Xiaomi's "Strongest Annual Report in History", This is How We See It
![]() 03/20 2025
03/20 2025
![]() 654
654
This article is written based on publicly available information and is intended for information exchange only, not constituting any investment advice.

Xiaomi's 2024 financial report was released after the market closed yesterday, and Lei Jun immediately posted on Weibo, calling it the "strongest annual report in history". This is undisputed, with Xiaomi's ADR rising by more than 4 points in the overnight market, greatly Inspire the market .
This is a pivotal moment for Xiaomi and a shining moment for China's core assets, worthy of recording.
Overall View:
In 2024, Xiaomi's revenue reached RMB365.906 billion, a year-on-year increase of 35.04%; gross profit was RMB76.56 billion, a year-on-year increase of 33.2%; and adjusted net profit increased by 41.31% year-on-year to RMB27.235 billion.
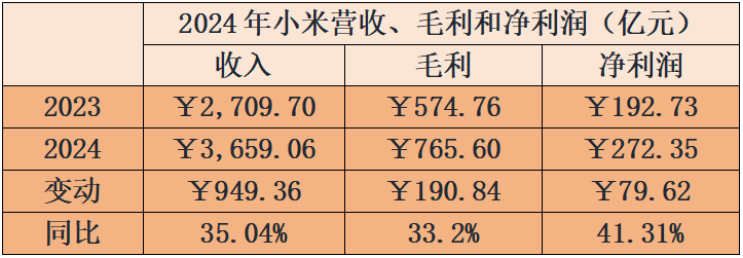
In Q4 2024, revenue exceeded RMB100 billion for the first time, reaching RMB109.005 billion, a year-on-year increase of 48.8%; gross profit increased by 43.8% year-on-year to RMB22.455 billion; and adjusted net profit increased by 69.4% year-on-year to RMB8.316 billion.
This financial report is indeed strong when compared year-on-year. However, from the perspective of long-term investors, we are well aware that this is Xiaomi's performance after two years of downturn. Over a longer time frame, compared to 2021, when revenue first exceeded RMB300 billion, revenue and net profit have increased by 11.45% and 23.58% respectively over the past three years, with a CAGR of only 3.68% and 7.31%.
After two years of low stock prices and adjustments, Xiaomi's performance suddenly hit a new high, and its beautiful main upward trend has indeed Inspire investors . At the same time, how should we view this rebirth journey and what outlook should we have for Xiaomi's future?
01 Auto Business Aims for RMB100 Billion Scale, 2025 as the Year of Break-even
Let's start with the hot-selling "Su7".
On April 3, 2024, Xiaomi Su7 officially began deliveries. Overall, the Su7 series delivered a total of 136,854 vehicles in 2024.
The "Intelligent Electric Vehicles and Other Innovative Businesses" segment, to which it belongs, generated a total revenue of RMB32.8 billion, mainly from vehicle sales amounting to RMB32.1 billion. The gross margin for the full year was 18.5%, and in Q4, due to increased deliveries, economies of scale, and price declines of some core components, the gross margin increased to 20.4%.
From a single-quarter perspective, as deliveries increased, the loss per vehicle was significantly reduced:
In Q2, 27,307 vehicles were delivered with a net loss of RMB1.8 billion, averaging a loss of approximately RMB66,000 per vehicle;
In Q3, 39,790 vehicles were delivered with a net loss of RMB1.5 billion, averaging a loss of approximately RMB37,700 per vehicle;
In Q4, 69,697 vehicles were delivered with a net loss of RMB700 million, averaging a loss of approximately RMB10,000 per vehicle.
According to the financial report's target of delivering 350,000 Su7 vehicles in 2025, the "Intelligent Electric Vehicles and Other Innovative Businesses" segment is expected to achieve pre-tax break-even in 2025.
Firstly, the Su7 is currently very popular, but due to capacity constraints, domestic orders have a waiting time of about six months.
According to guidance, capacity expansion to meet the delivery target of 350,000 vehicles is basically unobstructed. In other words, from the perspective of supply and demand, the guaranteed volume of the Su7 series in 2025 is around 350,000 vehicles.
PS: The 200,000th vehicle was delivered on the financial report date, and as of March 18, 63,206 vehicles have been delivered in 2025, still far from the target of 350,000 vehicles. Capacity needs to be increased.
Secondly, the gross margin of the auto business in Q4 2024 reached 20.4%, which is close to the limit.
Compared to NIO and Tesla, both are extremely adept at cost control, with the former's gross margin hovering around 20% for a long time and the latter fluctuating around this level; therefore, the economies of scale brought about by subsequent capacity expansion should narrow the margin, and it is unrealistic to significantly increase the gross margin, especially considering the need to offset the current overtime work.
Furthermore, the operating expenses of the auto business in 2024 - sales, management, and R&D expenses - amounted to RMB13.2 billion, including expenditures for the Ultra series, YU7 series, and other supporting items, corresponding to a three-fee rate of 40.24% for auto revenue - a simple shift is unreliable, and NIO's three-fee rate of around 17% can be used for reference.
Finally, we can provide an outlook for the auto business in 2025:
Based on the Q4 price of RMB234,500 per vehicle, delivering 350,000 vehicles throughout the year will generate revenue of RMB82 billion; corresponding to a gross margin of 20% and an estimated period cost rate of up to 20%, there should be no major issues with pre-tax break-even for the Su7 series; moreover, if the Ultra series and the upcoming Yu7 series are delivered in a timely manner, it will be easy for the "Intelligent Electric Vehicles and Other Innovative Businesses" segment to achieve the revenue target of RMB100 billion in 2025.
Above, the auto business, as Xiaomi's new growth curve, has been established in the short term.
02 Traditional Business Blooming in Multiple Areas, with Different Internal Logic in Three Major Segments
In addition to the new auto business, Xiaomi's traditional business segment, "Mobile X AIoT", also saw multiple areas of growth in 2024.
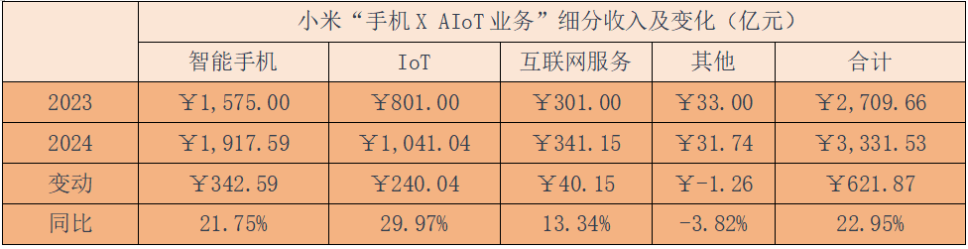
Overall, the "Mobile X AIoT Business" segment increased by 22.95% year-on-year to RMB333.153 billion, with a gross margin of 21.2%, which was flat compared to the base period.
Breaking it down:
1. The mobile phone business performed stably but still fell short of high-end expectations.
Annual shipments increased by 15.75% year-on-year to 169 million units. Under the high-end strategy, the average selling price increased by 5.2% year-on-year to RMB1,138.2, setting a new high.
Driven by the increase in both price and volume, mobile phone business revenue increased by 21.75% year-on-year to RMB191.759 billion in 2024, but gross profit only increased by 5.36% year-on-year. This was mainly due to the impact of rising prices of core hardware, resulting in a decline in gross margin of 1.97 percentage points to 12.65%.
In recent years, Xiaomi has been seeking high-end transformation, but it has not been smooth. Compared to 2021, shipments decreased by 11.05%, while the average selling price increased by 3.76%. However, focusing on high-end hardware - chips, camera modules, etc. - led to a significant surge in costs, and the gross margin only increased slightly by 0.75 percentage points compared to 2021.
2. IoT and consumer life products performed impressively, and the globalization journey of the "household appliance package" has only just begun.
Overall, this business segment experienced a simultaneous increase in price and quality: revenue increased by 29.97% year-on-year to RMB104.104 billion, and the gross margin increased by 3.94 percentage points year-on-year to 20.26%, setting a new high.
On the one hand, it benefited from its home appliance delivery, installation, and disassembly services. Since the launch of the one-stop air conditioner delivery, installation, and disassembly service in June 2024, it has been extended to a total of six categories throughout the year, including TVs, refrigerators, washing machines, water heaters, and smart door locks; on the other hand, it rode the wave of government subsidies, with air conditioner shipments in major appliances increasing by more than 50% year-on-year to 6.8 million units, refrigerators and washing machines increasing by more than 30% and 45% year-on-year to 2.7 million units and 1.9 million units, respectively; in terms of consumer electronics, tablet shipments increased by 73.1%, while wearable devices and wireless earphones performed averagely (growth rates were not mentioned).
Considering that Xiaomi's consumer life products segment is just beginning its globalization journey, we can still be optimistic about the trend of this business in the coming years.
Seeing such data trends, it is easy to understand the anxiety expressed by Gree's Chair Dong Mingzhu in public recently.
3. Benefiting from the scale of hardware users, internet services continue to be a cash cow.
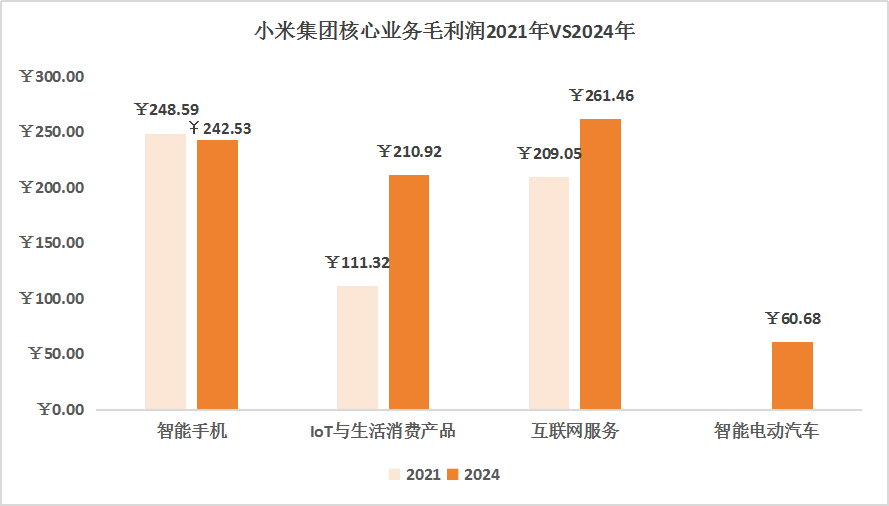
Overall, the internet services business increased by 13.33% year-on-year to RMB34.1 billion, with a gross margin increasing by 2.5 percentage points year-on-year to 76.6%, setting a new high. This business accounts for only 9.32% of Xiaomi's total revenue but contributes 34% of its gross profit.
In comparison, the mobile phone business generated revenue of RMB191.759 billion but only brought in a gross profit of RMB24.258 billion, less than the RMB26.1 billion of the internet services business. It truly is the case that the wool comes from the sheep.
This is also a major highlight of Xiaomi's ecosystem. As long as the overall sales of Xiaomi's mobile phones, TVs, tablets, wearable devices, and even cars are increasing, the number of users based on Xiaomi OS will also grow. In 2024, its global active user base increased by 9.5% year-on-year to 702 million; and its revenue sources are still primarily from advertising, mostly in the form of pre-installed apps, which is a rigid demand for most software developers.
However, when combining the mobile phone business and internet services, the gross margin of 22.31% is not much higher than the gross margin of IoT and auto businesses, which is just over 20%; combined with the mobile phone business's "trade-off between price and volume" in the high-end path, it is not easy to obtain excess profits solely through mobile phones/hardware, and the synergy of the entire ecosystem is Xiaomi's core moat.
03 Strong Expectation Support at 50x PE, Xiaomi's Future Logic is Still "Dare to Be the Last"
After three years and two years of decline, Xiaomi's revenue once again exceeded the RMB300 billion mark and hit a new high.
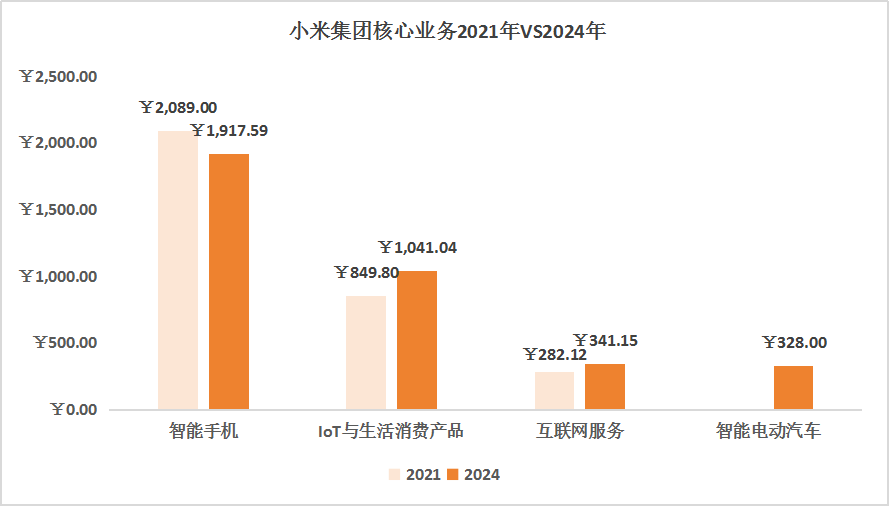
From the overall revenue situation, excluding auto revenue, 2024 revenue was RMB333.106 billion, an increase of only 1.46% compared to 2021; excluding auto gross profit, it increased by 20.99% compared to 2021. Among them, the mobile phone business's "trade-off between price and volume" in the high-end path actually dragged down the overall performance, while IoT-related products and internet services supported by the hardware base truly brought Xiaomi back to life.
This is also determined by Xiaomi's "internet gene".
The core of the internet is traffic, and the carrier of Xiaomi's traffic is not just devices but the OS that supports the unification of devices to the system platform. Moreover, through the interconnection between hardware products built within the same ecosystem, Xiaomi can not only distinguish itself from ordinary hardware device suppliers but also enhance user stickiness:
In 2024, the number of users with five or more devices connected to the AIoT platform (excluding mobile phones, tablets, and laptops) increased by 26.1% year-on-year to 18.3 million. When these consumers purchase new products or upgrade in the future, there is a higher probability that they will still choose products within the Xiaomi ecosystem.
Because of convenience and interconnection. Before entering the "full ecosystem interconnection of people, cars, and homes" in 2024, Xiaomi's strategy was "Mobile X AIoT", which meant that under the Xiaomi ecosystem, most operations and monitoring of all original IoT products could be completed using mobile phones; after entering the new ecosystem, Xiaomi's ecosystem extends beyond the home, encompassing the two rigid demand areas of housing and transportation.
After saying so much, I want to make one point clear: Xiaomi's birth was based on the internet, and its rebirth journey is also reliant on technological progress; without the rapid development of the Internet of Things, Xiaomi's traffic ecosystem would hardly be established, let alone reused.
And the future outlook is still centered on breakthroughs in AI technology:
"The financial report mentions that Xiaomi will fully embrace the rapid development trend of the AI industry and embed the latest AI technology into its product business; during the conference call, Lu Weibing also stated: "AI is one of the core areas of Xiaomi's R&D investment. Of the expected R&D expenditure of RMB30 billion in 2025, one-quarter will be invested in the AI field to fully promote the implementation of AI technology in various terminal products. In the future, AI will be used to reconstruct the underlying layer of the Pengpai OS...".
For example, the latest "Super Xiao'ai" essentially uses AI to empower interconnection, making it more convenient and powerful in application scenarios. Almost all hardware based on Xiaomi's OS ecosystem can be controlled through interaction with Xiao'ai.
Based on the current valuation of 50x PE of the latest profit, Xiaomi's short-term support is still sufficient. In the long run, Xiaomi's logic of "daring to be the last" and its hardware ecosystem-based approach will enable it to unleash greater synergies.
Regarding "future products" such as AI glasses and humanoid robots, although Xiaomi has not disclosed specific strategies to the public at present, from its development history, as long as it is a To C market with scale and products that have reached a certain stage of maturity, Xiaomi will find a way to intervene and conduct deep binding and collaborative operations within its ecosystem. In fact, its strategies for mobile phones and auto manufacturing can well illustrate Xiaomi's approach - it learns from Apple for mobile phones and Tesla and Porsche for auto manufacturing...
Xiaomi's strategy echoes the words of the founder of 3G Capital: "If you can emulate the world's most advanced companies, why waste time finding your own way?"







