Breaking NVIDIA's Monopoly: How DeepSeek Revolutionizes AI with Open-Source Innovation
![]() 02/11 2025
02/11 2025
![]() 664
664

Investors who bought NVIDIA stocks before the New Year might have had a less festive Spring Festival. On January 20, when DeepSeek officially released and open-sourced its DeepSeek-R1 model, NVIDIA's stock price experienced a steep decline the day before the New Year's Eve, falling from a high of $148 to $116.
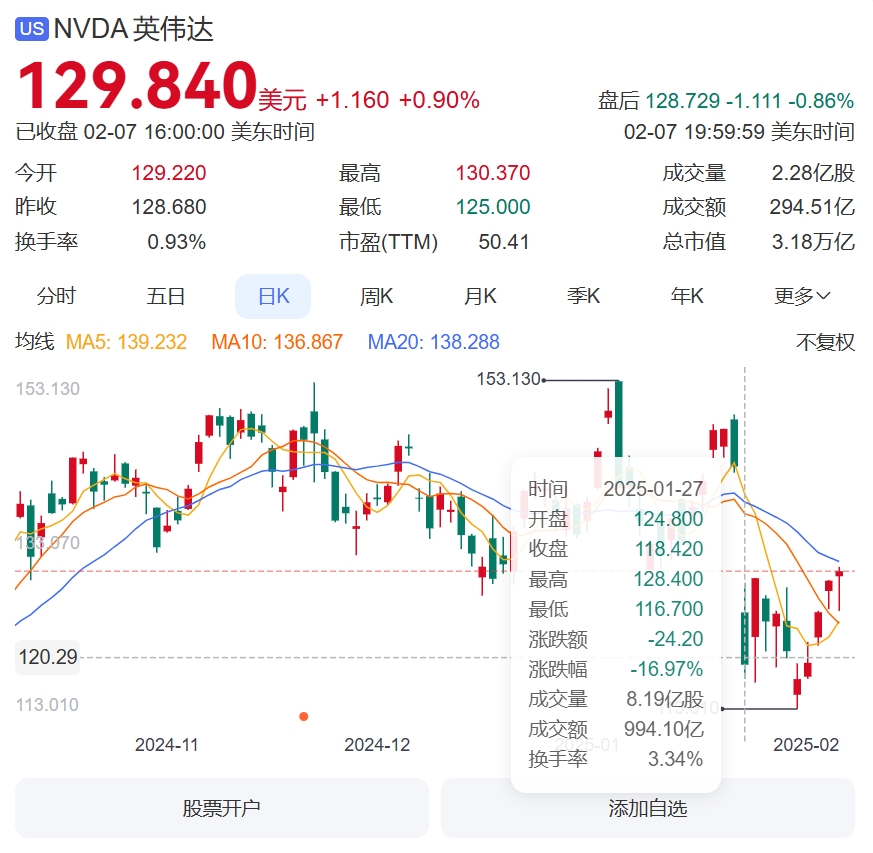
Image source: Baidu
Many reports attribute NVIDIA's stock price crash to the "AI-sector Pinduoduo" DeepSeek-R1 model, which is not entirely incorrect. DeepSeek-R1 has shattered NVIDIA's monopoly on AI computing power in a "brutal" manner. However, some people have misunderstood this as DeepSeek-R1 "not needing" NVIDIA graphics cards, which is incorrect. DeepSeek-R1's training servers still use NVIDIA compute cards, but the key lies in its open-source nature.
DeepSeek-R1, as an open-source model, employs a "distillation model" that significantly reduces the demand for computing power and decouples it from NVIDIA graphics cards. Despite this decoupling, it still demonstrates performance close to ChatGPT-o1 in terms of inference and other aspects, even surpassing it in some areas.
In essence, DeepSeek has made NVIDIA's high-computing-power graphics cards no longer a necessity for AI, akin to injecting a booster shot into the entire AI industry, especially the Chinese AI industry. However, this is not good news for NVIDIA, whose high profits stem from the "fragmentation" of the AI ecosystem.
Alias "CloseAI", OpenAI has never been Open
OpenAI's status is indisputable. As the pioneer and benchmark for AI large models, ChatGPT remains at the forefront. However, despite its name, ChatGPT is far from "Open" and is one of the most restrictive AIs in terms of user usage.
For instance, OpenAI recently accused DeepSeek of using ChatGPT data to "distill" its model, violating the user usage agreement. However, the controversy faded due to lack of evidence. The CEO of OpenAI publicly stated that there were no plans to sue DeepSeek and even praised DeepSeek for its great work.

Image source: Wikipedia
The ripples DeepSeek has sent through the AI industry are prompting OpenAI to reconsider its AI model openness strategy and reassess the possibilities of open-source models.
This is a significant blow to NVIDIA: ChatGPT is almost synonymous with being deeply tied to the NVIDIA AI ecosystem, serving as the cornerstone of the NVIDIA CUDA ecosystem. Microsoft and other OpenAI funders have always hoped for compatibility with more graphics card types, but so far, it has only been compatible with some AMD graphics cards, with efficiency and performance far inferior to directly using NVIDIA graphics cards.
CUDA + ChatGPT essentially form a closed AI ecosystem, forcing enterprises seeking top-tier AI support to cooperate with OpenAI and NVIDIA. Large AI models like Claude and Gemini are almost all deeply tied to NVIDIA, thanks to its leading performance computing cards and comprehensive CUDA ecosystem and development tool chain.
At first glance, it seems AI is predominantly closed. However, AI ecosystems such as AMD's ROCm and Khronos Group's OpenCL are open-source. With the CUDA ecosystem dominating, other ecosystems can only attract allies by being open-source.
DeepSeek is the Real OpenSeek: Has Open Source Won?
History repeats itself. In the PC industry, Microsoft and Intel jointly dominated, forming the "Win-Tel" alliance, with Windows consuming Intel's computing power, and Intel upgrading its manufacturing processes to promote PC ecosystem maturity. This even led to the famous summary, "Andy and Bill's Law," stating that "Andy gives, Bill takes away" (referencing Andy Grove, the CEO of Intel, enhancing hardware performance, while Bill Gates consumed this performance through Microsoft's operating systems and applications).
The two giants profited handsomely, and the remaining players followed suit. Under the closed Win-Tel alliance, open-source ecosystems like Unix and Linux absorbed allies.
Today's AI computing landscape mirrors the PC industry's history. The ecosystem of large AI models is increasingly fragmented, with OpenAI and NVIDIA leading through closure, forcing latecomers to respond with open source. For years, the open-source ecosystem couldn't compete with the comprehensive CUDA ecosystem, and no AI model comparable to ChatGPT emerged.
In 2024, Baidu CEO Li Yanhong repeatedly asserted that "open-source models will become increasingly outdated." He reasoned that the basic model Wenxin 4.0 could tailor smaller models suitable for various scenarios, considering factors like effectiveness, response speed, and inference cost, and supported fine-tuning and post-pretraining. Models tailored through dimensionality reduction were more effective and cost-efficient than directly adjusting open-source models of the same size.
In contrast, Zhou Hongyi held opposing views, believing that "without open source, there would be no Linux, no internet, and even ourselves would not have developed this far with open-source technology." He predicted that open-source technology's power would likely surpass closed-source technology within the next one to two years.
Opinions matter less than results. DeepSeek's sudden emergence proves the power of open source. (Note: DeepSeek is not fully open-source code; it only open-sourced part of the inference code and model weights. However, the industry recognizes it as an AI product under the open-source route, and its openness is sufficient for inspiration and learning.)
Not the First to Open Source, Why Did DeepSeek Win?
Before DeepSeek, the market was not short of high-quality open-source large AI models, like Meta's Llama and Alibaba's Qwen. However, among these models, only DeepSeek chose the MIT + OpenRAIL-like license for open sourcing.

Image source: DeepSeek
In simple terms, DeepSeek allows third parties to freely use, modify, copy, and distribute its code as long as the original author's copyright notice and license notice are retained, making it one of the most "Open" agreements in the open-source ecosystem.
Currently, the DeepSeek open-source community has multiple developers uploading dozens of operator libraries for different graphics cards. DeepSeek has built a foundation and set a basic template based on NVIDIA graphics cards, while also providing a basic version of heterogeneous deployment solutions, essentially saying, "The stage is set, now please start your performances."
Based on the MIT open-source agreement, third parties can freely modify DeepSeek's runtime code to make it compatible with different hardware devices, which is the first trump card for the popularization of DeepSeek-R1.
The second trump card is cross-platform API encapsulation. If you study the deployment code of DeepSeek-R1, you'll find that DeepSeek encapsulates underlying instructions like CUDA, ROCm, and OpenCL into a unified interface, allowing developers to migrate models between different AI hardware without modifying the code.
To better adapt to different hardware ecosystems, DeepSeek optimizes large AI models and code from the ground up, introducing just-in-time compilation technology. This allows AI models to dynamically generate optimal computation graphs based on graphics card types, enabling different computing devices to efficiently run DeepSeek models.
It may seem straightforward, so why haven't other AI companies tried using just-in-time compilation technology before? The reason lies in the code. To solve the H800 graphics card's performance deficiency and cross-chip communication bottleneck, DeepSeek bypassed CUDA and C/C++ and started coding from the lower-level PTX.
PTX can be understood as akin to assembly language. Developers can write instructions through PTX to directly mobilize hardware to run AI. Although PTX is part of the NVIDIA AI ecosystem, it doesn't target specific GPUs for execution. Therefore, translating it into instructions for other hardware platforms is far more efficient and convenient.
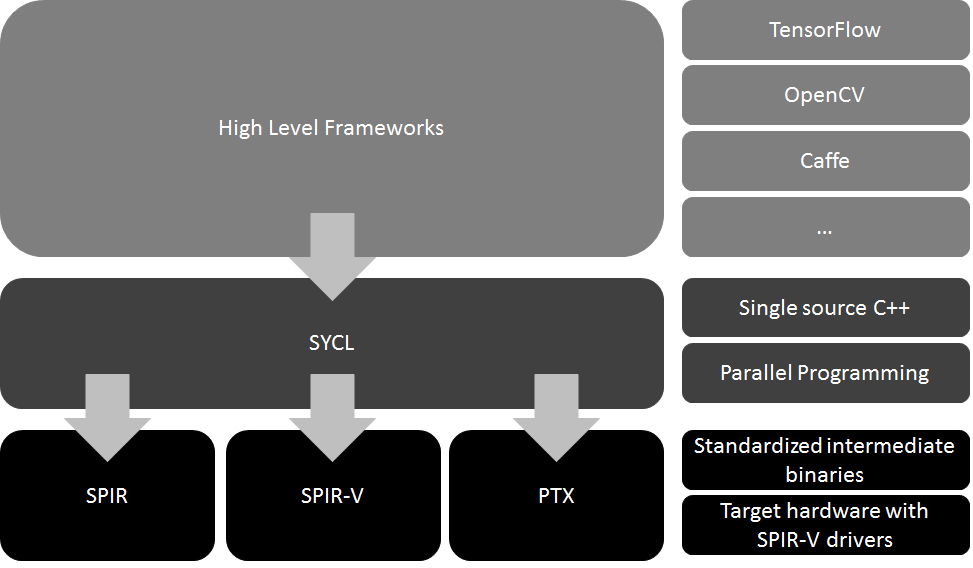
Image source: Codeplay
Think of AI as a project team: the user is the CEO, CUDA is the project manager, and PTX is the team member. In the normal process, if you want to execute a project, you need to first tell CUDA your needs, which then decomposes them into different work contents and transfers them to PTX for execution. DeepSeek established a new workflow: communicating directly with PTX and assigning work, bypassing CUDA and improving efficiency.
According to DeepSeek's published paper, they successfully increased the register usage rate of the stream processor (CUDA) from 78% to 92%, reduced the compute unit's idle time by 40%, and decreased global memory access latency from 600 cycles to 450 cycles, resulting in a surge in computing power efficiency and a drop in costs.
With a more fundamental code system, DeepSeek's AI models also have higher efficiency during translation and can bypass CUDA restrictions to some extent, adapting to different hardware. Many have already reproduced DeepSeek's AI model deployment using CPUs, leveraging virtual video memory and other technologies to convert memory into video memory and use integrated GPU computing power, greatly reducing thresholds and costs for deploying large AI models.
DeepSeek's innovations include optimizations in the mixed graphics card cluster scheduling algorithm, edge device adaptation, gradient accumulation video memory compression, and technologies enabling better adaptation to multi-graphics card systems.
A recent joke on social media noted that besides being strong enough, the biggest barriers for NVIDIA and DeepSeek are also related to the fact that "there are fewer and fewer people in the world who can speak assembly language." This is because both NVIDIA's CUDA and DeepSeek require assembly language-level development capabilities.
Many overlook DeepSeek's software development prowess. Optimizing code from the PTX level is akin to programming the system kernel using assembly language, a skill possessed by only a handful of top-tier developers. Its complexity is comparable to hand-drawing a "Black Myth: Wukong." DeepSeek's strong development capabilities enable deep cooperation with partners (like AMD and Huawei) to optimize inference efficiency.
In my opinion, DeepSeek's inspiration to the industry isn't just the "distillation" model implementation; it also demonstrates the huge potential of bypassing old ecosystems like CUDA and reconstructing large AI models from a lower-level code, likely sparking industry imitation and encouraging more AI companies to use assembly language for underlying optimizations.
Sparking Multiple Layers of Change: DeepSeek Has Truly Changed the World
In LeiTech's view, DeepSeek's changes to the AI industry are profound:
1. Unprecedentedly "affordable" AI provides the foundation for industrialized mass production of AI, creating the possibility for large-scale commercialized AI products like AI search to achieve product-market fit (PMF), which is crucial. The internet has Google, the mobile internet has the iPhone and WeChat, and 4G has TikTok. Without a nationwide killer AI application, the AI industry will ultimately be an ever-inflating bubble destined to burst.

(Image source: DeepSeek official website)
2. Breaking NVIDIA's monopoly in AI computing power and the dominance of the "OpenAI + NVIDIA" alliance allows more software AI developers and chip developers to seize and drive the AI wave. Deep down, DeepSeek also helps countries worldwide break through the US ambition to dominate the AI industry, making good technology accessible to everyone and ensuring equality for all entities in the face of AI.
3. The triumph of open source power heralds a new era of innovation in the AI industry, characterized by a vibrant competition among diverse schools of thought. DeepSeek introduces a groundbreaking open source paradigm to the AI sector, vividly illustrating the advantages and impacts of open source. This shift from closed to open source represents a pivotal turning point in the AI ecosystem. True innovation stems not from a handful of giants, but from the countless developers who have tasted both success and failure. Experts are among these developers, and it is their collective effort that drives progress.
Undoubtedly, DeepSeek and its team, which emerged brilliantly during this Spring Festival, have captivated the world and truly made a difference.








