Domestic Dexterity: The Rise of the 'Four Little Dragons'
![]() 06/11 2025
06/11 2025
![]() 722
722

A timeless law governs domestic markets: "As an industry grows in popularity, it inevitably becomes more competitive."
In the past two years, humanoid robots have maintained their allure, and as a crucial interface for human-robot interaction, dexterous hands have garnered significant industry attention.
According to incomplete statistics, in May alone, five companies collectively launched ten dexterous hand products. Among them, Jiangsu Leili and Xingji Guangnian unveiled new products for the first time, while Aoyi Technology, BrainCo, and Lingqiao Intelligence released iterative versions.
As an upstream industry for humanoid robots and a significant factor determining their cost and operational capabilities, dexterous hands have emerged as a multi-billion yuan market.
Data from the China Commercial Industry Research Institute indicates that the global market size for robot dexterous hands was USD 1.7 billion in 2024 and is projected to exceed USD 3 billion by 2030.
Currently, the domestic dexterous hand sector is thriving, with the term "Four Little Dragons of Dexterous Hands" emerging within the industry. These four companies are Aoyi Technology, BrainCo, InTime Robotics, and Lingqiao Intelligence.
Commonality of the 'Four Little Dragons': 'Technology + Capital' for 'Cross-Cycle' Success
Each of these 'Four Little Dragons' holds a 'first' title in their respective fields.
Aoyi Technology is the domestic company with the largest shipment volume of dexterous hands.
BrainCo is currently the global leader in non-invasive brain-computer interface technology.
InTime Robotics is the first domestic company to achieve commercial mass production of five-finger dexterous hands.
Lingqiao Intelligence is the fastest company to achieve mass production of five-finger dexterous hands.
A closer inspection of these four companies reveals four key common traits: robust technology, localization strategies, commercialization, and funding support. These traits have enabled the 'Four Little Dragons' to establish a comprehensive technology-to-business closed loop, allowing them to stand out amidst fierce competition.
For a long time, dexterous hands did not receive much attention. Wang Peng, a researcher at the Institute of Automation of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, once stated in an interview:
"In the first half of 2024, dexterous hands were not a popular direction, and investors needed explanations on their practical use. Starting from the second half of 2024, people gradually realized that the practical application of humanoid robots relies on upper limb capabilities."
Even before the popularity of dexterous hands, the 'Four Little Dragons' already possessed the strength to capture the spotlight.
The founders of all four companies graduated from prestigious universities such as Fudan University, Harvard University, Beihang University, and Shanghai Jiao Tong University. The founding teams also have strong science and engineering backgrounds.
Driven by an engineer's mindset, these four companies focus on solving the 'impossible triangle' of 'cost-system parameters-stability' in the field of dexterous hands. Rather than chasing popularity, they prioritize 'boiling down products', allowing them to lay a solid technological foundation before the industry's outbreak, thus becoming the 'Four Little Dragons'.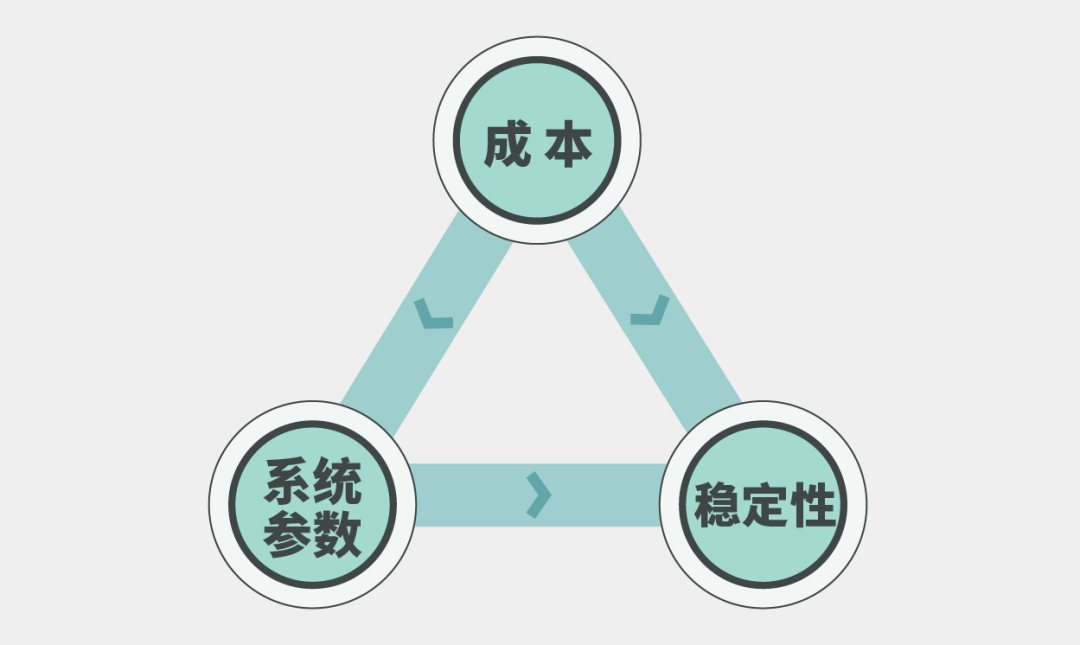
These four companies understand the need to create user-friendly domestic dexterous hands.
In the field of dexterous hands, foreign development generally leads domestic efforts. However, foreign bionic hands were expensive, often costing millions of yuan, with low product penetration and insufficient functional development.
For example, the British company Shadow Robot launched its first dexterous hand product, Shadow, in 2004. This product marked the transition of dexterous hand technology from the laboratory to practical applications, but its million-yuan price tag would indeed 'deter' ordinary users.
Early domestic companies in the dexterous hand sector, such as Aoyi Technology, faced the challenge of relying on costly and long-lead-time imported motors, leading to delays in research and development and ineffective products.
Facing pressure from foreign technologies and products, the Four Little Dragons unanimously chose the path of localization and independent development of core technologies.
Aoyi Technology and BrainCo have reduced the prices of their high-end bionic and dexterous hands to the tens of thousands of yuan level by independently developing motors, sensors, and brain-computer interface algorithms.
InTime Robotics has achieved domestic substitution and performance leadership through in-depth development of core components - micro servo cylinders. Lingqiao Intelligence, with its highly integrated and novel transmission solution ('motor drive + tendon transmission'), has quickly entered the high-cost-performance market.
This extreme cost control is the key to domestic enterprises catching up from behind.
For both humanoid robots and dexterous hands, besides controlling costs, there is an even more critical hurdle to overcome: achieving commercialization.
Now, the Four Little Dragons have successfully bridged the commercialization gap from the laboratory to the market.
Aoyi Technology and BrainCo initially focused on the medical rehabilitation field, primarily with bionic hand products, accumulating rich application experience and user feedback before expanding into embodied intelligence. Consequently, they are the only two companies among the 'Four Little Dragons' that possess both brain-computer interface and robot core technologies.
InTime Robotics first entered the biomedical and industrial automation fields using micro servo cylinders, which in turn supported the development of dexterous hands, securing orders from medical research and industrial sectors, and achieving the fastest commercial mass production of five-finger dexterous hands.
Relying on the incubation background and rapid iteration capabilities of the Shanghai Institute of Artificial Intelligence, Lingqiao Intelligence has quickly deployed in multiple scenarios such as industry, scientific research, and education. It has received orders from universities like Tsinghua and Shanghai Jiao Tong, as well as over ten companies including Jeka Robotics and Realman Intelligence.
A clear commercialization path is the guarantee for the sustained development of the 'Four Little Dragons'.
In addition to having strong technology and clear development strategies, creating a dexterous hand that can achieve human-like capabilities for robotic hands also requires significant external financial investment to support technological research and development.
Therefore, continuously obtaining capital infusion is crucial.
Among the 'Four Little Dragons', Aoyi Technology has completed seven rounds of funding in ten years, and also received two rounds of hundreds of millions of yuan in funding in the first half of this year, with a cumulative total funding exceeding 400 million yuan.
BrainCo has completed four rounds of funding totaling USD 300 million, ranking alongside Neuralink, founded by Musk, as the two companies with the largest funding in the global brain-computer interface field, entering the ranks of unicorns.
InTime Robotics has also completed seven rounds of funding, with a total funding amount exceeding 200 million yuan.
Lingqiao Intelligence, which was established only one and a half years ago, also completed its A round of funding this year. Linear drive leader Jiechang Drive not only participated in the investment but also cooperated with Lingqiao Intelligence to establish a mass production line.
Capital has invested heavily in the 'Four Little Dragons', solidifying their industry status.
Competition Among the 'Four Little Dragons': Similarities and Differences, Each Displaying Unique Strengths
Despite sharing common success genes, the Four Little Dragons exhibit distinct differences in technical routes, core advantages, target markets, and product strategies: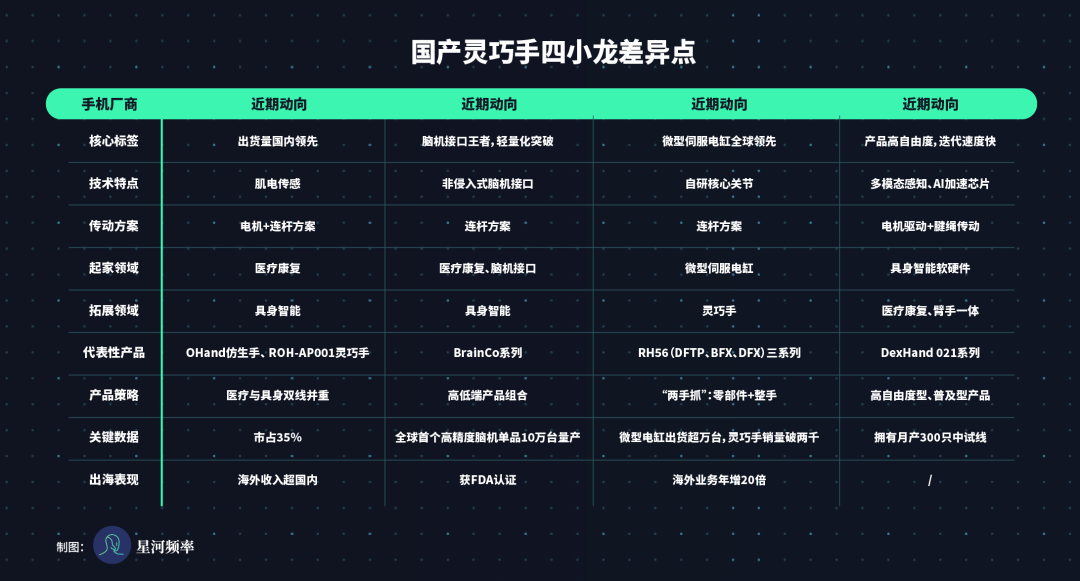
As the OG among the 'Four Little Dragons', Aoyi Technology has now become the leader in domestic shipment volume, with a market share of 35%.
The key to this success is that it found a promising market direction early on - the medical field.
Aoyi Technology focuses on a branch of prosthetics, bionic hands. In recent years, the number of disabled people in China has been on the rise, currently exceeding 80 million, one-third of whom require assistive devices.
Therefore, the market for bionic hands is a blue ocean. Whether for essential daily needs or lifestyle improvements, there is a stable market demand for prosthetics. Additionally, the medical field is an excellent testing ground for technology.
Achieving human-machine adaptation is challenging, requiring a wealth of clinical trial data, product iterations, and technological updates to support bionic hands with strong adaptability, high sensitivity, and comprehensive functionality.
It took Aoyi Technology five years to launch its first bionic hand, OHand, which can simulate human hands to perform various basic actions such as side gripping, side pinching, and pointing, and has achieved global commercial landings in countries like the United States, the Middle East, Russia, and India.
Relying on its deep accumulation and mature mass production capabilities in the field of medical rehabilitation, Aoyi Technology has replicated its advantages into the field of embodied intelligent dexterous hands, achieving the feat of launching two generations of dexterous hand products within one year.
Currently, Aoyi Technology's main revenue still comes from its bionic hand business, and since last year, the company's overseas revenue has exceeded its domestic revenue.
It will continue to maintain a dual-wheel drive strategy of 'medical rehabilitation + embodied intelligence' and a robust product iteration plan, with the expectation of releasing a third-generation dexterous hand product by the end of this year or next year.
Although BrainCo and Aoyi Technology both possess the underlying technologies of 'brain-computer interface + robot', BrainCo takes a more technologically advanced path.
Currently, BrainCo is the global leader in non-invasive brain-computer interface technology. Founder Han Bicheng, who graduated from Harvard Medical School's Department of Brain Science, initially targeted patients with brain diseases, followed by disabled people.
Similar to Aoyi Technology, for disabled people, prosthetics represent a potential market, so BrainCo developed bionic hands and legs.
For patients with brain diseases, BrainCo chose a more challenging but safer path, non-invasive brain-computer interfaces. Currently, it holds over 200 core patents in the field of brain-computer interfaces, about 60% of which are invention patents.
In 2022, BrainCo achieved mass production of 100,000 intelligent bionic hands, laying the foundation for technology, channels, and production lines for the launch of its robot dexterous hand product, BrainCo, in early 2024.
BrainCo has a clear positioning of its own advantages, so its business lines are divided into three major areas: intelligent bionics, intelligent health, and intelligent education. It is not only betting on the hot spot of embodied intelligence but also on the larger medical market.
For dexterous hand products, BrainCo offers both high-end BrainCo and the ten-thousand-yuan-level Revo 2, which breaks the weight threshold for professional-grade dexterous hands, demonstrating strong market competitiveness.
Currently, BrainCo's dexterous hands have been cooperated with companies such as Huawei, LEJU Robotics, and Tashan Technology.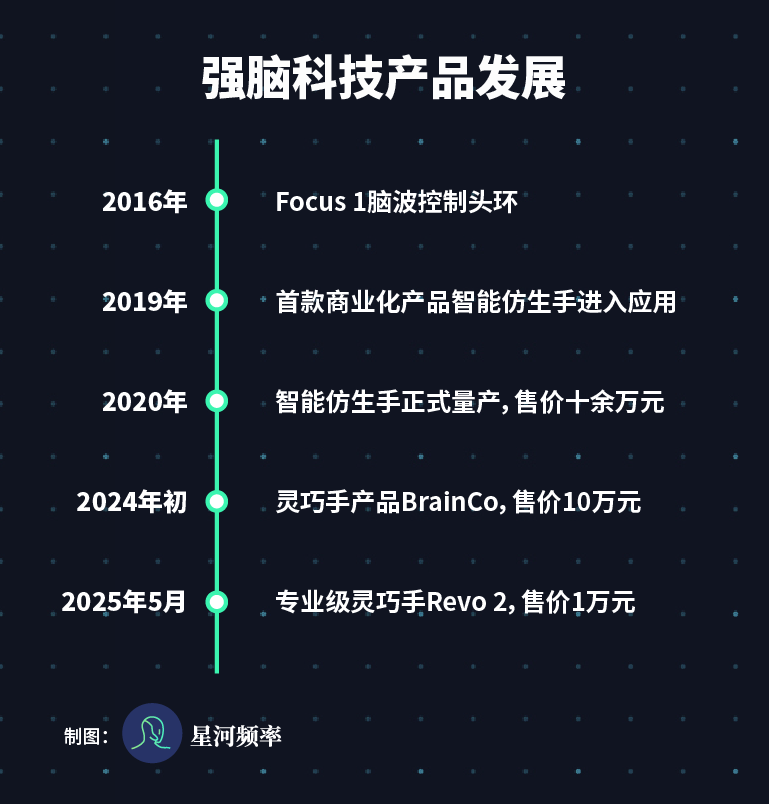
InTime Robotics has a unique path among the 'Four Little Dragons of Dexterous Hands'. It starts with micro servo cylinders and masters the underlying technology of robot joints.
The term 'micro servo cylinder' was coined by InTime Robotics, and what is commonly referred to as 'integrated linear joints' or 'integrated linear actuators' in the industry actually refers to micro servo cylinders.
It integrates high-performance hollow cup motors, precision planetary reducers, screw structures, sensors, and servo control systems, achieving drive-control integration while ensuring a smaller volume.
Currently, micro servo cylinders have become the company's core product, with an accuracy of ±2μm and a thrust/pull force of 40 kg, leading the world.
In 2020, the product achieved mass production and entered the market. Currently, it has launched the LA series, LAS series, LAF series, LASF series, and BLA series, with differentiated designs for different industries.
Although it is creating 'muscles' for robots, InTime Robotics first applied micro servo cylinders in the biomedical industry.
Because it does not directly contact biotechnology, the product is used in minimally invasive surgical instruments, successfully reducing equipment size while significantly improving equipment accuracy and force control capabilities.
This 'root technology' advantage naturally equips it with superior capabilities in cost control, reliability, and engineering implementation, particularly tailored for industrial and professional applications. 
By independently developing core joints, rigorously testing them in medical scenarios, and offering personalized solutions, it pioneered technology reuse, resulting in the domestic launch of the first commercially mass-produced five-finger dexterous hand, the RH56DFTP series.
Furthermore, this dexterous hand has successfully commercialized in fields such as healthcare and 3C manufacturing.
InTime Robotics is pursuing a dual-track strategy, focusing on both micro servo electric cylinders and anthropomorphic five-finger dexterous hands, aiming to be a leading supplier of both technologies.
It has achieved cumulative shipments of over 10,000 micro servo electric cylinders and nearly 2,000 dexterous hands. Additionally, its overseas business has grown 20-fold, with a compound annual growth rate exceeding 100%.
It is reported that InTime Robotics will introduce a series of new products within the year, including a high-degree-of-freedom dexterous hand. Its CMO revealed that this product will prioritize "solving needs" over parameter competition, potentially offering genuine value enhancement to the industry. 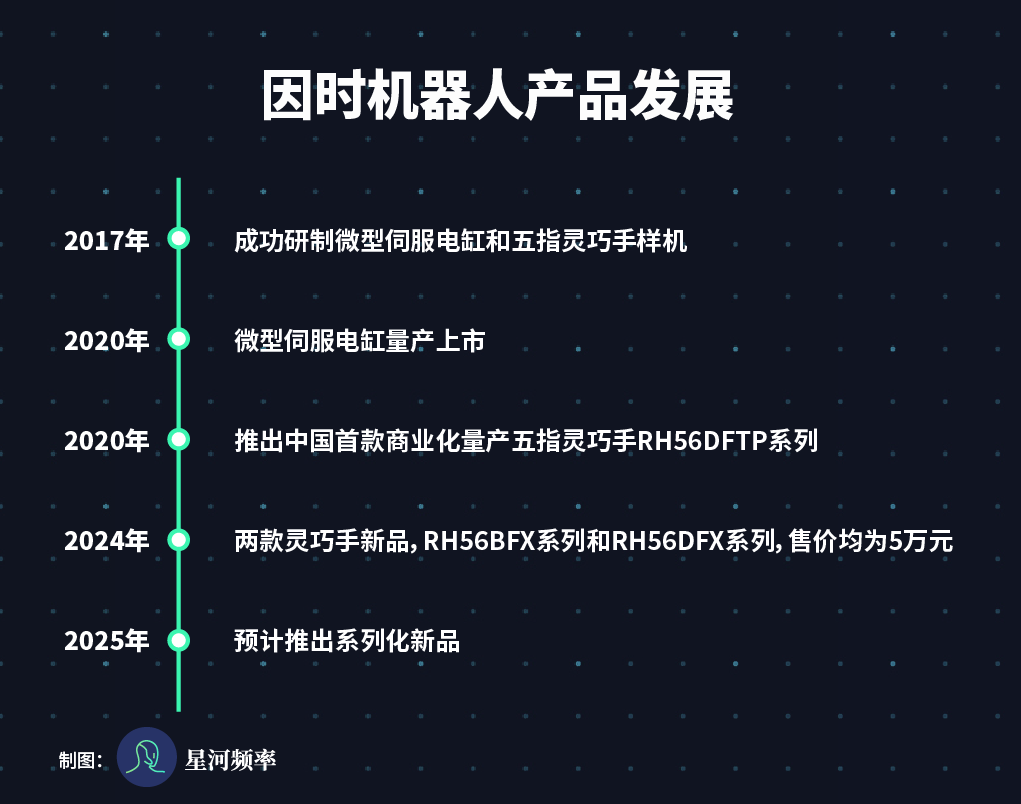
As the youngest "dragon," Dexterous Intelligence stands out for its "speed." Established in February 2024, it launched a prototype in May and mass-produced the DexHand 021 by October.
While it took the first three "dragons" four to five years to achieve mass production, Dexterous Intelligence accomplished this feat in just eight months.
This rapid progress is primarily due to the support of the "national team," including key players like the Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Research Institute and Zhejiang Provincial State-owned Capital. Additionally, a month before product launch, a partnership with industry leader Linear Motion to establish a pilot production line with a monthly capacity of 300 dexterous hands played a crucial role.
Another distinctive feature of Dexterous Intelligence is the high degree of freedom in its products. Unlike the initial six degrees of freedom offered by Aoyi Technology and InTime Robotics, Dexterous Intelligence debuted with a 19-degree-of-freedom five-finger dexterous hand.
DexHand 021 is the first domestically mass-produced high-degree-of-freedom five-finger dexterous hand, capable of performing 32 out of 33 human hand functional movements, with a lifespan exceeding 150,000 cycles and a price of RMB 96,000.
The decision to immediately challenge high degrees of freedom was fueled by Dexterous Intelligence's adoption of a novel "motor drive + tendon drive" solution.
Unlike the more traditional connecting rod or motor + connecting rod solutions employed by the first three companies, the tendon drive solution structurally resolves the "impossible triangle" and mimics human hand tendons, enabling a higher upper limit for degrees of freedom. 
In May of this year, Dexterous Intelligence also unveiled two new dexterous hand products: the high-dexterity DexHand021 Pro and the affordable three-finger DexHand021 S.
It is anticipated that Dexterous Intelligence will introduce arm-hand integrated products this year, further expanding the application of dexterous hands.
Worth mentioning is that by the end of 2024, Dexterous Intelligence had also established a brain-computer interface, broadening its service scenarios to include assistance for the disabled and elderly care.
It is evident that the "Four Little Dragons" unanimously recognize the vast potential market for dexterous hands in the medical field, each aiming to secure a share in both medical and embodied applications. 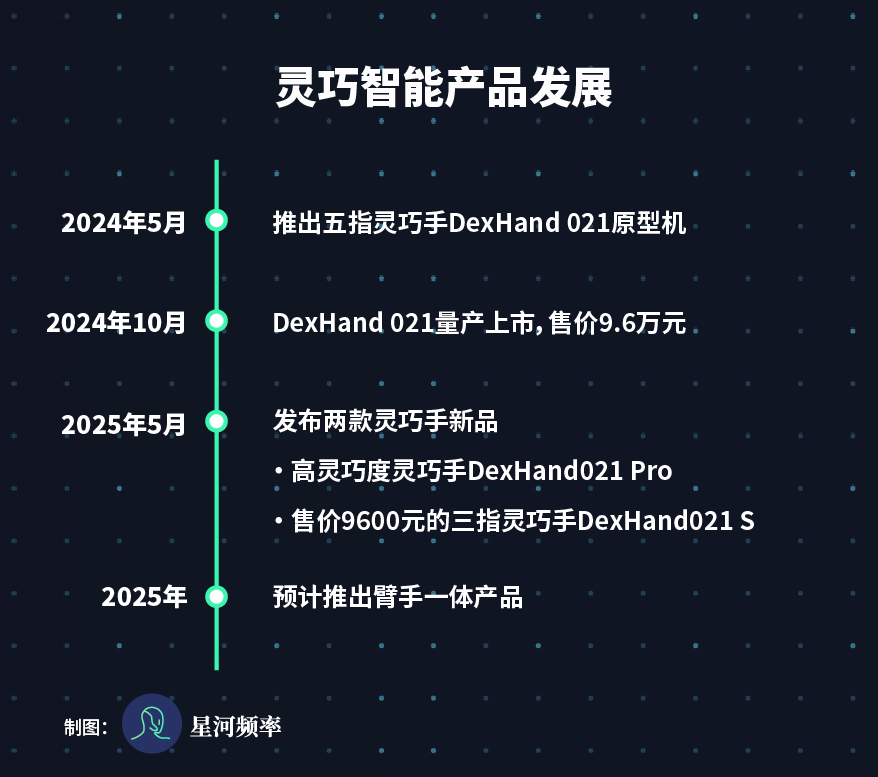
The dynamics among the "Four Little Dragons of Dexterous Hands" reflect the maturity of domestic industrial chain technology accumulation, engineering capabilities, and commercialization awareness in the field of core components.
Though entering through diverse paths, they ultimately compete on the same stage, jointly driving the development of domestically produced dexterous hands.
At the critical juncture of transitioning from the "technological breakthrough period" to the "scale application period," the challenge for the "Four Little Dragons" lies in continuously optimizing performance, reducing costs, and identifying genuine large-scale application scenarios.
While led by the "Four Little Dragons," the competition remains intense. For instance, Tesla's Optimus employs a three-stage transmission scheme of "planetary gear + lead screw + tendon," and Dymon Robotics' dexterous hand is equipped with the world's first millimeter-thick tactile sensor, both significantly enhancing hand dexterity.
Domestic leading enterprises such as Fulai New Materials and Riying Electronics are actively researching and developing electronic skin, which is more sensitive to humidity and temperature.
The ultimate objective of this breakthrough race around "robotic hands" is to bring this technology out of the laboratory and into every living scenario that requires "dexterous hands," at a lower cost and with higher reliability.




