Suspected of violating the Anti-Monopoly Law, Nvidia is under investigation in China!
![]() 12/10 2024
12/10 2024
![]() 670
670

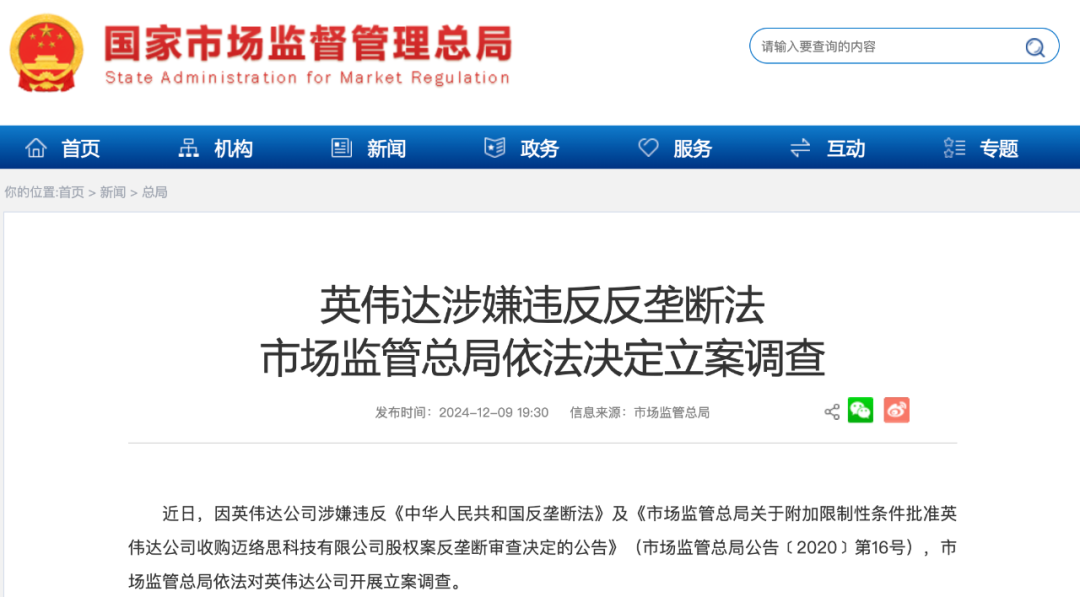
Nvidia is suspected of violating the Anti-Monopoly Law, and the State Administration for Market Regulation has decided to initiate an investigation in accordance with the law.
On December 9, the official WeChat account of the State Administration for Market Regulation, "City Talk", announced that due to Nvidia's suspected violation of the Anti-Monopoly Law of the People's Republic of China and the Announcement on the Anti-Monopoly Review Decision on Approving the Acquisition of Mellanox Technologies, Ltd. by Nvidia with Additional Restrictive Conditions (Announcement of the State Administration for Market Regulation [2020] No. 16), the State Administration for Market Regulation has initiated an investigation into Nvidia in accordance with the law.
Nvidia is under investigation
It is alleged that the investigation primarily focuses on Nvidia's acquisition of the Israeli chipmaker Mellanox in 2019.
In March 2019, Nvidia announced the acquisition of all shares of Mellanox for $6.9 billion. After the acquisition, Mellanox became a wholly-owned subsidiary of Nvidia.
Mellanox is a chipmaker that provides solutions for servers, storage, and hyper-converged infrastructure, including Ethernet switches, chips, and InfiniBand intelligent interconnect solutions.
Nvidia holds a significant share of the global GPU market, while Mellanox ranks first in the high-speed Ethernet adapter and network interconnect device markets.
Due to the vertical relationship in the data center server and general Ethernet adapter commodity markets, and the adjacent relationship in the GPU accelerator and dedicated network interconnect device, GPU accelerator and high-speed Ethernet adapter commodity markets, the merger of the two companies will have a significant impact on supercomputing, artificial intelligence, and other fields.
According to the relevant provisions of the Anti-Monopoly Law, China's State Administration for Market Regulation believes that this concentration has or may have the effect of eliminating or restricting competition in the global and Chinese GPU accelerator, dedicated network interconnect device, and high-speed Ethernet adapter markets.
After more than a year of review and communication, on April 16, 2020, the State Administration for Market Regulation issued an announcement approving Nvidia's acquisition of Mellanox with additional restrictive conditions.

In 2020, the State Administration for Market Regulation announced the approval of Nvidia's acquisition of Mellanox with additional restrictive conditions
The restrictive conditions include: First, when selling Nvidia GPU accelerators and Mellanox high-speed network interconnect devices to the Chinese market, Nvidia must not forcibly bundle them in any way or attach any other unreasonable trading conditions; it must not hinder or restrict customers from purchasing or using these products separately; and it must not discriminate against customers who purchase these products separately in terms of service levels, prices, software functions, etc.
Second, Nvidia must continue to supply its GPU accelerators, Mellanox high-speed network interconnect devices, and related software and accessories to the Chinese market based on the principles of fairness, reasonableness, and non-discrimination.
Third, Nvidia must continue to ensure the interoperability of its GPU accelerators with third-party network interconnect devices and Mellanox high-speed network interconnect devices with third-party accelerators.
Fourth, Mellanox must continue to uphold its open-source commitment for its high-speed network interconnect device point-to-point communication software and collective communication software.
Fifth, Nvidia must take protective measures for information about third-party accelerator and network interconnect device manufacturers.
The sixth and seventh items are confidential.
Currently, due to various factors, Nvidia has not met the above-mentioned additional conditions after the acquisition, leading to this investigation.
According to Article 58 of the Anti-Monopoly Law, if an enterprise violates its commitments during an acquisition and its conduct has the effect of eliminating or restricting competition, it may face a fine of up to 10% of its sales revenue for the previous year.
According to Article 63 of the Anti-Monopoly Law, if an enterprise violates the provisions of this Law and the circumstances are particularly serious, the impact is particularly adverse, or the consequences are particularly severe, the State Council's anti-monopoly law enforcement agency may determine the specific amount of the fine at twice to five times the amount specified in Articles 56, 57, 58, and 62 of this Law.
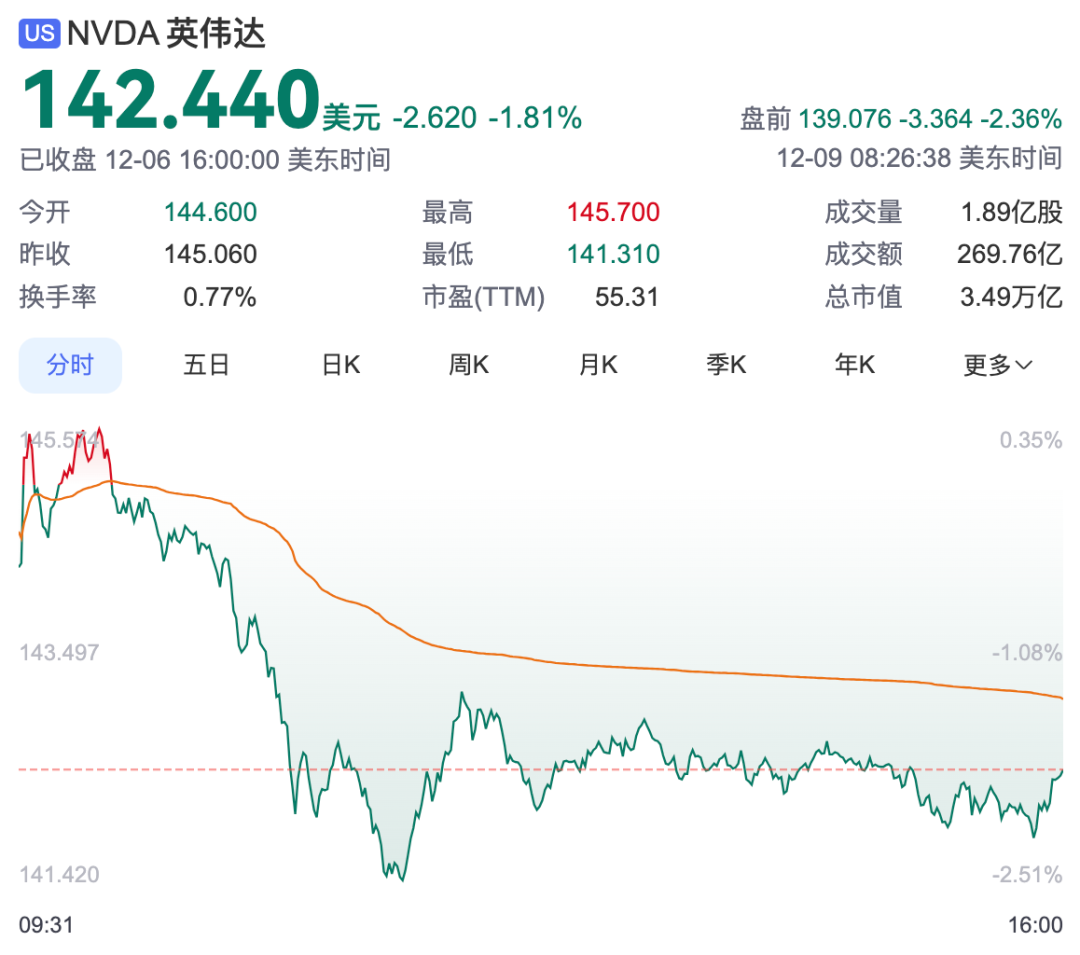
Changes in Nvidia's stock price
Affected by this, Nvidia's U.S. stock price plummeted before the market open. As of the close on December 6, U.S. Eastern Time, Nvidia's stock price was $142.44 per share.
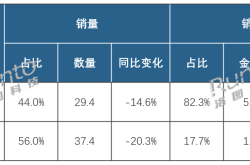
China has always been one of Nvidia's important markets, but in recent years, due to export controls, Nvidia's revenue share in the Chinese market has been declining, from approximately 24% in the 2019 fiscal year to approximately 13% currently.
According to Nvidia's latest quarterly financial report, for the third quarter of fiscal year 2025 ending October 27, 2024, Nvidia's revenue was $35.1 billion, up 94% year-on-year and 17% quarter-on-quarter; net profit reached $19.3 billion, up 109% year-on-year and 16% quarter-on-quarter.
Among them, the United States, Singapore, and China were the main sources of income for Nvidia in the third quarter. The United States contributed $14.8 billion in revenue, Singapore contributed $7.7 billion, mainland China contributed $5.4 billion, and Taiwan, China, contributed nearly $5.2 billion.
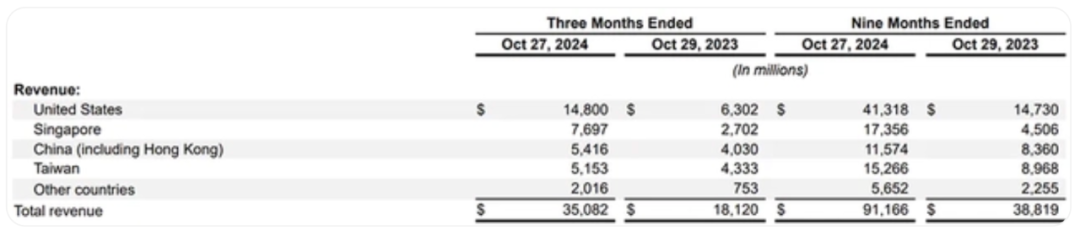
Nvidia's main sources of income in the third quarter of this year
During the earnings call, Nvidia CFO Colette Kress specifically pointed out that data center revenue in China increased quarter-on-quarter in the latest quarter, but it was still far below the level before export controls were implemented. However, she believes that the Chinese market will remain highly competitive in the future, and Nvidia will continue to comply with export controls while providing services to customers.
However, during Nvidia CEO Jen-Hsun Huang's visit to Hong Kong last month, his comments on the Chinese business were vague. He stated that Nvidia would continue to "retain" its business in China.
Meanwhile, in response to the question about what strategy Nvidia would adopt in the Chinese market in the future, Nvidia responded, "We do not comment on products that have not yet been released."
Not only in China, but Nvidia is also undergoing an anti-monopoly investigation by the U.S. Department of Justice.
In early August this year, according to a report by the U.S. magazine Information cited by Xinhua News Agency, the U.S. Department of Justice initiated an anti-monopoly investigation into Nvidia, primarily due to complaints from Nvidia's competitors that Nvidia may have abused its dominant market position when selling AI chips.
Based on this, the U.S. Department of Justice is investigating whether Nvidia is forcing cloud computing providers to purchase multiple Nvidia products. The investigation also involves whether Nvidia raises network equipment prices for customers who want to purchase AI chips from competitors such as Advanced Micro Devices (AMD).
It is alleged that the above investigation is still in its early stages.
Nvidia's B100 chip uses SK Hynix's HBM memory chip
It is worth mentioning that the United States recently imposed additional chip sanctions on China.
On December 2, local time, the U.S. Department of Commerce's Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) announced new rules for semiconductor export controls against China, adding 140 companies to the Entity List, including 136 Chinese companies, one Japanese company, one Singaporean company, and two Korean companies. At the same time, the new rules further restrict the export of 24 semiconductor manufacturing equipment and three software tools and control high-bandwidth memory (HBM) required for AI chips.
END-