ADAS Pioneer Moves Up the Robot Industry Chain
![]() 05/20 2025
05/20 2025
![]() 644
644
Author | Xiang Xin
The competition for upstream positions in the robot industry chain is intensifying, with leading Advanced Driving Assistance Systems (ADAS) companies now taking center stage.
In March of this year, ZhiXing Technology, a prominent ADAS solution provider, officially entered the robotics arena by establishing Aimoxing Robotics, a wholly-owned subsidiary.
Just two months later, Aimoxing Robotics announced its intention to acquire a majority stake in an intelligent integrated joint venture.
Recently, Aimoxing Robotics announced the signing of a framework agreement for equity transfer with Suzhou XiaoGongJiang Robotics Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as "XiaoGongJiang"), acquiring a controlling stake to become the majority shareholder.
This move grants Aimoxing Robotics control over XiaoGongJiang's decision-making, operations, management, and resource integration, among other aspects.
XiaoGongJiang, known for its intelligent integrated joints and customized robotic arms, boasts deep technical expertise in robotics, thus accelerating ZhiXing Technology's robotics strategy.
ZhiXing Technology, focusing on ADAS domain controllers, ranks second in market share among providers of integrated ADAS domain control hardware and software solutions.
Leading ADAS companies venturing into robotics is not uncommon. Horizon Robotics, for instance, spun off its robotics division in early 2024 to establish Digua Robotics, dedicated to developing robot-specific software and hardware products.
Automakers such as Tesla, XPeng, and Xiaomi also embarked on self-researching humanoid robots three to four years ago.
What truly stands out this year is the trend of investment institutions, enterprises across the automotive industry chain, and humanoid robot manufacturers stepping up their layouts in the upstream of the robot industry chain.
In robotics, the focus has shifted from "manufacturing complete machines" to "controlling cores." These enterprises are integrating resources around large models, component manufacturers, and other upstream enterprises, aiming to establish their own ecosystems.
Those who can secure key positions early may determine the competitive landscape in the coming years.

Core of Robot Hardware Systems: Integrated Joints
The crux of the acquisition lies in XiaoGongJiang's intelligent integrated joint technology.
A robot operating in the real world requires not just a "brain" but also "muscles" and "bones." Integrated joints serve as the interface between algorithms and the physical world, converting energy into movements and executing action commands. They are indispensable "muscle" components for any embodied robot.
Aimoxing's acquisition of XiaoGongJiang targets the most critical aspect of robot body engineering.
Integrated joints, often referred to as actuators or joint modules, are highly integrated robot modules comprising motors, reducers, sensors, servo drives, controllers, and other components.
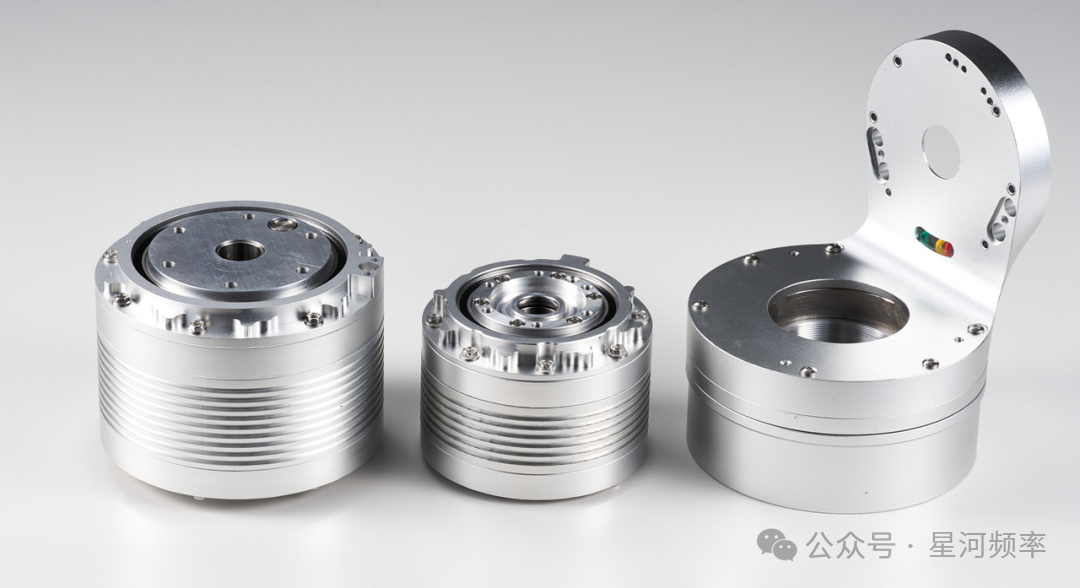

Intelligent integrated joints independently developed by XiaoGongJiang Robotics enhance intelligent attributes by integrating intelligent control algorithms and edge computing capabilities into traditional joint modules, enabling a "perception-decision-execution" closed loop. In essence, they add a "nervous system" to the joints.
These joints not only have a high technical threshold but also directly impact the three core indicators of robots: flexibility, performance, and cost.
In terms of flexibility, integrated joints enable robots to achieve multiple degrees of freedom, categorized into rotational and linear joints. Each joint module typically corresponds to one or more degrees of freedom.
Through the combination and coordinated movement of multiple joints, robots can execute complex movements and posture changes.
In terms of performance, the torque output, movement speed, accuracy, and stiffness of integrated joints directly influence how well a robot's degrees of freedom are utilized.
High-performance integrated joints provide greater torque, faster response speeds, and higher accuracy, enabling robots to move more flexibly, accurately, and stably across various degrees of freedom, thereby better completing complex tasks.
In terms of cost, currently, integrated joints account for approximately 35%-50% of the total cost of domestic mainstream humanoid robots.
Take Tesla's humanoid robot Optimus as an example. It has 28 actuators (which are integrated joints) throughout its body.
According to Morgan Stanley research, these 28 actuators account for up to 95% of the robot's total hardware cost.
In other words, for a product with a total cost of $50,000 (approximately RMB 360,000), the cost of joints alone is as high as $47,500 (approximately RMB 340,000).
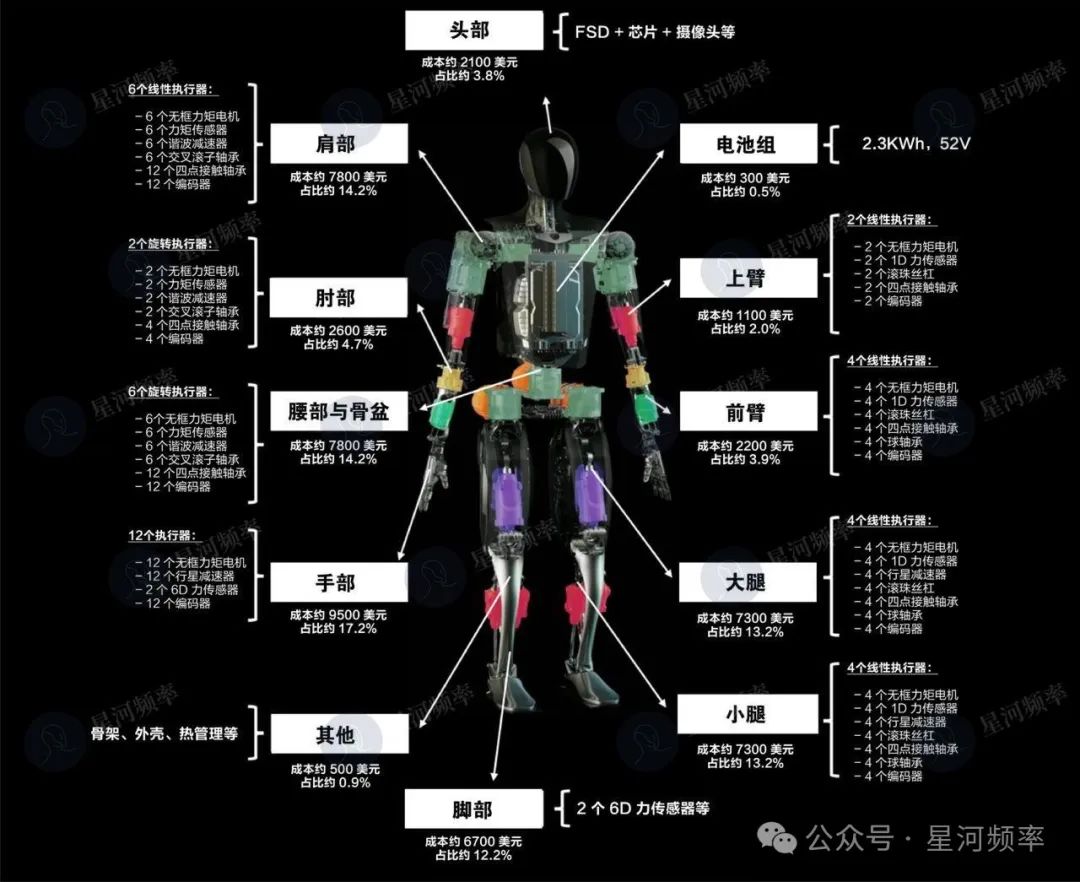
It is evident that mastering integrated joint research and development technology is crucial for achieving effective cost reduction.
Moreover, besides humanoid robots, integrated joints are widely used in quadruped robots, collaborative arms, rehabilitation robots, and other fields.
With the surge in demand for humanoid robots and industrial collaborative robots, the entire integrated joint market is on the verge of explosion.
According to data from Gongyan Industry Research Institute, domestic demand for robot joint modules reached 2.2417 million sets in 2024 and is projected to jump to 4.8201 million sets by 2030, with the market size expected to exceed RMB 68.927 billion.
Hence, the reason ZhiXing Technology chose to enter the market through integrated joints, rather than other components, is clear. It involves three considerations:
Technical Consideration: Mastering this underlying "bottleneck" technology can enhance robot performance.
Cost Consideration: Reducing joint costs can achieve cost control and profit improvement for complete machines under large-scale production.
Market Consideration: Integrated joints face a market with high technical barriers, broad coverage across multiple categories, and significant commercialization potential.
Among the numerous integrated joint enterprises, ZhiXing Technology chose XiaoGongJiang for two primary reasons.
First, XiaoGongJiang's emphasis on its technological tree. Founded in 2018, XiaoGongJiang is a national high-tech enterprise in the robotics field based in Suzhou. Besides intelligent integrated joints, its core products also include customized robotic arms, and it possesses design and development capabilities for key components such as motors, reducers, and drives.
Although XiaoGongJiang may not be as well-known as other joint enterprises, its technological innovation is impressive – it has obtained over 60 related intellectual property rights, surpassing some more established enterprises in the industry.
Second, XiaoGongJiang Robotics already has mass production capabilities. XiaoGongJiang's independently developed intelligent integrated joints are highly integrated with sensing, drive, and control systems.
By achieving the miniaturization of the key component in the joint – the RV reducer – and its integrated design with the motor, XiaoGongJiang's reducer solution offers higher reliability and longer lifespan.
Currently, XiaoGongJiang has developed three intelligent integrated joints suitable for mass production, with varying weights and performances to cater to the needs of diverse application scenarios, including humanoid robots and industrial robots.
Technological drive + mass production readiness are precisely what ZhiXing Technology values.
This also reflects that compared to finding a mature component supplier, ZhiXing Technology prefers to choose a technical partner with in-depth technology and the ability to evolve collaboratively.

Starting with Robotic Arms, Expanding to Any Type of Robot
To understand the logic behind this merger and acquisition, we must first examine the relationships and backgrounds of the three enterprises.
From the equity structure, this acquisition makes XiaoGongJiang a holding subsidiary of Aimoxing, which remains wholly owned by ZhiXing Technology.
In essence, this is a robotics core component integration with ZhiXing as the parent company and Aimoxing as the front-end. It represents ZhiXing Technology's "self-reinforcement" move in the robot industry chain to achieve supply chain autonomy and controllability.
What needs reinforcement is the hardware foundation, allowing ZhiXing Technology to focus on software technology.
By integrating perception, algorithm, and other software technologies from ADAS with hardware, ZhiXing Technology can build a full-stack robot research and development and production capability encompassing both hardware and software.
It is evident that ZhiXing Technology's robotics field layout is not to support the underlying ecosystem but to move to the midstream of the industry chain and become a provider of robot complete machines and core components integrating research and development, production, and sales.
When Aimoxing Robotics was first established, ZhiXing Technology positioned Aimoxing Robotics as a wholly-owned subsidiary dedicated to robot research and development and commercialization, with business covering various types of robots, core software and hardware, and related services.
Here are two keywords: commercialization and multiple types of robots.
In the latest promotional images of Aimoxing Robotics, illustrations of robotic arms, dexterous hands, and humanoid robot limbs are showcased.

This indicates that they are not only focusing on short-term commercializable scenarios such as industrial robots but are also proactively laying out future markets like humanoid robots.
Hints of the kind of robots ZhiXing Technology intends to make can also be gleaned from XiaoGongJiang's patent applications.
In October 2024, XiaoGongJiang applied for a patent titled "A Structure and Usage Method to Improve the Stability of Balanced Wheel Robots."
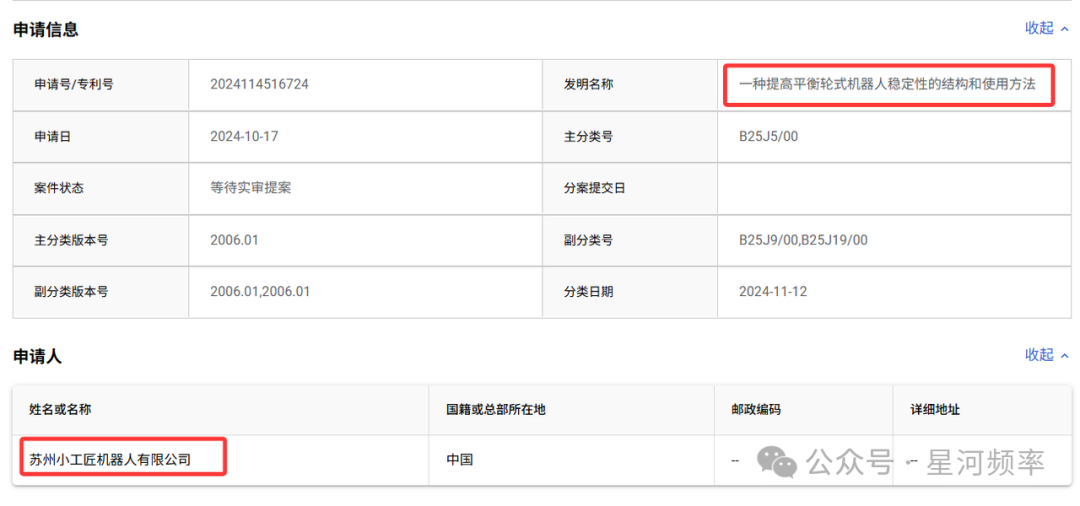
Previously, the company's patent applications primarily focused on core components such as robotic arms or reducers.
It can be speculated that the rapid implementation direction of ZhiXing Technology's subsidiary Aimoxing Robotics will be related to robotic arms.
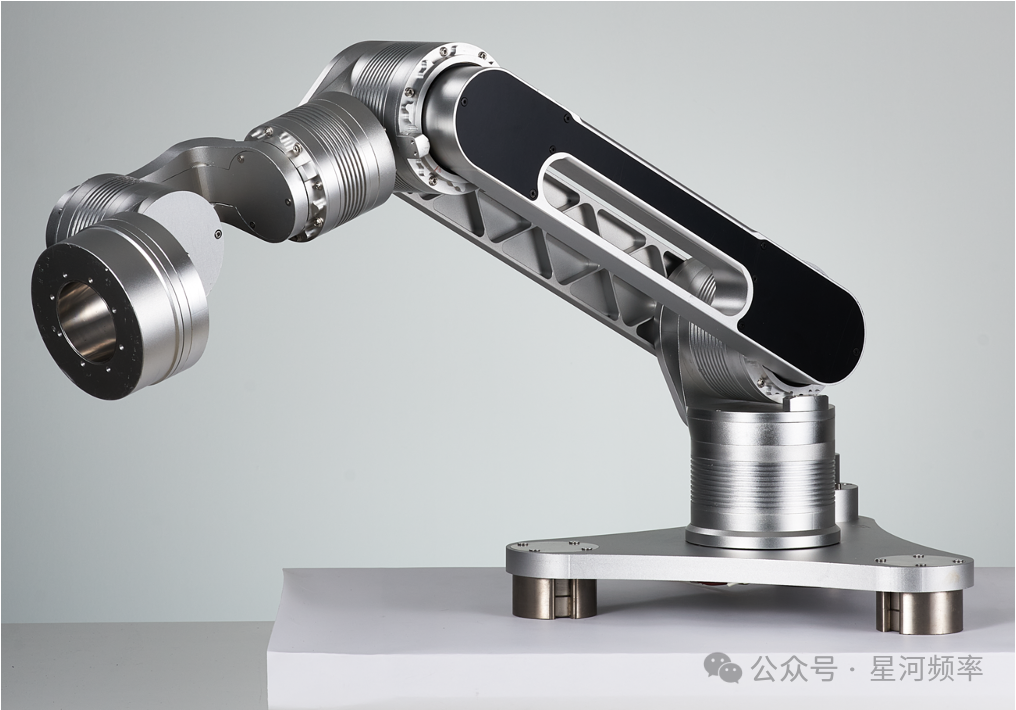

XiaoGongJiang Robotics' self-developed robotic arm
ZhiXing Technology has three major advantages in developing robots: technological research and development integration, engineering capabilities, and scenario application implementation.
In terms of technological direction, ZhiXing Technology's multi-sensor fusion perception technology, precise control algorithms, path planning technology, and other technologies accumulated in ADAS domain controllers can be transferred to the robotics field, enabling robots to perceive the surrounding environment more accurately and achieve more flexible and precise motion control.
In terms of engineering capabilities, ZhiXing Technology has years of experience in the mass production of supporting domain controllers.
Its quality management system accumulated in the automotive electronics field can be applied to the mass production process of robot core components, ensuring product consistency and high quality. This is a high-standard quality management experience in the automotive industry that traditional industrial robot manufacturers lack.
Moreover, similar to robot integrated joints, ADAS domain controllers are highly integrated.
ZhiXing Technology's experience in hardware selection, software architecture design, and other aspects can help it better integrate systems in the research and development and production of robot integrated joints.
In terms of scenario application implementation, ZhiXing Technology can not only apply robots in its own factories but also has numerous automaker partners, enabling it to expand robot application scenarios based on its established good cooperation foundation.
Data shows that in 2024, ZhiXing Technology secured 35 new cooperation orders from renowned OEM customers such as Geely Automobile, Polestar, Chery Automobile, and Dongfeng Motor, as well as several new carmakers, accumulating a total of 65 cooperation orders.
On one hand, ZhiXing Technology can complete self-owned scenario verification. On the other hand, it can also rely on the diverse scenario needs of automaker customers to accelerate the large-scale implementation of its robot products in fields such as automobile manufacturing, warehousing, and logistics.

Upstream of the Robot Industry Chain Becomes a Hotly Contested Area
XiaoGongJiang is not the first component company to be targeted and will not be the last.
Since the beginning of this year, a notable trend in the robotics industry is the shift in focus from the midstream to the upstream.
There have been increasingly frequent layout actions targeting enterprises in the upstream of the robot industry chain, such as joint modules, sensors, electronic control systems, and large models.
The "race for positions" in upstream resources has quietly commenced.
According to incomplete statistics, from January to April of this year, there were 60 financing events in the domestic humanoid robot sector, with 32 of them originating from upstream supply chain links, accounting for over 50% of the total.
Embodied intelligent large models, dexterous hands, tactile sensors, and joint modules are the four categories of enterprises that garner the most attention in the upstream market.
The primary reason for this focus is that the products and technologies of upstream manufacturers directly influence product performance, cost control, and industrial synergy capabilities.
With the commercialization path for humanoid robots remaining uncertain and potentially taking at least 5-10 years or longer to materialize, positioning oneself in the upstream and targeting the broader robotics market presents a choice with greater commercial potential.
Companies integrating upstream resources within the robot industry chain can be broadly categorized into four types:
- Automotive component suppliers: RoboSense, Zhongding Auto Parts, Wuzhou Xinchun, Zhejiang Rongtai, among others.
- Automotive software and hardware system integrators: Horizon Robotics, ZhiXing Technology, etc.
- Automakers: Xiaomi, BYD, etc.
- Humanoid robot manufacturers: Zhiyuan Robotics, Zhongqing Robotics, etc.
The specific methods of integration fall into three main categories:
- External cooperation: strategic alliances.
- Equity operations: further divided into investment and shareholding, acquisitions, and joint venture establishment.
- Internal development: encompassing team formation, self-production lines, and subsidiary establishment.
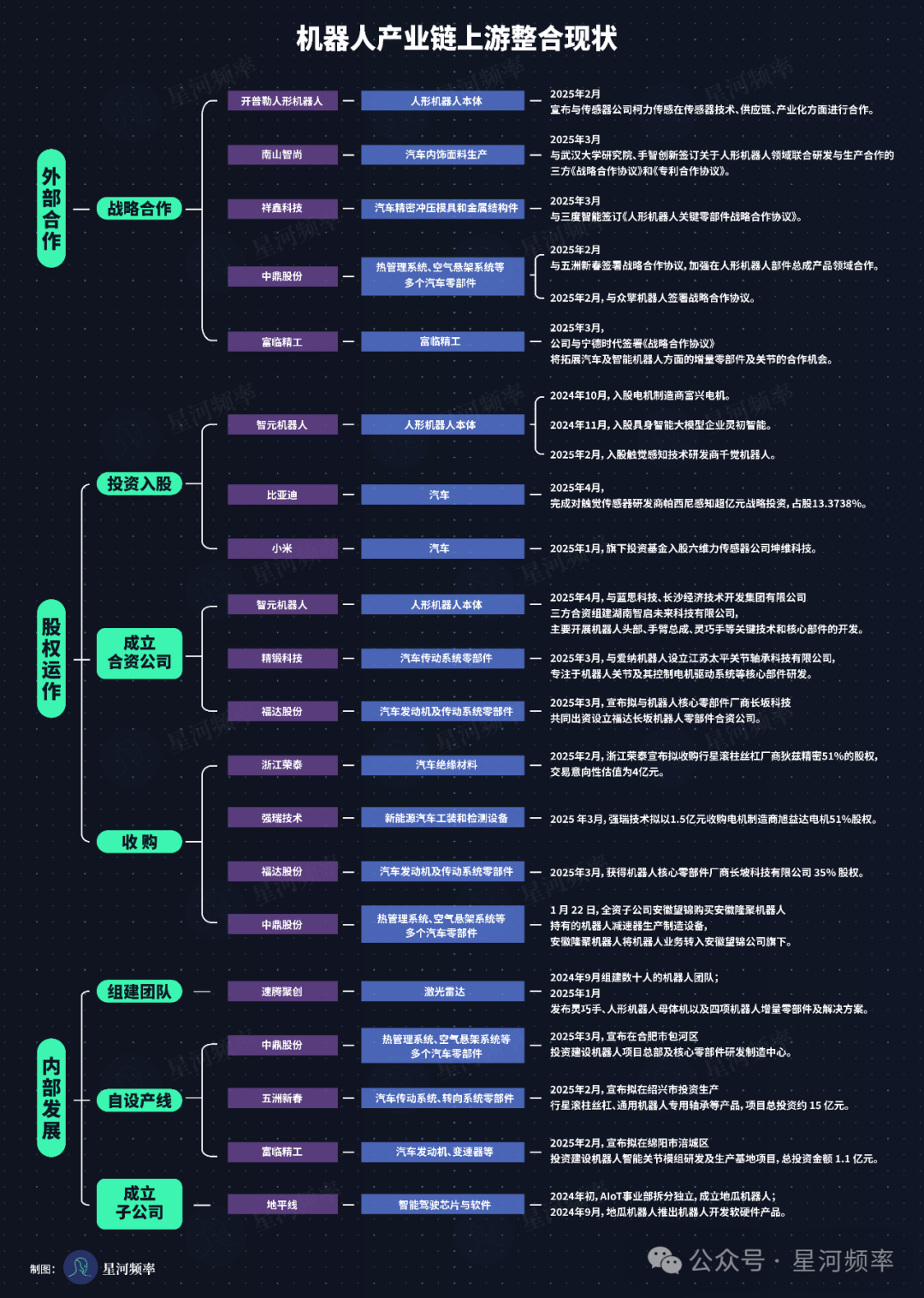
From a holistic perspective, the majority of companies opt for equity operations, with most integrators being upstream and midstream enterprises within the automotive supply chain.
Moreover, several companies, including Zhiyuan Robotics, Zhongding Auto Parts, and Fulin Precision, have ventured into the market through various integration methods.
Equity operations stand out as a relatively safe and rewarding approach compared to the other two integration methods.
They not only foster business and technical collaboration between enterprises, enhancing their industrial ecosystem, but also enable enterprises to reap multiple benefits in technology, market, and capital appreciation. This approach incurs lower costs than internal development, thereby avoiding the lengthy cycle and high risks associated with R&D from scratch.
Concurrently, the assisted driving industry has entered a phase of intense internal competition and price wars, prompting upstream and midstream enterprises in the automotive supply chain to seek a second growth trajectory.
Automotive parts technology and the robotics industry are inherently highly interlinked. Prior to the robotics era, these players can leverage their technical assets and accumulated supply chain and manufacturing strengths to venture into embodied intelligence at a relatively modest cost.
In the years to come, we anticipate witnessing more such integration initiatives, with this industrial crossover becoming increasingly prevalent.
Various companies will engage in a tug-of-war over core components such as modules, motors, reducers, and drive control boards, potentially leading to an uptick in acquisitions and integrations within related fields.
The focus of embodied intelligence development will gradually shift from competing over terminal products to securing key technical nodes required for large-scale implementation in advance.







