AI Search Wars: Where Have the Bullets Flown?
![]() 11/18 2024
11/18 2024
![]() 539
539
This article is written based on public information for the purpose of information exchange only and does not constitute any investment advice

On October 28, The Information reported that Meta is developing its own "AI-driven search engine" to reduce dependence on Google and Microsoft Bing. Meta's search will use generative AI to summarize user-input keywords or prompts.
On October 29, Google disclosed in its latest earnings report that AI Overviews have become popular among search engine users and will expand to 100 new countries, reaching 1 billion people. It has extended search advertising to Overviews, contributing to its strong earnings report.
On October 31, OpenAI released its AI search product, SearchGPT, adding fuel to the generative AI search trend.
On November 5, AI search startup Perplexity AI finalized its fourth round of funding in 2024, valued at $9 billion. It's hard to say that OpenAI's actions didn't reassure Perplexity's investors. Perplexity's valuation has tripled in a year, from $520 million at the beginning of 2024 to $3 billion by the end of June and $9 billion by the end of October.
The frequent actions of industry leaders alert us: Could AI search be the most significant narrative of the generative AI era?
01
Proposition Background and Analysis Framework
In February this year, Gartner released an analysis report stating that the rise of generative AI and AI agents will cause traditional search engine traffic to decline by 26% by 2026, within just four years from 2023 when generative AI officially entered the mainstream.
The mechanisms behind this report are currently unknown. But our analysis shows that generative AI is indeed capturing search engine users and addressing their needs.
Remember when ChatGPT first came out in 2023, many friends and colleagues exclaimed that it was much better than Baidu and Google! I wonder if Pichai and Robin Li would shiver at the thought.
When first encountering AI chatbots like ChatGPT, most people used them for everyday Q&A needs, gradually expanding to office assistance, writing inspiration, language learning, translation, etc.
As generative AI becomes more prevalent, ordinary users who don't understand or care about technology have become the mainstream. Based on our observations, we estimate that over 60% of users are not proficient in prompt techniques. The prompts they input to AI are essentially the same as keywords input to search engines. For such users, AI chatbots are search engine alternatives.
Moreover, AI chatbots' friendliness and speed in handling general questions already show potential to replace search engines. At least 10 out of the 100 search needs we once met with search engines can now be met by generative AI – this may be the logical basis for Gartner's 26% prediction.
With AI technology advancements, once-criticized issues like hallucinations and fabrications are on the path to resolution.
How do we determine if a sought-after emerging trend will become a towering industry – will AI search, as giants are betting on, become a new cash cow comparable to traditional search engines?
For this proposition, my research is divided into two stages: 1) Identify an analysis target, 2) Use common sense to analyze the company.
Fortunately, the AI search field offers good observation samples. Within this nascent industry, the few observation targets we have clearly fall into two categories: generative AI giants developing AI search to complement their product matrices, like Meta, Google, and OpenAI's search; and vertical AI search enterprises like Perplexity.
In the relatively niche AI search sector, Perplexity is one of the earliest players, and its technical direction, product actions, and business model can define the future direction of this sector, leading other players.
02
In-depth Analysis of AI Search with Perplexity as an Example
1. User Base
Perplexity shares limited public data, so our research method involves estimating key indicators like user volume based on multiple foreign media reports and third-party data platforms like Similar Web and Qimai.
The primary indicator is search queries.
Reports state that Perplexity processed about 230 million search queries monthly in August 2024, increasing to 400 million by October, an eightfold increase in queries over 12 months.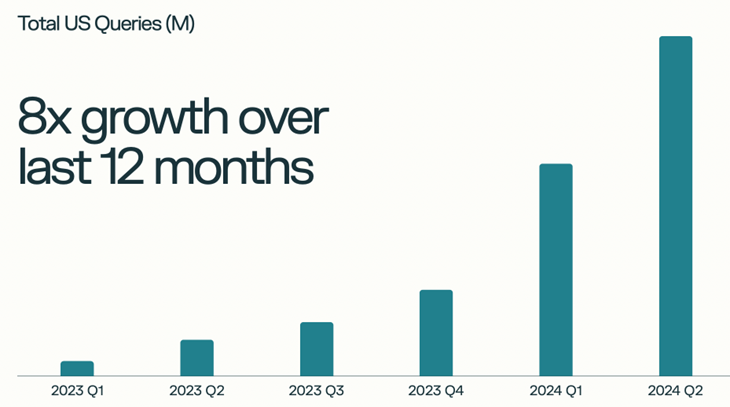
Next is user volume.
According to Similar Web data, weekly web visits range from 16 to 19 million, with about 72 million monthly visits.
On the mobile app side, based on Perplexity's pitch deck for advertisers, cumulative downloads reached 2 million in August, with 7.5 daily queries per DAU. Combining this with monthly search query data, we roughly estimate its DAU at around 1.7 million, with 55% active on web and 45% on mobile.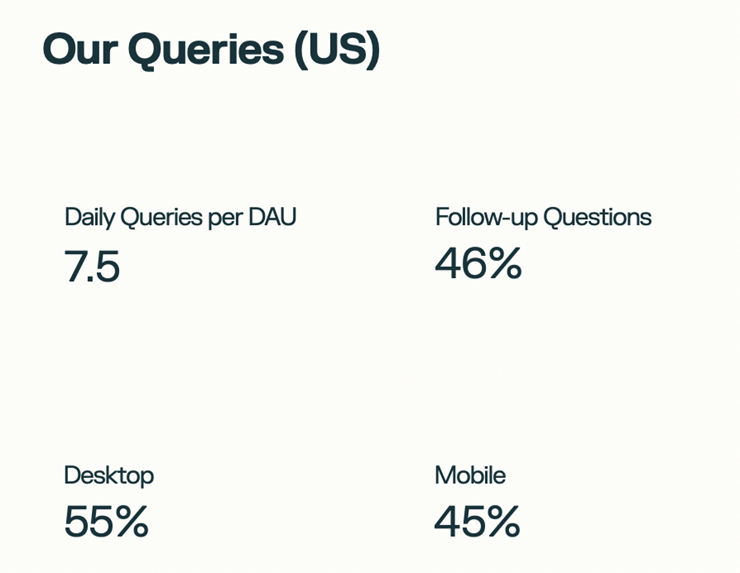
2. Business Model
Subscription
Perplexity offers free search query services, but if users are unsatisfied with the results, they can choose other models to regenerate answers. Some advanced models require the Pro version, currently priced at $20 per month.
In October 2024, The Wall Street Journal reported that Perplexity's annualized revenue was about $50 million, almost entirely from subscriptions.
Relying solely on subscription revenue in the tens of millions Obviously with $9 billion valuation doesn't match. Perplexity needs to explore more revenue streams or delve deeper into AI search advertising to prove its worth to investors.
Advertising
Perplexity plans to launch its advertising business in Q4 and has already sent pitch decks to advertising agencies.
Analyzing this document, we find that Perplexity's current advertising business model is relatively simple and basic, with an experimental nature in ad placement and data dashboards provided to advertisers.
Perplexity's ad placements focus on the Answer page, with positions like Answer page takeover, Sponsored "Related Question" below answer, Sponsored media alongside answer, and Additional branded explanatory text. These positions revolve around the summary of user search results.
Unlike Google search, which uses traditional web crawling and ranking to display multiple web links, AI search results are primarily text blocks with limited ad insertion points, potentially affecting user experience if not handled well.
Perplexity's current ad placements show ingenuity within its product design but may still impact user experience. While banner ads are easily identifiable, text link ads like "Additional branded explanatory text" are harder to distinguish and more likely to be clicked by mistake.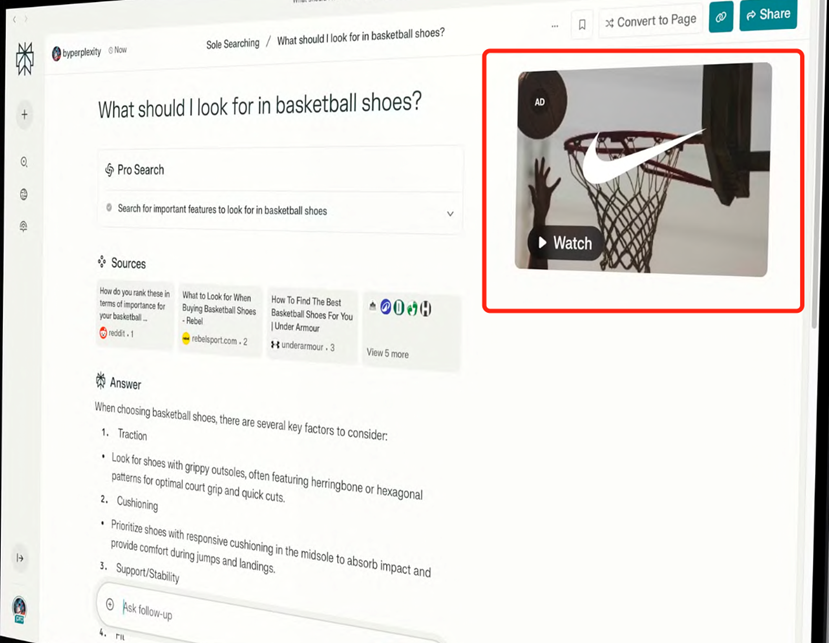
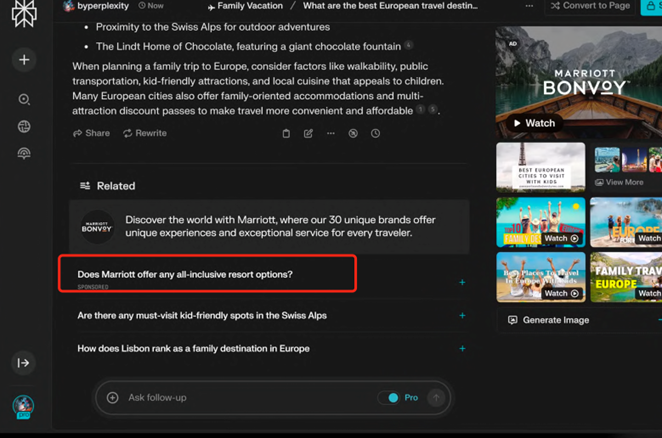
Perplexity hasn't provided ad placement or billing methods yet, stating that it will launch advertising in Q4 and initially open to 15 industries. However, we haven't encountered any ads in recent days.
Google has strict guidelines for traditional search engine advertising, making it challenging for Perplexity to stand out and gain acceptance from advertisers and agencies.
The biggest challenge is how Perplexity can prove it offers better value than Google.
3. Revenue Sharing Plan
In June 2024, amidst media scrutiny and complaints from major web media giants about content theft, Perplexity announced a revenue sharing plan in July 2024 to address content sourcing and pave the way for future commercialization.
The sharing model is: When a user asks a question and Perplexity generates ad revenue by citing a publisher's article in the answer, it shares a portion of that revenue with the content provider. Conversely, if user interaction with the content doesn't generate revenue, no sharing occurs. The interaction likely refers to future ad clicks.
To help publishers optimize their output and understand which content is popular, Perplexity partners with ScalePost.ai to provide data analysis services for cited content, similar to SEO optimization. Now, content producers must navigate both Google's SEO rules and work for Perplexity.
03
When Will AI Search Replace Traditional Search?
Our recent analysis of Perplexity has left us with significant uncertainty:
Part of this uncertainty stems from search engines already being perfectly defined by Google and Bing. New challengers haven't completely overturned the old empire, facing excessive attention and criticism for the turbulence they cause. Perplexity's response has been too simplistic, and the old empire isn't willing to be replaced, already on a path of self-renewal.
The same applies to traditional players in AI search. Google must confront both new and old versions of itself. The AI Overview already launched on search results pages hasn't garnered praise but criticism due to the ineffective Demini model.
We triggered AI Overview while using Google search and found the summary of results too broad, providing less useful answers than reading multiple search results ourselves.
OpenAI stands out in the generative field, with other large models competing against it after launch. SearchGPT also impressed users upon launch. But what others consider crucial, AI search, is just a strategic complement for OpenAI.
Judging by OpenAI's current product deployment, search isn't a priority. Voice, vision, and model iterations – the foundations of OpenAI's business – require significant funding and manpower.
When will AI search revolutionize traditional search? In our view, it's unlikely in the next one to two years, at least not for Perplexity.
The primary issue is technical implementation. There may be a huge technological gap between AI and traditional search. It's not just about scraping web content and summarizing it with a large model. If that were the case, Google's Gemini would have taken off already.
Search is an ecosystem involving not just search engine companies but every webpage owner worldwide – content providers. Will they cooperate, produce content according to your search rules, and optimize their pages?
Traditional search engines have set global standards more universal than laws or the UN Charter, not easily broken in one to two years, likely not by a single entity.
From a user perspective, search engine results provide content quality and reliability ordering through page ranking. Users only need to click and view from top to bottom, judging if the content meets their needs.
In contrast, AI search typically provides a seemingly "comprehensive" result but can't guarantee reliability. For in-depth understanding, users must re-enter keywords or click related questions. Users can't control this process; AI decides smoothness and satisfaction. It's uncertain if and how many searches are needed for a match.
At least for now, AI search has a long way to go before replacing traditional search engines. But new things always have extra vitality, attention, and forgiveness, like people being more lenient with children's mistakes. So, AI search players should seize the opportunity and boldly try and error.