2024 in Retrospect: Ten Key Technological Milestones
![]() 12/28 2024
12/28 2024
![]() 662
662

As 2024 draws to a close, it has been a remarkably dynamic year for the technology sector, marked by groundbreaking innovations and conflicting perspectives.
Some argue that the overall technological environment is bleak, while others quietly reap significant profits. Critics complain about the challenges and unprofitability of AI, while optimists foresee a bright future and advocate for timely investments. Proponents of pre-training see limitless potential, whereas skeptics warn of an impending large model winter. Advocates herald multimodality as the future, while detractors dismiss its necessity.
From a broader perspective, numerous technological advancements capable of transforming human destiny emerged this year, alongside incessant internal strife among human civilizations. Despite appearances of rising technological globalization, geopolitical maneuvering and technological isolation strategies continue to dominate the landscape.

To encapsulate the main technological developments of this complex year, two keywords stand out: AI and self-sufficiency. AI drives the evolution of nearly every technological domain globally, while self-sufficiency embodies China's technological mission in the current era. Irreversibly, autonomy and controllability are transitioning from alternative strategies to central importance.
Guided by these themes, we present the top ten technological hallmarks of 2024 that deserve to be remembered, serving as both recent memories and harbingers of the future.

The year's first major technological event was the February 15 release of OpenAI's text-to-video large model, Sora. In its demo, Sora created lifelike one-minute videos based on text prompts, deeply simulating the physical world. Its exquisite effects and powerful visual impact sparked global excitement, with many believing AI's advancement could render the film and television industry, and even the physical world, obsolete. This astonishment extended beyond the tech industry, with various sectors marveling at Sora's disruptive power and envisioning an AI-driven future.

However, subsequent developments fell short of initial hype. Sora remained in a closed beta accessible only to artists throughout the year, opening to the public only at OpenAI's year-end conference, sans the 'world simulator' label. Text-to-video technology revealed shortcomings, such as difficulty in understanding physical laws and numerous detail flaws. Unlike ChatGPT, Sora didn't garner widespread following or imitation in the AI field. High computational costs and limited commercial benefits led many tech giants and AI companies to shelve video generation models or prefer simpler image-to-video alternatives.
For multimodality, represented by Sora, to truly thrive in the AI world, more effort is needed.

If 2023 marked the inception of large models in smartphones, with all manufacturers incorporating them, consumers were less aware of their practical applications. In contrast, 2024 can be deemed the inaugural year of AI phones, as manufacturers explored systematic and application-oriented AI capabilities, leveraging AI as a smartphone differentiator beyond an arms race for large models.
Apple's hint at Apple Intelligence made AI the primary keyword for all new phone models in 2024. Whether overseas giants like Samsung and Apple or Chinese manufacturers like Huawei, Honor, OPPO, vivo, and Xiaomi, the core shift this year was from individual AI capabilities like photo editing and summarization to system-level AI applications.

One imaginative development was Honor's pioneering autonomous driving function for screen reading on phones. The system-level AI agent bypassed third-party app compatibility issues, performing automatic operations by understanding screen information, enabling actions like AI-driven cancellation of paid subscriptions and AI-ordered takeout. Honor's conference demonstration of ordering thousands of coffee cups with a single AI command was undoubtedly a unique technological spectacle of 2024.

Elsewhere, AI bridged gaps between phones and other devices. Huawei's Mate 70 series introduced the AI air transfer feature at year-end, enabling AI to sense user gestures, recognize hand movements, and facilitate wireless image or screenshot transfers across devices.
Reflecting on recent phone conferences, this year's innovations were the most significant and intriguing, proving AI phones are well worth the effort.
Sometimes, intentional efforts yield no fruit. While the globally sensational Sora didn't inspire industry imitation, OpenAI's September release of the o1 large model with slow-thinking capabilities triggered genuine industrial agglomeration. The o1 model supports more problem-solving thinking by extending the model's thought chain, tackling complex issues like math problems. Combined with traditional generative AI, this 'slow-thinking' model processes different problems separately, eliminating large model 'hallucinations.'
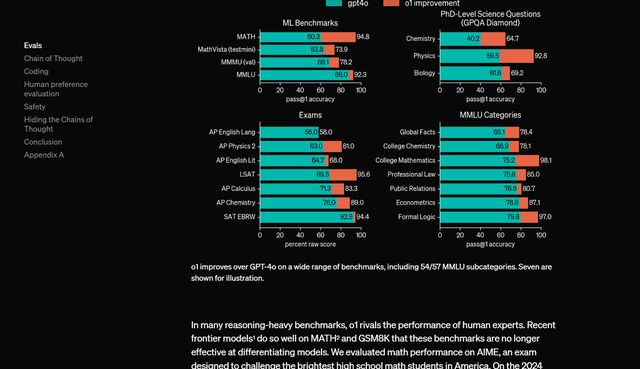
This technical approach quickly gained followers. Many technology vendors claimed to have had similar issues and solutions before o1's popularity. Within months, all large models acquired slow-thinking capabilities, ushering in renewed AI technology performance. As OpenAI founder Sam Altman noted, 'It proves AI development hasn't slowed and that we have a good grasp of the coming years.' The deeper industrial significance of the slow-thinking model demonstrates untapped possibilities on the pre-trained model path, suggesting the AI technology bottleneck is farther than pessimists speculate.

No thriving industry is complete without a price war, evident in this year's cloud computing and AI markets. While AI dominated cloud computing's technical side, discounted AI characterized the market side.

In May 2024, ByteDance launched the Doubao large model, introducing an ultra-low price of 0.0008 yuan per thousand tokens in the enterprise market. This meant processing 1,500 Chinese characters cost only 0.8 cents, a 99.3% reduction compared to the industry average, shifting large model pricing from cents to fractions of a cent.
Cloud computing vendors followed suit. Alibaba Cloud announced price reductions for nine large models, while Baidu Intelligent Cloud made two main ERNIE series models free. At the 2024 Yunqi Conference, Alibaba Cloud further reduced prices for three main Tongyi Qianwen models, with the highest reduction reaching 90%.
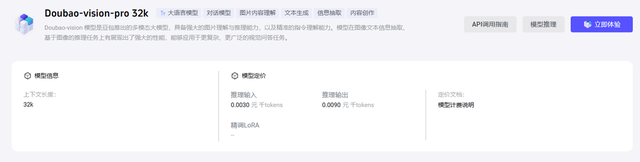
By year-end, at the December 18 Volcano Engine Force Conference, the Doubao visual understanding model launch was accompanied by across-the-board price reductions, setting the price for input of one thousand tokens at just 3 cents, 85% lower than the industry average. The commercialization of large models will likely be accompanied by fiercer price wars and market competition in the future.

After the autonomous driving sector's boom since 2021, it fell silent. In 2024, the sector witnessed new changes, notably Robotaxi's sudden popularity. The reasons for this popularity may not be entirely clear, but major global Robotaxi manufacturers significantly benefited this year. Luobo Chapao, in the public eye, announced over 8 million orders and welcomed a new generation of vehicles with lower prices and better performance. Other domestic Robotaxi companies also achieved goals like going overseas and listing. Multiple provinces and cities introduced autonomous driving-related policies this year, bringing significant policy benefits to the Robotaxi model.

In the US, Waymo achieved substantial growth, and Tesla joined with significant resources. The global autonomous driving spring seems to be in the air once again.

Hopefully, there will be more good news about intelligent vehicles in the future. However, for driving professionals, let's hope the comedy show joke doesn't come true: 'Luobos, run faster!'

For five years, the tech circle has asked: How long can the HarmonyOS banner fly? Creating a domestic mobile operating system under extreme circumstances is akin to achieving a miracle.
In 2024, this miracle continued. Huawei's release of the native HarmonyOS operating system marked the official farewell to the Android kernel and transition to a completely independent stage.

By then, there were over 15,000 native HarmonyOS applications and meta-services, with over 1 billion HarmonyOS-connected devices and 6.75 million registered developers. The path of pure-blooded HarmonyOS's success should already have a phased answer. Many of my friends and I became native HarmonyOS users, experiencing its native intelligence, security, and other technological systems while acknowledging its current immaturity. 'More needs to be done' should be the consensus among all HarmonyOS users and developers.

Huawei's Rotating Chairman, Xu Zhijun, said, 'According to our analysis, 100,000 applications signify HarmonyOS ecosystem maturity to meet consumer needs. This is the key goal for the HarmonyOS ecosystem in the next six months to a year.'
Whether the miracle happens depends on us all. Let's wait 'til the mountains are ablaze with flowers.
In principle, 'Black Myth: Wukong' should be considered a cultural phenomenon rather than a technological event. Admittedly, Black Myth showcases technological capabilities in game engines, rendering, game AI, and other fields, boosting the popularity of gaming laptops, cloud computers, gaming peripherals, monitors, and other technological products.

For China's technology industry in 2024, the significance of "Black Myth: Wukong" extends beyond that. In August, amid our merciless defeat by the White Robed Scholar and Tiger Vanguard, we witnessed a peculiar phenomenon: nearly all technology vendors across fields leveraged Black Myth's IP, a spectacle unmatched by other blockbusters or internet memes.
This resonates with spiritual cores. At this juncture, China's technology industry essentially redoes almost all human technological achievements. From chips to operating systems, AI frameworks to databases and EDA tools, well-trodden paths need retracing. It's not just gamers who are "re-embarking on the journey to fetch the Buddhist scriptures."
Isn't this precisely what destiny intended?
Since the first "Black Myth: Wukong" trailer on August 20, 2020, countless gamers have wondered how far China's first 3A game could go. Amid high expectations, four years later, the final product exceeds imagination. The same is true for China's path to technological self-reliance. Even under the spotlight, we must become the Monkey King.

Beneath the surge of AI algorithms lies the burgeoning IT industry, reaping the first wave of dividends from the AI era. As the adage goes, those who sell shovels to gold miners often strike it rich first. With the rise of large models, the global demand for AI computing power has skyrocketed, prompting industries to revamp their AI infrastructure and cities to establish smart computing centers. This has spurred a surge in demand for AI computing infrastructure, particularly smart computing servers. Simultaneously, the ICT market, encompassing AI network switches and AI storage, has undergone a comprehensive upgrade.
Parallel to the demand for smart computing, a wave of domestic substitution is also sweeping through the IT market. This confluence makes autonomy coupled with intelligence the definitive game-changer for the IT industry in 2024.

Leading IT companies, including Huawei, Sugon, Lenovo, Inspur, and H3C, have converged their efforts on the path of autonomous smart computing. Meanwhile, cloud computing providers like Huawei Cloud and China Telecom Cloud are also offering cloud-based solutions aligned with autonomous smart computing.
In the foreseeable future, autonomy combined with intelligence will remain the dominant theme in the technology market. Those who navigate this high ground will undoubtedly triumph in the next era.
The full unveiling of this strategic window signifies that another round of transformation in the IT market is imminent.

Let's delve into AI once more. Another shift in the AI realm in 2024 is the comprehensive evolution of the role of AI developers.
Historically, when discussing AI developers, their full title should have been "AI algorithm developers." They were responsible for data cleaning, model training, parameter tuning, and eventual deployment. However, today's AI developers are better described as "developers whose ideas are realized through AI." They no longer need to comprehend models, frameworks, or even programming; all they need is creativity.

The heart of this transformation lies in the realization of agent development. Last year, OpenAI introduced the new GPTs development model, enabling developers to complete application development solely through natural language, sans coding. This model was later termed the AI agent model, hailed as the optimal approach for leveraging large AI models.
In 2024, agent development has finally become a reality. For instance, Baidu launched the ERNIE Bot platform, leveraging the ERNIE large model to lower the barrier for developers and enhance distribution efficiency. As of November 2024, the ERNIE Bot platform had garnered 150,000 enterprises and 800,000 developers.
We have always held a steadfast belief: the success of every software era hinges on the success of developers; the proliferation of every technology aims for the broadest possible benefit.
Code-free, ultra-simplified agent development paves the way for the AI era to advance towards this goal.

In 2024, the value of "abandoning fantasies" has continued to escalate.
On December 2, the U.S. Department of Commerce announced the third round of sanctions against Chinese semiconductor chip companies. The list encompasses as many as 140 companies, including over 20 semiconductor firms, 2 investment companies, and over 100 semiconductor equipment manufacturers. Furthermore, the United States has imposed export restrictions on semiconductor equipment manufacturing companies in Singapore, Malaysia, Israel, and other nations, intensifying the blockade of China's semiconductor supply chain. Additionally, the new ban has been expanded to cover high-bandwidth memory chips (HBM) and various semiconductor manufacturing equipment and software tools.
Prior to this, hundreds of Chinese semiconductor and technology companies had already been blacklisted by the U.S. Department of Commerce. Compared to when the chip iron curtain first descended, the Chinese technology community now feels a sense of numbness and absurdity. Glancing at the Entity List, one might realize that scarcely any notable Chinese semiconductor companies are exempt. Some have joked that companies not on the list should reflect on their development trajectory.
At this juncture, a consensus emerges: from chips to the entire technology landscape, self-reliance is China's sole option.
Having no retreat is the path to victory.

For the technology industry, this year has been tumultuous, a blend of clouds and blue skies.
Ordinary individuals confront the uncertainty and apprehension of being supplanted by AI; AI practitioners, entrepreneurs, and developers embark on arduous journeys yet brim with hope; confronted with geopolitical challenges, Chinese companies rally for technological self-reliance.
These emotions linger as the legacy of 2024 and become the impetus for tomorrow.
This year has been replete with uncertainties. Can AI truly transform the world? Is intelligence merely a bubble? Will domestic chips and operating systems prevail? Perhaps each individual harbors a firm answer, albeit unverifiable at present.
Yet, as 2024 wanes, we may soon yearn for its uncertainties and the days when everyone strived to uncover answers.