Three failed listings, can Shanhui Technology realize its IPO dream this time?
![]() 10/08 2024
10/08 2024
![]() 449
449

Seven months later, Shanhui Technology is once again eyeing an IPO on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange.
Although it ranks third in China's used mobile phone recycling market, Shanhui Technology holds a relatively low market share of only 1.4%. Wanwu Xinsheng (Aihuishou) and Zhuanzhuan rank first and second, respectively, with market shares of 9.1% and 8.4%.
Apart from the internal disparities within the industry, 7 Finance notes that Shanhui Technology has been in a state of loss since 2021, with slowing revenue growth and declining gross margins. Furthermore, after three failed listing attempts based on valuation agreements, Shanhui Technology is now under pressure to fulfill another valuation agreement, making the urgency of an IPO undeniable.
01
Losses exceeding RMB 280 million over three and a half years, gross margins declining year after year
On February 26th of this year, Shanhui Technology submitted its initial listing application to the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, with Qingke Capital as the sole sponsor. However, the listing application expired on August 26th after failing to pass the listing hearing within six months.
On September 17th, Shanhui Technology resubmitted its listing application to the Hong Kong Stock Exchange and disclosed its latest financial results for the first half of 2024.
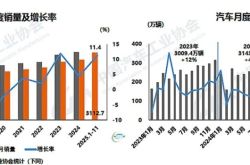
According to the prospectus, from 2021 to 2023, Shanhui Technology generated revenues of RMB 750 million, RMB 919 million, and RMB 1.158 billion, respectively. The corresponding net losses were RMB 48.71 million, RMB 99.08 million, and RMB 98.27 million, with a compound annual growth rate of approximately 26%.
In the first half of 2024, Shanhui Technology recorded revenues of RMB 577 million, a year-on-year increase of 11%, with a corresponding net loss of RMB 40.126 million. In other words, while the company's revenue is growing, its year-on-year growth rate is declining, and the company's net losses over three and a half years exceed RMB 280 million.
From 2021 to the first half of 2024 (also known as the reporting period), Shanhui Technology's gross margin has also decreased, from 8.2% in 2021 to 4.5% in the first half of this year.
Regarding the decline in gross margin, Shanhui Technology admitted in its prospectus that it was due to increased procurement costs for used mobile phones and increased commission costs paid to front-desk sales staff at upstream procurement partner stores.
When it comes to cost increases, it is inevitable to look at Shanhui Technology's business. As a provider of used mobile phone recycling services, Shanhui Technology owns two brands: "Shanhui Recycle" and "Shanhui Youpin." The former is the company's offline recycling business brand, while the latter is a platform for selling used electronic products.
During the reporting period, Shanhui Technology's revenues from selling used mobile phones and used consumer electronics accounted for 98.3%, 98.1%, 98.4%, and 98.6% of total revenues, respectively, with other service revenues accounting for less than 2%.
Over the same period, Shanhui Technology's cost of sales has been increasing year by year, amounting to RMB 688 million, RMB 863 million, RMB 1.08 billion, and RMB 551 million, respectively. Among them, the year-on-year increase in the first half of 2024 was 15.27%.
Furthermore, the prospectus mentions that approximately 85.3%, 86.1%, 88.4%, and 87.6% of the above-mentioned cost of sales represents the company's procurement costs for used consumer electronics. In other words, under the pressure of heavy assets, Shanhui Technology's gross margins are gradually declining.
02
Fierce market competition, market share of only 1.4%
In terms of the domestic market, China's mobile phone recycling market has considerable room for growth. In terms of trade volume for mobile phone trade-ins, the Chinese market has rapidly increased from RMB 4 billion in 2019 to RMB 14.2 billion in 2023, with a compound annual growth rate of approximately 37.3%, and is expected to further increase to approximately RMB 56.5 billion by 2028.
Despite this, according to Frost & Sullivan data, among used mobile phone service providers in 2023, Shanhui Technology ranked third with only a 1.4% market share, while Wanwu Xinsheng (Aihuishou) and Zhuanzhuan ranked first and second with market shares of 9.1% and 8.4%, respectively.
Therefore, in addition to the continuous compression of profits due to increasing costs, Shanhui Technology's prospectus also repeatedly mentions the "intensifying competition in the mobile phone recycling service market."
Shanhui Technology stated that the company primarily faces competition from other top service providers engaged in recycling services domestically, who may have significantly more resources (including financial, technological, and marketing resources) than the company.
These resources enable competitors to develop new service lines, adapt more quickly to technological changes, and carry out broader marketing campaigns, which may reduce the attractiveness of Shanhui Technology's platform to upstream business partners and customers and lead to the company losing market share.
Data shows that while Shanhui Technology has yet to turn a profit, Wanwu Xinsheng, which listed in 2021, has achieved profitability for eight consecutive quarters. In the second quarter of this year, Wanwu Xinsheng's total revenue increased by 27.4% year-on-year to RMB 3.78 billion, with an adjusted net profit of RMB 80.49 million.
In contrast, Shanhui Technology, which is eyeing an IPO on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, still has a long way to go to catch up with the industry leader, Wanwu Xinsheng.
To break through the "siege" and increase revenue growth points, Shanhui Technology plans to expand its business scale to Hong Kong and Southeast Asian countries.
According to the prospectus, its strategic goal is to strengthen strategic cooperation with its upstream procurement partners to continuously consolidate its market position in China's offline mobile phone trade-in recycling services and expand the company's transaction services to Hong Kong and other Southeast Asian countries.
In November last year, Shanhui Technology began providing offline mobile phone trade-in recycling services for a consumer electronics brand in Hong Kong.
Interestingly, Frost & Sullivan's report also notes a unique "first" for Shanhui Technology. According to Frost & Sullivan, in terms of total transaction value for mobile phone trade-ins from consumers in 2023, Shanhui Technology was China's largest provider of offline mobile phone trade-in recycling services.
03
Three failed valuation agreements, the company is insolvent
This IPO attempt comes with significant pressure on Shanhui Technology due to valuation agreements.
Founded in 2016, Shanhui Technology is led by founder and legal representative Liu Jianyi. In terms of shareholder relations, founder Liu Jianyi and CEO Yu Hairong jointly hold 45.35% of the company's issued shares.
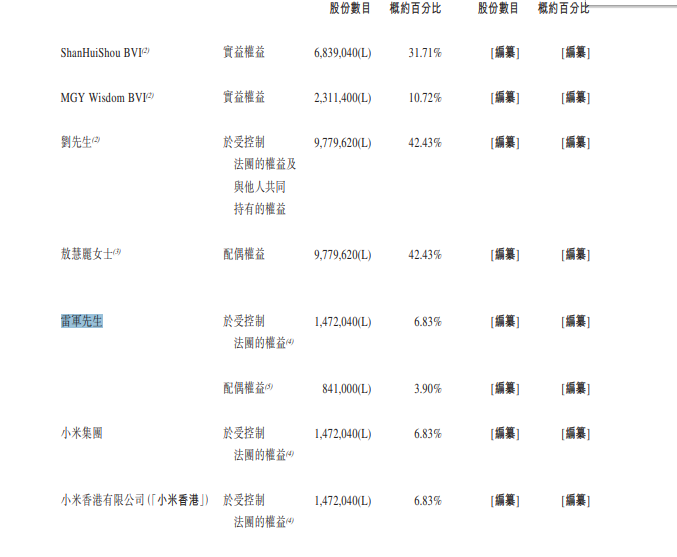
Additionally, according to the prospectus, Shanhui Technology has close ties with Xiaomi Inc., with Shunwei Capital and Xiaomi-affiliated companies collectively holding 10.73% of Shanhui Technology's shares, making them the second-largest shareholder.
In fact, since its inception, Shanhui Technology has undergone five rounds of financing. In 2018, it received nearly RMB 100 million in Series A funding from Xiaomi Group and Shunwei Capital; in 2019, it received Series B funding from Qingtong Capital; in 2020, it received Series B+ funding from Ganzhou Ganyue Fund Management Co., Ltd.; in 2021, it received Series C funding from Shenzhen Guarantee Group, Tongchuang Weiye, and Shenzhen Zhicheng Investment; and in December 2023, it completed an USD 80 million Series D1 funding round.
Despite these multiple rounds of financing, Shanhui Technology remains insolvent.
From 2021 to the end of 2023, Shanhui Technology's net liabilities increased annually, reaching RMB 235 million, RMB 333 million, and RMB 622 million, respectively. As of July 31st, 2024, Shanhui Technology's net liabilities had reached RMB 673 million.
Simultaneously, Shanhui Technology's current liabilities have also been increasing, amounting to RMB 237 million, RMB 336 million, and RMB 631 million, respectively; as of the end of July this year, this figure had increased to RMB 662 million.
In response, Shanhui Technology stated that the increase in current liabilities was primarily due to changes in the book value of redemption obligations arising from the preferential rights granted to investors, which increased redemption liabilities from approximately RMB 307 million as of December 31st, 2021, to RMB 751.4 million as of June 30th, 2024.
These redemption liabilities are related to four valuation agreements signed between Shanhui Technology and investors. In February 2018, Shanhui Technology signed a share transfer agreement with three Series A investors, requiring Shanhui Technology to complete an IPO within 48 months; otherwise, investors could redeem their shares.
In February 2019 and March 2021, Shanhui Technology signed two equity investment agreements with investors, both of which included provisions requiring Shanhui Technology to successfully list within a specified timeframe, but both ended in failed valuation agreements.
The most recent agreement was signed in February of this year, when Shanhui Technology received USD 8 million in Series D funding from Anji Guorong Holdings Co., Ltd. The investment agreement also required Shanhui Technology to complete an IPO by December 31st of this year; otherwise, Shanhui Technology would face a share repurchase obligation.
In summary, Shanhui Technology faces immense pressure in this IPO attempt—on the one hand, from external competitive pressures and rising costs from upstream partners; on the other hand, from its own lack of profitability and the burden of valuation agreements.
Let's wait and see if Shanhui Technology can succeed in its fourth valuation agreement.