H20 Export "Unbound", Domestic GPU Faces a Breakthrough Moment
![]() 07/18 2025
07/18 2025
![]() 584
584

Turbulence and turning points in the GPU market always come faster than expected.
On July 15, NVIDIA announced the resumption of supply of its China-specific H20 computing power chips. NVIDIA stated that the U.S. government has assured the company of granting licenses, and the company hopes to start deliveries as soon as possible.
Subsequently, AMD also plans to restart exporting MI308 chips to China.
This comes just three months after the issuance of the relevant ban in April.
As soon as the news came out, it triggered widespread discussion within the industry, with "whether this resumption of supply will impact domestic GPUs?" becoming a hot topic of public concern.
Before exploring the answer to this question, let's first take a look at the current state of the domestic GPU market in the first half of the year.
01
Domestic GPUs Exploded in Orders in the First Half
For NVIDIA and AMD, the two leading GPU companies, the return of their related products to the Chinese market is undoubtedly good news. However, after three months of development and iteration, the market landscape for domestic GPUs has quietly changed.
Recently, several domestic chip industry insiders said that in the first half of this year, the production capacity of several mainstream domestic chip manufacturers has been fully booked, and "Kunlunxin, Cambricon, and others have seen an explosion of orders."
The previous disruption in H20 chip supply brought the following two main benefits to domestic GPU companies:
Firstly, domestic GPU companies quickly gained the opportunity for market validation.
Enterprises that originally relied on imported GPUs (such as cloud providers and data centers) had already stockpiled a large number of chips, but under the uncertainty of the "supply disruption," they have begun to conduct independent chip research and development while conducting testing work based on domestic chips as a backup plan. This allows domestic chips to move from "laboratory testing" to "actual scenario implementation," quickly collecting real application feedback and providing a direct basis for product iteration.
During the performance exchange meeting in May this year, Tencent executives stated that the company would consider both imported chips and chips available on the domestic market.
Secondly, domestic GPU companies have received a tilt of resources, and the formation of ecological synergy has accelerated.
Under the uncertainty of the supply disruption, domestic downstream customers are actively establishing closer cooperation with domestic GPU companies - from jointly debugging hardware and adapting software to jointly optimizing computing power solutions for specific scenarios. This cooperation not only brings immediate orders but also provides an opportunity for the initial establishment of a domestic ecosystem.
As we all know, the H20 and MI308 chips are AI chips customized by NVIDIA and AMD for the Chinese market, respectively.
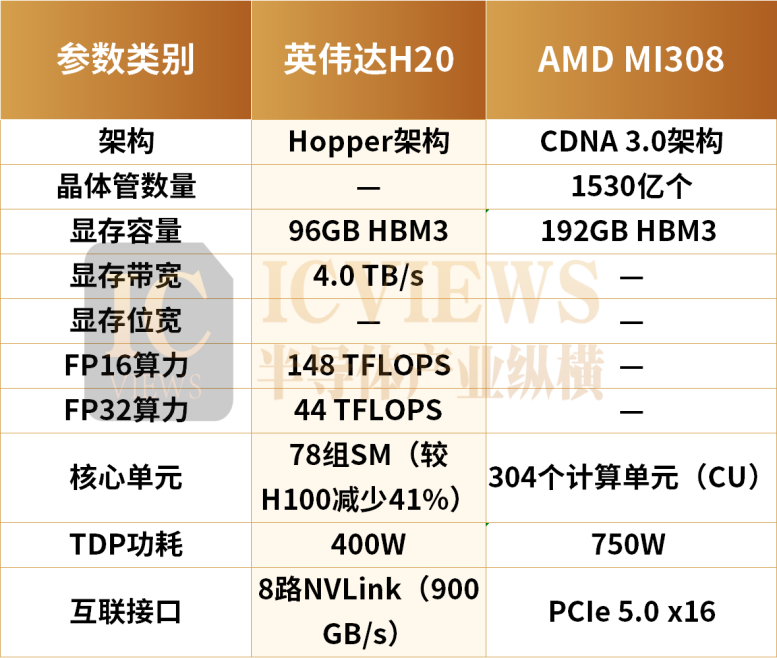
Chinese technology giants such as ByteDance, Tencent, and Alibaba are important buyers of H20 chips. A report released by international market research firm Omdia at the end of 2024 showed that the largest global buyers of NVIDIA's Hopper (including H100, H200, and the China-specific H20) series chips in 2024 were Microsoft (485,000 units), ByteDance (230,000 units), Tencent (230,000 units), Meta (224,000 units), Amazon (196,000 units), xAI (196,000 units), and Google (169,000 units).
Now, this market is changing.
"There are plenty of alternatives to H20 in China, and most domestic chips are targeting H20 in terms of specifications and price. These are currently the main competitors for domestic chips," analyzed an industry insider.
The popularity of domestic GPUs is not just a slogan.
Domestic GPU companies have indeed launched multiple products with performance comparable to H20, such as Kunlunxin's third-generation chip P800, Moore Threads MTT S80, Huawei Ascend 910C, Cambricon Thought Engine 590, etc.
Even when discussing NVIDIA's approval to export H20 chips, U.S. Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen noted that China has already developed chips with performance comparable to H20.
It can be said that the previous supply disruption has instead become an opportunity for domestic GPUs to accelerate adaptation and enter domestic supply chains.
Next, let's explore the impact of this resumption of supply on domestic GPU companies.
02
Is the "Unbinding" of H20 Exports Harming Domestic GPUs?
Industry insiders told Semiconductor Industry Insights that the resumption of GPU supply is mainly beneficial to those customer groups that were already using NVIDIA GPUs and will not cause substantial "harm" to domestic GPU companies. Due to differences in technology ecosystems and scenario needs, these two groups have formed a relatively stable market division of labor, and the development pace of domestic GPUs on their own track will not be easily disrupted.
The insider also analyzed the main reasons for the above conclusion, which mainly include two points:
Firstly, the "path dependence" of technology routes and ecosystems has formed barriers.
NVIDIA has built extremely high user stickiness and migration costs in the global high-performance computing, AI training, and high-end graphics fields with its monopolistic CUDA ecosystem. Customers who rely on it for cutting-edge research and development or global business (such as large cloud service providers and AI laboratories) have deeply integrated their technology stacks, development tools, and talent systems with CUDA, pursuing ultimate performance and ecological maturity.
Therefore, after the resumption of H20 supply, these customers may be more inclined to return to NVIDIA, as switching to domestic GPUs would require reconstructing code, debugging operators, and even replacing adaptation tools, resulting in relatively high migration costs.
On the contrary, domestic GPUs initially focused on meeting the rigid demand for the "secure and controllable" information technology and innovation market (such as basic information systems in key industries like government, finance, and energy) and areas like desktop rendering, lightweight AI inference, and edge computing, which do not require ultimate absolute performance but are more sensitive to cost, localized services, or policy compliance. The "usability," "compliance guarantees," and "supply chain security" provided by domestic GPUs in these scenarios are their core values.
This "each has its own range of adaptation" situation makes it difficult for the two types of users to easily switch due to the resumption of supply.
Secondly, the "dual-track" supply of GPUs has become an industry consensus.
After experiencing the impact of supply disruptions, some domestic enterprises have formed a dual supply chain strategy of "ensuring stability in core scenarios (using NVIDIA) and ensuring autonomy in secure scenarios (using domestic products)." For example, leading cloud service providers and other enterprises are simultaneously paying attention to both imported and domestic chips, essentially incorporating the two types of products into different demand pools: NVIDIA ensures the continuity of high-end computing power, while domestic chips consolidate the security of basic computing power. The "dual-track" demand brings a channel of continuous growth to domestic GPUs.
In addition, "GPU localization" was also a high-frequency term during my interviews.
03
GPU Localization, the General Trend
"GPU localization is the general trend." "The domestic GPU market has seen robust sales in the first half of the year, and this trend will continue in the second half." The judgments of many industry insiders all point to the direction of localization.
The market has also given positive feedback - on July 16, GPU and related companies saw a general rise in stock prices.
TrendForce data shows that there are three types of AI server chip vendors in the domestic market: one is the outsourcing of NVIDIA, AMD, etc., another is cloud vendors' self-developed ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits), and the third is domestic local suppliers. The market share of the outsourcing segment was about 63% last year and is expected to drop to 41.5% by 2025. With the support of national AI chip policies, Chinese local chip suppliers are expected to increase their share to 40% by 2025, almost equal to the proportion of outsourced chips.
The cultivation achievements of domestic GPU companies in the GPU field over the past two years have been evident in the financial reports released by various companies.
Moore Threads' prospectus shows that the company's main business revenue reached 432 million yuan in 2024, a year-on-year increase of 257.02%. In the past three years, the company's revenue focus has continued to change, with desktop-level graphics acceleration business contributing 71.44% of main business revenue in 2022; professional graphics acceleration accounted for a similar proportion in 2023; by 2024, the newly added AI intelligent computing business became the company's 77.63% of main business revenue.
Muxi Integrated's prospectus shows that the company's main business revenue was 742 million yuan in 2024, a year-on-year surge of 1354.9%. In addition, Muxi also disclosed data for the first quarter of this year, during which the company's main business revenue reached 320 million yuan, already accounting for 43% of the previous year's main business revenue. In the first three months of this year, the revenue share of GPU boards in the training and inference series soared to 97.55%; the second largest share was GPU boards in the intelligent computing and inference series, accounting for 1.25% of revenue.
Cambricon has achieved profitability since the fourth quarter of 2024; in the first quarter of 2025, it achieved revenue of 1.111 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 4230.22%, and net profit attributable to shareholders of listed companies of 355 million yuan, a year-on-year increase of 256.39%.
Hygon achieved total revenue of 9.162 billion yuan in 2024, a year-on-year increase of 52.40%; net profit attributable to shareholders of listed companies was 1.929 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 52.73%. In the first quarter of this year, it achieved revenue of 2.4 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 50.76%, and a year-on-year increase of 75.33% in net profit attributable to shareholders of listed companies.
Moreover, domestic GPU companies have also been active in the capital market. On June 30, 2025, the IPO applications of two domestic GPU enterprises, Moore Threads and Muxi, were both accepted by the Shanghai Stock Exchange. Moore Threads plans to raise 8 billion yuan for chip research and development projects and to supplement working capital; Muxi plans to raise 3.904 billion yuan for projects such as the research and development of new high-performance general-purpose GPUs. Previously, several domestic GPU companies have initiated listing guidance , and the attention and support of the capital market for domestic GPU enterprises have injected strong momentum into their development.
The market is eagerly awaiting who will become the "first domestic GPU stock."
04
H20 and MI308 Face Fierce Competition
China is an important market that NVIDIA and AMD cannot easily part with.
In 2024, AMD generated revenue of 25.8 billion USD, with China contributing 6.2 billion USD, accounting for 24% of its total revenue.
NVIDIA's financial report shows that revenue in China in fiscal year 2025 was 17.108 billion USD, the highest in history, representing a 66% increase from the previous year's 10.306 billion USD. At the same time, in fiscal year 2025, 53% of NVIDIA's revenue came from regions outside the United States, with China being NVIDIA's second-largest sales region: the United States accounted for 47% in first place, and mainland China accounted for 13% in second place.
However, the increased trade control over H20 may lead to a loss of market share for NVIDIA in China.
NVIDIA revealed in May this year that relevant restrictions on H20 and other policies would cost the company approximately 5.5 billion USD in losses. Morgan Stanley analysts subsequently downgraded their revenue expectations for NVIDIA, concerned that U.S. chip export restrictions on China would impact the company, predicting that NVIDIA's data center revenue may decline by 8% to 9% in the coming quarters.
In a recent interview, NVIDIA founder Jen-Hsun Huang said that the company has received a large number of orders, and some Chinese enterprises are waiting for the official delivery of the chips. At the same time, Huang also announced the launch of a new and fully compatible NVIDIA RTX PRO GPU, which NVIDIA described as "the ideal choice for creating digital twin AI for smart factories and logistics."
However, for NVIDIA and AMD, the resumption of supply is only the starting point of a new round of competition. In the future, as the industry's demand for GPU computing power continues to escalate, and with the possibility of more potential competitors entering the market, competition in the GPU market will usher in more highlights.







