Can Google hold onto the crucial threshold of a $2 trillion market capitalization?
![]() 12/09 2024
12/09 2024
![]() 626
626
Preface:
Since 2024, driven by artificial intelligence, two of Google's main businesses have achieved rapid growth, catapulting the company into the ranks of publicly traded companies with a market capitalization of $2 trillion for the first time in April this year.
This makes Google the fourth company globally, after Microsoft, Apple, and NVIDIA, to cross this significant threshold.
Author | Fang Wensan
Image Source | Network

Core Business Continues to Grow in Q3 Financial Report
Before the release of its third-quarter earnings report, which exceeded market expectations, Alphabet Inc., Google's parent company, announced its financial results for the third quarter ending September 30, 2024.
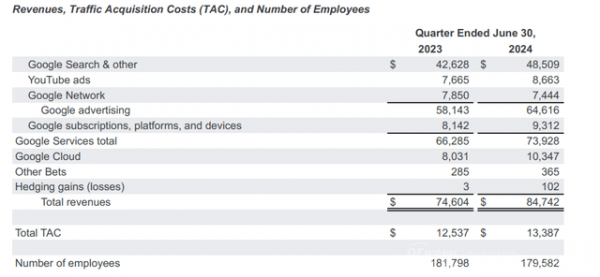
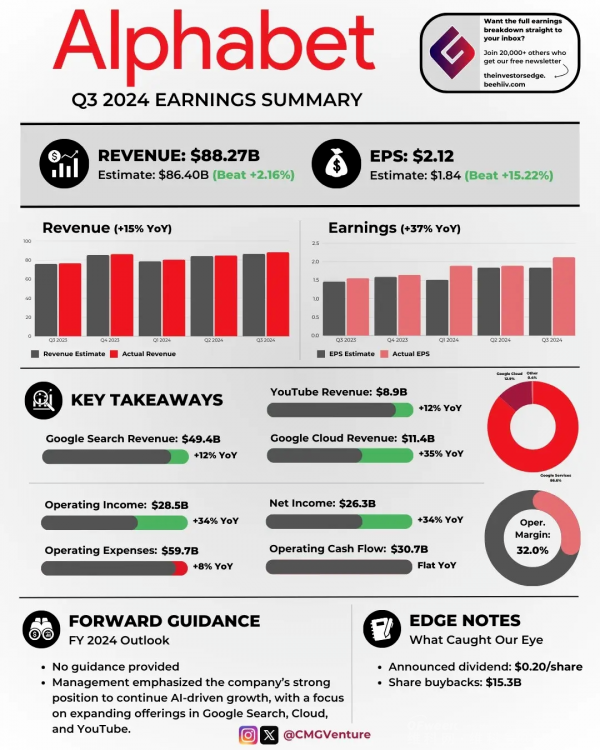
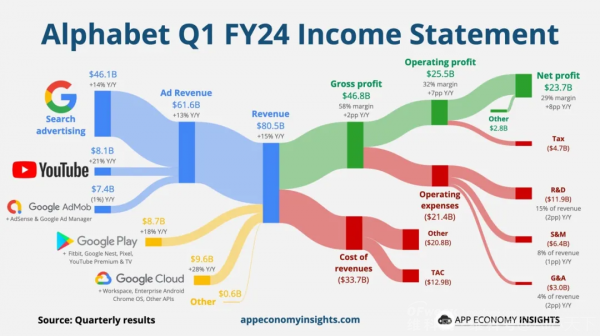
According to the report, Google's revenue for the third quarter of this year reached $88.268 billion, a 15% increase year-on-year, exceeding analysts' forecast of $86.44 billion;
Under Non-GAAP (Non-Generally Accepted Accounting Principles), net income was $26.301 billion, a 34% year-on-year increase;
Diluted earnings per share were $2.12, a 37% year-on-year increase, exceeding market expectations of $1.83.
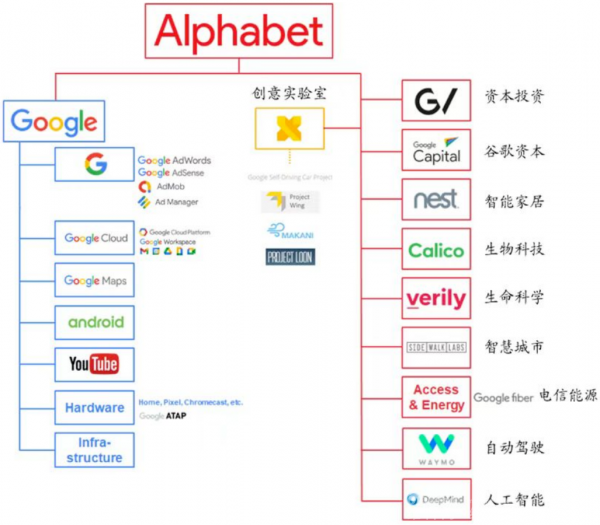
From the revenue structure analysis, Google's main business is divided into three parts: Google Services, Google Cloud, and Other Google Investments (including AI, robotics, autonomous vehicles, healthcare, etc.);
Among them, Google Services are further divided into Advertising Business and Other Google Services (including Google Play, hardware, YouTube subscription revenue). Within these businesses, the advertising business and cloud business constitute the company's two core pillars.
According to the financial report, in the third quarter of 2024, Google Services generated revenue of $76.510 billion, a year-on-year increase of over 12%;
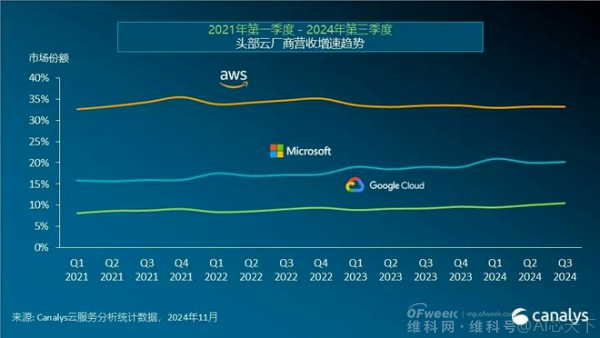
Google Cloud's revenue increased from $8.411 billion in the same period last year to $11.353 billion, a 35% year-on-year increase;
Revenue from emerging businesses, including driverless and robotics, was $388 million, also higher than the $297 million in the same period last year.
As the company's core business, Google's advertising business increased from $59.647 billion in the same period last year to $65.854 billion, exceeding market expectations of $65.5 billion.
Among them, revenue from search advertising increased from $44.026 billion in the same period last year to $49.385 billion, a 12% year-on-year increase and the primary contributor to the company's revenue growth;
Revenue from YouTube advertising was $8.921 billion, a 12% year-on-year increase, slightly slower than the growth rate in the second quarter (13%).
AI Product Demand Drives Strong Cloud Computing Performance
Regarding this, Sundar Pichai, Google's CEO, stated during the third-quarter earnings call that seven of Google's products and platforms with over 2 billion monthly active users are currently integrating the Gemini model, and 30% of existing customers have adopted a deeper portfolio of AI products;
Simultaneously, Google is internally leveraging AI technology to optimize coding processes, enhance productivity and efficiency, with over a quarter of new code generated by AI technology.
Although Google was one of the first companies to propose the concept of cloud computing, it once lagged behind giants like Amazon, Microsoft, and Alibaba in this field.
Since Thomas Kurian, the former president of Oracle, took over as CEO of Google Cloud, the company has continuously increased investment in technological innovation, product development, and market expansion.
According to official data, as of September 2024, user adoption of Google's enterprise AI platform Vertex has significantly increased, while the number of Gemini API calls has increased nearly fourteenfold in the past six months.
In fact, among major cloud service providers, Google Cloud has seen the most significant AI-driven revenue growth, with its revenue growth rate also leading the pack.
AI Overviews in Search Addresses the Impact of AI Search
Since the advent of ChatGPT, discussions about the potential disruption of search engines have been relentless.
Clearly, if AI-generated content replaces search engine output, it would pose a significant threat to Google, which heavily relies on its search advertising business.
However, after observing for over a year, Google's search engine does not seem to have been significantly affected, and ChatGPT has not dealt a devastating blow to Google as search engines once did to the Yellow Pages telephone directory.
On the contrary, with the assistance of AI technology, Google still maintains a dominant position in the search field.
As of the end of February 2024, Google held a 91.02% share of the global search market.
In fact, facing challenges from competitors like ChatGPT and Microsoft, Google has not been idle.
In recent years, Google has significantly improved its search functionality using advanced AI technology.
This improvement not only enhances the quality of search results but also changes the way users interact with information.
In May 2024, Google launched the AI Overviews in Search feature in the US and expanded it to some international markets in August of the same year.
This feature integrates AI search technology from the Gemini large model, aiming to optimize AI summaries of search results and help users quickly find high-quality content.
Simultaneously, Google introduced advertising into AI Overviews, using generative AI to summarize content from various sources and provide concise results for search queries.
In October 2024, Google officially announced that its AI Overviews in Search would be rolled out to over 100 countries and regions worldwide.
This move not only provides a convenient way for over a billion monthly active users to retrieve information but also ensures that the feature is fully available across platforms such as the web, mobile devices, and browsers, enhancing the search engine experience.

Supports AI Development with Large-Scale Internal Departmental Integration
Recently, Google announced a reorganization of its finance department to allocate more resources to the field of AI.
Meanwhile, the AI model development team at Google Research will be integrated into Google DeepMind to further enhance AI development efficiency.
Although Google's market capitalization has just reached new heights, the company has taken cost-saving measures, disbanding the core team responsible for maintaining the Python infrastructure.
On April 27, news quickly spread through the tech industry that Google had disbanded its internal core team responsible for the Python infrastructure and planned to form a new Python team in Munich, Germany.
In January this year, Google CEO Sundar Pichai warned in an email to employees that layoffs would continue throughout 2024.
Pichai stated that through layoffs, Google aims to reduce management layers and accelerate product development in specific areas.
Another crucial factor is that Google's strategic focus has shifted to the development of its AI business.
To attract and retain top AI professionals, Google needs to improve the compensation of its core R&D personnel.
Although Google is a highly profitable large enterprise, Wall Street's expectations for its earnings remain high.
Therefore, cost-cutting has become part of the company's strategy.
Facing the Potential Divestiture of Chrome Browser and Google Play
On November 20, the U.S. Department of Justice officially filed a motion with the court requesting that the judge order Google to sell its Chrome web browser.
Previously, Google had been found to violate U.S. antitrust laws regarding its search business.
The Department of Justice believes that divesting Chrome from Google will give competitors the opportunity to gain their rightful market share and help break Google's long-standing monopoly on the search engine market.
Simultaneously, the U.S. Department of Justice is also considering a potential divestiture of Google's Android operating system division and Google Play store.
It is reported that the Department of Justice hopes the judge will give Google two options: either sell Android or prohibit Google from forcing users to use its services on Android-powered phones, further weakening Google's market monopoly.
Informed sources indicate that the U.S. Department of Justice is considering forcing Google to sell AdWords or, at the very least, requiring interoperability to allow seamless operation with other search engines.
As a core part of Google's ecosystem, the Chrome browser is crucial to Google's advertising business and serves as an essential traffic driver for AI products like Gemini.
If Google permanently loses control of this critical search entry point, as suggested by relevant U.S. government departments, it will have significant and far-reaching impacts on Google's core advertising business and AI products.
According to the current plan, Google can submit a revised proposal in December, and federal agencies will submit a revised proposal the following March, with the judge expected to make a final ruling in May.
If Google is ultimately forced to divest, it would be the largest U.S. corporate divestiture since the breakup of AT&T in the 1980s.
A few days ago, Google held its annual hardware event, showcasing its latest smartphone and other hardware product lines, including the Google Pixel smartphone.
During the event, Google executives demonstrated the Gemini AI effect using the Pixel and unveiled the voice mode Gemini Live, preempting OpenAI's AI voice function.
Without Android, Google would lack a hardware foundation and be unable to ensure that billions of people will prefer Gemini-driven chatbots in their daily lives.
With Gemini but without Android, Google would find itself in a predicament in this crucial area.
Currently, the likelihood of Google being divested does not seem significant.
Google's sheer size and the valuation of its individual businesses, which could rival the entire assets of mid-sized enterprises, make it extremely difficult to find suitable buyers.
Simply splitting Google into two independent entities maintaining the current model would have minimal significance.
Moreover, the firm stance of the U.S. Department of Justice is more about demanding adjustments to Google's business model and revenue sharing rather than merely divesting Chrome, which cannot substantially resolve the issue.
Conclusion:
Although Google may currently face dual threats, it does possess multiple coping strategies.
Over the past 20 years, Google has achieved remarkable success at various stages of internet development.
It has not only succeeded in AI models and applications but also demonstrated immense potential in AI cloud computing and autonomous driving technology.
On balance, Google's current valuation already reflects the risks it faces, but once market conditions improve, Google is likely to regain strong market favor.
References: Lishi Business Review: "Resilient Google, Standing at $2 Trillion", Securities Times: "Outstanding Performance! Google Joins the '2 Trillion Club'", US Stock Research Institute: "All Businesses Moving Forward Together, Will Google Continue Its 'Steady Happiness'?", Zuihua FunTalk: "Google Needs to Cling to Musk's Leg", Chuangyebang: "Google Shares Surge 15% After Earnings Report, Growth of Tech Giant Continues", Toubutech: "Market Capitalization Exceeds $2 Trillion for the First Time, but Google Disbands Its US Python Team", Hengsao Wall Street: "Google: The Most Undervalued Tech Giant"