"Chip Wars: Qualcomm, the King of Cockpits, Takes on NVIDIA, the Master of Autonomous Driving"
![]() 10/25 2024
10/25 2024
![]() 474
474

Since the beginning of this year, Qualcomm has placed increasing emphasis on its automotive business. Following its success in PC and mobile chipsets, Qualcomm has also introduced self-developed CPUs for its automotive chips.
On October 23, after unveiling its latest flagship mobile SoC, the Snapdragon 8 Elite, Qualcomm dedicated an entire day to the announcement of the Snapdragon Cockpit Elite Platform and the Snapdragon Ride Elite Platform. These two platforms cater to smart cockpits and autonomous driving, respectively.
According to Nakul Duggal, general manager of Qualcomm Technologies' automotive, industrial solutions, and cloud business group, both platforms are scheduled to ship samples in 2025.
The Snapdragon Cockpit Elite Platform supports up to 16 4K high-resolution displays, with a new GPU offering triple the performance, enabling real-time ray tracing and immersive 3D experiences. Additionally, the NPU boasts a 12-fold increase in AI performance, capable of handling large language models with billions of parameters.
Meanwhile, the Snapdragon Ride Elite Platform supports over 40 multi-modal sensors and cameras, enabling environmental recognition across various conditions.
"Both platforms adopt a unified architecture, namely Qualcomm's Oryon CPU, specifically designed for automotive applications, which offers a three-fold speed improvement over its predecessor," said Nakul. This allows automakers to seamlessly run digital cockpit and autonomous driving functions on the same SoC.

With new products come new partnerships. At the event, Qualcomm announced its collaboration with Google to leverage Qualcomm's Snapdragon Digital Chassis and Google's in-vehicle technology to provide a standardized reference framework for developing generative AI-enhanced digital cockpits and software-defined vehicles (SDVs). Future Mercedes-Benz and Lixiang models will also adopt Qualcomm's Snapdragon Cockpit Elite Platform.
Interestingly, shortly after the announcement, Bloomberg reported that ARM had abruptly notified Qualcomm of its intention to terminate their architecture licensing agreement, six months earlier than scheduled. The two companies were originally set to resolve a two-year-long legal dispute in the Federal Court of Delaware in December.
As a major ARM customer, ARM's decision, while seemingly detrimental to both parties, reflects its desire to gain a stronger voice in the AI landscape.
01 New Product from the Cockpit "King"
Although mobile chipsets remain Qualcomm's core business, accounting for over 60% of its revenue, Qualcomm's automotive business has emerged as the fastest-growing segment this year. In the third quarter of fiscal year 2024, Qualcomm's automotive chipset revenue surged 86.9% year-over-year to $811 million, primarily driven by the growth of its cockpit business.
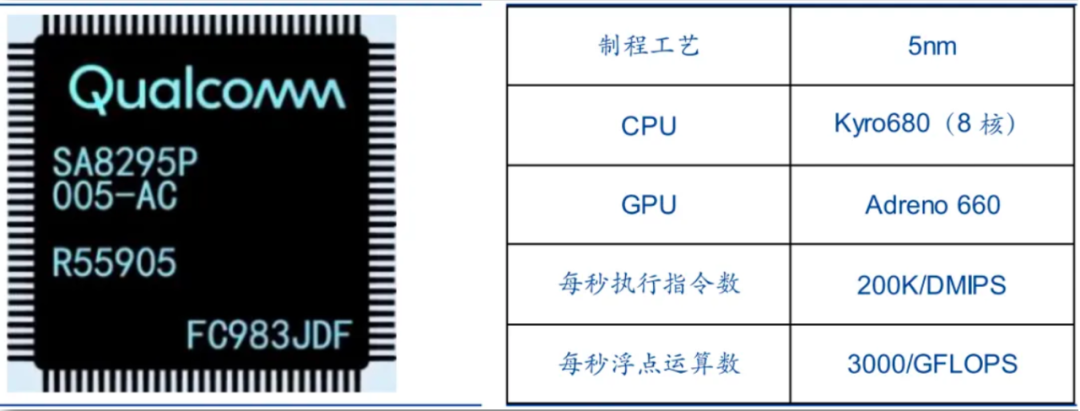
Key Performance Parameters of Qualcomm Snapdragon SA8295P
According to Sigmaintell data, Qualcomm held approximately 67% of the installed base share in China's passenger vehicle cockpit chip market in the first half of 2024, maintaining its top position. This achievement is largely attributed to its SA8155 and SA8295P cockpit chips.
While these two chips lead the cockpit chip market, they are not exactly "new." The flagship SA8295P, for instance, utilizes the Adreno695 GPU, which shares the same architecture as the Snapdragon 8cx Gen3 released in 2022.
The newly launched Snapdragon Cockpit Elite Platform, however, features Qualcomm's self-developed Oryon CPU, offering a three-fold performance improvement over its predecessor. This enables simultaneous operation of multiple applications without any performance loss or latency, ensuring seamless cross-domain and cross-system functionality in vehicles.
In other words, it supports the simultaneous use of multiple apps on the in-vehicle infotainment system.

Significant Performance Boost with the Snapdragon Cockpit Elite Platform
Qualcomm claims that the heterogeneous platform, enabled by software virtualization and multi-operating system support, offers flexible centralized processing, enabling the seamless operation of multiple applications without compromising performance. Automakers can also develop configurable software-defined vehicles (SDVs) across all tiers, simplifying vehicle architecture while maintaining flexibility and scalability.
The Elite Automotive Platform adopts Qualcomm Technologies' comprehensive software stack, supporting hardware virtualization through a Type-1 hypervisor that allows multiple client virtual machines with unique operating systems to run independently and concurrently without interference.
The platform's latest DPU display processing unit is also more powerful, supporting up to 16 4K high-resolution displays simultaneously.
The dedicated neural network processor (NPU), designed for multi-modal AI, aims to offer a 12-fold performance improvement over previous cockpit platforms. It supports real-time processing of external and in-vehicle data, enabling the handling of large language models with billions of parameters. This enhancement strengthens real-time decision-making, adaptive responses, and proactive assistance capabilities.
Overall, the chip's technical architecture resembles that of mobile devices, with similar CPU, NPU, and GPU configurations, gradually unifying hardware architecture.
However, there are slight differences in specific scenarios and functions. For instance, automotive chips incorporate dedicated radar, lidar sensor modules, and camera ISP modules.
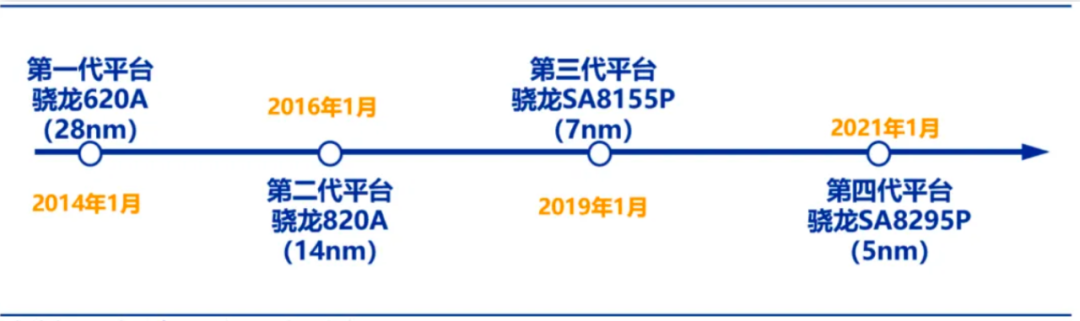
Qualcomm's Journey in Cockpit Chip Iterations
From the launch of its first-generation cockpit chip, the 602A, in January 2014, to the second-generation Snapdragon 820A platform in 2016, and subsequently the Snapdragon SA8155 and Snapdragon SA8295P, Qualcomm has leveraged its Android ecosystem advantage to virtually dominate the high-end automotive cockpit market over seven years and four generations.
Now, Qualcomm has unveiled the Snapdragon Cockpit Elite Platform, marking a new milestone with its updated architecture and accelerated deployment.
02 Strategic Shift: Autonomous Driving Begins to "Bloom in Multiple Places"
If Qualcomm is the "King" of smart cockpits, it has struggled to assert itself in the autonomous driving arena.
As early as January 2020, Qualcomm introduced its Snapdragon Ride autonomous driving platform, featuring a scalable and modular high-performance heterogeneous multi-core CPU, energy-efficient AI and computer vision engines, and a GPU. The platform also includes the Snapdragon Ride safety system-on-chip, safety accelerator, and autonomous driving software stack.
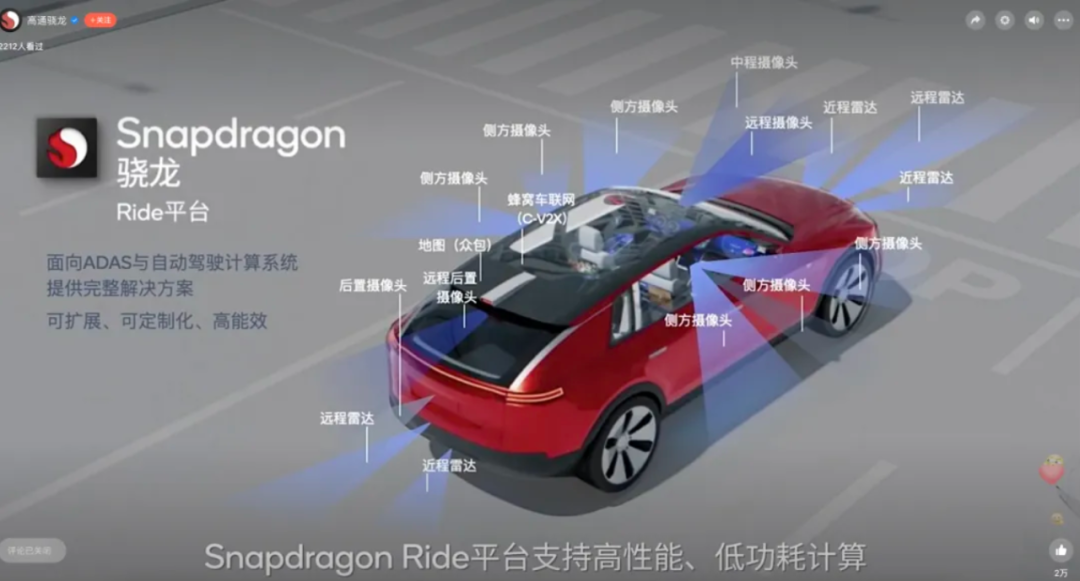
Qualcomm Snapdragon Ride Platform
Shortly after, Qualcomm announced partnerships with automakers such as General Motors, Great Wall Motors, and BMW to integrate the Ride platform into their next-generation vehicles, with mass production models set to roll out soon.
Initially, Qualcomm aimed to establish a comprehensive hardware and software strategy. In 2021, it invested heavily in acquiring Arriver, intending to bolster its autonomous driving algorithm software capabilities. Shortly thereafter, Qualcomm and BMW announced their collaboration, including the development of autonomous driving solutions for BMW.
However, sources told CyberAuto that the Arriver acquisition was effectively a failed investment, as the partnership with BMW encountered difficulties, and Qualcomm subsequently did not pursue further software-related projects.
For a long time, there was little news of Qualcomm's autonomous driving chips reaching the market, particularly in the high-end segment.
But this year, the Snapdragon Ride computing platform has seen a surge in design wins, seemingly turning the tide overnight.
Around the Beijing Auto Show, Qualcomm announced collaborations with Momenta and DJI, involving automakers like Toyota, FAW, and BYD. Honsun Electronics and Nezha Automobile also announced partnerships with Qualcomm.

Qualcomm and Momenta Announce Collaboration
Recently, Qualcomm announced a partnership with autonomous driving developer Yuanrong Qixing.
Behind these collaborations lies Qualcomm's refined business model: focusing on hardware, fostering an open development ecosystem, and offering cost-effective solutions.
In the case of Momenta, sources close to Qualcomm told CyberAuto that Momenta primarily decides on chip selection, with automakers directly engaging with Momenta to purchase comprehensive autonomous driving solutions. Qualcomm primarily provides chips, surrounding development toolchains, and underlying software.
As a hardware provider, Qualcomm boasts significant advantages. Its ecosystem is highly open, offering more flexibility in software algorithms and scenario functions (in contrast to NVIDIA's focus on graphics and image processing toolchains).
Naturally, third-party software algorithm developers like Momenta prefer such flexible deployment options when selecting chips, leading to increased orders.
03 Gradual Unification of Hardware Architecture Amid the AI Trend
However, this alone may not be enough to challenge NVIDIA's position, especially as high-performance chips remain a focal point for next-generation platforms.
On the one hand, the trend of cockpit and autonomous driving integration is unstoppable, necessitating both high performance and functional segregation in chip design. On the other hand, the increasing demand for large language models is driving up compute requirements, a consensus within the industry.
We can see this reflected in products like NVIDIA's Thor, Horizon Robotics' Journey 6, and Qualcomm's Snapdragon Ride Flex, where high performance and cockpit-driving integration are fundamental requirements.

At this stage, software capabilities may be a crucial aspect Qualcomm can no longer ignore, given the strong coupling between large neural network models and chip architecture design.
With the introduction of the Snapdragon Ride Elite Platform, Qualcomm may seek to address this software "gap."
According to Qualcomm, the Snapdragon Ride Elite Platform is designed for the industry's transition to software-defined vehicles. It offers an end-to-end solution, emphasizing software reusability through a unified software framework for upgradability. The platform aims to accelerate feature development, simplify software development processes for continuous improvement, and expedite time-to-market for new features and services through cloud-based workbenches.
Its NPU is equipped with Transformer accelerators and vector engines, supporting mixed precision for low-latency, high-precision, and efficient end-to-end Transformers, optimizing energy efficiency and performance.
"The Snapdragon Ride Elite Platform embodies the concept of software virtualization, providing an end-to-end autonomous driving system with advanced features like visual perception, sensor fusion, path planning, localization, and vehicle control, all running independently and without interference," said Nakul.

Simultaneously, its camera system and image signal processor (ISP) offer clear and responsive visuals under extreme driving conditions, supporting over 40 multi-modal sensors, including up to 20 high-resolution cameras for 360-degree coverage and in-cabin monitoring.
In terms of user experience, the new platform supports context-aware applications designed for hands-free autonomous driving, enabling real-time driver monitoring and enhanced object detection.
Regarding safety, the platform is designed to meet the ASIL-D automotive safety standard, utilizing a dedicated safety island controller and robust hardware architecture for isolated and non-interfering operation, contributing to reliable service quality for specific ADAS functions.
While performance enhancements are crucial, Qualcomm's strategic shift is equally important.
Upon closer inspection, Qualcomm previously distinguished between cockpit and autonomous driving chips. However, during the recent event and in subsequent materials, Qualcomm rarely emphasized whether a platform was for the "Snapdragon Cockpit" or "Snapdragon Ride."
Furthermore, Nakul stated that automakers can seamlessly run digital cockpit and autonomous driving functions on the same SoC.
Behind this strategic shift lies the gradual unification of hardware architecture amidst the AI trend.
"Qualcomm is transforming into an AI-processor-driven connected computing company. AI represents the most disruptive change in mobile computing today," said Cristiano Amon, President and CEO of Qualcomm, during the event's opening speech. The newly launched Snapdragon 8 Elite mobile SoC, he added, "heralds a new era of generative AI on the device side."

Snapdragon 8 Elite incorporates the second-generation custom Qualcomm Oryon CPU, Qualcomm Adreno GPU, and enhanced Qualcomm Hexagon NPU, enabling multimodal generative AI applications on smartphones powered by Snapdragon platforms.
Qualcomm's official implementation of the Oryon architecture on mobile phones has indeed set a precedent for ARM, demonstrating Qualcomm's capability to design top-tier chips from the ground up, extending this capability into the automotive sector as well.
Faced with this situation, how could ARM not feel a sense of urgency?
After all, amidst the AI wave, the strategies of chip manufacturers will become even more intense. Naturally, this will also spur the creation of more imaginative products.