On the Eve of the Low-Altitude Economy Boom: Riding the AI Wave
![]() 12/20 2024
12/20 2024
![]() 639
639
SHEN MOU

Original: Shenmou Finance (chutou0325)
On November 29, CATL-backed Fengfei Aviation successfully completed the maiden flight of its 2-ton eVTOL; the same day, Lanyi Aviation unveiled the full-scale engineering prototype of its passenger eVTOL LE200. On November 27, Hefei issued the "Detailed Rules for Implementing Policies Supporting the Development of the Low-Altitude Economy," while the Zhoushan Municipal Government recently released the "Opinions on Promoting the Development of the Low-Altitude Economy Industry." Furthermore, following its designation as a national civil unmanned aerial vehicle test area, the Shijiazhuang Equipment Manufacturing Industrial Park was approved as the largest drone test airspace in North China, spanning approximately 600 square kilometers and extending up to an altitude of 4,000 meters, marking a breakthrough in drone flight airspace restrictions. In the realm of AI + low-altitude economy, the first version of China's domestic "Low-Altitude Brain" was launched in Shenzhen at the end of November. As the country's first city-level low-altitude airspace digitization system, it integrates a city-level CIM base with intelligent computing power, representing a profound application of AI in empowering the low-altitude economy. At the 2024 Global Digital Trade Conference, Wang Jinping, President of the China Information Industry Association, emphasized that modern society cannot function without AI, and the low-altitude economy must keep pace with this significant trend. Over the past month, announcements related to the low-altitude economy have been frequent, highlighting the unprecedented role of AI in supporting its development. So, what revolutionary power can AI bring to eVTOL? On the cusp of the low-altitude economy's explosive growth, to what extent will AI-enhanced eVTOL reshape our travel patterns, business models, and daily lives?
01
Low-Altitude Flight: AI Takes the Lead
The low-altitude economy has transitioned from science fiction to reality at an astonishing pace. Notably, logistics and distribution, along with short-haul passenger transport, are two "pioneer" scenarios accelerating their implementation both domestically and internationally. From "air delivery" in urban streets to "air commuting" between cities, the low-altitude economy is moving from concept to practice. The core driving force behind this qualitative transformation is the comprehensive integration of AI technology. Through AI empowerment, low-altitude aircraft can achieve intelligent, precise, safe, and efficient operations, laying a technological "foundation" for the low-altitude economy to tap into the trillion-yuan market.
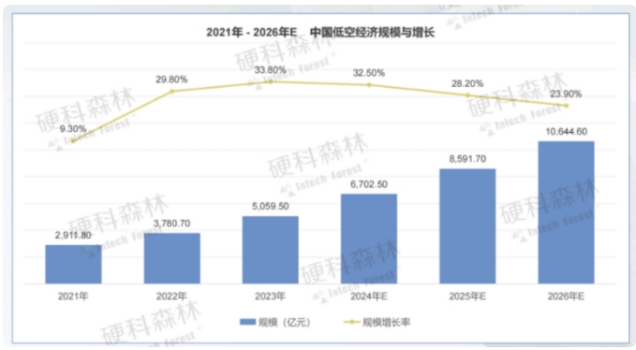
According to the "Report on the Development of China's Low-Altitude Economy (2024)" released by the CCID Research Institute of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, China's low-altitude economy reached 505.95 billion yuan in 2023 and is projected to exceed one trillion yuan by 2026. Behind this growth, AI technology stands as the most critical driving force, not only facilitating the early implementation of logistics and short-haul passenger transport but also paving the way for the construction of a smart society through the low-altitude economy.
Source: Entrepreneur Magazine WeChat Official Account
Logistics and passenger transport are just the basic applications of the low-altitude economy. Low-altitude flight holds even greater potential in emergency rescue, smart agriculture, and other fields. Here, we delve into how AI accelerates the development of the low-altitude economy and achieves cost reduction and efficiency enhancement in logistics and distribution, as well as short-haul passenger transport, two major commercial scenarios.
First, logistics and distribution are among the earliest areas where small-scale applications of the low-altitude economy have been realized, with AI technology serving as the core driving force.
Taking Meituan as an example, data reveals that in 2024, the platform's drones completed over 360,000 delivery services across 43 routes in Shenzhen, with each delivery costing only 60% of traditional methods.

Source: Southern Metropolis Daily
The key to this cost reduction and efficiency enhancement lies in the AI-driven path optimization system. Through intelligent algorithms, AI enables drones to operate efficiently, with delivery efficiency per hour exceeding that of manual delivery by over 300%.
More importantly, AI enhances the adaptability of drones in complex terrains and environments. For example, SF Express uses AI technology to plan precise routes for drones, solving the challenge of delivery in mountainous areas and islands.
Data shows that in 2023 alone, SF drones completed over 40,000 flights in remote areas of Tibet, covering 450 plateau townships and increasing delivery efficiency by 70%.
Furthermore, AI excels in logistics scheduling. For instance, Meituan's drone scheduling system, combined with 5G and big data technology, can handle the operational needs of thousands of drones per square kilometer simultaneously.
In early 2024, this system supported a daily delivery peak of over 20,000 orders in Shenzhen, providing a solid guarantee for instant retail and fresh food delivery and unlocking the potential of the low-altitude economy in broader fields.
Second, the acceleration of air travel is making short-haul passenger transport move from "science fiction" to reality, becoming another popular scenario in the low-altitude economy.
According to an ECNS report on February 27, 2024, Fengfei Aviation's 5-seater eVTOL aircraft, the Shengshilong, completed a 20-minute flight between Zhuhai and Shenzhen, saving 80% of the time compared to land travel.
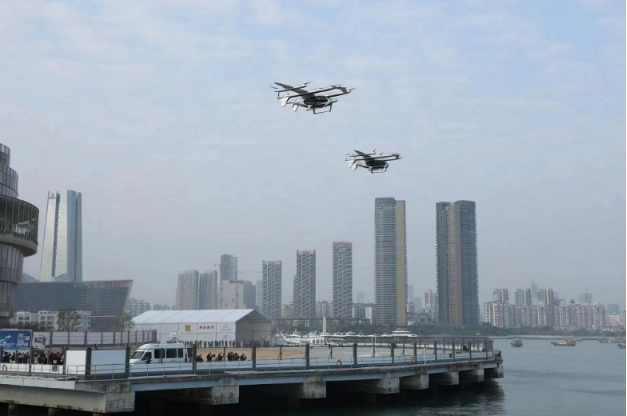

Source: ECNS
AI-enabled autonomous flight technology is becoming the core driving force for the development of air taxi companies like Joby Aviation. Its eVTOL aircraft utilizes AI algorithms to achieve automatic take-off, landing, and cruising operations, successfully completing multiple test flights in complex urban environments.
Meanwhile, Volant Aerospace's passenger management system effectively improves scheduling efficiency and passenger load factors by analyzing flight dynamics and passenger needs in real-time. In early 2024, its air taxis operating in Southeast Asia averaged 4.7 passengers per flight with a 94% passenger load factor.
Whether in logistics and distribution or short-haul passenger transport, AI is emerging as the "behind-the-scenes pusher" accelerating the development of the low-altitude economy, propelling it from its nascent stage to large-scale implementation.
02
The Low-Altitude Economy Soars: AI Escorts the Journey
For the low-altitude economy to enter the fast lane of sustainable commercial development, artificial intelligence is undoubtedly the "backbone" providing "escort" and protection. Achieving more precise, efficient, and safe low-altitude flight necessitates the empowerment of AI. Furthermore, AI can equip eVTOL with a "smart brain," effectively reducing costs and enhancing efficiency to accelerate full commercialization.
Just as intelligent driving is the "soul" of new energy vehicles, the AI intelligent driving navigation system can be considered the "steering wheel" of eVTOL. By integrating multi-source data such as BeiDou navigation and 5G communication, it reduces positioning errors to the centimeter level, providing a guarantee for commercial low-altitude flight.
Combined with LiDAR and visual perception technology, eVTOL can achieve millisecond-level response capabilities with the support of AI. For example, DJI's obstacle avoidance system can navigate obstacles within tens of milliseconds.
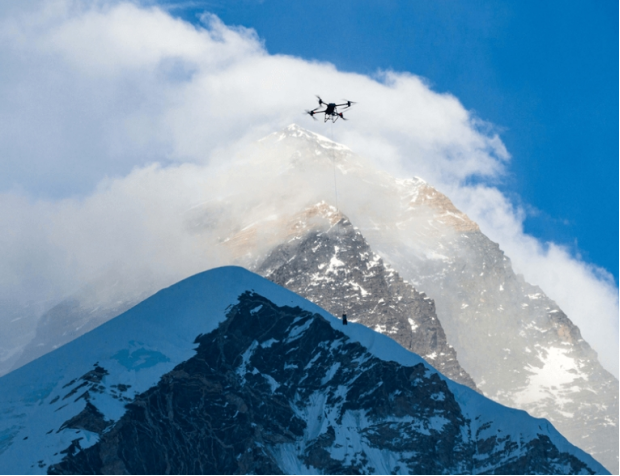

Source: DJI Official Website
In 2024, Joby Aviation's AI obstacle avoidance technology achieved a 100% obstacle avoidance success rate in complex urban environments, providing robust support for commercial low-altitude flight.
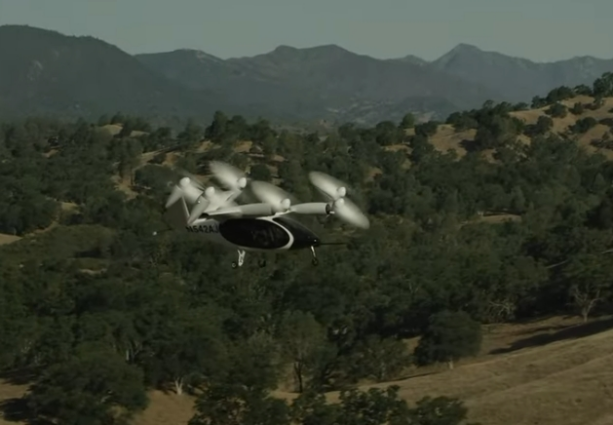

Source: Joby Aviation Official Website
Autonomous flight is another core capability of AI, endowing low-altitude aircraft with decision-making abilities such as path planning and speed control. Experimental data shows that eVTOL equipped with an AI flight control system achieves a 98% success rate in fully automated missions, significantly higher than manual operations.
AI also provides full-chain support for low-altitude flight, ensuring both safety and cost reduction and efficiency enhancement.
On the one hand, by analyzing sensor data in real-time, AI can predict potential faults in aircraft. For instance, analyzing battery status through AI can improve the accuracy of battery life predictions, thereby reducing aircraft operation interruptions.
Simultaneously, AI can optimize routes and costs by integrating flight data. In Meituan's drone delivery in Shenzhen, the AI path algorithm saved an average of 25% of delivery time and reduced energy consumption by 15%.
Even in environmental perception, AI enables real-time perception of the surrounding environment through multi-dimensional sensors, allowing aircraft to "fly more stably" in complex scenarios. According to some data, an AI perception system in Boston can reduce aircraft out-of-control rates to 2% even under windy conditions.
Moreover, AI plays a pivotal role in promoting the design and innovation of low-altitude aircraft. Leveraging AI-based simulation and optimization technology, designers can find the optimal balance between material strength and weight.
For example, Boeing uses AI to optimize materials, effectively reducing aircraft weight by 20% and increasing strength by 15%. In the manufacturing process, Airbus's AI-assisted production line shortens the aircraft production cycle by 37% and reduces costs by 20%, paving the way for commercialization.
Artificial intelligence not only drives technological revolutions across various industries but also serves as a "talisman" for the sustainable "soaring" of the low-altitude economy.
From precise navigation to data analysis, from dynamic monitoring of the "health status" of low-altitude aircraft to the intelligent manufacturing of new, lightweight, and lower-cost low-altitude aircraft, and their application in more scenarios, AI is accelerating the continuous "high flight" of the low-altitude economy.
Data suggests that the global low-altitude economy is expected to reach a scale of 2 trillion dollars by 2030. Only by allowing AI to consistently play a "core" role in this process can we drive the low-altitude economy to significantly transform travel, logistics, and production methods, among other commercialization processes.
03
Challenges Remain for Large-Scale Commercialization: Can AI Respond?
As the commercialization of the low-altitude economy accelerates, technical bottlenecks will inevitably emerge and urgently need to be addressed.
For example, issues such as insufficient battery life, poor flight stability in complex environments, and relatively low intelligence to some extent limit the large-scale commercialization of low-altitude aircraft.
So, can AI technology provide support for solving these challenges and, in turn, promote a smoother path for the low-altitude economy to embrace the trillion-dollar market?
First, battery life is a critical challenge, particularly due to the limited energy density of ternary lithium batteries, which have a short maximum endurance and cannot meet the demands of long-distance transportation.
In this regard, AI can be applied in battery management systems (BMS) to optimize the charging and discharging processes, improve battery efficiency, and extend service life by analyzing battery status in real-time.
An example is Tesla's AI battery management technology, which has been applied in the field of aircraft to enhance battery performance.
Second, flight stability in harsh environments is crucial. However, complex climates and weather conditions, especially strong winds, high temperatures, and low temperatures, significantly affect the stability of low-altitude aircraft.
AI-empowered low-altitude aircraft can leverage technologies such as LiDAR and visual sensors to improve wind resistance and optimize flight stability.
For instance, the AI stabilization system developed by the German electric flight company Volocopter can maintain flight stability under wind speeds of up to Force 8.

Source: Volocopter Official Website
Furthermore, AI can analyze historical meteorological data to predict severe weather and adjust flight paths, thereby further enhancing the safety and efficiency of aircraft in extreme conditions.
Third, the safety and scheduling of high-density flights within airspace pose a significant "bottleneck" challenge.
As low-altitude flights move towards large-scale commercialization, the density of flights within airspace increases significantly, highlighting safety and scheduling issues. In this regard, AI can intervene in the unmanned aerial vehicle traffic management (UTM) system to process flight data in real-time, enabling dynamic collision avoidance based on AI, thereby effectively reducing the risk of collisions between aircraft.
Public data shows that with AI intervention, the system can reduce collision risks by over 90% and improve airspace efficiency by 45%. Additionally, AI can optimize aircraft scheduling and path planning, ensuring safety and efficiency in high-density flight environments.
Moreover, given the trillion-dollar potential of the low-altitude economy, more and more scenarios will inevitably need to be implemented.
The greater the diversity of scenarios, the more flexible and adaptable low-altitude flight must become to satisfy a myriad of, often conflicting, demands.
In this context, AI's modular design capabilities prove indispensable, enabling aircraft to reconfigure themselves according to varying mission requirements.
For instance, in agricultural settings, AI can optimize spraying routes based on multispectral data. In multitasking scenarios, drones from Zipline International in the United States are pioneering simultaneous delivery and survey missions, supported by AI technology, thereby expanding the horizons for multi-scenario applications in the low-altitude economy.
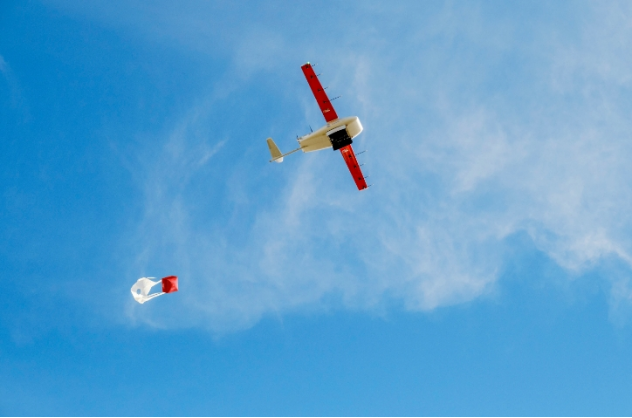

Source: Zipline Official Website
However, for the low-altitude economy to attain a trillion-yuan market size, it must pass two critical tests: cost-effectiveness and user acceptance.
On the cost front, high expenses pose a significant hurdle to the commercialization of low-altitude aircraft. AI can mitigate this by optimizing production and operational processes.
This can be achieved through various means, such as reducing manufacturing costs—Boston Dynamics, for example, leverages AI to enhance production efficiency and lower costs by 15%—or optimizing energy consumption, as demonstrated by Amazon Prime Air drones, which cut delivery costs to 30% of traditional methods.

Source: Amazon Prime Air official website
Regarding user acceptance, safety and convenience are paramount concerns.
AI technology, with its comprehensive support in these areas, can gradually instill confidence in aircraft safety, subtly enhancing user perception.
Combined with AI-driven convenience and cost savings, peak user acceptance could coincide with the low-altitude economy reaching its trillion-dollar milestone.
So, will the low-altitude economy truly become the next trillion-dollar industry? Can AI-powered flight technology revolutionize the existing business landscape? How swiftly and profoundly will this dual transformation of technology and industry reshape our daily lives? The answers loom on the horizon, filled with anticipation and mystery, leaving us to wait and see.
* Images sourced from the internet. Please contact us for removal if infringement is suspected.