["Industry In-depth Research"] DeepSeek's Surge in Popularity: Why Is the Banking Industry Feeling Anxious First?
![]() 02/07 2025
02/07 2025
![]() 519
519
Author | Meng Xiao For more financial information | BT Finance Data Hub This article is approximately 3,511 words, with an estimated reading time of 10 minutes.
Has DeepSeek's surge in popularity only disrupted the tech industry?
During the Spring Festival, the domestic large model DeepSeek emerged as a dark horse, significantly impacting the US tech industry and causing a substantial downturn in US stocks. NVIDIA, particularly hard-hit, saw its market value plummet by over 4 trillion overnight. Additionally, the share prices of other American tech giants such as Microsoft, Meta, Google, AMD, Broadcom, and Vistra also declined to varying degrees.
DeepSeek's popularity has also sparked global debates about whether AI will accelerate the disruption of various industries. Some experts believe that the banking industry may be the first to feel the brunt. According to a Caijing report, the latest surveys indicate that AI will gradually encroach on tasks currently performed by humans, with the banking industry being significantly affected. Global banks are expected to cut up to 200,000 jobs in the next three to five years. The analysts who authored the report stated that back-office, middle-office, and operational departments in banks may face the greatest risk of layoffs.

Reports indicate that the concept of front, middle, and back offices is prevalent in the banking system and can be broadly understood as follows: The front office directly interacts with customers and is responsible for marketing and service roles, such as tellers, lobby managers, and account managers. The middle office provides professional management and guidance to the front office, including risk management and product development. The back office handles more administrative and operational tasks, such as accounting, human resources, and IT support.
As AI begins to manage customers, customer service may evolve, and job responsibilities will face risks. Analysts stated, "Any work involving repetitive tasks is at risk. However, AI will not completely eliminate these tasks but will lead to a transformation of the workforce."
"AI cannot fully replace humans at this stage, but it can make banks more efficient through process optimization and save a significant amount of labor costs. If an individual's job can be replaced by AI, layoffs are inevitable," an anonymous bank marketing executive told the media. The banking industry may face a major reshuffle in the future, with a significant number of bank employees being laid off.
Will the banking industry be directly impacted by AI? Let's analyze the possibility of a major reshuffle in the banking industry by examining the changes in the total number of employees and salary proportions of major banks.
1. Decline in the Total Number of Banking Industry Employees
Currently, the 2024 annual reports of major banks have not been released, so we will use the 2023 annual reports and 2024 semi-annual or third-quarter reports as references.
As of the end of June 2024, the total number of employees at 40 listed banks was 2.5484 million, a decrease of 37,497 from the previous year, representing a 1.45% decline.
As of the end of 2023, Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (ICBC) had 419,252 employees. Compared to the previous year, the number of ICBC employees decreased by 8,335, a decline of 1.95% from the previous year, which was the largest decrease in nearly a decade. 2015 was the year with the highest number of employees at 466,300. Since 2016, the number of employees has been experiencing negative growth, equivalent to a decrease of 47,000 over eight years, with an average annual reduction of 5,857 employees. The total number of ICBC employees in the third quarter of 2024 was 408,691, a further decrease of 10,561, which was also the largest annual reduction in staff (not including the fourth quarter of 2024). Among the six major banks with over 100,000 employees in 2023, half of them experienced staff reductions.
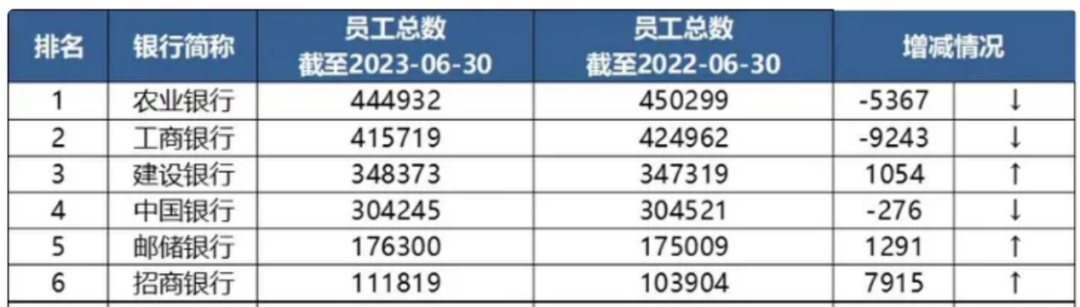
In the first half of 2024, except for Bank of China, which saw an increase in headcount, the other five major banks collectively reduced their staff by 25,422. Agricultural Bank of China reduced its staff by 4,980, second only to ICBC. Staff reductions were also common among joint-stock banks, with China CITIC Bank reducing its staff by 3,070 and Ping An Bank by 2,289.
City commercial banks, known for their high welfare benefits, have also experienced staff reductions. Taking Ningbo Bank as an example, the number of employees in the first half of 2024 was 27,540 (group basis), a decrease of 1,669 from the same period last year. From a regional perspective, the Shanghai, Beijing, Wenzhou, and Shenzhen branches reduced their staff by 130, 128, 121, and 85 people, respectively, which were relatively high numbers. From other perspectives, the head office reduced its staff by 175, and the "Ningbo Bank Consumer Finance" subsidiary reduced its staff by 122, seemingly indicating a "streamlining" of the workforce and adjustment of human resources in consumer finance.
However, it is worth mentioning that Ningbo Bank's "streamlining" has actually improved efficiency, and per capita productivity indicators have significantly increased. As of the first half of 2024, Ningbo Bank's total assets were 3.0337 trillion yuan, with per capita managed assets reaching 110 million yuan, marking the first time that per capita assets have exceeded 100 million yuan.
In the first half of 2024, Ningbo Bank's total salary was 7.237 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 4.4%, significantly higher than the average of -0.38% for A-share listed banks. In comparison, China Merchants Bank had 115,407 employees, a decrease of 1,122 from the end of the previous year. Unlike Ningbo Bank, which reduced staff but increased salaries, China Merchants Bank saw a 1.99% decrease in its total salary in the first half of 2024, with a total salary of 35.769 billion yuan during the same period. China Merchants Bank has truly achieved "reducing staff and increasing efficiency."
BT Finance's statistics on employee changes at 32 listed banks in the first half of 2024 revealed that only 8 banks saw an increase in their total number of employees, accounting for 25% of the total, but the number of increases was far lower than the number of reductions. Overall, the 32 listed banks reduced their staff by 36,274.
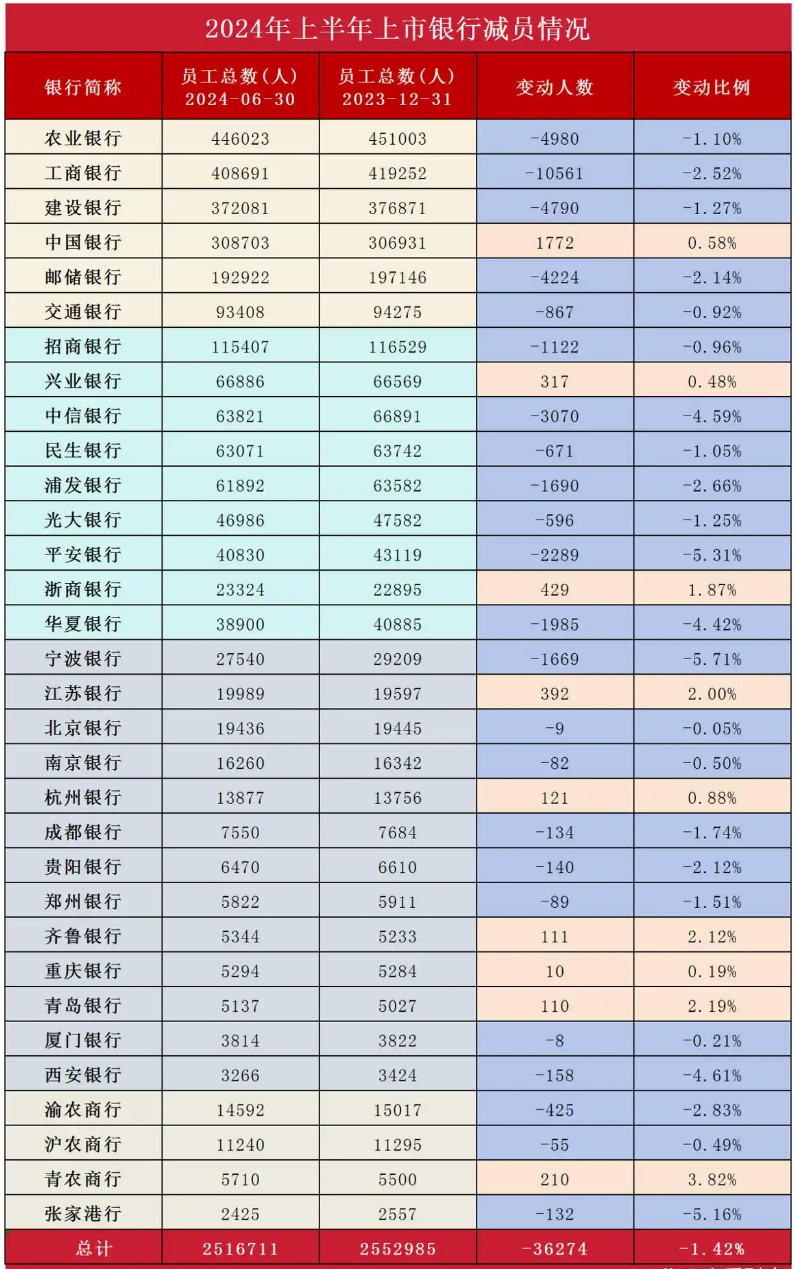
These sets of data provide a glimpse into the fact that the entire banking industry is undergoing "staff reduction," which is significantly different from the "stable growth" seen in the previous two years. In 2022 and 2023, the changes in the number of employees at the six major banks were an increase of 22,161 and a decrease of 4,156, respectively. Among the 12 joint-stock banks, the number of employees increased by 22,715 and 17,452, respectively. Among the 27 A-share and H-share listed city commercial banks, the number of employees increased by 21,135 and 10,362, respectively. These two years coincided with the booming development of AI.
2. Is Staff Reduction Already a Major Trend in the Banking Industry?
The labor costs of major banks have always been one of the main operating expenses. Taking ICBC, known as the "Universal Bank," as an example, in 2023, the employee compensation of ICBC was 134.57 billion yuan, accounting for 16% of the total revenue of 843.1 billion yuan and 37% of the net profit of 365.1 billion yuan. This includes 95.048 billion yuan for salaries, bonuses, allowances, and subsidies; 9.854 billion yuan for employee welfare and other benefits; 7.831 billion yuan for social insurance fees; 8.995 billion yuan for housing provident funds; 3.204 billion yuan for trade union funds and employee education funds; and 18.776 billion yuan for post-employment benefits (including pensions, unemployment insurance, and corporate annuities).
At the end of 2023, China Construction Bank had a total of 376,871 employees with an average salary of 355,000 yuan. Based on these figures, the employee compensation expenditure of China Construction Bank in 2023 was 133.78 billion yuan, accounting for 17% of the total revenue of 769.7 billion yuan and 40.2% of the net profit of 332.7 billion yuan during the same period.
At the end of 2023, Agricultural Bank of China had a total of 451,003 employees with an average salary of 341,100 yuan. The compensation expenditure was approximately 153.84 billion yuan, accounting for 22% of the total revenue of 694.8 billion yuan and 57% of the net profit of 269.4 billion yuan during the same period. In 2023, Bank of China's compensation expenditure was 109.84 billion yuan, accounting for 18% of total revenue and 47.4% of total net profit. China Communications Bank's compensation expenditure in 2023 was approximately 41 billion yuan, accounting for 16% of total revenue and 44% of net profit during the same period.
Agricultural Bank of China has the highest proportion of employee compensation in total revenue and net profit. Employee compensation accounts for 37%-57% of the net profits of the major banks, making it the primary cost expenditure for these banks. After "staff reduction," the per capita profit of major banks has increased to a certain extent. Bank of Communications, with the highest per capita salary, has a per capita profit of 989,100 yuan, the highest among the six major banks, but it experienced a 1.32% decline. ICBC, with the largest number of layoffs, has a per capita profit of 870,900 yuan, a year-on-year increase of 3.14%. Agricultural Bank of China, with the second-largest reduction in staff, has a per capita profit of 598,300 yuan, a year-on-year increase of 4.6%, higher than the industry average.
Li Qiang (pseudonym), the president of a branch of a bank in Tongzhou, Beijing, stated that at present, AI is most likely to replace customer service positions. "AI chatbots and voice assistants can provide services 24/7, handling customer inquiries, complaints, and simple transactions. Intelligent customer service robots can provide quick and accurate answers, significantly reducing the need for human customer service. They can also provide all-day service, and AI can also enhance efficiency and reduce risk factors in operational roles and risk assessment positions. The premise of reducing staff and increasing efficiency is the continuous strengthening of AI applications in the industry."
3. How Is AI Disrupting the Banking Industry?
Although intelligent customer service can provide 7x24 online Q&A, and semantic understanding optimization has been significantly improved, it is still criticized by many consumers. Besides the lack of emotional interaction in communication with consumers, some intelligent customer service operations are cumbersome and unable to solve personalized problems. For example, the intelligent customer service of certain platforms has complex hierarchical settings after being connected, with human service "hidden deeply." This makes it difficult for consumers to obtain timely and effective help through intelligent customer service when facing problems. Many consumers call customer service hotlines specifically to seek personalized human solutions from service representatives.

"Although AI robots are rapidly gaining popularity, they cannot completely replace human customer service, especially when it comes to handling complex and personalized customer needs." Li Qiang also pointed out the shortcomings of AI robots, believing that besides process optimization, they cannot completely replace humans in the short term.
The biggest advantage of AI lies in precise recommendations, which are based on behavioral analysis of user big data to achieve personalized marketing outreach. Many banks use AI large models and knowledge graphs to create intelligent marketing assistants. Their advantage lies in collecting multi-dimensional customer data through customer relationship network graphs to construct deeper knowledge graphs. Based on deep learning of these graph data, AI can automatically generate marketing strategies and recommend financial products based on customers' transaction records and investment needs. After implementing AI, one bank saw a 30% increase in customer satisfaction and a 40% increase in marketing efficiency.
At the same time, virtual digital humans can provide services anytime and anywhere, without being limited by time and location, greatly expanding the coverage of financial services. Data predicts that by 2025, over 80% of domestic banks will deploy digital humans, with 90% of customer service and financial advisory services being handled by virtual digital humans.
In public opinion management, the use of AI addresses the pain points of the banking industry's lagging response and slow reaction to sudden public opinion, enabling it to quell public opinion in the first instance and minimize negative impacts. It can also help banks adjust their strategies in a timely manner when facing market changes.
Currently, although AI can provide precise recommendations, there is still no solution to the problem of avoiding "over-marketing," which may lead to customer dissatisfaction. Finding a balance between personalized recommendations and user privacy is a challenge that the banking industry urgently needs to address. At the same time, when using AI, banks must also consider regulatory compliance, as AI has difficulty grasping subtle changes in regulatory documents and understanding the wording adjustments of relevant documents like humans. If banks rely entirely on AI and directly use AI-generated product descriptions, they may cross regulatory red lines, facing penalties and significant negative impacts on their reputation.
With the advent of the AI era, significant staff reductions in the industry are inevitable, and major changes in the industry are imperative. Currently, major banks are exploring the use of AI and refining larger models that are more "human-like" and suitable for the industry through learning. However, it will be a long process before AI can fully replace humans at this stage.
This article, authored by BT Finance, is an original piece and its use, copying, distribution, or adaptation without prior permission is strictly prohibited. Infringement of these terms will result in legal action.








