NVIDIA's new move targets the industrial sector
![]() 09/19 2024
09/19 2024
![]() 521
521

As the old saying goes, ducks know the water is warm before spring arrives. NVIDIA's recent actions are hinting at new trends in the industry.
Not long ago, NVIDIA unveiled a generative AI service for 3D modeling, attracting widespread attention in the industry. While previous generative AI primarily focused on creating content in the two-dimensional world, such as text, images, and videos, NVIDIA is now leveraging generative AI to assist businesses in building 3D assets, accelerating the development of digital twins and simulation industries, and facilitating the application of AI in the physical world.
01
'CUDA-native' Focuses on Industry
As the global leader in accelerated computing, NVIDIA's actions are hinting at new trends.
In two fireside chats at SIGGRAPH 2024, NVIDIA's founder and CEO, Jen-Hsun Huang, shared his latest insights on AI, particularly generative AI and accelerated computing, and how they can transform industries like manufacturing through visualization. During the conference, NVIDIA also launched a new set of NIM microservices.
SIGGRAPH is a forum for discussing the latest innovations in computer graphics. NVIDIA unveiled generative AI models and NIM microservices tailored for OpenUSD, geometry, physics, materials, and more. OpenUSD, an open-source software for internal data exchange in 3D scenes, has gradually become the standard in industries such as 3D visualization, architecture, design, and manufacturing.
These models and services empower developers to accelerate the development of applications in industries like manufacturing, automotive, and robotics.
During the fireside chats, Huang discussed the importance of building digital twins and virtual worlds. He noted that industries can enhance efficiency and reduce costs by creating large-scale digital twins of cities. "For example, AI can be trained in such virtual worlds before being deployed in next-generation humanoid robots," he said.
Why is Huang emphasizing industrial visualization, virtual worlds, or digital twins? And why is NVIDIA introducing new NIM microservices into its CUDA ecosystem at this time?
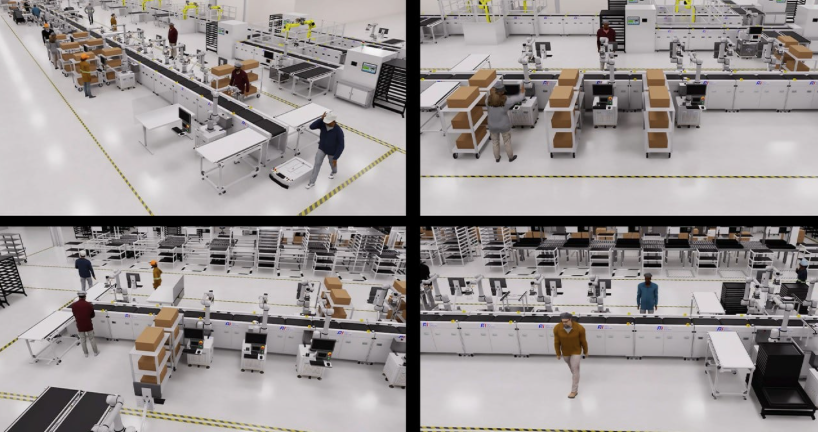

Image courtesy of NVIDIA
As NVIDIA's Vice President of Omniverse and Simulation Technologies, Rev Lebaredian, noted, the tide of generative AI in heavy industries has arrived. According to Digital Frontline, generative AI is moving from simple scenarios to complex production processes. The aforementioned technology ecosystem can accelerate this transition.
'Until recently, the primary users of the digital world were in the creative industries. Now, with the enhancements and accessibility NVIDIA NIM microservices bring to OpenUSD, various industries can create physics-based virtual worlds and digital twins, preparing them for this new wave of AI technology,' said Lebaredian.
In the automotive industry, domestic automakers are embracing digital twins. 'Tesla is about to release FSD 12.5 and is actively promoting its deployment in China,' shared an AI expert from a large Chinese automaker with Digital Frontline. 'Tesla views simulation as a strategic goal, and we're also working on the metaverse to address closed-loop data issues in autonomous driving.' Previously, collecting 'pop-out' data was challenging and costly for automakers. Now, they can tackle training for long-tail scenarios in a metaverse simulation environment.
In the robotics industry, a power inspection robot company is training AI in a simulation environment to enable robots to perceive complex environments and physical spaces in real-time, plan movement routes, and monitor thousands of meters along various devices.
Architectural design is a complex and time-consuming endeavor, with 3D modeling being an essential deliverable. Reconstructing 3D models for complex geometries and irregular structures can be daunting. Now, some design firms are collaborating with AI companies to generate models from images, sketches, and text. They can also assign different materials to architectural designs to enhance their perfection.
In the steel industry, metallographic analysis involves examining material slices under a microscope to understand their internal defects and structures, thereby assessing their overall performance. Traditional manual methods are inefficient and heavily reliant on human experience. Many steel companies now aspire to leverage their existing knowledge bases and train specialized AI to comprehensively analyze materials.
NVIDIA's new NIM microservices enable enterprises to call services directly without starting from scratch, rapidly realizing applications by integrating their data. Hence, some enterprises describe this as 'CUDA-native.'
As generative AI permeates deeper into various scenarios, Huang asserted, 'Everyone will have an AI assistant.' Furthermore, the integration of AI and image technology is deepening, impacting nearly every industry, from scientific computing predicting weather with better accuracy and less energy to collaborating with creators to generate images or create virtual scenes for industrial visualization, Huang remarked, 'Generative AI will also revolutionize the field of robotic autonomous vehicles.'
02
New NIM Microservices Spark Imagination
These industrial applications rely heavily on 3D modeling and simulation technologies.
Constructing 3D content and scenes has been a challenging task due to the complex chain and process, encompassing modeling, shading, animation, lighting, rendering, and more.
Over the past few decades, animation, visual effects, and game studios have struggled to improve interoperability among various tools in their workflows, with limited success. Migrating data from one location to another is cumbersome, prompting studios to develop complex workflows to manage data interoperability.
Moreover, traditional 3D production processes involve linear collaboration across multiple departments and individuals, necessitating format conversions and revisions, which are time-consuming and labor-intensive.
OpenUSD, an open-source universal 3D data exchange framework established in 2023 by NVIDIA, Pixar, Apple, and others, facilitates the creation of virtual worlds through interoperability between software tools and data types. It offers high interoperability and compatibility, addressing multiple challenges related to workflow and complexity in creating 3D scenes.
OpenUSD serves as the foundation for NVIDIA's Omniverse platform. In a conversation with a senior writer from Wired magazine, Huang noted that OpenUSD is the first format that integrates multimodal expressions from almost all tools. Ideally, over time, people can introduce almost any format, enabling collaboration and preserving content indefinitely. Generative AI is poised to enhance Omniverse's simulation capabilities.
NVIDIA's new NIM microservices for OpenUSD are the world's first generative AI models tailored for OpenUSD development. They integrate generative AI capabilities into the USD workflow through NIM microservices, significantly lowering the barrier to entry for using OpenUSD. Additionally, NVIDIA has released new USD connectors for robotic data formats and Apple Vision Pro streaming.
Image courtesy of NVIDIA
Currently, three NIM microservices have been launched: 1) USD Code NIM microservice, which answers general OpenUSD questions and automatically generates Python code based on text prompts. 2) USD Search NIM microservice, enabling developers to search vast OpenUSD, 3D, and image databases using natural language or image inputs, significantly accelerating enterprise-level retrieval and material processing. 3) USD Validate NIM microservice, which checks the compatibility of uploaded files with OpenUSD releases and generates RTX ray-traced render paths driven by NVIDIA Omniverse Cloud API.
Apart from NVIDIA's native NIM microservices, ecosystem partners are creating popular AI models based on these microservices to optimize inference for users.
Shutterstock, a globally renowned creative content platform, has launched a new text-to-3D service leveraging NVIDIA's latest Edify visual generation model, enabling the creation of 3D prototypes or virtual environments.
Crafting accurate reflections for virtual scenes is a complex task. Previously, creators needed expensive 360-degree camera equipment to create backgrounds from scratch on location or search similar content in vast libraries.
Now, with 3D generation services, users can describe their desired environment with text or images and receive 16K HDRi panoramic images. These scenes and components can be quickly swapped, such as placing a sports car in a desert, tropical beach, or winding mountain road.
Besides creating lighting, creators can rapidly add various rendering materials like concrete, wood, or leather to build their 3D assets. These AI-generated assets can be edited and provided in popular file formats.
NVIDIA's Edify AI model also assists Getty Images in enabling artists to control image composition and style freely. For instance, they can float a red beach ball over a perfect coral reef photo. Creators can also fine-tune the base model with enterprise data to generate images that align with specific brand creative styles.
These model microservices and tools significantly accelerate the creation of 3D assets for brands, making digital twin development more accessible and convenient.
03
Pioneering Enterprises Have Begun Experimenting
As 3D content and asset creation become more convenient and accurate, industries like manufacturing, autonomous driving, engineering, and robotics are enjoying the technological dividends brought by generative AI. In particular, pioneering enterprises in manufacturing and advertising creative industries are actively leveraging NVIDIA's Omniverse platform to accelerate the application of digital twins and simulations.
Coca-Cola is the first brand to use generative AI provided by Omniverse and NIM microservices in marketing scenarios. In a demo video, users simply input, 'Create a table with tacos and salsa, bathed in morning light,' in natural language.
The USD Search NIM microservice swiftly retrieves corresponding 3D assets from a vast 3D asset library and invokes them via API. USD Code NIM then combines these models into a scene, and developers receive Python code for creating novel 3D worlds with their input prompts, significantly enhancing their creative capabilities. Through generative AI, Coca-Cola can customize personalized imagery in over 100 global markets, enabling localized marketing strategies.
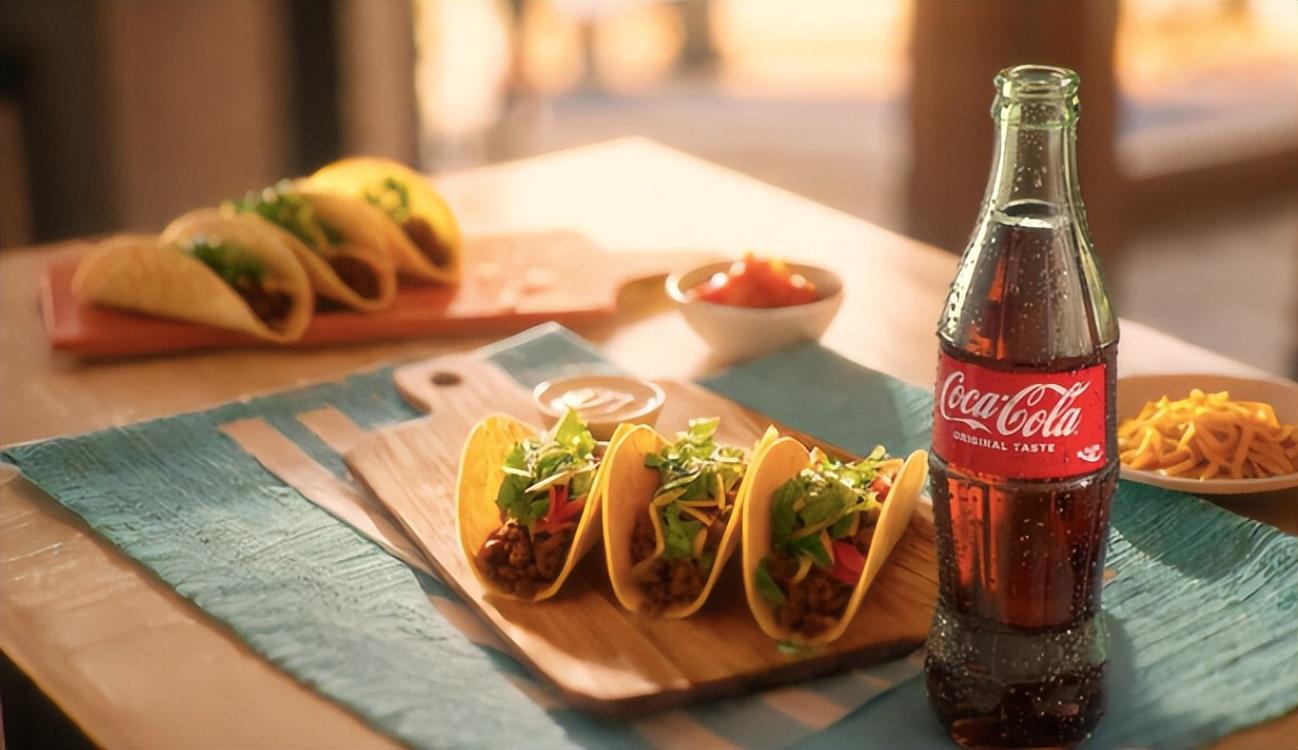

Image courtesy of NVIDIA
As Coca-Cola's advertising service provider, WPP has launched a smart marketing operating system leveraging the Omniverse development platform and OpenUSD. This system streamlines and automates the creation of multilingual text, images, and videos, simplifying content creation for advertisers and marketers. By serving clients with generative AI, WPP brings innovative ideas to life.
As WPP's CTO noted, 'The beauty of these innovations lies in their compatibility with our workflows and their utilization of open standards. They accelerate future work and enable us to consolidate and expand our investments in standards like OpenUSD. By using NVIDIA NIM microservices and Omniverse, we can collaborate with companies like Coca-Cola to launch innovative new production tools at an unprecedented pace.'
As the world's largest contract electronics manufacturer, Foxconn built a virtual digital twin factory for a new plant in Mexico. Engineers can define processes and train robots in the virtual environment, enhancing factory automation, productivity, and efficiency while saving time, cost, and energy.
Foxconn also employs the Omniverse platform to construct its digital twins, integrating all 3D CAD elements into a single virtual factory. They use NVIDIA Isaac Sim, a scalable robotic simulation platform developed on Omniverse and OpenUSD, to train robots, providing physically accurate and visually realistic presentations for their digital twins.
Apart from Foxconn, electronic manufacturing enterprises like Delta Electronics, MediaTek, and Pegatron are also leveraging NVIDIA AI and Omniverse to build factory digital twins.
Xiaopeng Motors' MPV model, the Xiaopeng X9, utilizes the Omniverse platform during its design process. By introducing the vehicle development workflow into the virtual world, Xiaopeng Motors circumvents bottlenecks in traditional workflows.
For instance, Omniverse's strong interoperability eliminates the need for complex conversions of files and data used in industrial modeling, rendering, and 3D effects, accelerating communication and collaboration among Xiaopeng Motors' design teams. Furthermore, with Omniverse's real-time rendering and ray tracing capabilities, Xiaopeng Motors achieves instant visualization of car colors and interior changes, enhancing virtual realism and user experience, ultimately refining product designs based on customer demands.
While generative AI's popularity over the past two years has primarily focused on ToC and collaborative office applications, the physical world is poised for a new wave of growth and opportunities.







