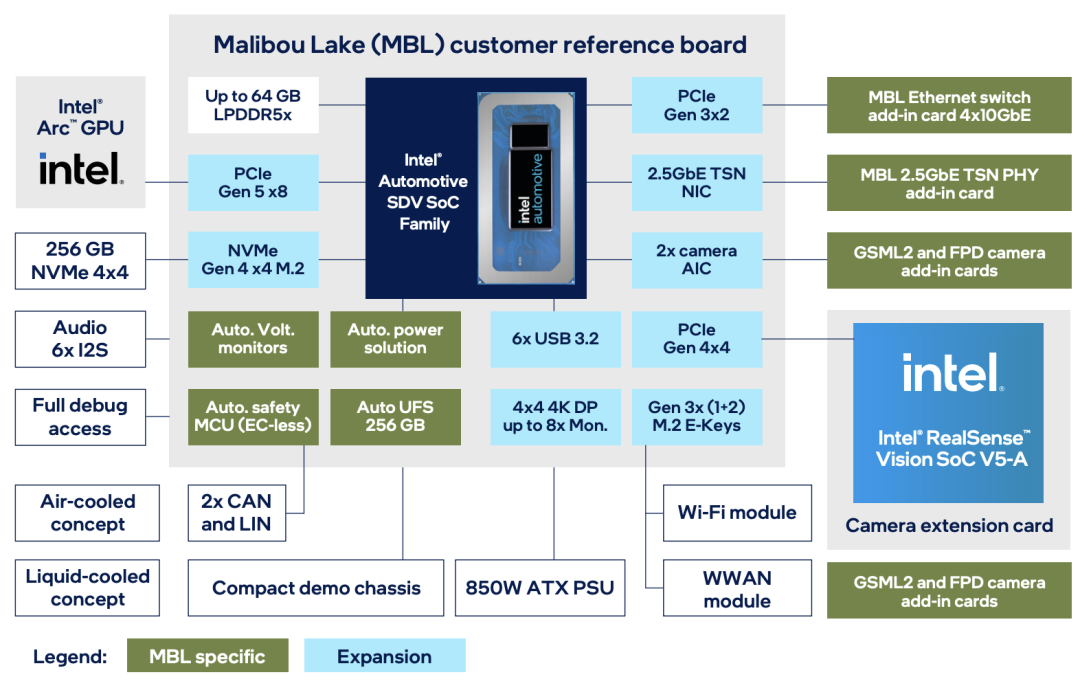
Intel's automotive-grade SoC platform, Malibou Lake, is a system-on-chip specifically designed for software-defined vehicles. Its core design philosophy revolves around meeting the multifaceted demands of modern vehicles for computing power, flexibility, and security through integration and intelligence.
Highlighting its hybrid architecture, hardware virtualization, AI acceleration, and high security, this platform not only strikes a balance between performance and energy efficiency but also provides automakers with a future-oriented technological foundation.
However, like any technological innovation, it comes with limitations. Its complexity and cost pose challenges for potential users.
Zhineng Automobile will delve into the technical details to comprehensively analyze its features, advantages, and disadvantages.
Intel has introduced a hybrid architecture (Performance-cores + Efficient-cores) in automotive SoCs for the first time, achieving dynamic load distribution through a collaborative design of large and small cores. The high-performance cores focus on real-time rendering and complex computations, while the efficient cores handle background tasks, resulting in an overall power consumption reduction of approximately 30%, which is crucial for the endurance of electric vehicles.
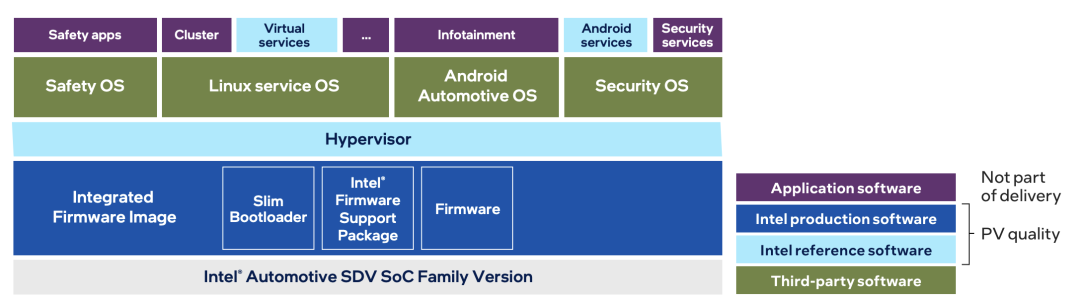
Simultaneously, hardware virtualization technology (supporting SR-IOV) allows a single chip to run multiple independent operating systems, providing physical-level isolation for functional domains such as security, entertainment, and communication. This eliminates the redundancy of traditional distributed ECUs and significantly reduces hardware costs.
AI acceleration is supported by the VNNI instruction set and GNA accelerator, enabling full-stack in-vehicle AI applications. This boosts inference speeds by 4x and reduces latency to below 10ms, facilitating the realization of L3+ autonomous driving and smart cockpits.
● In terms of security, the platform employs hardware-level encryption (Intel® SGX), a secure boot chain, and functional safety mechanisms (meeting ISO 26262 ASIL-B/D), making it the first x86 architecture automotive SoC to receive AEC-Q100 Grade 3 certification.
● These features collectively constitute its technical advantages: balancing high performance with low power consumption, integrating resources to reduce costs, supporting intelligent upgrades with AI capabilities, and meeting the demands of the connected vehicle era with multi-layered security designs.
However, the scheduling algorithm for the hybrid architecture requires deep integration with automakers' operating systems, potentially increasing initial development costs by 20%-30%. The high power consumption of AI accelerators necessitates thermal management optimization, and the complexity of security mechanisms drives up manufacturing and maintenance costs, placing higher demands on automakers' software capabilities and budgets.
Part 2: Will Automakers Adopt It?
While Intel's SoC platform undoubtedly offers automakers a powerful tool for transitioning to software-defined vehicles, its actual adoption rate is constrained by multiple factors.
Automakers' decisions hinge not only on the technology itself but also on comprehensive considerations such as market competition, supply chain stability, and internal capabilities.
The following analysis explores why automakers might choose or forgo this platform, considering its advantages and potential obstacles.
● The platform's advantages are evident:
◎ Aligning with the trend of software-defined vehicles, this SoC platform provides high-performance computing and OTA update support, assisting automakers in transitioning from a hardware-centric to a software-centric model.
◎ Its open ecosystem attracts third-party developers through standardized interfaces and APIs, enabling automakers to quickly customize features and reduce development costs.
◎ AI acceleration and hardware virtualization provide the hardware foundation for autonomous driving and smart cockpits, satisfying consumers' demand for intelligent experiences.
◎ Lastly, high security and industry compliance offer automakers protection in the connected vehicle era.
● The reasons for automakers' hesitation are equally significant:
◎ In the competitive landscape, Qualcomm's Snapdragon Ride and NVIDIA's DRIVE Thor, both scheduled for mass production in 2025, present existing partnerships and technological path dependencies that may deter automakers from risking a switch to Intel.
◎ The difficulty of technical integration cannot be overlooked. The hybrid architecture and virtualization require strong software capabilities, and the high initial costs pose a barrier for small and medium-sized automakers.
◎ On the supply chain front, the platform relies on TSMC's 7nm process, which is susceptible to geopolitical influences and capacity fluctuations, potentially causing automakers to worry about supply stability.
◎ While long-term cost-effectiveness is promising, the high initial investment and software optimization costs may deter budget-constrained automakers. Despite its technological lead, Intel's platform faces dual challenges in market penetration: ecological lock-in and cost barriers.
Conclusion
Intel's automotive-grade SoC platform, Malibou Lake, through its collaborative innovation in hybrid architecture, AI acceleration, open ecosystem, and robust security, provides a solid technological foundation for software-defined vehicles.
Its breakthroughs in performance, flexibility, and security not only meet the current demands of automotive intelligence but also pave the way for future technological evolution. Faced with the dominant influence of NVIDIA and Qualcomm, automakers must weigh short-term costs against long-term benefits when considering the adoption of this platform.








