NVIDIA Hits a Major Setback
![]() 12/11 2024
12/11 2024
![]() 704
704
NVIDIA's slowing growth is just a microcosm of intertwined multiple factors.
On the evening of December 9, China's State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) announced that it had initiated an investigation into NVIDIA due to suspected violations of the Anti-Monopoly Law of the People's Republic of China and the Announcement on the Anti-Monopoly Review Decision of the State Administration for Market Regulation on Approving the Acquisition of Mellanox Technologies, Ltd. by NVIDIA Corporation with Additional Restrictive Conditions (SAMR Announcement [2020] No. 16).
Upon the announcement, NVIDIA's share price immediately fell.
As of the market close on December 9 local time, NVIDIA closed nearly 3% lower, with its market value evaporating by RMB 640 billion overnight; major US semiconductor companies such as Intel, AMD, ASML, TSMC, and Arm also generally closed lower, with AMD falling by almost 6%.
However, for domestic chip stocks, this news brought positive sentiment to the capital market.
On December 10, A-share chip-related stocks saw a wave of gains. Among the stocks in the sector, the following stocks led the gains, such as Dongfang Zhizao reporting RMB 6.03 per share, up 10.04%; Shengjing Micro reaching its daily limit at RMB 46.26 per share; and Huada Jiutian reporting RMB 133.96 per share, up 8.72%...
Notably, the Chinese market was still one of NVIDIA's major sources of revenue in the third quarter.
Below-expectations performance, AI asset bubble?
As a globally renowned chip company, during the boom in global generative AI and large models, all computing power demand was converted into NVIDIA's financial report data.
According to Wells Fargo data from February this year, NVIDIA held a 98% market share in the global data center graphics processing unit (GPU) market in 2023. AMD, in second place, had a market share of only 1.2%, and Intel, in third place, had less than 1%.
On November 20 local time, NVIDIA released its fiscal third-quarter financial results for the period ending October 27, with revenue of $35.082 billion, a year-on-year increase of 94% and a quarter-on-quarter increase of 17%; net income of $19.309 billion, a year-on-year increase of 109%; and diluted earnings per share of $0.78, a year-on-year increase of 111%.
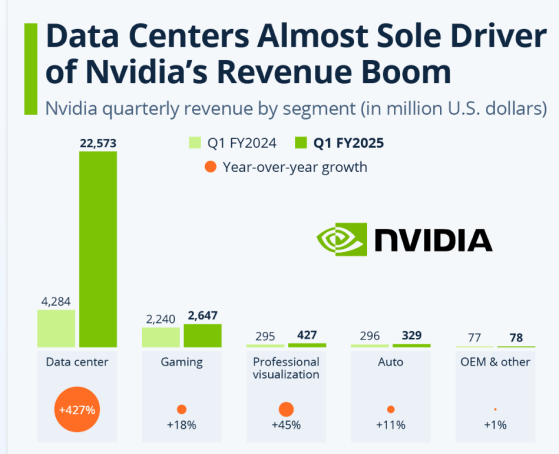
Specifically, NVIDIA's Q3 data center business revenue was $30.8 billion, exceeding market expectations of $28.82 billion. This segment contributed the majority of NVIDIA's revenue and encompassed the most market-focused AI chips.
Gaming business revenue for Q3 was $3.28 billion, compared to analyst expectations of $3.03 billion; graphics workstation chip and automotive chip revenues for Q3 were $486 million and $449 million, respectively.
NVIDIA's professional visualization business (selling graphics chips for enterprise use) had third-quarter revenue of $486 million, a year-on-year increase of 17% and a quarter-on-quarter increase of 7%.
NVIDIA's automotive business had third-quarter revenue of $449 million, a year-on-year increase of 72% and a quarter-on-quarter increase of 30%.
Meanwhile, NVIDIA provided guidance for the next quarter, predicting sales of $37.5 billion for the fourth fiscal quarter of FY2025, with a fluctuation range of ±2%, higher than the market's average expectation of $37 billion but lower than some analysts' highest expectations. NVIDIA will maintain its quarterly dividend per share at 1 cent.
Although NVIDIA's performance is still growing rapidly, the growth rate is gradually slowing down. The company's third-quarter revenue increased by 94% year-on-year, compared to growth rates of 265%, 262%, and 122% from the fourth quarter of last year to the second quarter of this year.
In fact, NVIDIA's slowing growth is just a microcosm of intertwined multiple factors.
First, the global anti-monopoly wave is targeting technology giants. Many countries and regions, including the United States and Europe, are strengthening regulation of technology giants to prevent them from forming monopolies and stifling market competition. As a leading enterprise in the AI chip field, NVIDIA has naturally become a key focus of regulatory agencies.
Secondly, NVIDIA is also facing fierce market competition.
Traditional competitors AMD and Intel are eyeing the market, continuously launching new products and technologies in an attempt to erode NVIDIA's market share. More concerningly, a group of emerging AI chip startups have also emerged, such as Silicon Valley's Cerebras, whose chips have even surpassed NVIDIA's products in some aspects.

In addition, some of NVIDIA's major customers, such as cloud computing giants like Amazon, have also begun designing and developing their own AI chips to reduce their dependence on NVIDIA.
These factors are further weakening NVIDIA's market position and profitability.
On the other hand, there is the Chinese market. According to NVIDIA's financial results, NVIDIA's revenue in mainland China (including Hong Kong) was $11.57 billion, accounting for 12.7% of its total revenue. It can be seen that the Chinese market accounts for a significant proportion of NVIDIA's revenue.
Just after the financial report was released, on November 24, a photo of NVIDIA's founder and CEO Jen-Hsun Huang drinking beer at a food stall in Sham Shui Po, Hong Kong, circulated online. Media reports stated that just ten days earlier, he had a brotherly conversation with SoftBank's founder and chairman Masayoshi Son at NVIDIA's Japan Summit.
Outsiders believe that Huang's frequent trips to Asia recently undoubtedly send many signals, especially regarding the Chinese market. However, in recent years, NVIDIA has faced many challenges in the Chinese market. In addition to this anti-monopoly investigation, NVIDIA also needs to deal with the rise of domestic Chinese enterprises and changes in policy environment.
Dealing with Many Adverse Factors
Taking the automotive industry as an example, automotive-grade chips are a core component of automotive electronic systems. Not long ago, China's new energy vehicle production exceeded 10 million units for the first time annually. With the rapid development of new energy vehicles and the increasing popularity of autonomous driving and smart cabins, the market demand for automotive chips is surging.
Data previously released by the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers showed that a traditional fuel vehicle requires 600-700 automotive chips, while an electric vehicle will require up to 1,600 chips, and more advanced smart vehicles will require up to 3,000 chips.
According to BIS Research data, the global and Chinese automotive chip markets were valued at RMB 279.364 billion and RMB 65.818 billion, respectively, in 2023, with China accounting for 23.56% of the global market. It is estimated that the global automotive chip market will grow to RMB 530.525 billion by 2029.
In 2023, Tesla's FSD chips sold over 1.2 million units in China, accounting for 37% of the market share in China's intelligent driving domain control chip market. NVIDIA's Orin-X chips sold 1.095 million units, accounting for 33.5% of the market share. Together, they accounted for over 70% of the market share.

In fact, with the increasing demand for chips from automakers, the substitution of domestically produced automotive-grade chips is accelerating.
For example, BYD has been developing automotive chips since 2004 and has become one of China's powerful automotive chip enterprises, capable of producing MCU, PIM, IGBT, and other chips. It also has its own chip manufacturing plant, achieving independent design and manufacturing.
In terms of advanced intelligent driving chips, many Chinese automakers are also making layouts, with some automakers already adopting self-developed intelligent driving chips in their vehicles. For example, Geely established Xinchip Technology as early as 2019 and released its first 7nm smart cockpit chip, "Longying No. 1," in 2021. In 2023, Longying No. 1 was equipped in the Lingke 08, and more models have since adopted Xinchip's self-developed chips. NIO's self-developed intelligent driving chip is named "Shenji," XPeng's is "Turing Chip," and Lixiang's is "Schumacher."
Moreover, before entering the automotive intelligence race, Huawei had already begun investing heavily in the third-generation semiconductor industry to promote the localization of chips, especially in the popular field of silicon carbide.
These domestically produced chips and solutions are gradually approaching international giants in performance and application scenarios, posing significant pressure on NVIDIA's development in the Chinese market.

On the other hand, changes in the policy environment also pose challenges to NVIDIA.
Affected by new regulations issued by the US government, NVIDIA's export of multiple high-end products to China is restricted. In its latest financial statements, NVIDIA mentioned that it had not yet received a license to ship restricted products to China as of the reporting date, and to its knowledge, neither its partners nor customers had received licenses to ship these restricted products.
Huang previously warned US officials, "If we are deprived of the Chinese market, we have no contingency measures. There is no other China, only one China." Huang said that the Chinese market is irreplaceable and that being unable to trade with it would cause "tremendous damage" to US companies.
Not only NVIDIA but also Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) was reported by the Financial Times to have stopped supplying advanced chips for artificial intelligence (AI) applications to mainland Chinese customers as of November 11, in response to US demands. The report pointed out that with Donald Trump winning the US presidential election this year and about to return to the White House, TSMC was particularly concerned about being viewed as "unreliable or uncooperative."

On October 28, the US Treasury finalized a new rule aimed at prohibiting US individuals and companies from investing in the development of a range of advanced technologies in China. It is understood that the restrictions focus on advanced semiconductors and microelectronics and their manufacturing equipment, technologies used in quantum computing, and artificial intelligence systems.
The change of US government administration is undoubtedly a risk that cannot be ignored for many companies, including NVIDIA, that have cooperative relationships with the government. However, analysts generally expect that chips will once again become an important part of the US plan to suppress China's normal trade.
Therefore, even though it has already reached the peak of the stock market, NVIDIA still faces a tumultuous road ahead.
A year ago, NVIDIA's market capitalization was only $1.2 trillion. This year, it has continuously created stock market myths, with its share price increasing by over 190% this year. Its market capitalization surpassed $2 trillion in February, $3 trillion in June, and regained its position as the world's most valuable listed company this month. NVIDIA has also replaced Silicon Valley chip giant Intel as a component of the Dow Jones Industrial Average.
As of the latest market close, NVIDIA's market capitalization was $3.31 trillion.
According to data from market research institutions, NVIDIA's market share in the AI chip field exceeds 80%. Undoubtedly, in the foreseeable future, the demand for NVIDIA chips will remain strong, but how to face the challenges and opportunities in the Chinese market remains uncertain.
Note: Some images are sourced from the internet. Please contact us for removal if there is any infringement.