"Local radish" collides with "foreign radish", is Tesla paying tribute to Luobukuaipao?
![]() 10/11 2024
10/11 2024
![]() 633
633

The field of autonomous driving has been getting livelier by the day, just a week after the National Day holiday.
Right after the first trading day after the holiday, Baidu's Luobukuaipao concept stocks all turned red, with companies like Zhonghaida and Tianmai Technology on the A-share market hitting the daily limit. Immediately after that, Luobukuaipao was reported to be planning to expand overseas and would also release Apollo Autonomous Driving Open Platform 10.0, equipped with the autonomous driving large model ADFM.
On October 11, Tesla officially unveiled its Robotaxi named Cybercab, adding fuel to the autonomous driving fever.
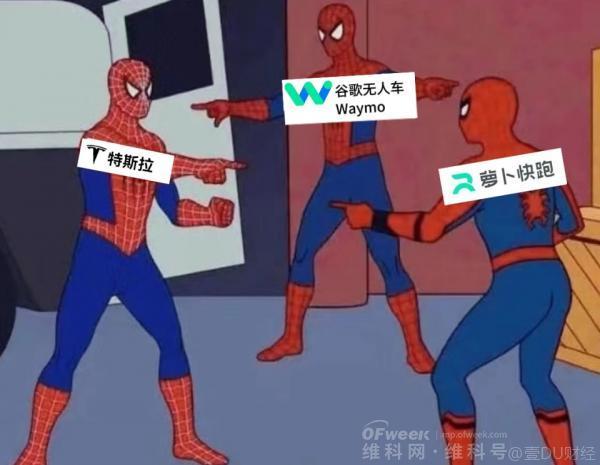
With Tesla's entry, coupled with Luobukuaipao and Google Waymo, which have already ventured out of the lab and started commercial deployment, the global autonomous driving "Big Three" landscape is taking shape.

In 2024, autonomous driving has reached a new turning point in terms of technological breakthroughs, cost reductions, and large-scale application deployments. Nowadays, under the "Big Three" market landscape, "local radishes" collide with "foreign radishes." Although Chinese and American autonomous driving players have different driving paths, they are both accelerating.
01 The Formation of the "Big Three" Landscape in Autonomous Driving
Tesla's Robotaxi, which was delayed for two months, finally met the public on October 11, Beijing time. At the press conference, Tesla CEO Elon Musk rode in the Cybercab for a demonstration of driverless driving around the venue.

Musk did not mention technical details at the press conference, but he introduced that the cost of the Cybercab will be less than $30,000, with production expected to start in 2026. The comments from overseas netizens were also interesting, "Baidu Apollo's real robot taxi is already on the road for less than $30,000," suggesting that Tesla's announcement was somewhat of a tribute to China's autonomous driving efforts.
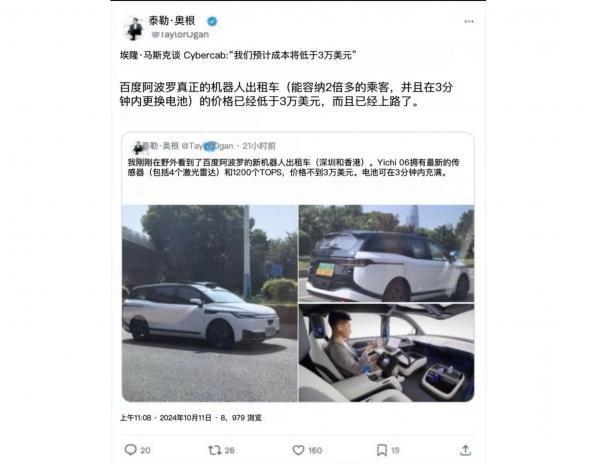
Musk also mentioned that Tesla expects to launch unsupervised Full Self-Driving (FSD) capabilities in Texas and California next year.
Tesla's entry into this field has also begun to shape the "three-way competition" landscape in the autonomous driving market.
For many ordinary people, autonomous driving may still be something they've "heard of but never seen." However, it's important to note that the technological foundation for this has spanned over a century, from early radio control to the rapid advancements of the past two decades.
During this period of explosive growth, there have been many players entering the autonomous driving market, including Google's Waymo and Cruise, Amazon-acquired Zoox overseas, and Luobukuaipao, WeRide, Pony.ai, and others domestically.
In October, Waymo also announced that its self-driving taxi service in Austin, Texas, would be open to the public and partnered with Hyundai Motor to conduct preliminary road tests of IONIQ 5 vehicles equipped with Waymo technology by the end of 2025. Uber also partnered with Avride, expanding its autonomous vehicle partner network beyond Waymo, Motional, and WeRide.
However, the autonomous driving landscape has been up and down, with players facing challenges along the way. Cruise temporarily suspended its autonomous driving operations last year due to a traffic accident, and Wenyuan Zhixing's IPO plans have been postponed twice.
In the ups and downs of the autonomous driving industry, there has been a saying that "America looks to Google Waymo, and China looks to Baidu Luobukuaipao."
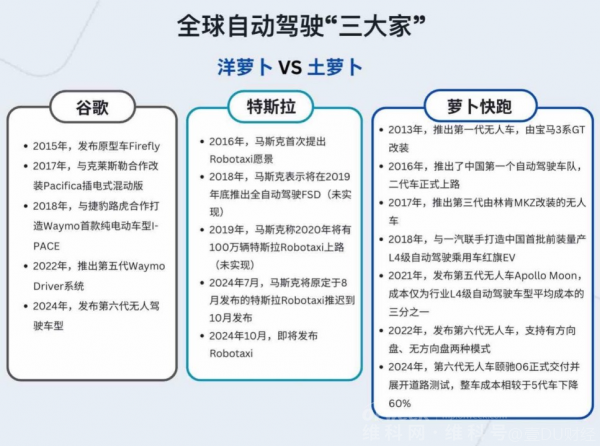
After all, Baidu has been laying the groundwork for autonomous driving since 2013, investing up to 150 billion yuan. Luobukuaipao's sixth-generation autonomous vehicle is already on the way, equipped with ApolloADFM (Autonomous Driving Foundation Model), Baidu's first global large model supporting L4 autonomous driving.
According to Baidu, the ApolloADFM large model reconstructs autonomous driving based on large model technology, balancing safety and generalization, achieving safety levels over 10 times higher than human drivers, covering complex urban scenarios, and enhancing data processing efficiency through self-annotation.
The upcoming Baidu Apollo Autonomous Driving Platform 10.0, equipped with the ADFM large model, will significantly enhance the safety, intelligence, and ease of use of the autonomous driving open platform.
As for Waymo, as Google's "firstborn" and the "elder brother" of autonomous driving in the US, it has been navigating the autonomous driving landscape since 2009, raising over $10 billion in funding over five years.
In June this year, Waymo's sixth-generation Robotaxi began road tests, with upgraded sensor configurations enabling it to handle variable weather conditions like rain and fog. By August, Waymo had secured 100,000 paid orders in a week, bringing its total paid orders to over 2 million.
Tesla, which officially entered the market in October, is more like a catalyst. Unlike companies like Waymo that rely on lidar solutions for environmental perception, Tesla has always advocated for software algorithms to achieve autonomous driving, fully promoting its Full Self-Driving (FSD) system.
Tesla's FSD system is an "end-to-end system" that uses a pure vision-based approach without high-precision maps to control the vehicle. As of July 2024, Tesla's FSD had accumulated over 1.6 billion miles of driving.
The high level of interest in Tesla's Robotaxi stems from the belief that its FSD system will continue to iterate its algorithms by refining its road data collection database, driving a new wave of industry enthusiasm.
With Tesla's "aggressive" entry, alongside Luobukuaipao and Waymo, a "Sino-US technology race" is unfolding.
02 The Advantages of Chinese and American Autonomous Driving Routes
Against the backdrop of the emerging "Big Three" landscape in global autonomous driving, the debate over technical routes in autonomous driving has intensified.
Over the years, there have been many disputes in the autonomous driving field, with tensions flaring up and subsiding, but never truly resolving.
Regarding implementation paths, there has long been heated debate between the incremental and leapfrog routes. The incremental route (starting with lower-difficulty assisted driving and gradually achieving L4/L5 autonomous driving), represented by Tesla and many traditional automakers, and the leapfrog route (directly developing L4/L5 high-level autonomous driving), represented by Luobukuaipao and Waymo, each have their merits but are neck and neck.
However, after years of debate, the industry has come to realize that these two approaches are not mutually exclusive but rather complementary, with different methods suitable for different business models and scenarios.
In terms of perception solutions, the debate between pure vision and lidar fusion has become even more intense in 2024, following breakthroughs in end-to-end large models.
Tesla is firmly in the pure vision camp, "emphasizing software over hardware," relying solely on data accumulation and training within its software system to handle road conditions. Following breakthroughs in end-to-end large models, several domestic models like Xpeng P7+ and WENJIE M7 Pro have also reduced their reliance on lidar.

Waymo and Luobukuaipao, on the other hand, prefer lidar solutions. Musk has publicly questioned the feasibility of lidar technology multiple times this year, citing high hardware costs as one of his concerns. Despite technological breakthroughs reducing lidar hardware costs, it remains the first choice for some enterprises.
The debate continues, and it's unlikely that one approach will replace the other in the short term. Instead, autonomous driving companies need to consider factors such as manufacturing costs, operating costs, and technological accumulation to choose the right solution. Some industry insiders predict that future smart driving models in the lower price range will adopt pure vision solutions, while models in the mid-to-high price range will adopt fusion perception solutions.
Beyond these two major routes, the focus of the 2024 route debate has centered on whether to prioritize "single-vehicle intelligence" or "vehicle-to-infrastructure cooperation," essentially a question of "going it alone" versus "working together." China and the US are clearly on different paths here.
The US has firmly chosen the single-vehicle intelligence route, leveraging its strengths in AI algorithms and decision-making chips to enable vehicles to recognize road conditions and make decisions using their own sensors, with a focus on strengthening the vehicle end and individual capabilities.
China, though a late starter in autonomous driving research and development, has chosen the vehicle-to-infrastructure cooperation route as a way to catch up. This route involves more dimensions of coordination, aiming to integrate the physical and information spaces of people, vehicles, roads, and clouds to achieve safe, energy-efficient, comfortable, and efficient operation of intelligent and connected vehicle transportation systems.
This "working together" approach is more challenging, requiring not only technological advancements from enterprises but also improvements in new infrastructure from the government and society.
However, this aligns with China's strengths, as the country has been making corresponding industrial supporting efforts, vigorously promoting new infrastructure such as 5G, satellite internet, data centers, and intelligent transportation. It has resolutely implemented the 5G LTE-V2X technology standard for road upgrades, supporting the smooth evolution from LTE-V2X (Long Term Evolution-Vehicle to Everything) to 5G-v2X.
Earlier this year, multiple departments jointly issued the "Notice on Carrying Out the Application Pilot Work of 'Vehicle-Road-Cloud Integration' for Intelligent and Connected Vehicles," announcing the launch of the "Vehicle-Road-Cloud Integration" application pilot program from 2024 to 2026. In July, 20 cities were designated as pilot cities for the "Vehicle-Road-Cloud Integration" application of intelligent and connected vehicles.
Under China's vehicle-to-infrastructure cooperation route, Luobukuaipao has chosen the "single-vehicle intelligence + vehicle-to-infrastructure cooperation" approach. At the end of 2018, Baidu officially open-sourced the Apollo vehicle-to-infrastructure cooperation solution, comprehensively constructing an intelligent road network with comprehensive data perception across people, vehicles, roads, and clouds, supporting the wide-area perspective, redundant perception, and over-the-horizon perception needs of autonomous vehicles.
03 Luobukuaipao Continues to 'Run Fast,' Accelerating the Explosion of China's Autonomous Driving Industry
While China and the US take different routes in autonomous driving, the competition continues, and whoever can establish the industry chain first will have a voice.
The choice of the vehicle-to-infrastructure cooperation route reveals that China's autonomous driving industry has entered a period of rapid development, supported by policies and industrial supporting measures.
In 2024, policies across various regions have converged to promote autonomous driving, with cities vying to become the "first city of autonomous driving." Wuhan has led the way in terms of open road mileage and open areas, as well as being the first to issue commercial pilot licenses for intelligent and connected vehicles. Beijing has been deeply engaged in vehicle-to-infrastructure cooperation technology, Shanghai boasts rich autonomous driving road scenarios, and Shenzhen is home to approximately a thousand autonomous driving-related enterprises.
According to incomplete statistics, there were at least 60 normative and supportive documents issued by domestic provinces and cities regarding autonomous driving in the first three quarters of this year, with more than ten cities enacting local legislation to regulate the development of autonomous driving.
In terms of "Vehicle-Road-Cloud Integration" construction, while it is still in its infancy, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology has disclosed that China has established 17 national-level intelligent and connected vehicle test zones, seven vehicle-to-everything (V2X) pilot zones, and 16 "dual-intelligence" pilot cities, with over 32,000 kilometers of open test roads, over 7,700 test licenses issued, and over 120 million kilometers of test driving. Many places have also initiated the construction of cloud-controlled infrastructure platforms.
On the technical front, significant progress has been made in recent years in high-precision maps, lidars, and in-vehicle computing chips for autonomous driving perception layers, leading to economies of scale and continuous cost optimization.
Taking Luobukuaipao as an example, due to technological maturity and cost averaging, the sixth-generation autonomous vehicle from Luobukuaipao costs only 204,600 yuan, a 60% decrease from the fifth-generation model.
With more comprehensive infrastructure support, increasingly sophisticated policy standards, and maturing technical reserves, the closed loop for the implementation and application of autonomous driving is being established. As a result, Luobukuaipao has seen a significant increase in orders this year, with cumulative travel services exceeding 7 million trips.
As autonomous taxi services gradually achieve large-scale applications, upstream companies providing intelligent hardware and software in the industry chain, as well as midstream and downstream players such as autonomous driving solution providers and vehicle manufacturers, will all benefit. Luobukuaipao, which has been tested domestically, has already driven the development of the upstream and downstream industry chain.
Huace Navigation has disclosed that it is currently the exclusive supplier of Luobukuaipao's sixth-generation autonomous vehicle P-Box products. Ruida Electronics has stated that it provides battery swapping and high-voltage connectors for Luobukuaipao's battery swapping projects. Horn Automotive Electronics has disclosed a cooperation with Luobukuaipao on products such as automatic parking and ultrasonic radars, which will go into mass production this year.
As the autonomous driving sector becomes active, it's no surprise that Luobukuaipao concept stocks surged across the board on October 8.
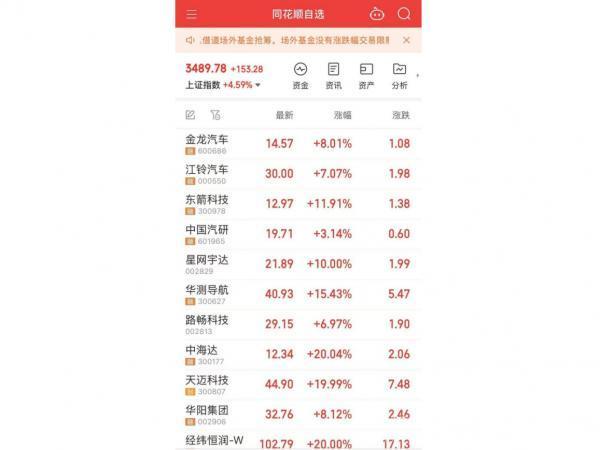
Returning to the macro market, reports predict that the market size of China's intelligent and connected vehicle industry is expected to exceed 5 trillion yuan by 2030, with the "Vehicle-Road-Cloud Integration" market exceeding 14 trillion yuan. Focusing on the Robotaxi segment, Kaiyuan Securities points out that the domestic market is expected to reach 500 billion yuan by 2030 and attract users through lower unit travel costs, with the potential to exceed 1 trillion yuan in the long run.
In 2024, autonomous driving is no longer just a gimmick or hype but a genuine transportation revolution underway. The industry's singularity has arrived, and with leaders like Luobukuaipao, the explosion of a trillion-yuan market is just around the corner.
Competition in the Robotaxi sector is heating up, with Chinese and American tech giants fiercely competing in this silent battle. With the initial establishment of the global autonomous driving "Big Three" landscape, every detail of this technological race captivates the world's attention.
The competition in autonomous driving is not just about technology and capital but also about market insight and strategic layout. It's a race for technological prowess and future industry dominance. Chinese autonomous driving enterprises must maintain a sense of urgency, continuously break through bottlenecks, and enhance the safety and reliability of autonomous driving. Only in this way can they excel in the Sino-US autonomous driving race and win the future.