NVIDIA's Stock Slips as DeepSeek Opens the Floodgates to Innovation
![]() 03/03 2025
03/03 2025
![]() 635
635
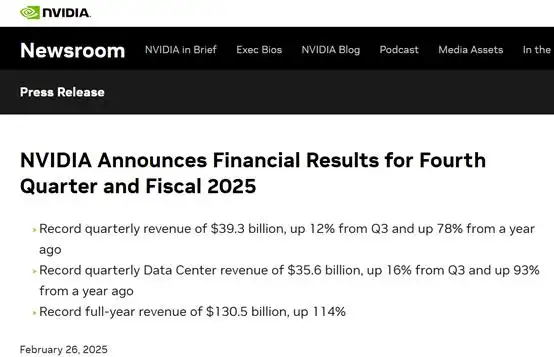
On February 27, 2025, NVIDIA unveiled its financial report for the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2025, revealing impressive growth.
The company boasted Q4 revenues of $39.3 billion and a net profit of $22.091 billion, marking an 80% year-on-year increase. Adjusted earnings per share stood at $0.89, surpassing analysts' projections of $38.05 billion in revenue and $0.84 in earnings per share. Furthermore, NVIDIA anticipates first-quarter revenue to hit $43 billion, significantly outpacing analysts' forecasts of $41.78 billion.
For the full fiscal year, NVIDIA set a new record with $130.5 billion in revenue, a 114% year-on-year jump.
Despite these stellar financial results, NVIDIA's stock price took a dramatic tumble on the same day.
Shares plummeted by 8.48%, marking the largest single-day decline in a month, and erasing approximately $271.6 billion (roughly RMB 1.98 trillion) from the company's market capitalization.
What prompted this sudden turn of events?
A week prior, DeepSeek announced the commencement of an "Open Source Week," a move that would see the release of a portion of open-source technology each day, mirroring OpenAI's strategy.
However, unlike OpenAI's gradual rollout, each open-source tool unveiled by DeepSeek served as a direct challenge to NVIDIA, hitting its mark with precision.

Let's delve into what DeepSeek has open-sourced this week, breaking it down in simple terms for everyone to understand.
Day 1: FlashMLA Emerges, Revolutionizing GPU Computing Power Scheduling
The launch of FlashMLA was a game-changer, addressing the issue of wasted AI computing power head-on. Traditional GPUs often overcompensate when processing tasks like natural language, leading to inefficiencies. FlashMLA, akin to an intelligent traffic controller, dynamically allocates computing resources based on sequence length, ensuring optimal utilization. This innovation not only boosts GPU performance but also signifies a crucial step towards enhancing domestic GPU capabilities. Within six hours of its release, FlashMLA amassed over 5,000 stars on GitHub, underscoring its impact.
Day 2: DeepEP Unleashes MoE Model's Full Potential, Skyrocketing Communication Efficiency
MoE (Mixture of Experts) is a cornerstone of large AI models, with its efficiency heavily reliant on communication between expert models. DeepEP, the first open-source EP communication library tailored for MoE models, acts as a "data superhighway." It supports optimized all-to-all communication and natively integrates FP8 low-precision arithmetic scheduling, ensuring high-speed data transfer while minimizing resource consumption. DeepEP elevates MoE model training and inference efficiency to unprecedented levels.
Day 3: DeepGEMM Targets Matrix Computation, Pushing FP8 Performance Boundaries
Matrix multiplication is fundamental to AI computation, and its optimization directly affects training costs and efficiency. Leveraging DeepSeek-V3's advanced scaling technology, DeepGEMM achieves efficient FP8 general matrix multiplication with just 300 lines of code. On Hopper GPUs, it delivers over 1350 FP8 TFLOPS, rivaling or surpassing expert-tuned libraries. Remarkably, DeepGEMM requires no compilation and utilizes a lightweight JIT module for runtime compilation, lowering the entry barrier.
Day 4: DualPipe + EPLB Form a Dynamic Duo, Boosting Parallel Computing Efficiency by 30%
Parallel computing is vital for enhancing AI computing power, but traditional methods suffer from the "bubble" problem, leading to resource wastage. DualPipe employs a bidirectional pipeline parallel algorithm to overlap computation and communication phases, increasing hardware utilization by over 30%. EPLB, tailored for MoE architectures, optimizes GPU load distribution using a redundant expert strategy and heuristic allocation algorithm, reducing GPU idleness. Together, they provide a significant boost to large AI model training.
Day 5: 3FS Filesystem Introduced, Setting New Data Access Speed Records
AI model training and inference depend on rapid access to vast datasets. The 3FS filesystem, designed for modern SSDs and RDMA network bandwidth, enables high-speed data access, significantly enhancing AI model efficiency. Its introduction adds another powerful tool to address AI computing power bottlenecks.
It's evident that each open-source project released during these five days has maximized NVIDIA card performance.
This explains how DeepSeek can train large models using just a few thousand cards, matching the performance of OpenAI models trained with tens of thousands of cards.
Crucially, all these technologies are open-source and accessible to all.
As a result, large model enterprises no longer require as many cards, disrupting NVIDIA's overestimation logic.
DeepSeek's parent company is HuFang Quant, a quantitative trading firm. One can't help but wonder if they might have anticipated these developments and taken preemptive actions.








