The starting gun of the global Robotaxi competition has sounded, and Chinese players need to speed up
![]() 10/12 2024
10/12 2024
![]() 402
402

Editor | Liu Jingfeng
This morning, the tech world's attention was focused on one event: Tesla's "Robotaxi Day" in California, where it officially launched its self-driving taxi, the Robotaxi. Tesla's driverless vehicle is steering wheel-free and pedal-free, with a cost expected to be below $30,000.
Upon seeing Tesla's Robotaxi launch, some netizens joked that it was paying homage to "Made-in-China Radish." As early as 2022, Radish Go (a Baidu subsidiary) launched its sixth-generation driverless vehicle, available in both steering wheel and steering wheel-free modes, at a cost below $30,000.
Just two days ago, news emerged that Radish Go, Baidu's autonomous taxi service, was actively pursuing a global strategy, engaging in in-depth discussions with multiple international companies and planning to enter global markets.
The global Robotaxi market is finally heating up.
Tesla's Full Self-Driving (FSD) technology has always been highly regarded in the industry, and its Robotaxi is equipped with Tesla's latest FSD technology. Radish Go's Robotaxi, on the other hand, relies on Baidu's upcoming Apollo Autonomous Driving Open Platform 10.0 version. This platform will incorporate Baidu's latest Autonomous Driving Foundation Model (ADFM), aiming to significantly enhance the platform's safety, intelligence, and ease of use.
It is rumored that Radish Go plans to test and deploy its driverless taxis in Hong Kong, Singapore, the Middle East, and other regions. Informed sources revealed that Radish Go has been discussing relevant plans with businesses and regulatory agencies in these regions. In response, Hong Kong's Transport and Logistics Bureau stated that the new regulatory framework for autonomous vehicles was implemented in March 2024, and the Transport Department expects to announce successful autonomous vehicle projects in batches before the end of 2024.
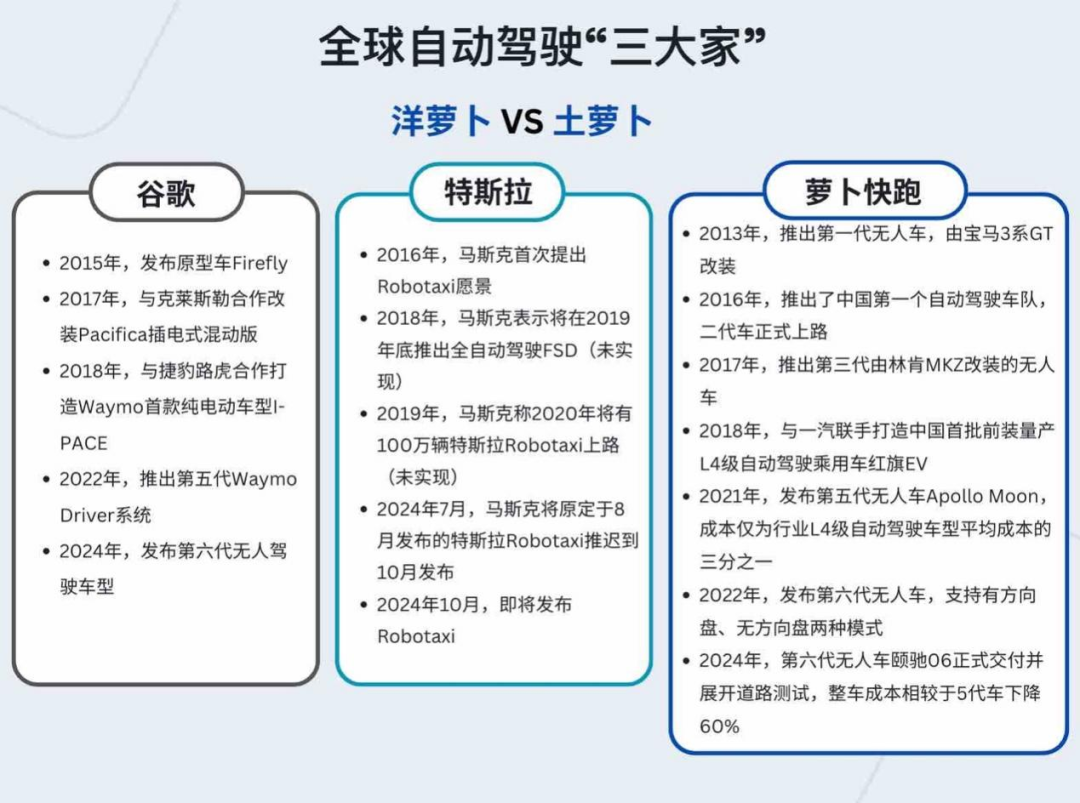
As Radish Go's global expansion plans unfold, the competitive landscape of the global autonomous driving market may witness new changes. In the global autonomous driving landscape, Radish Go, Google Waymo, and Tesla's Robotaxi are gradually emerging as the three major players.
As Radish Go embarks on its global strategy, how will it catch up with and potentially surpass Tesla and Google in the fiercely competitive global autonomous driving market?


The global autonomous driving market is increasingly dominated by leading players, primarily Chinese and American companies.
In this global autonomous driving competition, Radish Go has emerged as a Chinese player capable of competing with Google Waymo and Tesla for market share in overseas markets. For Chinese companies venturing abroad, global commercial autonomous driving is not just about market competition but also a strategic battle for the future.
The autonomous taxi market, in particular, is a blue ocean with intense competition. The development of autonomous driving technology will disrupt the traditional automotive industry, making it a crucial battleground for automotive and technology industries worldwide. China and the United States, with the largest number of autonomous driving enterprises globally, will define the playing field and export technology products to other countries based on who can first establish relevant industrial chains. In the context of Sino-US technological competition, this is a "battle that cannot be lost" for either side.
In this context, the overseas expansion of Chinese autonomous driving enterprises, represented by Radish Go, is crucial for upstream and downstream Chinese autonomous driving-related enterprises. Successfully entering international markets can not only expand the global market share of Chinese autonomous driving enterprises but also enhance their brand influence and international competitiveness through cooperation and competition with leading international enterprises.
Regarding the current global competition in autonomous driving, Wang Xianjin, member of the National Committee of the CPPCC, deputy director of the Transportation Research Institute of the Ministry of Transport, and chief engineer, stated, "The window of opportunity for global autonomous driving development is fleeting. China's autonomous driving technology is internationally leading. We should actively support industry development, further strengthen our technological advantages, and achieve overall leadership in technology application, policies and regulations, and industrial development."
Chen Yanyan, a professor at the School of Urban Transportation at Beijing University of Technology, also highlighted the inevitable competition between China and the United States in autonomous driving technology: "China and the United States have always been the most influential forces at the global autonomous driving table. Over the past decade, China has been striving to catch up with the United States in autonomous driving and has now achieved parity in technology."
She believes that China needs to take bolder steps in autonomous driving legislation, vigorously supporting autonomous driving enterprises in expanding their operational areas and facilitating large-scale implementation. On the other hand, autonomous driving enterprises should be encouraged to innovate independently, achieve self-sufficiency in key autonomous driving technologies as soon as possible, improve the technical performance of autonomous driving, and avoid being held back.
Amidst the increasingly fierce global competition in autonomous driving technology, China's autonomous driving industry needs to "sprint" to maintain its lead in this global race.

The wave of autonomous driving is sweeping the globe unstoppably, becoming the intersection of the automotive and technology industries.
Tesla's introduction of its driverless vehicle showcases the US's leadership in autonomous driving technology. Meanwhile, China's Radish Go plans to enter overseas markets, leveraging Baidu's upcoming Apollo Autonomous Driving Open Platform 10.0, which will incorporate Baidu's latest Autonomous Driving Foundation Model (ADFM), significantly enhancing the platform's safety, intelligence, and ease of use. This version, tailored for global users, will drive the global expansion of Chinese enterprises.
Let's start with Tesla. Tesla dominates the US Robotaxi market, with its Full Self-Driving (FSD) system having accumulated over 1.6 billion miles of driving. Tesla's FSD system has amassed substantial mileage, providing rich data and experience to continually optimize its algorithms.
Tesla plans to introduce FSD in Europe and China in the first quarter of 2025, indicating its intention to expand globally. Tesla's FSD and Robotaxi services will reinforce each other. For instance, data collected from Robotaxi services will enrich FSD's road test database, aiding in algorithm improvement. Additionally, Tesla's AI computing power is rapidly expanding, with projections to reach nearly 90,000 NVIDIA H100 chip-equivalent units by 2024, supporting autonomous driving technology training.
Meanwhile, Google Waymo is also active. On October 2 (local time), Waymo announced the upcoming public launch of its driverless taxi service in Austin, Texas, accessible through the Waymo One app and planned for integration into the Uber app in early 2025.
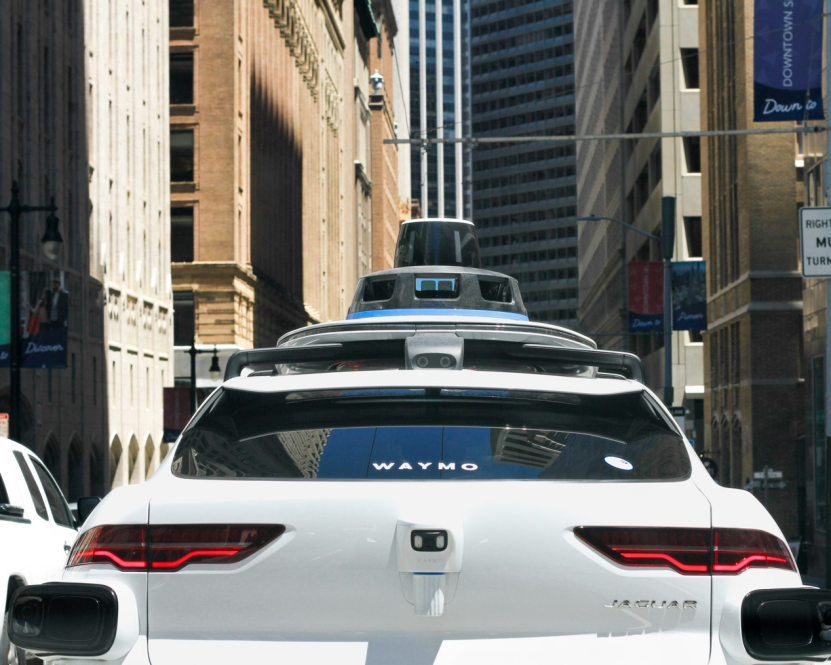

Waymo expanded its driverless ride-hailing service on the San Francisco Peninsula in March and made it available to all San Francisco users in June. Waymo's driverless taxi service has become an integral part of San Francisco residents' daily lives, with about 30% of users utilizing it to visit local businesses and 36% connecting to other modes of transportation. Currently, its weekly paid rides exceed 100,000, double that of May.
Waymo and Uber also announced their collaboration to launch a driverless taxi service in early 2025. Notably, Uber recently established partnerships with General Motors' autonomous driving subsidiary Cruise and UK-based autonomous driving startup Wayve.
The rapid expansion of Tesla and Google Waymo in driverless taxi services has put pressure on China's autonomous driving enterprises expanding overseas. US-based competitors' rapid advancements in technology and services pose a formidable challenge to Chinese autonomous driving enterprises venturing abroad.

Radish Go's overseas expansion represents not only China's autonomous driving technology's international presence but also showcases the competitiveness of domestic travel platforms and intelligent driving solution providers.
According to a research report by Huajin Securities, China's Robotaxi enterprises fall into two main categories: autonomous driving technology companies and traditional automakers. Among them, technology companies like Radish Go, WeRide, and Pony.ai have made significant progress in landing cities and test mileage. While traditional automakers started road testing later, they are accelerating Robotaxi deployment through collaborations with autonomous driving technology providers.
While Chinese automakers, travel platforms, and intelligent driving solution providers are actively deploying, only a handful, including Radish Go, have achieved large-scale and routine testing in China. Despite a gap with international leaders, Radish Go's progress showcases China's potential and hope in autonomous driving technology.
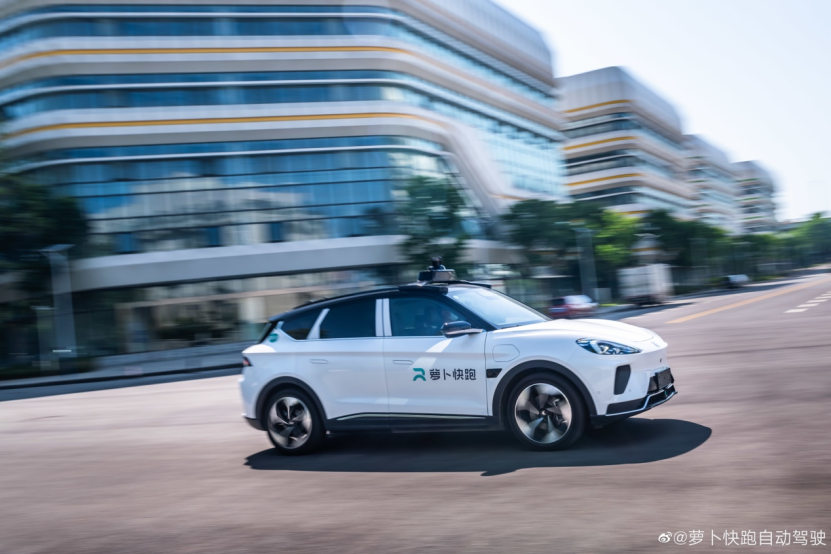
Currently, Radish Go's services have expanded to over ten Chinese cities, offering driverless ride-hailing in several of them. Technologically, Radish Go is confident and capable of competing head-to-head with international giants like Tesla.
Safety remains Radish Go's core focus in autonomous driving. By June 2024, its autonomous vehicles had traveled over 100 million kilometers in real-world tests and demonstration runs without significant casualties. Additionally, it provides insurance coverage of up to RMB 5 million per vehicle and passenger. Over the past two years, Radish Go's accident rate was only one-fourteenth that of human drivers.

In autonomous driving technology, Baidu Apollo has achieved new breakthroughs through large model technology. At the Apollo Day in May, Baidu unveiled Apollo-ADFM, the world's first large model supporting L4 autonomous driving. This technology has significantly improved safety and generalization, outperforming human drivers by over tenfold in safety and capable of covering complex urban scenarios.
China's vast automotive market offers ample opportunities for autonomous driving technology commercialization, enabling rapid deployment in specific areas. Comprehensive industrial supporting facilities and robust policy support have also fostered a favorable environment for autonomous driving technology development, driving the rapid advancement of key technologies such as high-precision maps, LiDAR, and in-vehicle computing chips in the autonomous driving industry.
These advantages not only nurture Radish Go's growth but also lay a solid foundation for the thriving Chinese autonomous driving industry as a whole.
Overall, the development of autonomous driving is accelerating, with increasingly fierce competition between China and the United States. Radish Go (under Baidu), Google Waymo, and Tesla's Robotaxi are shaping a "big three" competitive landscape in the global autonomous driving sector. Each boasts technological advantages and demonstrates strategic layouts in commercialization.
Radish Go's aggressive pursuit of a global strategy marks a significant step forward for Chinese enterprises in the autonomous driving field.
In reality, overseas markets generally demonstrate high acceptance of autonomous driving, particularly in the Middle East's United Arab Emirates and Southeast Asian countries like Thailand and Singapore, where policies are relatively open. In technology-leading regions like the US and Europe, intense competition is already underway.
Under these circumstances, it's time for Chinese autonomous driving enterprises, with their vast automotive market, comprehensive industrial supporting facilities, and technological accumulation, to venture abroad and test their mettle in international markets. Radish Go, having achieved large-scale and routine testing in multiple cities, is leading the strategic layout, showcasing China's ambition to accelerate the globalization of autonomous driving.
While Made-in-China Radish is already off to a fast start, China's autonomous driving sector now faces a dual challenge from US giants Waymo and Tesla. As the global competition in autonomous driving intensifies, domestic Radish must sprint faster to seize the high ground of technological innovation.