Baidu Regains Strategic Initiative as AI Business Growth Surpasses 50%
![]() 11/19 2025
11/19 2025
![]() 573
573
Produced by | Yiguan Finance
Author | Xuan Ye Bai Xue
As the year-end approaches, we take stock of the AI industry’s development over the past two years. Overall, from 2024 to 2025, the AI sector is undergoing a pivotal transition from explosive growth to commercial realization: shifting from “demonstrating technical capabilities” to “large-scale deployment.” In other words, model size and flashy technical prowess are no longer the core competitive edge. The ability to identify sustainable, scalable commercial scenarios will determine who holds the initiative in the next round of industrial competition.
This year, AI commercialization has accelerated. Segments like AI cloud services, AI search, AI-native ad generation, and autonomous driving have led the way in achieving rapid revenue and user growth, with tech giants such as Microsoft, Google, and Baidu beginning to derive measurable growth from their AI businesses.
This explains why Baidu, in its Q3 2025 financial report, disclosed detailed AI revenue data for the first time—the industry has reached a stage where “data speaks volumes.”
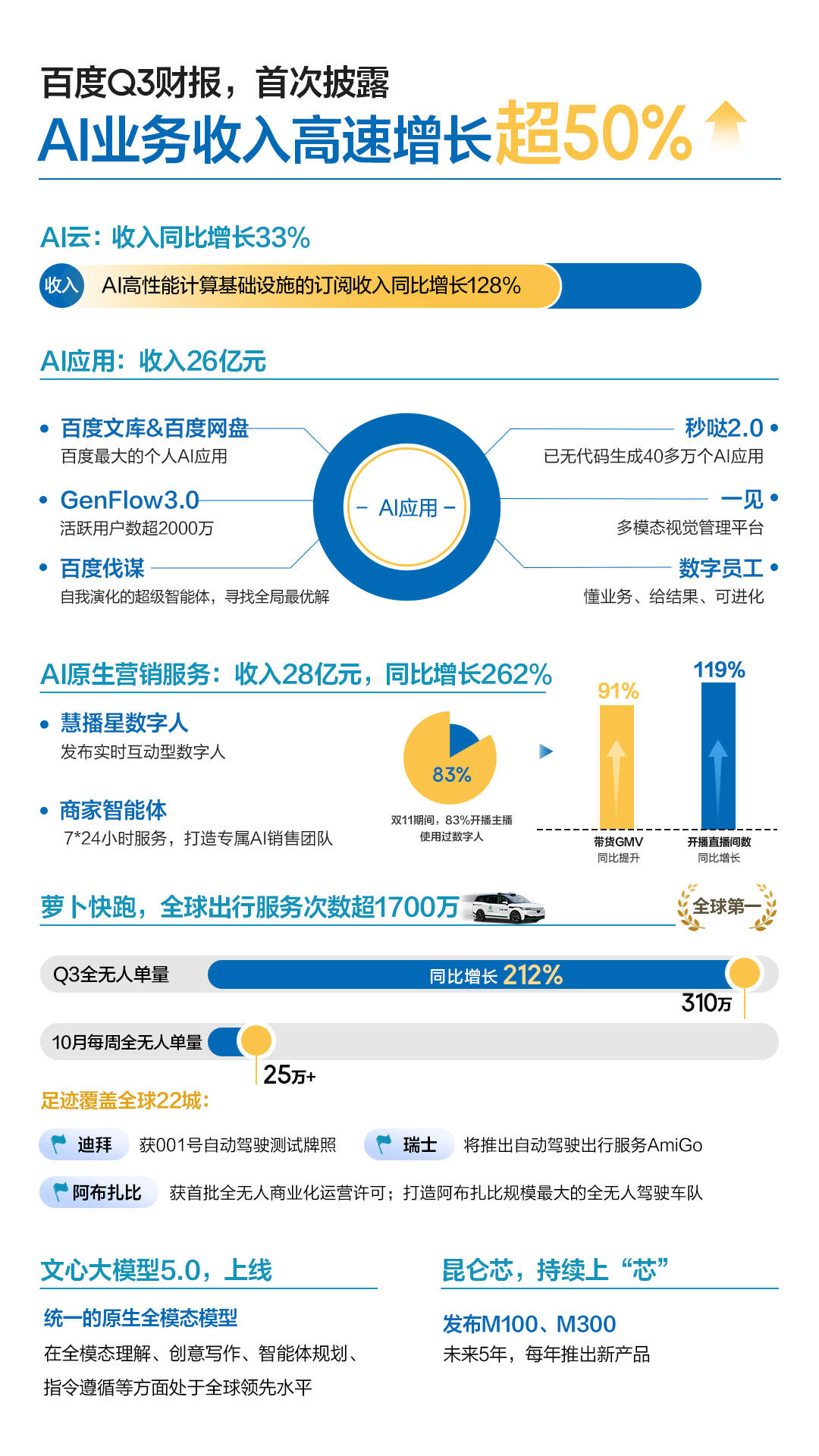
On the evening of November 18, Baidu released its Q3 2025 financial results, reporting total revenue of RMB 31.2 billion, with core business revenue at RMB 24.7 billion. Among these, AI cloud revenue grew 33% YoY; AI application revenue reached RMB 2.6 billion; and AI-native marketing service revenue surged 262% YoY to RMB 2.8 billion.
Capital markets reacted swiftly. Baidu’s Hong Kong shares opened nearly 4% higher today.
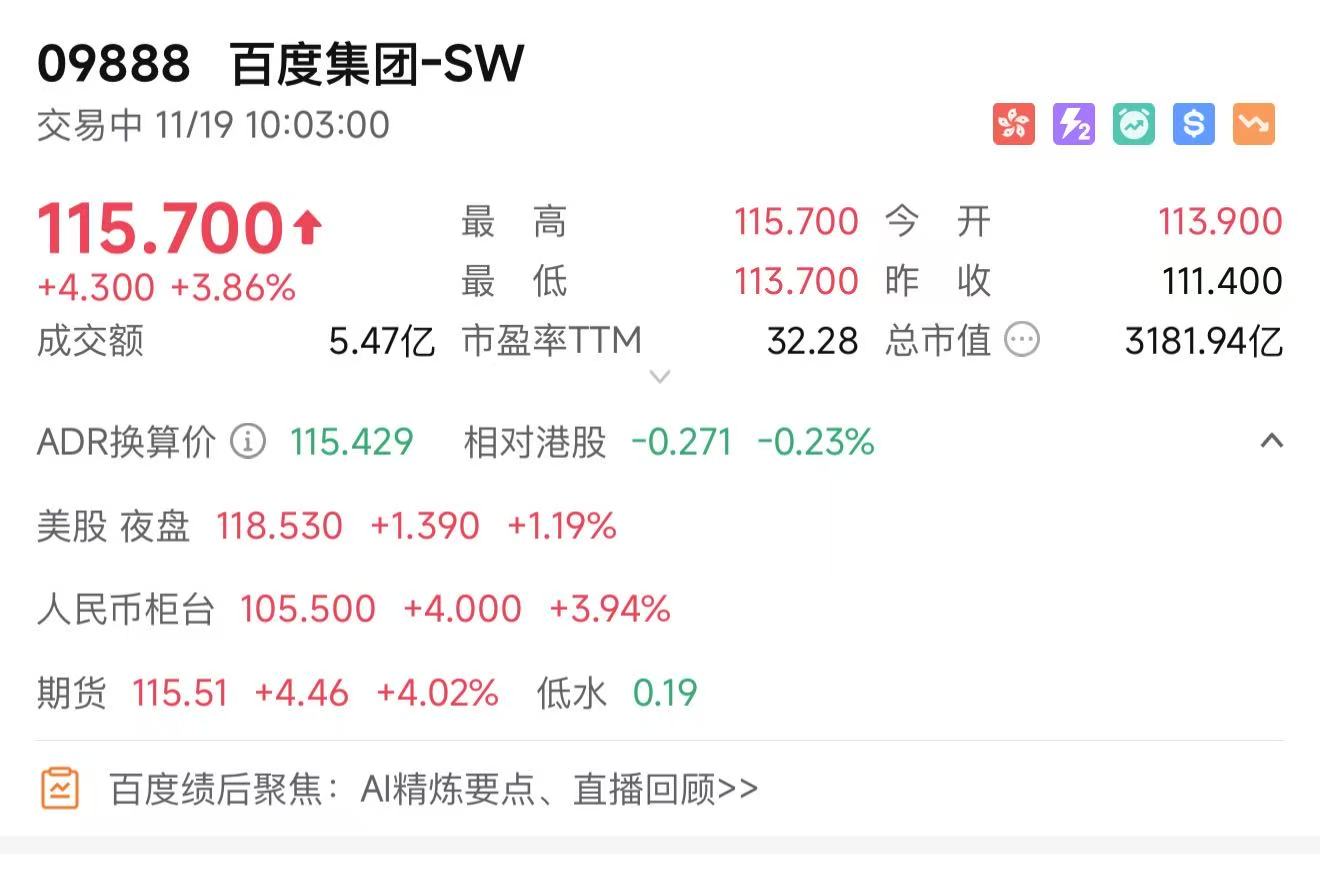
These figures not only validate the value of Baidu’s AI strategy but also signal the industry’s shift from technical experimentation to tangible economic contributions—AI is no longer just a concept or lab achievement but a driving force behind corporate revenue and market competitiveness.
This month, Baidu World brought comprehensive updates spanning chips, models, and applications, while its latest financial report disclosed detailed AI business data for the first time, delivering results to the market. We see a more aggressive Baidu, prioritizing AI and remaining at the forefront of technology. Through its AI business, Baidu is reclaiming the initiative for future growth.
01
Commercialization: AI Starts Generating Real Revenue
AI commercialization manifests in three key areas.
First, AI cloud services are emerging as a primary growth driver. Major cloud providers have achieved rapid growth through AI accelerators and expanded inference clusters, with customers moving swiftly from pilot deployments to large-scale adoption. AI capabilities are now deeply integrated into core enterprise operations.
Second, enterprise AI adoption is accelerating. Productivity tools and office applications have entered a per-user payment cycle, with enterprises willing to pay for AI solutions that directly enhance efficiency rather than flashy demonstrations.
Third, AI is reshaping the internet revenue pool—advertising and search. AI-native ads enable automated delivery and content generation, while AI-powered search evolves from simple answers to conversational tasks and rich media interactions, redistributing the internet’s most critical revenue share. Overall, AI is driving a reshuffle across the trillion-dollar markets of cloud computing, office software, and search advertising.
Against this global backdrop, Baidu stands out. Its Q3 2025 financial report showed core revenue of RMB 24.7 billion, with AI business revenue accounting for nearly 40%, marking the realization of its long-term AI strategy. While most industry players remain focused on chatbot applications, Baidu’s AI business is transitioning from investment to growth contribution, driving a substantive shift in its revenue structure.
Specifically, Baidu AI Cloud generated RMB 4.2 billion in Q3 2025 revenue, up 33% YoY, with subscription revenue for AI high-performance computing infrastructure surging 128% YoY. Baidu Intelligent Cloud has maintained its lead in China’s public cloud market for six consecutive years, ranking first in government large model platforms and enterprise solutions. Its clients include 65% of central SOEs, 100% of systemically important banks, over 800 financial institutions, top 10 smartphone makers, top 15 automotive brands, and top 10 new energy vehicle companies. It also leads in embodied AI industry penetration.
AI application revenue reached RMB 2.6 billion in Q3. The portfolio includes flagship products like Baidu Wenku, Baidu Netdisk, and Digital Employees, addressing diverse needs across personal and enterprise scenarios. Notably, most AI applications adopt high-retention subscription models, ensuring sustainable, high-quality revenue.
Behind this lies Baidu’s diversified application ecosystem. At Baidu World 2025, Baidu Wenku and Baidu Netdisk jointly launched GenFlow 3.0, a cross-platform universal agent with over 20 million active users. The no-code development tool “Miaoda” evolved to version 2.0, having powered over 400,000 AI applications through no-code development. Baidu also unveiled Famo, a globally leading, self-evolving super agent capable of finding “global optimal solutions” in real-world industries, with applications in finance, energy, transportation, logistics, and research.
AI-native marketing revenue hit RMB 2.8 billion, with digital humans and merchant agents enhancing conversion rates and operational efficiency. The 262% YoY growth underscores Baidu’s aggressive AI transformation. A growing client base, seeking AI-driven solutions and willing to pay for technology, has achieved dual efficiency gains in productivity and marketing through agent and digital human services. Meanwhile, Baidu’s decade-long search overhaul has yielded significant results. AI search boasts 382 million monthly active users, ranking first domestically. The search system has upgraded from traditional text links to a rich media-centric AI application, with first-result rich media coverage reaching 70% and 625 vendors integrated into its AI search API.
Evidently, with AI cloud, AI applications, and AI-native marketing driving growth, Baidu’s revenue structure is undergoing profound change: its reliance on online marketing is being reshaped by AI, which now contributes significantly more, enhancing growth certainty and securing Baidu’s early-mover advantage in global AI commercialization.
02
Autonomous Driving: Global Scale-Up
As AI capabilities are deployed, legacy products like search and cloud services have found new leverage, achieving substantial efficiency and experience improvements through AI-driven transformation. Meanwhile, Apollo Go is accelerating its global expansion.
Financial reports show Apollo Go handled 3.1 million trips globally in Q3, up 212% YoY, accelerating from Q2’s 148% growth.
From a global perspective, 2025 marks a pivotal year for large-scale autonomous driving deployment.
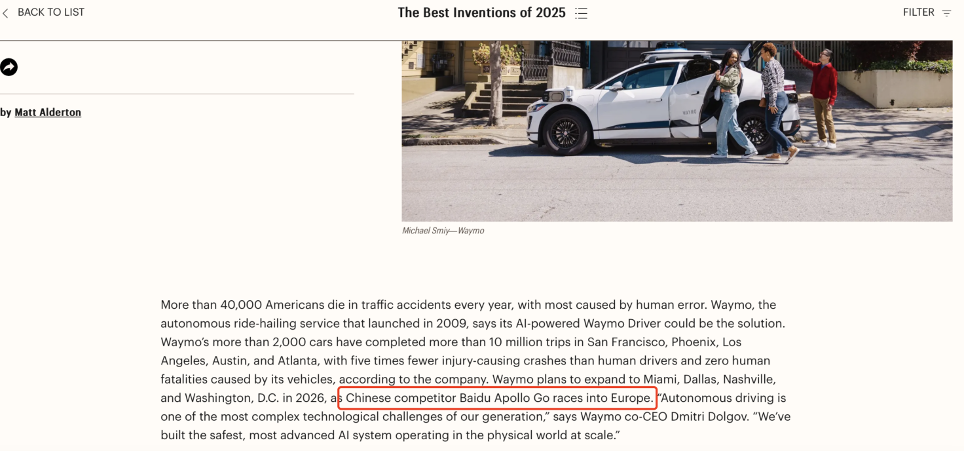
Waymo operates over 2,000 autonomous vehicles across multiple U.S. cities, completing over 10 million trips with an accident rate five times lower than human drivers and zero fatalities. Meanwhile, Baidu’s Apollo Go has rapidly expanded globally, accumulating over 17 million trips, 140 million kilometers of fully driverless mileage, and over 250,000 fully driverless orders per week, with plans for large-scale deployment in Europe, the Middle East, and Hong Kong. Tesla, focusing on driver assistance, continues to optimize its FSD system using data from millions of global vehicles, laying the groundwork for future fully autonomous commercialization.
The core of autonomous driving commercialization now lies not in technical flair but in building a safe, cost-effective, and replicable commercial closed loop (closed loop).
In terms of safety, Apollo Go’s fully driverless vehicles average one airbag deployment incident every 10.14 million kilometers, with no fatalities or major injuries. This far exceeds the human driver average and surpasses Google Waymo’s safety record. Previously, Waymo disclosed similar data, with its fully driverless vehicles averaging one airbag deployment every 4.54 million kilometers, compared to 970,000 kilometers for human drivers.
Apollo Go has also reduced vehicle costs to RMB 204,600 with its sixth-generation driverless car, just 1/7 of Waymo’s costs and lower than Tesla’s planned 2026 CyberCab.
Autonomous driving is forming a new global competitive landscape. Time Magazine views Apollo Go as Waymo’s rival, while Fortune included it in its “Companies Changing the World” list, signaling China’s proactive shaping of global strategic rhythms in autonomous driving technology. Apollo Go adopts a “technology platform + local operational giant” model, partnering with Uber and Lyft to deploy complete driverless mobility systems, reducing policy risks and operational costs for rapid, sustainable scale-up.
03
Full-Stack Capabilities: The Foundation of Commercialization and Strategic Initiative
The realization of large-scale AI deployment hinges on comprehensive full-stack capabilities.
Take Baidu as an example: its AI business’s rapid growth reflects market recognition of full-stack players. Baidu’s AI ecosystem spans self-developed chips (Kunlunxin), deep learning frameworks (PaddlePaddle), large models (Wenxin), and scenario-based applications (search, agents), forming a four-layer architecture that underpins long-term competitiveness.
Baidu’s full-stack strategy forms an inverted triangular closed loop (closed loop)—chips as the foundation, models creating value, and applications amplifying productivity.
Under this logic, Baidu deployed China’s first fully self-developed 30,000-card cluster and launched the next-gen Kunlunxin chip and Tianchi super-node products, ensuring computing power for large model training and multimodal inference. PaddlePaddle, China’s sole open-source platform competing with TensorFlow and PyTorch, supports 23.33 million developers. Wenxin 5.0, a native full-modality model with 24 trillion parameters, excels in multimodal understanding, instruction following, creative writing, factual accuracy, and agent planning. At the application layer, search, agents, and AI marketing products translate capabilities into quantifiable productivity.
Globally, only Google and Baidu possess full-stack AI capabilities.
In comparison, Google’s AI strategy also emphasizes full-stack integration but with a different focus. Unlike Baidu’s “full product reconstruction” approach, Google tends to internalize AI capabilities within existing businesses, embedding new technologies into mature ecosystems rather than rebuilding from scratch. This strategy ensures stability and relatively controlled risks in large-scale commercialization but may limit flexibility in exploring new business models.
For both Baidu and Google, full-stack capabilities are the bedrock of large-scale commercialization. An end-to-end closed loop (closed loop) of underlying computing power, model capabilities, and application deployment directly determines market competitiveness. Baidu’s case of self-developed chips and full product reconstruction exemplifies how full-stack strategies accelerate AI’s transition from technical accumulation to commercial impact.
The depth of full-stack capabilities is undoubtedly critical for long-term strategic initiative. As AI full-stack capabilities further commercialize, enterprise success will hinge on closed-loop execution from technical accumulation to application deployment.
During the earnings call, Baidu’s CFO stated that the company has invested over RMB 100 billion in AI since 2023 and will continue to ramp up AI spending.
Supported by its full-stack AI layout, Baidu has not only reshaped its revenue structure and technical moat but also laid the foundation for regaining market and capital initiative. AI is no longer a concept but quantifiable productivity, driving Baidu’s transformation from a search company to an AI platform company and establishing the core impetus for long-term growth.
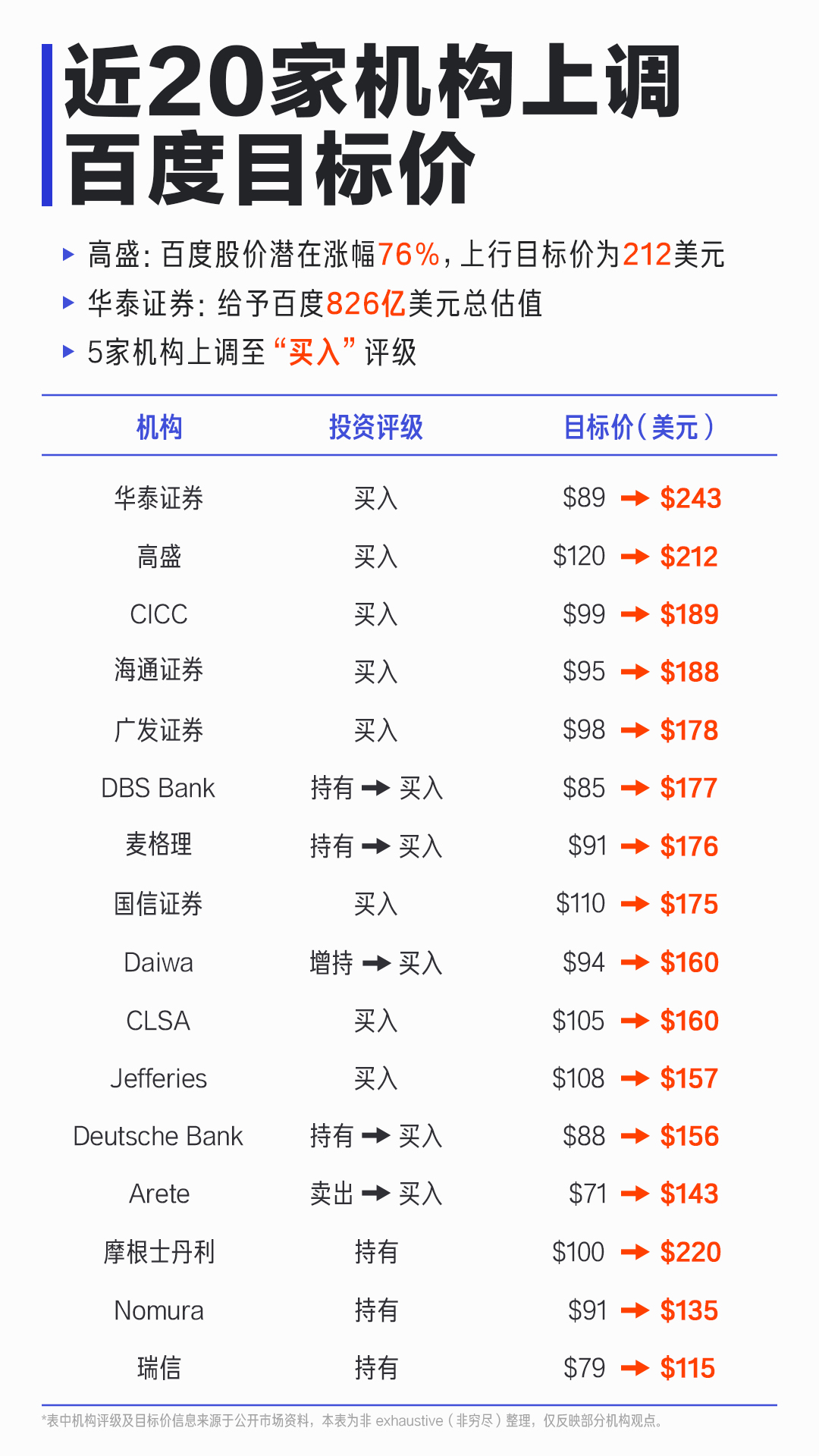
Recently, nearly 20 institutions have raised Baidu’s target price, with Huatai Securities valuing it at up to USD 82.6 billion, reflecting capital markets’ rising recognition and expectations for Baidu’s AI strategy.
Baidu’s long-term AI strategy is not merely about technical accumulation but a systemic reconstruction from cognition to industry. As Li Yanhong noted, when AI capabilities become native, intelligence shifts from a cost to a productivity driver. On this long-term path, Baidu has secured the initiative for the next round of technological and market competition, offering the industry a replicable blueprint for AI development.







