Apple: "Lying flat" is easy, but running fast is hard?
![]() 05/09 2025
05/09 2025
![]() 649
649
Apple (AAPL.O) released its fiscal Q2 2025 financial report (ending March 2025) after the US market closed on the morning of May 2, 2025, Beijing time. The key points are as follows:
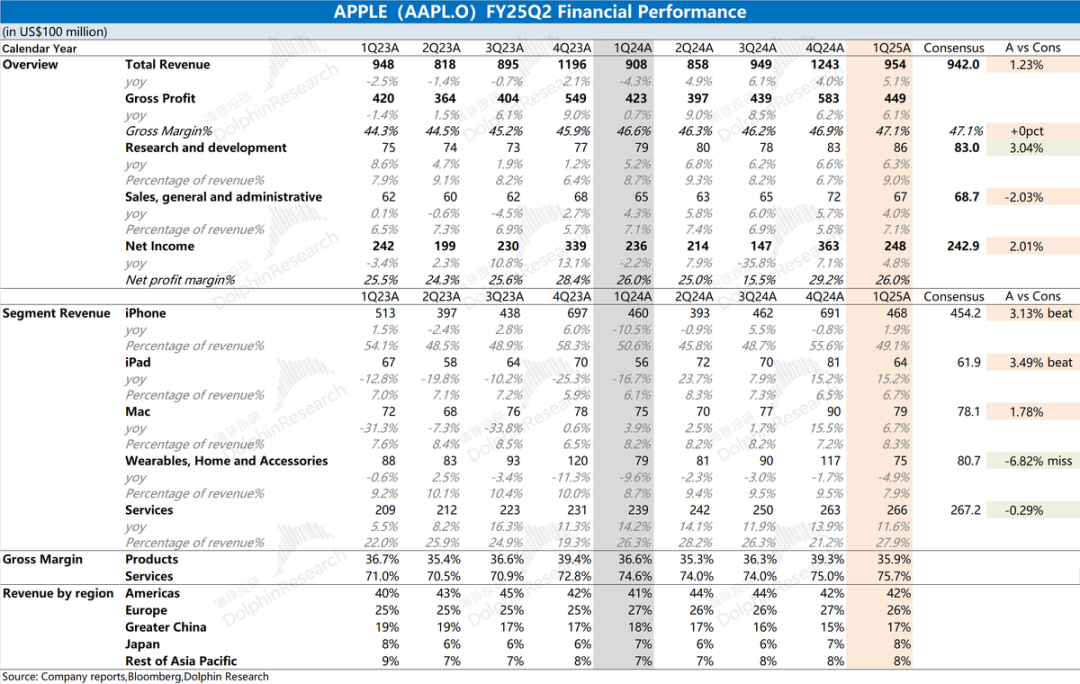
1. Overall performance: Revenue & profit, steadily increasing. This quarter, Apple achieved revenue of $95.4 billion, a year-on-year increase of 5.1%, slightly better than market consensus expectations ($94.2 billion). The increase in revenue this quarter was mainly driven by the growth of iPhone, Mac, iPad, and software services businesses. Apple's gross margin was 47.1%, an increase of 0.5 percentage points year-on-year, in line with market consensus expectations (47.1%). This quarter, the gross margin of the software services business continued to increase to 75.7%.
2. iPhone: ASP decline, shipment growth. This quarter, the company's iPhone business achieved revenue of $46.8 billion, a year-on-year increase of 1.9%, better than market consensus expectations ($45.4 billion). The growth of the mobile phone business this quarter was mainly driven by the launch of iPhone16e and early purchases by some consumers in response to tariffs. For this quarter, Dolphin estimates that overall iPhone shipments increased by 10.1% year-on-year, while the average shipping price declined by 7.4% year-on-year.
3. Other hardware besides iPhone: Wearables and other businesses will still be under pressure. Driven by new products and replacement demand, the company's Mac and iPad businesses continued to grow this quarter. As for other hardware businesses such as wearables, although benefiting from China's subsidy policies, revenue in this quarter still declined, indicating that the overall demand side is still quite weak.
4. Software services: Setting a new high. Software services revenue was $26.6 billion this quarter, slightly lower than market consensus expectations ($26.7 billion). This quarter, software business revenue reached a new high, and the gross margin continued to increase to 75.7%. With high gross margins, the company's software business, with nearly 28% of revenue, generated 45% of the company's gross profit.
Dolphin's overall view: Although this quarter was not bad, there are hidden risks in "low growth".
The company's financial report data for this quarter was overall good, with steady growth on both the revenue and profit sides. The growth on the revenue side was mainly driven by the growth of iPhone, Mac, iPad, and software services businesses; the increase in software services gross margin structurally drove the overall gross margin upwards.
However, while this financial report seems "steady", it hides some risks: 1) Even with the support of iPhone16e this quarter, the iPhone business only showed slight growth; 2) Demand for wearable and other hardware products remained weak, and revenue was still negative; 3) Although software services revenue continued to grow, the growth rate showed a downward trend; 4) Wearable and other hardware products will still be affected by tariffs, thereby increasing the company's related costs.
Regarding the market's concern about the impact of tariffs, the company's management expects the impact on next quarter's cost side to be around $900 million. Dolphin believes that this mainly comes from products such as Airpods and Apple Watch, while core products (iPhone, Mac, and iPad) are exempted. Therefore, compared to the company's quarterly hardware cost of nearly $40 billion, the impact of $900 million is relatively small but will still erode gross margins.
From a short-term perspective, the company expects the growth range of revenue for the next quarter to be 0-5%. Although the iPhone16e was launched this quarter, the company's growth for the next quarter will still be weak. Under the influence of tariff policies, wearable and other hardware businesses will continue to be under pressure, which will also erode the company's overall gross margin for the next quarter.
Considering the company's current market value of $3.2 trillion, corresponding to nearly 29 times PE for fiscal 2025 (assuming a revenue growth rate of +4% and a profit growth rate of +7% after excluding the impact of last year's EU tax reimbursement). Although the company values shareholder interests (this quarter, it paid $3.8 billion in dividends and repurchased $25 billion in shares, and will additionally approve $100 billion for share repurchases), multiple risks on the operating side will still put pressure on the company's valuation.
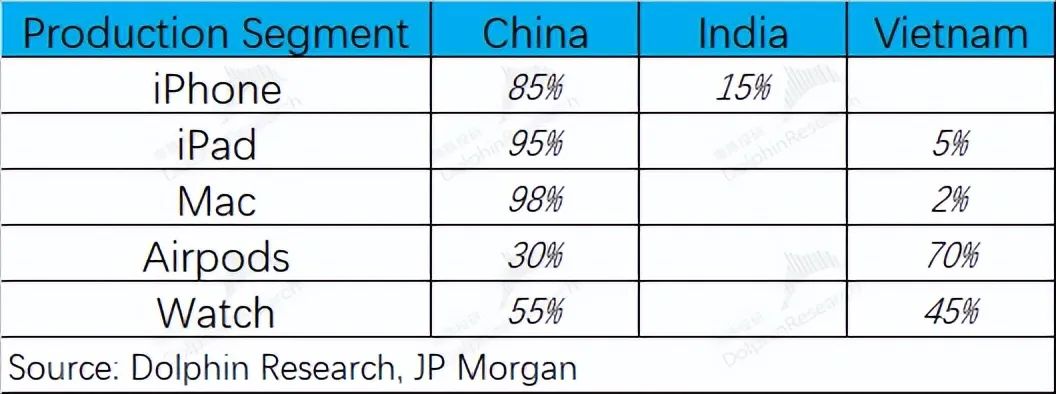
From a medium to long-term perspective, although the company has transferred some of its production capacity to Vietnam and India, as long as it is not manufactured in the United States, there will still be tariff risks in the future. In addition, the company will increase the proportion of chip procurement in the United States in the future, which may also increase the cost of the company's hardware side in the future. If Apple cannot launch AI functions or new popular hardware products that exceed expectations, the company's operating side will still face growth pressure, making it difficult to boost market confidence.
Below is a detailed analysis
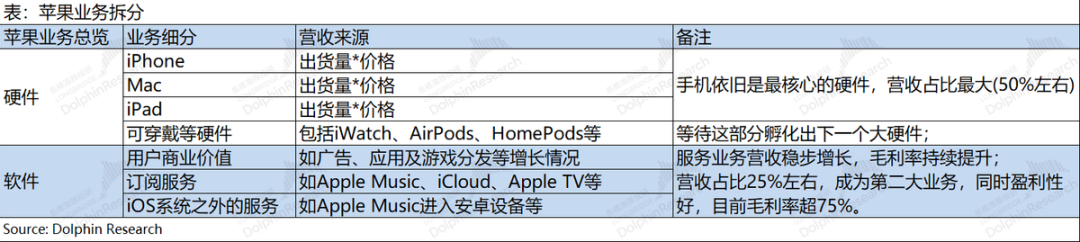
I. Overall performance: Revenue & profit, steadily increasing
1.1 Revenue side: In the second quarter of fiscal 2025 (i.e., 1Q25), Apple achieved revenue of $95.4 billion, a year-on-year increase of 5.1%, slightly better than market consensus expectations ($94.2 billion). The increase in revenue this quarter was mainly driven by the growth of iPhone, Mac, iPad, and software services businesses, while only wearable and other hardware businesses still declined year-on-year. In this quarter, only revenue in Greater China declined, while revenue in other regions increased to varying degrees.
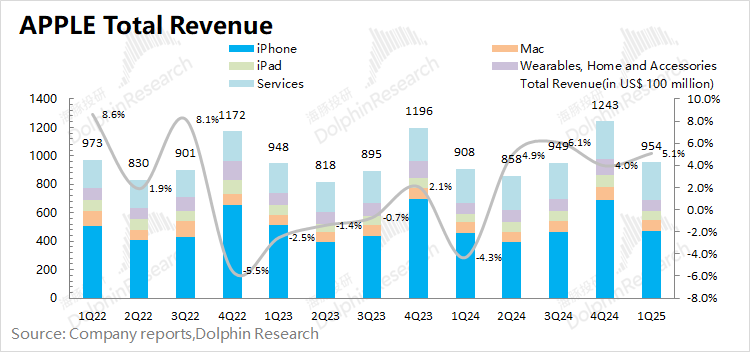
From both hardware and software perspectives:
① Apple's hardware business grew by 2.7% this quarter. The hardware business continued to grow this quarter. Although wearable and other businesses were still declining, the company's core hardware products (iPhone, iPad, and Mac) all increased to varying degrees, driving positive growth on the hardware side;
② Apple's software business grew by 11.6% this quarter, maintaining double-digit growth. The software business has certain risk resistance. Even during periods of relatively low hardware revenue, software services have maintained growth. However, it cannot be ignored that the current growth rate of the company's software business is showing a downward trend.
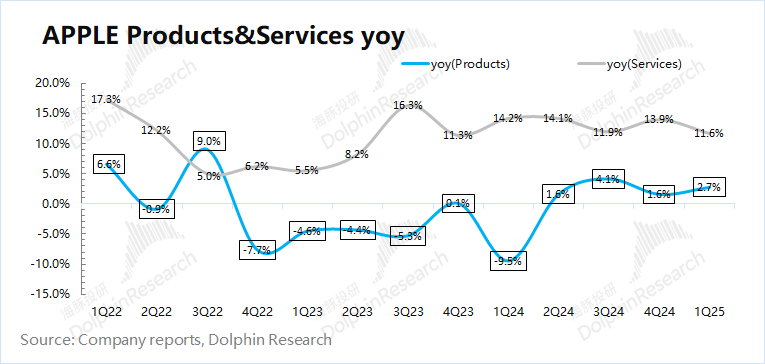
From a regional perspective: In this quarter, Apple's revenue only declined in Greater China, while it increased to varying degrees in other regions. The company's weak performance in Greater China was mainly affected by intense market competition. Although China has introduced subsidies for mobile phones and other electronic products, they are actually more beneficial to domestic Android brands, and Apple's market share in China has been eroded.
The Americas, Europe, and Greater China are the company's three main sources of revenue. Specifically, the Americas accounted for 42.3% of revenue, with an increase of 8.2% this quarter; Europe showed a slight increase of 1.3% this quarter; while revenue in Greater China declined by 2.3% year-on-year.
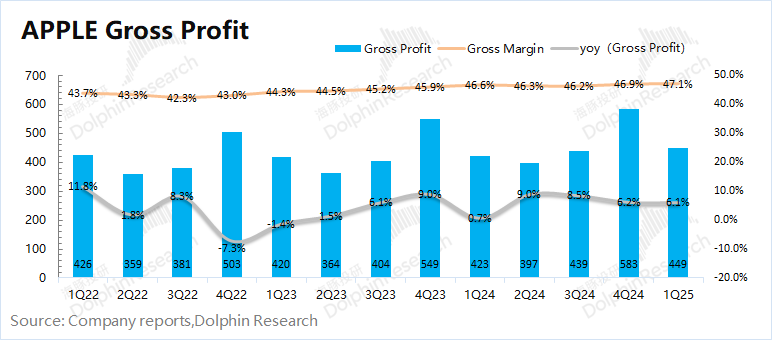
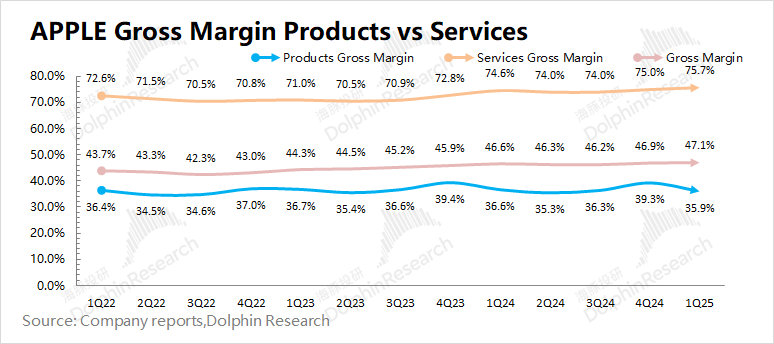
1.2 Gross margin: In the second quarter of fiscal 2025 (i.e., 1Q25), Apple's gross margin was 47.1%, an increase of 0.5 percentage points year-on-year, in line with market consensus expectations (47.1%). The increase in the company's gross margin was mainly driven by the growth in software business gross margin.
Dolphin breaks down the gross margins of hardware and software:
Apple's software gross margin this quarter continued to increase to a record high of 75.7%, which was the main source of the company's gross margin increase this quarter. The hardware gross margin fell to 35.9%, a year-on-year decline of 0.7 percentage points, mainly affected by factors such as product mix, foreign exchange, and seasonality. Among them, the relatively low-priced iPhone16e launched by the company this quarter had a corresponding impact on the company's product mix average price and gross margin.
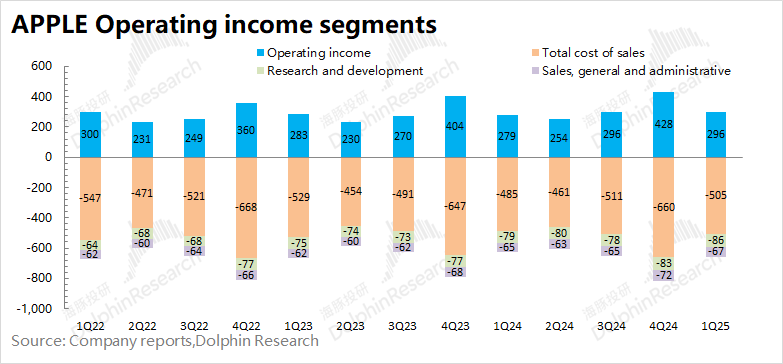
1.3 Operating profit: In the second quarter of fiscal 2025 (i.e., 1Q25), Apple's operating profit was $29.6 billion, a year-on-year increase of 6.1%. The increase in the company's operating profit this quarter was driven by the increase in revenue and gross margin.
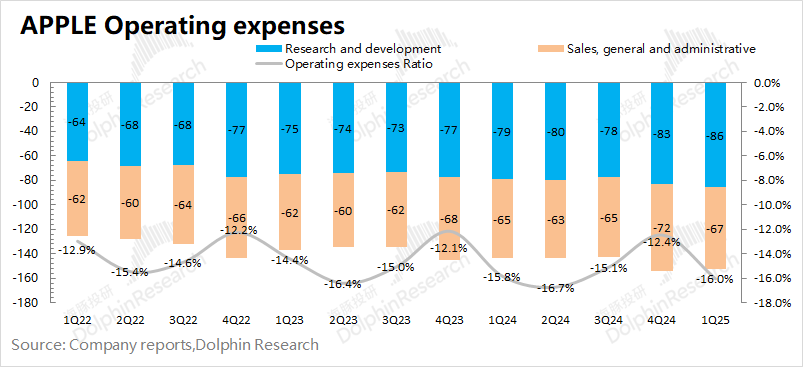
This quarter, Apple's operating expense ratio was 16%, an increase of 0.2 percentage points year-on-year. The company's selling and administrative expenses remained stable, but Apple's investment in AI is mainly reflected in R&D expenditures, and the additional expenses this quarter are also mainly reflected in R&D expenditures.
It can be reasonably inferred that regardless of Apple's revenue in the future, R&D will rigidly increase. If AI-driven phone replacements cannot be delivered as scheduled, the company may rely on faster growth in software revenue to continuously improve its gross margin structure, but the release of operating leverage on the expenditure side is likely to be compressed.
II. iPhone: ASP decline, shipment growth
In the second quarter of fiscal 2025 (i.e., 1Q25), iPhone business revenue was $46.8 billion, a year-on-year increase of 1.9%, better than market consensus expectations ($45.4 billion). The growth of the company's iPhone business this quarter was mainly due to the increase in shipments. The decline in the average iPhone price was mainly affected by the low-priced version of iPhone16e launched this quarter.
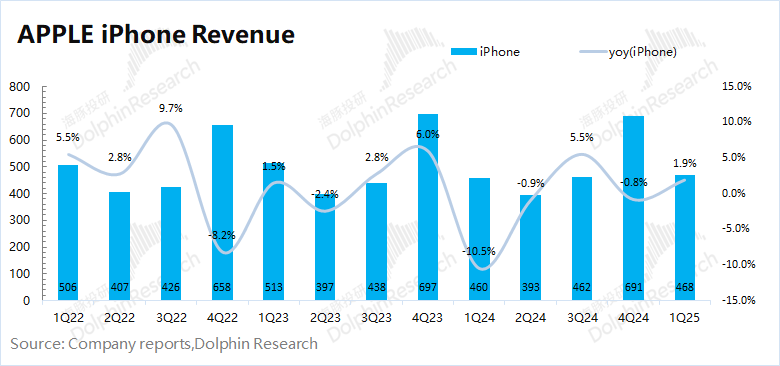
Dolphin specifically looks at the relationship between quantity and price to see the main sources of iPhone business growth this quarter:
1) iPhone shipments: According to IDC data, the global smartphone market increased by 1.5% year-on-year in the first quarter of 2025. Apple's global shipments increased by about 10% year-on-year this quarter, and the company's shipment performance was better than the overall market. Dolphin believes that this is mainly due to two reasons: 1) The company launched iPhone16e, and the launch of new products drove an increase in demand; 2) The uncertainty of US tariff policies brought about price increase expectations, stimulating some consumers to purchase in advance.
2) iPhone average shipping price: Combining iPhone business revenue and shipments, the average shipping price of iPhone this quarter was around $809, a year-on-year decline of 7.4%. This is mainly because the low-priced version of iPhone16e launched by the company this quarter structurally lowered the average product price of the company's iPhone portfolio.
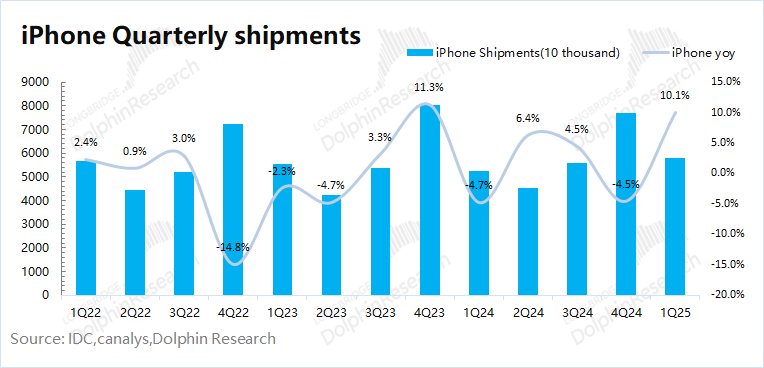
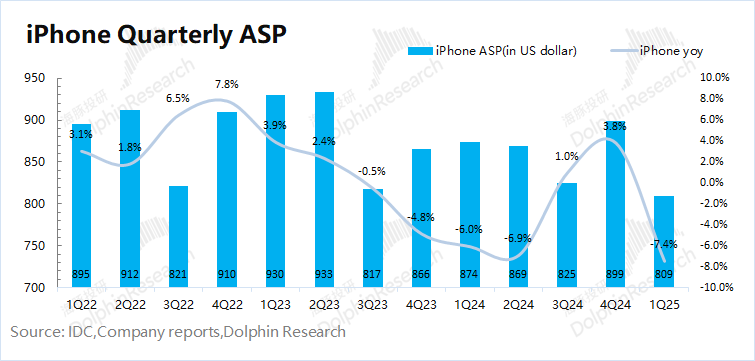
III. Other hardware besides iPhone: Wearables and other businesses will still be under pressure
3.1 Mac business
In the second quarter of fiscal 2025 (i.e., 1Q25), Mac business revenue was $7.9 billion, a year-on-year increase of 6.7%, basically in line with market expectations ($7.8 billion).
According to IDC's report, global PC market shipments increased by 5% year-on-year this quarter, while Apple's PC shipments increased by 14.6% year-on-year. The company's performance was significantly better than the overall market, mainly due to the promotion of the latest MacBook Air, MacBook Pro, and Mac mini models.
Combining company and industry data, Dolphin estimates that the average shipping price of the company's Mac this quarter was $1,445, a year-on-year decline of 6.9%. The growth of the company's Mac business this quarter was mainly driven by the increase in shipments.
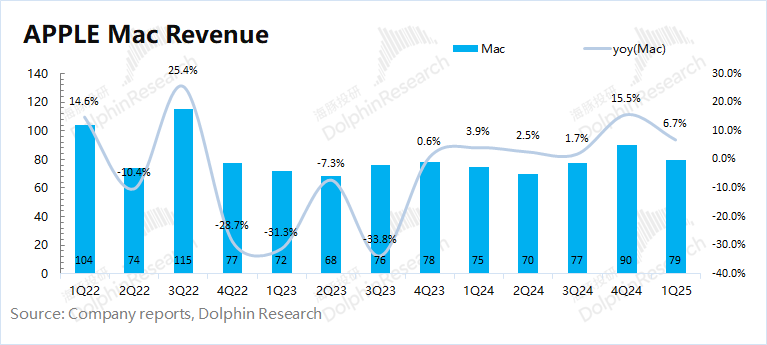
3.2 iPad Business
In the second quarter of fiscal year 2025 (1Q25), iPad business revenue reached $6.4 billion, a year-on-year increase of 15.2%, surpassing market consensus expectations ($6.2 billion), primarily driven by the new iPad Air equipped with the M3 chip.
From an industry perspective, the tablet market has shown signs of recovery, achieving year-on-year growth in the past three quarters. Since the public health incident, there has been a demand for replacement in the tablet market. Additionally, due to China's subsidy policies, some iPad products fall within the relatively favorable subsidy range, which is also expected to boost related sales.
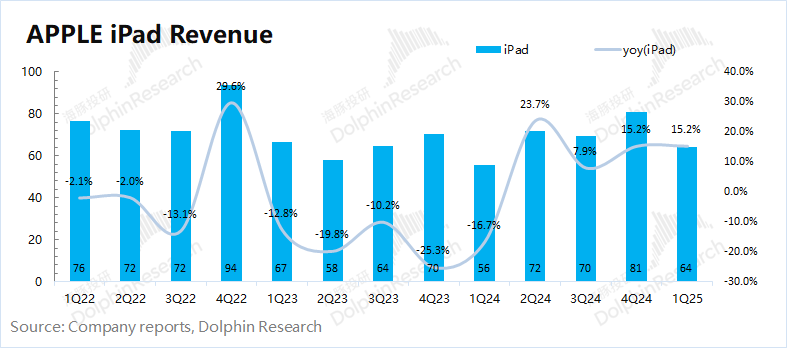
3.3 Wearables and Other Hardware
In the second quarter of fiscal year 2025 (1Q25), revenue from wearables and other hardware was $7.5 billion, a year-on-year decrease of 4.9%, falling short of market consensus expectations ($8.1 billion). Wearables and other businesses have experienced declines for seven consecutive quarters, indicating that downstream demand remains sluggish.
With the implementation of subsidies in China, wearable products such as watches will benefit from policy incentives. However, it cannot be ignored that the US tariff policy currently exempts iPhones, Macs, and iPads, while products like AirPods and Apple Watches remain unexempted, which will also put pressure on the wearables and other hardware business.
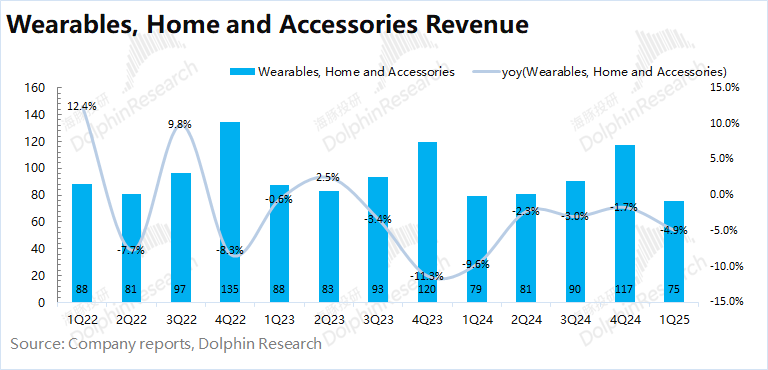
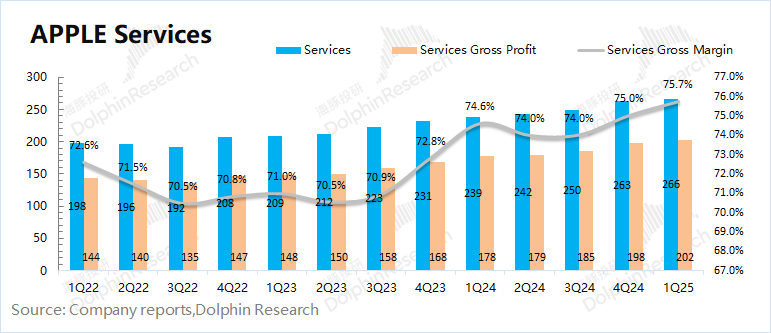
IV. Software Services: Reaching New Heights
In the second quarter of fiscal year 2025 (1Q25), software services revenue was $26.6 billion, a year-on-year increase of 11.6%, slightly lower than market consensus expectations ($26.7 billion). Although the business still maintained double-digit growth, the growth rate showed a downward trend. The growth in software services was primarily driven by user accumulation and an increase in revenue per user.
According to Sensor Tower data, Apple's App Store revenue for this quarter increased by 13% year-on-year, with downloads increasing by 3.8% year-on-year.
Among software services, the gross margin level is of great concern. In this quarter, the gross margin of software services continued to rise to 75.7%, remaining above 74% for five consecutive quarters and reaching a new high. With its high gross margin, the company's software business generated 45% of the company's gross profit with nearly 28% of revenue in this quarter.
- END -