Analyzing the New Energy Vehicle Industry through Financial Lens
![]() 05/20 2025
05/20 2025
![]() 714
714
Reflecting on 2024, the domestic new energy vehicle market was a whirlwind of activity, punctuated by numerous pivotal moments. Amidst price wars, technological advancements, and a relentless pursuit of scale, the Chinese automotive industry was dominated by a single word: "competition".
This year witnessed the self-reinvention of established automakers, the ascendancy of emerging brands, and the inevitable demise of those unable to adapt. The clash between new and old forces in the new energy vehicle market throughout 2024 was akin to a dramatic tale of fire and ice.
01. Intensifying Industry Differentiation: Dual Divergence in Sales and Profits
The first prominent aspect of this tale is differentiation. In the new energy vehicle industry, this differentiation is most evident in sales. The trend of leading companies fortifying their positions has become increasingly clear.
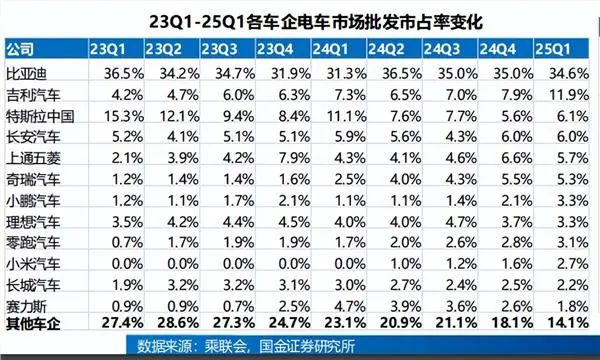
Within the realm of new energy vehicles, the dominance of leading companies continues to expand. As the industry bellwether, BYD recorded revenues of 777.102 billion yuan in 2024, marking a 29.02% year-on-year increase. Its net profit stood at 40.254 billion yuan, a 34% year-on-year jump. This marked the first time in BYD's history that annual revenue surpassed 700 billion yuan.
In the first quarter of 2025, BYD achieved revenues of 170.36 billion yuan, a 36.35% increase compared to the same period last year. Net profit amounted to 9.155 billion yuan, surging 100.38% year-on-year. This robust performance is attributed to BYD's vertical integration strategy—from batteries to vehicle manufacturing, the company exercises autonomous control over the entire supply chain, thereby gaining significant advantages in cost control and technological innovation.
Similarly, Geely Automobile and Great Wall Motor also shone brightly in 2024, with revenues reaching 240.19 billion yuan and 202.195 billion yuan, respectively, representing year-on-year increases of 34% and 16.7%. Notably, Geely Automobile's net profit in 2024 hit a record high of 16.632 billion yuan, a 213% year-on-year surge. Great Wall Motor's net profit amounted to 12.692 billion yuan, a 80.8% year-on-year increase.
However, as the saying goes, joy rides alongside sorrow. Automakers with a higher proportion of joint venture brands, such as GAC Group and Changan Automobile, underperformed both for the full year of 2024 and the first quarter of 2025. Taking GAC Group as an example, in the first quarter of this year, its revenue was 19.879 billion yuan, a year-on-year decrease of 7.82%. Net profit turned negative, recording a loss of 731 million yuan.
The profitability of new energy vehicle startups also exhibited differentiation. Li Auto's revenue surpassed 100 billion yuan in 2024, reaching 144.46 billion yuan, a 16.6% year-on-year increase. The company maintained profitability with a net profit of 8.05 billion yuan. In contrast, XPeng Motors and NIO recorded revenues of 40.87 billion yuan and 32.16 billion yuan, respectively, in 2024, but incurred net losses of 5.79 billion yuan and 2.82 billion yuan.
02. Industry-wide Profit Decline: Shifting from Price to Value Competition
Amidst this differentiated landscape, many automakers have already been eliminated. According to incomplete statistics, between 2020 and 2024, multiple automakers, including Dongfeng Yulong, Lifan Automobile, Zotye Auto, Borgward, Hengchi, WM Motor, ENOVATE, AITO, HiPhi, and JYEV, exited the market due to factors such as bankruptcy liquidation, share transfer, bankruptcy reorganization, and company dissolution. These encompassed both traditional automakers and recent new energy vehicle startups.
Moreover, from an industry-wide perspective, sales growth was accompanied by price declines. According to the China Automobile Dealers Association, the "price war" in the national passenger vehicle market intensified in 2024. From January to December 2024, the average price reduction for new energy vehicle models reached 18,000 yuan, with a price reduction rate of 9.2%. For conventional fuel vehicle models, the average price reduction was 13,000 yuan, representing a 6.8% decrease.
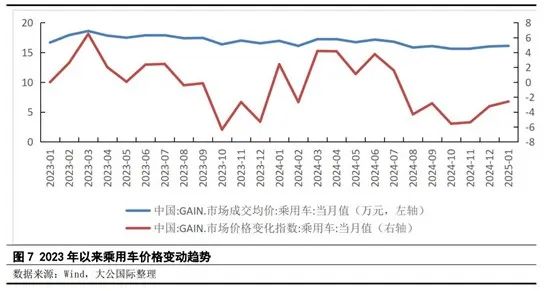
Against this backdrop, the industry's overall profit margin declined significantly. The report by the China Automobile Dealers Association revealed that the automotive industry's profit margin in 2024 was only 4.3%, lower than the profit margin of the entire downstream industry and the level recorded in 2023. In August 2024, the overall discount rate in the new car market reached 17.4%, further underscoring the intensity of market competition. From January to November 2024, the "price war" resulted in a cumulative loss of 177.6 billion yuan in the overall new car retail market, significantly impacting the industry's healthy development.
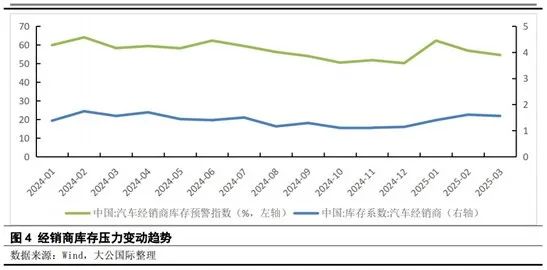
Therefore, the new energy industry will inevitably shift from price competition to value competition. A prime example of this shift is the increasing standardization of intelligent driving features in new energy vehicles.
03. Intelligence and Globalization: The New Frontier of Industry Competition
The second significant aspect of this tale is the emergence of a new frontier. These four words are epitomized in new energy automakers through intelligence and globalization.
First, intelligence has evolved from a differentiating factor to a survival threshold. Following electrification, intelligence has become the new battleground for the global automotive industry. Systems such as Tesla's FSD, Huawei's ADS, and XPeng's XNGP continuously push the boundaries of intelligent driving capabilities. Simultaneously, traditional automakers like BYD, Changan, and Geely are accelerating their self-research or collaboration efforts. In 2025, BYD announced that all its models would come standard with high-speed NOA functionality and achieve tiered coverage of intelligent driving through the "Tian Shen Zhi Yan" system, spanning entry-level models priced at 70,000 yuan to luxury vehicles priced in the millions.
Behind this trend lie three primary drivers. Firstly, market demand is driving change. Data indicates that in 2024, sales of domestic models equipped with high-level intelligent driving functions surged 147.9% year-on-year. Consumer acceptance of functions like automatic parking and highway navigation has significantly improved. The competition logic among automakers has shifted from addressing "range anxiety" to mitigating "intelligent driving anxiety," meaning that products lacking basic intelligent driving features may be directly excluded from consumers' purchasing considerations.
Secondly, there are considerations for business model upgrades. McKinsey notes that leading automakers need to break through profit bottlenecks through models such as "carbon credit trading" and "telematics services." Tesla's FSD (Full Self-Driving) subscription revenue share continues to rise, while Xiaomi enhances user loyalty through its "human-vehicle-home ecosystem." These explorations suggest a shift from hardware sales to "software-defined profits."
Thirdly, intelligent driving has transitioned from a differentiating factor to a brand moat. On one hand, intelligent driving capabilities have become a tangible emblem of a brand's technological prowess, driving automakers towards transformation into technology service providers. On the other hand, the competitive landscape is being reshaped, and the choice of intelligent driving technology paths will determine the definition of industry standards.
Next, let's turn to globalization. This trend was particularly pronounced in 2024: China's passenger vehicle exports approached 5 million units, a 20% year-on-year increase. Among these, new energy vehicle exports exceeded 1 million units, accounting for 21% of the total.
In the first quarter of this year, data from the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers showed that new energy vehicle exports reached 441,000 units, a 43.9% year-on-year increase. Specifically, new energy passenger vehicle exports amounted to 419,000 units, a 39.6% year-on-year rise; new energy commercial vehicle exports were 23,000 units, marking a 2.3-fold year-on-year increase. Pure electric vehicle exports totaled 290,000 units, a 16.7% year-on-year increase, while plug-in hybrid vehicle exports reached 152,000 units, representing a 1.6-fold year-on-year jump.
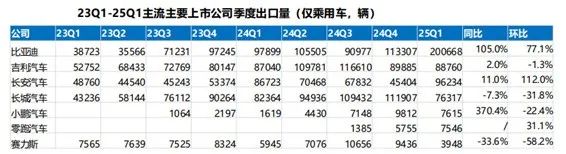
(Image source: GF Securities)
04. Conclusion: Identifying Long-term Players Amidst Differentiation
The new energy vehicle industry in 2024-2025 was a blend of the "best of times" and the "cruelest of times." As the penetration rate of new energy vehicles surpassed 50%, the market transitioned from a phase of rapid expansion (competing for new users) to a phase of maturity (competing for existing users). At this juncture, companies place greater emphasis on brand loyalty, product differentiation, and service experience rather than solely attracting consumers through low prices.
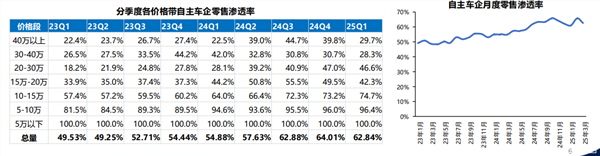
(Image source: GF Securities)
Against this backdrop, technology, ecosystem, and global capabilities have emerged as new competitive moats. Therefore, in this fierce competition, only enterprises possessing both scale resilience, technological depth, and ecological breadth will navigate through cycles and emerge as the ultimate winners.
- End -




