Large Model Daily | ByteDance Releases New Multimodal Breakthrough Amid Soaring HBM Etching Demand
![]() 01/09 2026
01/09 2026
![]() 554
554
01
Major Releases (New Models/Products/Open Source)
① Alibaba QianWen Doubles Down on Open Source: Introduces Embedding and Reranker Series
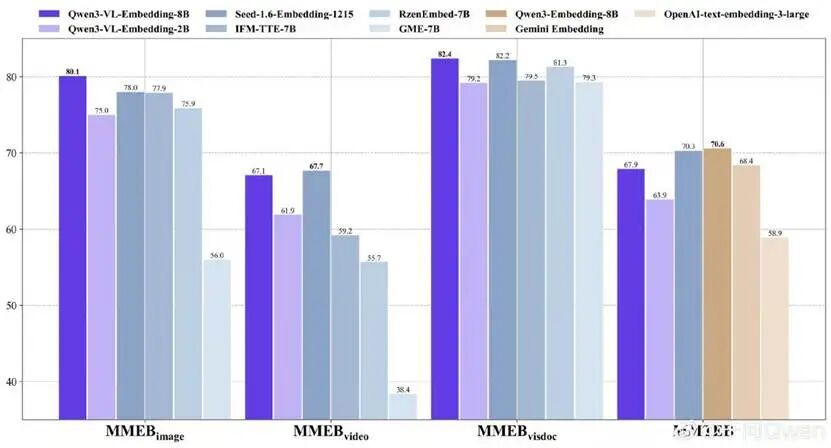
On January 8, the Alibaba Tongyi QianWen team released two open-source models: Qwen3-VL-Embedding and Qwen3-VL-Reranker.
These models mark the industry's first open-source multimodal embedding and re-ranking solutions built on the Qwen3-VL architecture. They enable unified mapping of multimodal and mixed-modal content (including text, images, audio, and video) into a high-dimensional semantic space, supporting cross-modal retrieval tasks such as "image-to-text search" and "text-to-video search."

Available in 2B and 8B parameter versions, both models support 32K context windows and customizable task instructions. They are now fully open-sourced on Hugging Face, ModelScope, and GitHub.
Short Comment:
Current AI multimodal systems still struggle with complex content recognition, with even Gemini 3 Pro falling short of expectations. Alibaba QianWen's open-source approach provides foundational tools for cross-modal recognition, offering fresh perspectives for the industry. As closed-source models face growing "black box" criticism, open-source strategies may drive breakthroughs in multimodal AI.
② OpenAI Expands Healthcare Footprint: Industry-Specific Suite Launched Across Top Hospitals
OpenAI unveiled OpenAI for Healthcare yesterday, a HIPAA-compliant AI suite tailored for medical applications. This marks its second healthcare-focused release, demonstrating systematic entry into core medical scenarios.
The suite comprises two main components:
1. ChatGPT for Healthcare: Built on GPT-5.2, it optimizes clinical, research, and operational workflows. The system cites millions of peer-reviewed articles, clinical guidelines, and public health recommendations with complete references while integrating hospital policy databases to ensure institutional alignment.
2. OpenAI API for Healthcare: Designed for developers, it supports custom tool creation for medical record summarization, follow-up scheduling, and environmental auscultation. Companies like Abridge and Ambience have already begun developing clinical assistance applications using this platform.
Leading institutions including Boston Children's Hospital, Cedars-Sinai, Stanford Medicine Children's Health, UCSF, and HCA Healthcare have deployed the system. Early pilots show AI assistance reduces diagnostic errors.
Short Comment:
Compared to its predecessor ChatGPT Health, OpenAI's new offering dives deeper into healthcare, where expanded demand brings higher risks. The system maintains physician oversight with its "Clinicians stay in charge" principle, avoiding direct diagnosis or medical advice while focusing on auxiliary integration, document generation, and evidence-based recommendations. If widely adopted, hospitals integrating with OpenAI's ecosystem may develop platform dependency, positioning GPT-5 as foundational infrastructure for intelligent healthcare.
③ Zhipu GLM-5 Announced: Targeting AGI Breakthroughs
Coinciding with Zhipu's IPO announcement, a Tsinghua University computer science professor revealed plans for Zhipu's next-generation large model, GLM-5.
In 2025, Zhipu led domestic AI progress with rapid model iterations: from GLM-4.1's tentative release in early 2025 to GLM-4.5's official launch in July, followed by GLM-4.6 in September and GLM-4.7 in December. The startup now competes with international top-tier models.
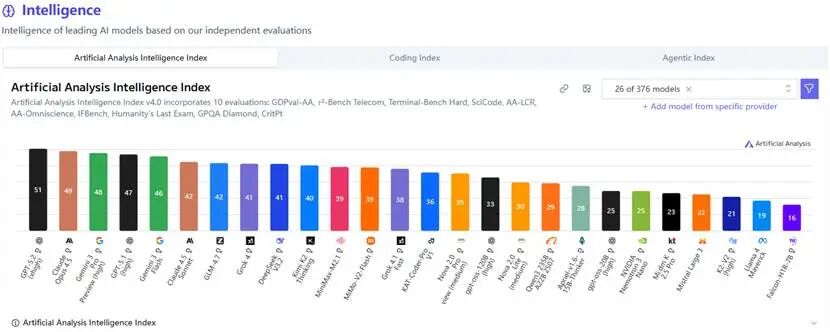
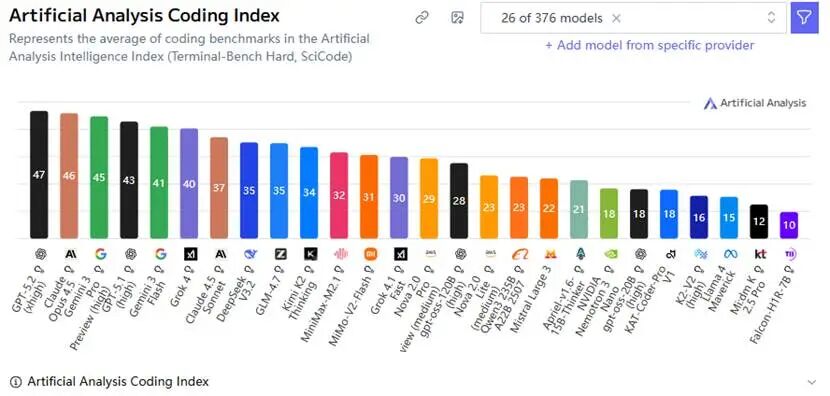
Released two weeks ago, GLM-4.7 achieved multiple SOTA (State-of-the-Art) results in open-source and domestic models for coding, agent, and multilingual tasks. It currently ranks 7th globally and 1st domestically on Artificial Analysis' intelligence leaderboard.
Tang Jie outlined three technical breakthroughs for GLM-5:
1. Transformer-alternative architecture: As AI capabilities expand and application scenarios grow, the Transformer's computational overhead for long contexts and rigid memory mechanisms become pronounced. Zhipu aims to develop new architectures and advance "chip-algorithm co-design" for improved energy efficiency.
2. Universal reinforcement learning paradigm: Model training will extend beyond verifiable environments like code to support complex, multi-hour task execution.
3. Continual learning and autonomous evolution: Current models' intelligence levels plateau post-training. Zhipu will explore online learning to enable real-time intelligence enhancement during inference.
Short Comment:
The proposed breakthroughs address well-recognized AI challenges, making short-term product implementation difficult. Real-world reliability and cost-effectiveness warrant closer examination.
④ Grok Code Set for Major Upgrade
Elon Musk announced yesterday that xAI will release a significant update to its programming reasoning model, Grok Code, next month. The new version will enhance programming capabilities for complex scenarios.
Previous models required developers to provide step-by-step guidance and multiple debugging rounds for large programming projects. The upcoming update aims to enable single-prompt task completion.
Short Comment:
Coding applications are expanding. Facing Claude Code's dominance, Google, OpenAI, and xAI have all entered the market. Currently, Grok 4 trails slightly behind the top three on Artificial Analysis' programming leaderboard. This update is expected to close the gap. Future competition will focus on performance parity and token pricing strategies.
⑤ Alibaba Cloud Debuts Multimodal Interaction Development Suite
Alibaba Cloud unveiled its new multimodal interaction development suite at the Tongyi Intelligent Hardware Expo.
Key features include:
1. Low-cost, rapid integration: Compatible with over 30 mainstream terminal chips, with planned hardware-software integration optimization alongside XuanTie.
2. Ultra-low latency: End-to-end voice response takes 1 second, while video interaction requires 1.5 seconds. The system supports full-duplex dialogue and real-time visual understanding.
3. Ready-to-use ecosystem: Pre-installed with common agents, integrated into Alibaba Cloud's Bailian ecosystem, and compatible with third-party agents via the A2A protocol for flexible business expansion.
Short Comment:
This release marks Alibaba's strategic focus on AI application layers and agent deployment. By encapsulating Tongyi model capabilities into hardware development kits, intelligent agents with perception, planning, and execution abilities can genuinely integrate into users' lives. In the competition for next-generation human-machine interfaces, terminal interaction experiences will shape AI's future form.
02
Technical Advancements (Papers/SOTA/Algorithms)
① ByteDance DreamStyle: Tri-Modal Guided Video Stylization Framework
ByteDance introduced an innovative multimodal framework called DreamStyle, recently uploaded to GitHub. This unified, efficient video stylization system supports three input methods—textual descriptions, style reference images, and first-frame guidance—to generate videos in specific styles. Through self-developed data pipelines and token-level LoRA fine-tuning, it improves long-video style consistency and visual quality, outperforming existing methods in real-world evaluations.
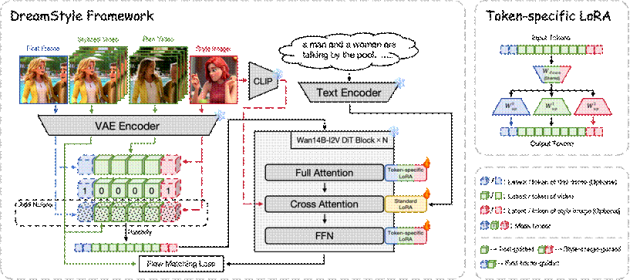
Traditional video stylization tools typically handle single-style inputs (e.g., text-to-video or image-to-video), resulting in unstable effects and temporal flickering in longer videos.
DreamStyle utilizes a self-built high-quality training dataset incorporating SDXL (Stability AI's open-source text-to-image framework), Seedream 4.0, and ControlNet (controllable image generation technology) to ensure accurate style transfer and motion coherence. Based on Alibaba's open-source Wan14B-I2V architecture, it introduces Token-specific LoRA technology to distinguish signals under different conditions and reduce semantic confusion.
Short Comment:
Designed for style transfer tasks, this framework holds commercial potential for short video platforms and advertising companies. However, deployment thresholds may be high, and compatibility with lightweight or edge devices remains uncertain.
03
Computing Power and Infrastructure (Chips/Cloud/Data Centers)
① Tokyo Electron Boosts AI Investment: 48% Capital Expenditure Increase for HBM-Driven Etching Demand
According to Nikkei News, global semiconductor equipment leader Tokyo Electron plans to significantly increase AI infrastructure investment. The company expects to raise FY2026 capital expenditure by 48% to ¥240 billion (a record high), with R&D spending growing 16% to ¥290 billion.
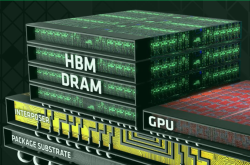
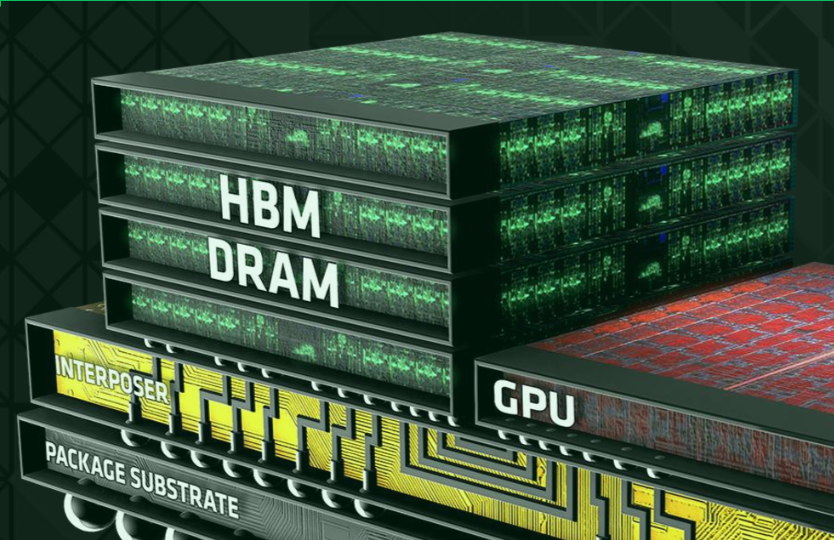
This aggressive investment targets the surge in advanced etching equipment demand driven by HBM (High Bandwidth Memory) expansion.
As NVIDIA and other high-end AI manufacturers adopt multi-layer stacked HBM in chip products, major DRAM producers like Samsung and SK Hynix are accelerating capacity expansions. Both companies have announced multi-billion-dollar investments in new HBM production lines, expected to start operations between 2027 and 2028. Each additional HBM layer requires precision etching equipment to construct intricate chip interconnects—a key business area for Tokyo Electron.
In FY2025, Tokyo Electron's DRAM interconnect etching system sales exceeded ¥100 billion, with cumulative sales projected to reach ¥500 billion by 2030. To meet demand, the company is expanding R&D, production, and logistics centers across Japan.
Short Comment:
The AI boom shows no signs of slowing, and HBM supply shortages currently hinder computing power growth. Thus, this investment carries minimal risk. The competition for AI hardware has expanded from GPUs to HBM and now upstream to manufacturing equipment.