Huawei's Resurgent Return to Overseas Markets: Are Samsung and Xiaomi Ready?
![]() 02/20 2025
02/20 2025
![]() 553
553
Typesetting | Xiaoying
Huawei chose Southeast Asia as the venue for its first mobile phone launch event of the year.
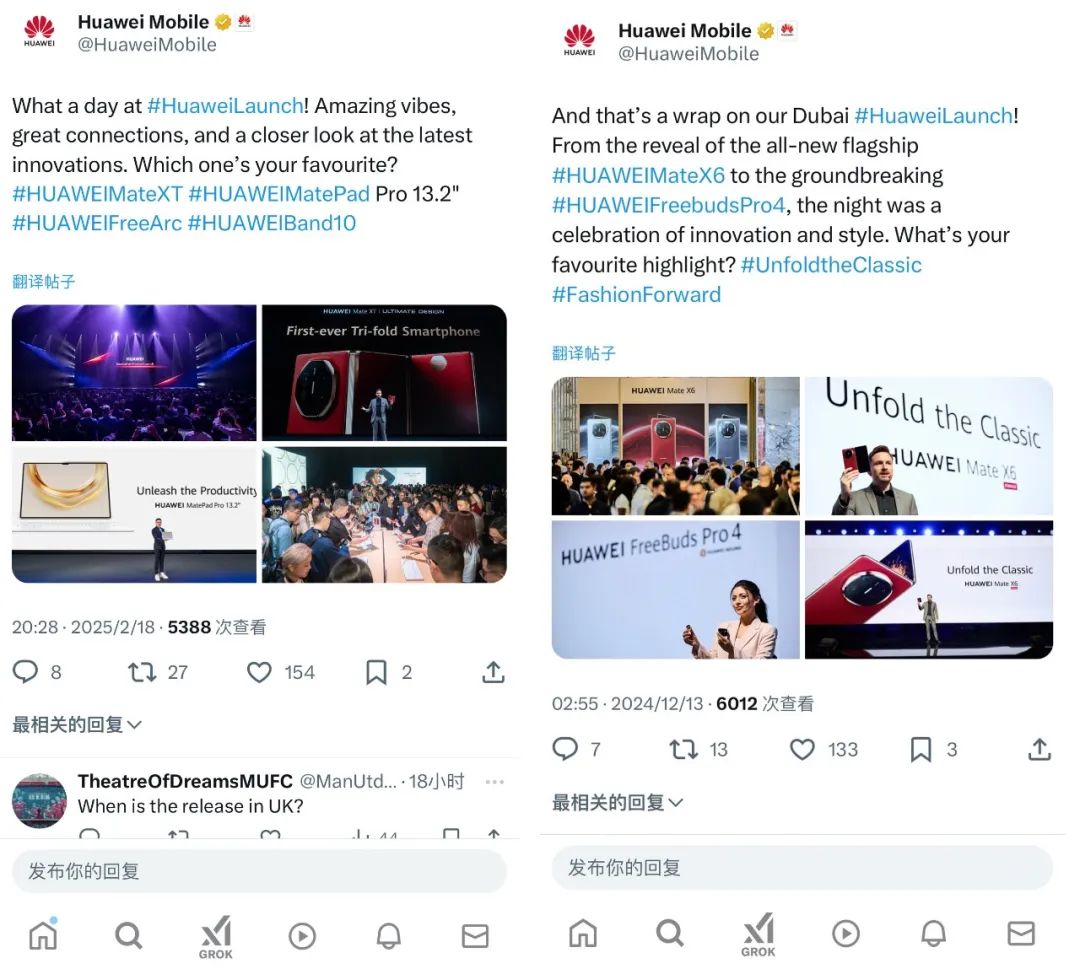
On February 18, Huawei held a product launch event in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, introducing the triple-folding Huawei Mate XT Extraordinary Master to overseas markets, a device previously launched in China.

From last year's Dubai launch event, featuring huge billboards in key global locations, to this year's Malaysian event, Huawei's counterattacks on overseas markets have intensified.
After being sanctioned in 2019, Huawei encountered significant hurdles in chip supply and disruptions to Google GMS services, leading to a steep decline in its performance in overseas markets, particularly in Europe and the United States.
Having regained its position among the top five domestic market shippers in 2023, Huawei has become increasingly active in the global arena. Is Huawei poised for a triumphant return to the global market?
| Huawei Returns to the Seas: Embarking on a Phase of Comprehensive Recovery |
Huawei selected Malaysia for the international debut of its triple-folding Mate XT phone, which left a strong impression on local users upon release. Some netizens even inquired online about its UK launch date.
▲ Source / X
Just over two months prior, on December 12, 2024, Huawei hosted a global launch event in Dubai, unveiling products such as the foldable Mate X6.
Huawei's strategy for re-entering overseas markets has become increasingly streamlined.
However, as early as 2023, Huawei had already declared its intention to return to the global stage. In May 2023, Huawei held launch events in Munich, Germany; Dubai, United Arab Emirates; Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia; and Mexico, introducing products like the P60 series and re-entering overseas markets.
At that time, Huawei's return to overseas markets was relatively low-key and yielded average results. Reports indicate that in 2023, overseas sales of Huawei mobile phones accounted for only about 10% of total sales.
Since 2024, Huawei's counterattacks on overseas markets have accelerated. In the first half of last year, Huawei also introduced the Pura 70 series to overseas markets. Since its release in the first half of 2024, the Pura 70 series has entered dozens of overseas countries and regions.
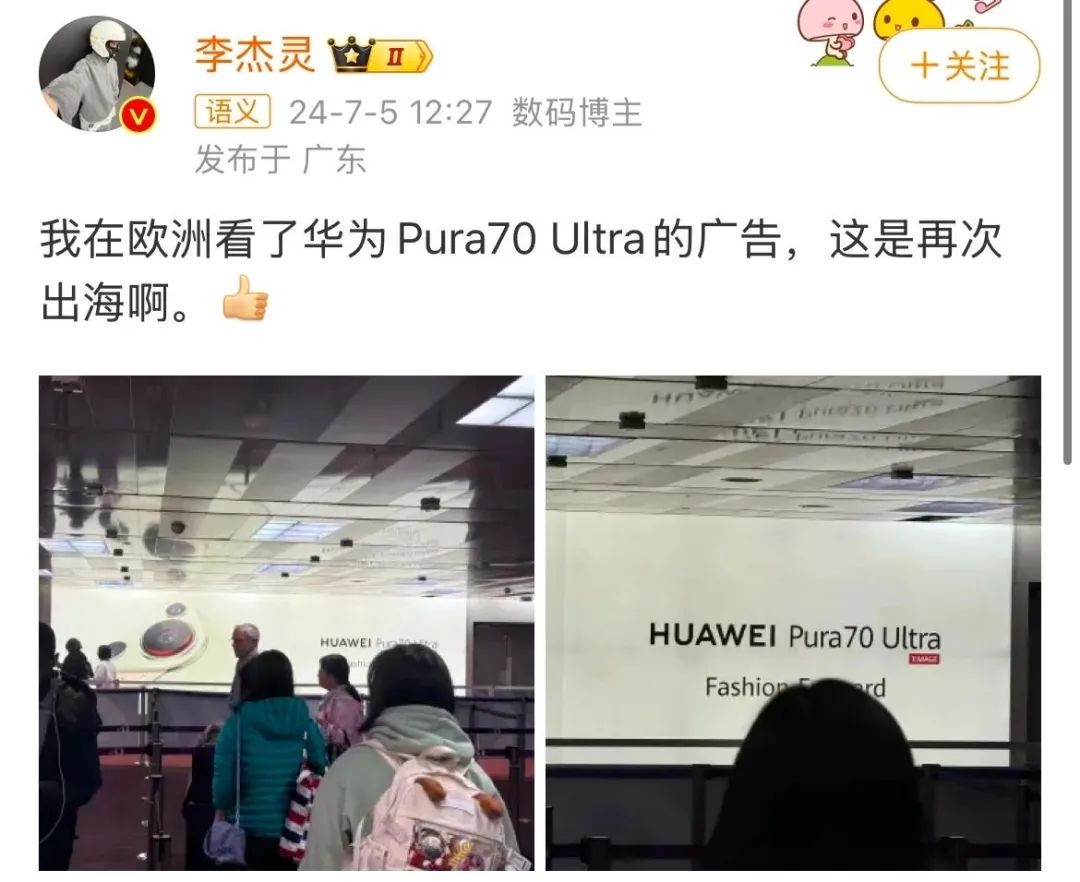
Huawei has also been heavily investing in overseas marketing, placing prominent advertisements in Munich, Germany; Dubai, United Arab Emirates; Istanbul; and key markets globally such as Paris, Milan, Warsaw, Singapore, and Mexico City.
According to Wall Street CN, under this "fast, accurate, and fierce" strategy, Huawei's overseas mobile phone sales increased to about 20% of total sales in 2024.
Notably, as Huawei intensifies its counterattacks on overseas markets, its mobile phone shipments in China have stabilized in the top five in 2024, even securing the top spot in Q1.
With a victory in reclaiming the domestic market, the timing for Huawei's counterattacks on overseas markets has matured.
In early January this year, media reports revealed that Huawei was vigorously planning its new globalization strategy, aiming to enter up to 60 countries and regions, which Huawei has confirmed.
Judging from the locations chosen for Huawei's recent launch events, the Middle East and Southeast Asian markets are the focal points of its return to overseas markets.
This may be due to the rapid growth and huge potential of these markets. In particular, Middle Eastern countries like the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia are witnessing rapid development in digital construction and have high demand for high-end technology products, while Southeast Asian countries have a relatively high acceptance of foldable screens.
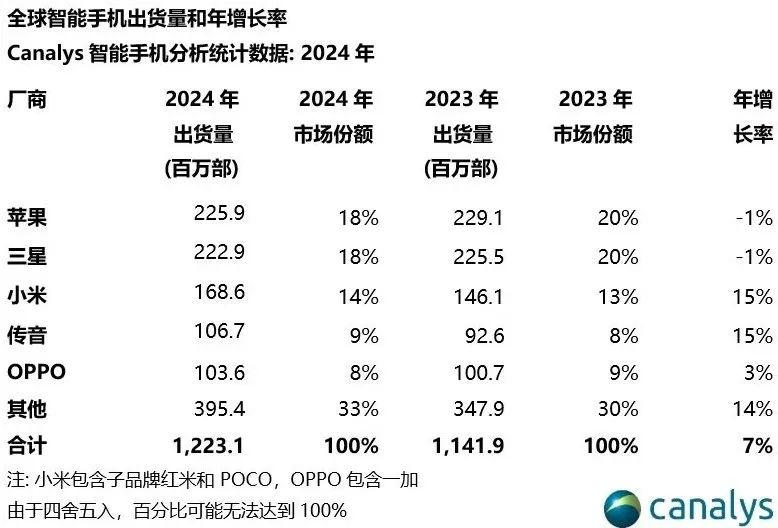
According to Canalys data, while the global mobile phone market grew by 7% in 2024, smartphone shipments in the Southeast Asian market increased by 11% year-on-year, and shipments in the Middle Eastern smartphone market achieved a growth rate of 14%, double the global rate.
Moreover, after losing support for Google GMS services, Huawei began building the HarmonyOS ecosystem. The markets Huawei is now targeting have relatively low dependence on Google services, which also aids Huawei in establishing its own user ecosystem with the "HarmonyOS system".
In addition to the Middle East and Southeast Asia, the Latin American market has gradually become a key expansion area for Huawei mobile phones. In 2024, multiple Huawei products were launched for sale in Latin American countries such as Mexico. Huawei is also continuously expanding its market coverage through partnerships with local operators and channel partners.
Various signs indicate that Huawei is making a strong comeback in the global market.
| Overseas Markets Once Supported Half of Huawei's Business |
Before being sanctioned in 2019, Huawei's globalization process served as a benchmark for Chinese technology companies expanding overseas.
Starting with the launch of the first-generation P series phone in 2015, Huawei embarked on a strategy of "high-end products + localized operations".
In terms of high-end products, Huawei's self-developed Kirin chips performed on par with Qualcomm Snapdragon; Huawei's 5G technology was widely adopted globally, making it the first vendor to launch 5G commercial mobile phones; Huawei also focused on photography, collaborating with Leica to introduce Leica triple cameras and optimize AI photography technology. These innovations gave Huawei mobile phones strong differentiated competitiveness in the high-end market.
In terms of distribution channels, Huawei chose to partner with local operators, swiftly opening up markets in Europe, the Asia-Pacific region, the Middle East, and other areas. For instance, Huawei's rapid entry into the European market was closely tied to its collaborations with top operators such as Vodafone and Deutsche Telekom.
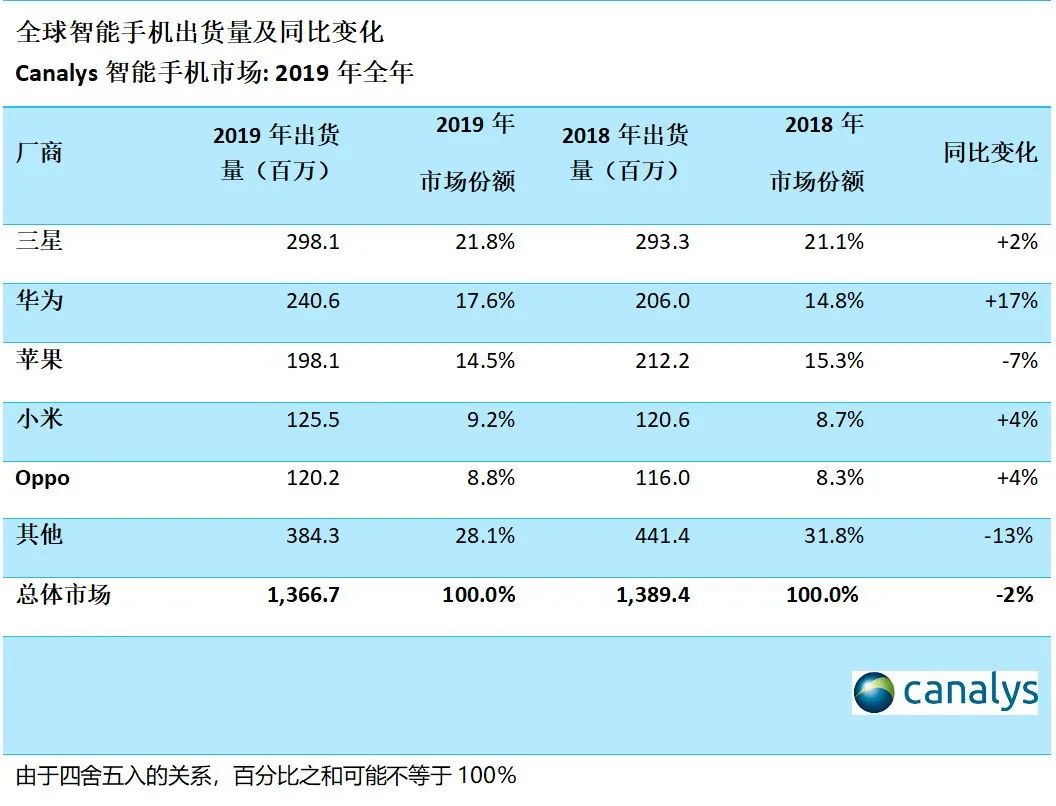
Relying on the "high-end products + localized operations" strategy, by 2019, Huawei's global mobile phone shipments reached 240 million units, with a market share of 17.6%, surpassing Apple and ranking second globally after Samsung.
▲ Source / Canalys
Of these, overseas markets accounted for nearly half of Huawei's business, contributing nearly 100 million units in sales, representing over 40% of total sales.
In that year, Huawei's market share in Europe also surged to 26%, surpassing Apple and approaching Samsung.
However, after 2020, Huawei began to experience a comprehensive collapse in the global market, with a significant contraction in its business scale.
Due to overseas restrictions, Huawei was at a disadvantage for an extended period and even had to sell its sub-brand Honor to ensure the company's survival and growth.
According to incomplete statistics, in 2020, Huawei had branches providing smartphone after-sales services in 105 countries and regions worldwide, but by 2023, this number had halved.
Huawei's share of the global smartphone market also fell from over 17% in 2019 to less than 7% in 2023.
Following Huawei's decline, the high-end market it previously dominated was quickly carved up by Apple, while the vacated mid-to-low-end market was swiftly captured by Xiaomi, OPPO, vivo, and Honor.
In the years since Huawei temporarily fell due to various challenges, besides Xiaomi briefly taking the second spot in global smartphone shipments in individual quarters, no other domestic vendor has yet to reach Huawei's previous industry position.
Huawei once earned high recognition in the global market with its self-developed Kirin chips, powerful 5G technology, and comprehensive product line. The technological accumulation and brand influence it left behind, along with the deep user base it established in multiple global markets, have formed a profound competitive advantage.
Even though it has been away from its peak state for several years, Huawei remains difficult for newcomers to catch up with.
| Can Huawei Reshape the Global Mobile Phone Industry Again? |
In the years of Huawei's absence, although there have been few comparable competitors, the global mobile phone market landscape has been in constant flux. For example, in 2024, Transsion, known as the "King of Africa," actually outpaced vivo to rank among the top five globally.
▲ Source / Canalys
Mobile phone vendors such as Xiaomi, OPPO, vivo, and Honor have long regarded overseas markets as a top priority.
Taking the third quarter of last year as an example, Xiaomi's global shipments reached 42.8 million units, approximately four times its domestic shipments of 10.2 million units. Honor, spun off from Huawei, is also accelerating its overseas expansion. It entered Europe as its "second home market" in 2023 and basically achieved parity in overseas mobile phone sales with domestic sales by the end of 2024.
In the new round of shuffling in the global mobile phone market, leading domestic mobile phone vendors are still fiercely competing. Vendors are also striving to sprint towards the high-end market and enhance their competitiveness by focusing on AI, photography, foldable screens, and other aspects.
Compared to before 2020, Huawei has become more independent and autonomous in this counterattack on overseas markets, achieving dual autonomy in hardware and software. The pure-blooded HarmonyOS operating system now shares the market with Apple and Android, and the return of self-developed Kirin chips has reduced dependence on overseas suppliers.
Huawei has once again emerged as a catalyst in the global mobile phone market. However, can Huawei regain its former glory?
Undoubtedly, Huawei has targeted the high-end market as a breakthrough point and currently holds an advantage in niche areas such as foldable screens. Through the autonomy of software and hardware, Huawei is also promoting the development of the mobile phone industry towards multipolarization.
However, Huawei still faces challenges in ecological restructuring and user habits. Google GMS services remain unavailable to Huawei, and overseas users, particularly those in mature markets like Europe, still find it difficult to replace their dependence on Google GMS in the short term.
The supply chain and production capacity bottlenecks faced by Huawei have not yet been fully resolved. Although Huawei's domestic supply chain has made progress, chip capacity remains limited. Even in China, Huawei often faces shortages. If overseas demand surges, Huawei may face insufficient supply.
In addition, geopolitical risks persist. The US ban remains in place, and some regions restrict Huawei's participation in communication network construction due to "security risks," which also impacts the development of its mobile phone business.
Whether Huawei can reclaim lost ground remains to be seen. This process is fraught with difficulties and challenges, and the test of Huawei's strength and resilience continues.
Images sourced from officials. Please delete if infringing.