Why is NIO, with heavy losses, determined to tackle the tough nut of 'intelligent driving chips'?
![]() 08/12 2024
08/12 2024
![]() 660
660
Lead
For NIO, being able to launch the industry's first automotive-grade 5-nanometer high-performance intelligent driving chip will undoubtedly put it in a favorable position in the future competition in the field of intelligent driving. However, the successful tape-out is just the first step of a long journey, and the challenges facing Li Bin and NIO will only increase.
Produced by | Heyan Automotive
Written by | Zhang Dachuan
Edited by | Heyanzi
2453 words in total
4 minutes to read
Recently, Li Bin, Chairman of NIO, announced at the '2024 NIO Innovation Day' that the company's 'Shenji NX9031,' the world's first automotive-grade 5-nanometer high-performance intelligent driving chip, has successfully completed tape-out.
NIO's 'Shenji NX9031' chip is the industry's first high-end intelligent driving chip manufactured using 5-nanometer automotive-grade process technology. Not only has NIO developed the chip itself, but it has also developed the underlying software that drives it. From NIO's perspective, creating an exclusive 5nm autonomous driving chip is expected to further strengthen its advantage in intelligent driving.

△Tape-out of NIO's 'Shenji NX9031,' the world's first automotive-grade 5-nanometer high-performance intelligent driving chip
In the hardware system of intelligent driving, the intelligent driving chip is the most critical component, even determining whether a vehicle can achieve L4-level high-end intelligent driving capabilities. Globally, only a handful of automakers are developing intelligent driving chips. Before NIO, only a few automakers like Tesla developed their own intelligent driving chips. Most automakers procure intelligent driving chips from NVIDIA, Qualcomm, and Mobileye. However, these chips are designed with versatility in mind to expand their usage, which can limit their performance to some extent. Tesla's previous development of exclusive intelligent driving chips partially addressed this concern.

△The intelligent driving chip is the most critical component in the hardware system of intelligent driving
The 'Long March' of the Chip Industry
However, the successful tape-out of the 5nm chip is just the first step of a long journey. For NIO to truly use its own chip, it must first address two main issues:
1. Chip Fabrication: Chips are broadly categorized into design and foundry. NIO's successful tape-out of the Shenji chip is essentially a success in design. There are many cases of successful tape-outs of advanced process chips in China, including Horizon Robotics, Huawei, Black Sesame Technology, and Geely. However, beyond design success, the greater challenge lies in chip manufacturing, which is largely monopolized by TSMC and Samsung globally.

△ASML's lithography machines are a bottleneck
2. Product Revenue: The chip industry is also a field where scale effects matter. Only with high sales volumes can the initial investment be amortized. However, based on NIO's official sales figures, it delivered 57,373 new vehicles in the second quarter of this year and 87,426 in the first half. Such sales volumes are insufficient for achieving scale effects, making it difficult to recoup investments in the chip sector solely through NIO's sales. To make the chip business viable, NIO needs to sell chips to other automakers. However, both foreign and domestic players like Horizon Robotics already have mature solutions and significant sales, making it challenging for NIO to compete.

△It is difficult for NIO to achieve economies of scale with its current sales volume
Taking Horizon Robotics, a leading domestic automotive intelligent driving chip company, as an example, its gross margin reached around 70% from 2021 to 2023, according to its prospectus filed with the Hong Kong Stock Exchange. Unlike NIO's nascent chip efforts, Horizon Robotics collaborates with most domestic automakers like Lixiang, Volkswagen, and SAIC Motor. However, despite this, Horizon Robotics has incurred net losses exceeding 17 billion yuan in the past three years due to high investments. In this context, the profitability of NIO's chip business remains to be seen.

△Horizon Robotics still faces challenges in achieving profitability
Is NIO's Investment Sustainable?
In the first quarter of this year, NIO's total revenue was 9.909 billion yuan, down 7.19% year-on-year, with a net loss of 5.258 billion yuan, a further decline of 9.46% year-on-year. NIO invested 2.86 billion yuan in R&D during the quarter, consistent with its investment levels over the past two to three years. According to Li Bin, NIO currently invests approximately 3 billion yuan in R&D each quarter, totaling over 10 billion yuan annually, with 60-70% allocated to fundamental research areas like chips, batteries, and operating systems.

△According to Li Bin, NIO invests over 10 billion yuan in R&D annually
Apart from R&D expenses, NIO's battery swap business is another significant cost. To date, NIO has deployed over 2,400 supercharging stations globally, with an estimated cost of 3 million yuan per station, resulting in investments exceeding 7 billion yuan, excluding ongoing operation and maintenance costs. If daily business volumes are insufficient, NIO's swap stations may incur losses, which ultimately need to be subsidized by NIO.
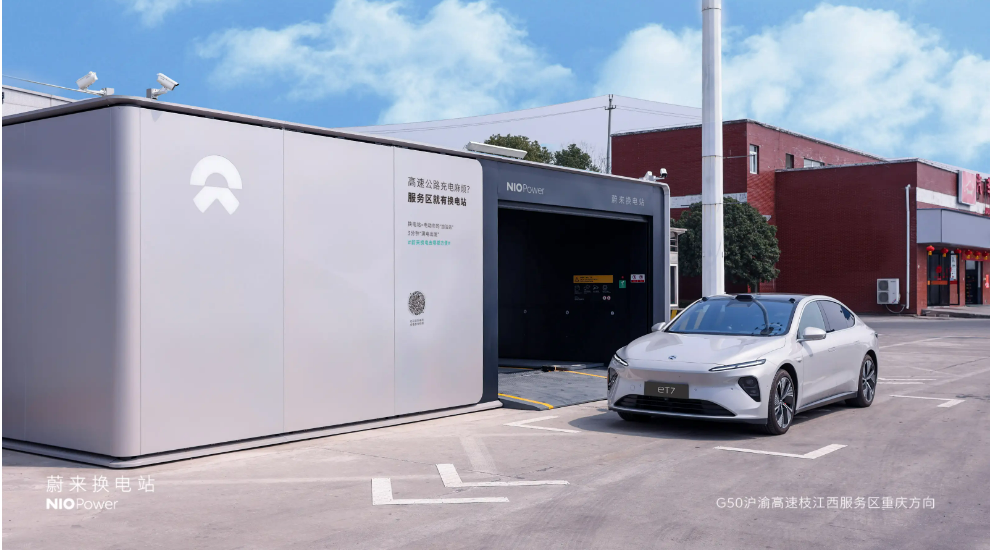

△NIO has invested heavily in the battery swap sector
How Can NIO Achieve Profitability in Its Chip Business?
Given the fierce competition in the domestic smart electric vehicle market, why is NIO determined to pursue businesses that may not directly benefit its core automaking operations? Strengthening its development capabilities through underlying technology research may be NIO's intention. Alternatively, Li Bin may be considering spinning off these businesses for separate financing.
Once mature, both the battery swap and chip businesses will be spun off for IPO financing. However, domestic IPOs are challenging, and Hong Kong and U.S. stock markets present their own limitations. Listing in the U.S. faces greater uncertainties due to the geopolitical climate.

△The likelihood of NIO's chip business replicating the success of its vehicle business in U.S. listings is low
If these businesses cannot be spun off for separate listings, they will become a heavy burden on NIO's development. Li Bin will either need to fund these businesses through NIO or raise funds from third-party investors, who will expect clear returns and a definite listing timeline, potentially leading to a vicious cycle.

△Middle Eastern oil capital is unlikely to continue funding NIO indefinitely without conditions
However, if the U.S. government suddenly bans Qualcomm, Mobileye (now a separately listed entity after being acquired by Intel), and NVIDIA from selling chips to China, domestically developed intelligent driving chips like NIO's will become crucial, presenting opportunities for peer procurement. Nonetheless, the manufacturing challenges of advanced process chips persist across the Chinese chip industry.

△For NIO's chips, the greatest opportunity lies in becoming a domestic alternative like Horizon Robotics
Commentary
In recent years, NIO has invested heavily in R&D, covering a wide range of areas. Pursuing long-termism and investing significantly in underlying core technologies is justified. However, automakers must balance long-term goals with short-term needs, especially for companies like NIO that are still losing money and unable to self-finance. Whether it is wise to pursue long-term goals without focusing resources on areas with the greatest potential returns may only be known to Li Bin himself.
(This article is originally written by Heyan Automotive and may not be reproduced without authorization)