Four attempts to list in Hong Kong finally succeeded: How can DMALL break out of the “dependency phase” under the opportunity of digital transformation?
![]() 12/04 2024
12/04 2024
![]() 675
675

This article is the 868th original work of Shen Qian atom
"Unable to walk independently, how to stand out overseas"
Meng Fanliao | Author
Shen Qian atom studio | Editor
Since submitting its prospectus to the Hong Kong Stock Exchange for the first time on December 7, 2022, DMALL has made four consecutive attempts to list on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange and has finally passed the hearing and obtained listing qualification.

On November 28, 2024, DMALL launched its share offering, planning to issue 25.774 million shares globally at a price of HK$30.21 per share, raising up to approximately HK$779 million. DMALL's preference for the Hong Kong Stock Exchange is partly for fundraising and partly perhaps to better penetrate the overseas market.
Amidst the current red ocean of retail digitalization in China, despite being backed by Wumart, DMALL still finds it difficult to maintain a stable position, turning to overseas markets as a way to cope with domestic competition. However, in this new challenge, DMALL's background advantages are significantly reduced, financial pressure is greatly increased, and breaking the deadlock is not easy.
While receiving financial support and incurring losses, DMALL remains popular
In 2015, Zhang Wenzhong embarked on his second entrepreneurial venture, bringing in Liu Jiangfeng, former president of Huawei Honor, as CEO, Lin Jie, former executive of JD.com, as COO, and Han Xin, former executive of VIPShop, as CTO. Together with his nephew Zhang Feng, they founded DMALL. Positioned as a one-stop omnichannel digital retail solutions service provider, DMALL entered the retail digital transformation race.
DMALL is the second venture of the founder of Wumart. In Zhang Wenlong's view, it has ushered in a "new" era for the Chinese retail industry, but it also seems like a service optimization project for Wumart.
DMALL's early development was inseparable from Wumart's financial support, with many users encountering DMALL through Wumart supermarkets. Moreover, entities related to the Wumart Group, such as Metro China, Chongqing Department Store Group, Yinchuan Xinhua Group, and pan-Asian retailer DFI Retail Group, have all become DMALL users, involving supermarkets, department stores, convenience stores, and many other retail vendors. DMALL has collaborated with over 660 customers. Of course, some large customers were acquired through mergers and acquisitions, such as Guoquan Shihui.
According to DMALL's prospectus, from 2021 to the first half of 2024, the Wumart group contributed RMB 599 million, RMB 966 million, RMB 1.201 billion, and RMB 735 million, respectively, accounting for 70.6%, 72.7%, 75.9%, and 78.2% of revenue. As the proportion of revenue from the Wumart group increases, it means that DMALL's identity as a Wumart-affiliated company is deepening, making it more difficult to gain recognition from other customers.
DMALL's heavy reliance on the Wumart group is also a sweet dilemma. In the prospectus, DMALL stated that any significant changes in related entities would have a material adverse impact on the company's operations and financial condition. However, DMALL still believes that future revenue from related entities will continue to increase.
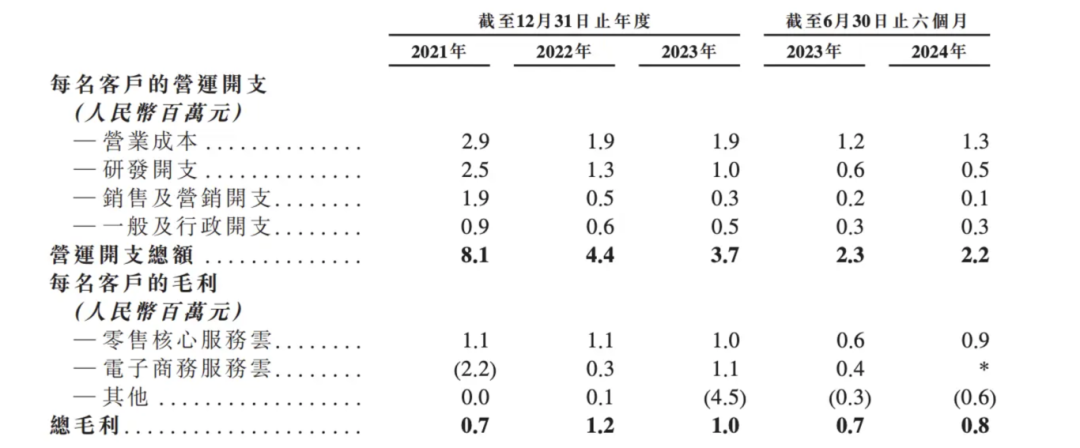
Perhaps for this reason, DMALL has reduced sales and marketing expenses for individual customers, from RMB 1.9 million in 2021 to RMB 0.3 million in 2023. Still in the customer acquisition phase, the reduction in customer investment is not conducive to DMALL's user expansion.
With the support of the Wumart group, DMALL has already become the largest digital retail service provider of retail cloud solutions in China and Asia. Despite having a high market share and financial support from Wumart, DMALL still fails to shake off losses.
The prospectus shows that from 2021 to 2023, DMALL's operating revenue was RMB 1.045 billion, RMB 1.501 billion, and RMB 1.750 billion, respectively, with losses of RMB 1.825 billion, RMB 841 million, and RMB 655 million. In the first half of 2024, DMALL incurred another loss of RMB 482 million, accumulating nearly RMB 1 billion in losses during the reporting period.
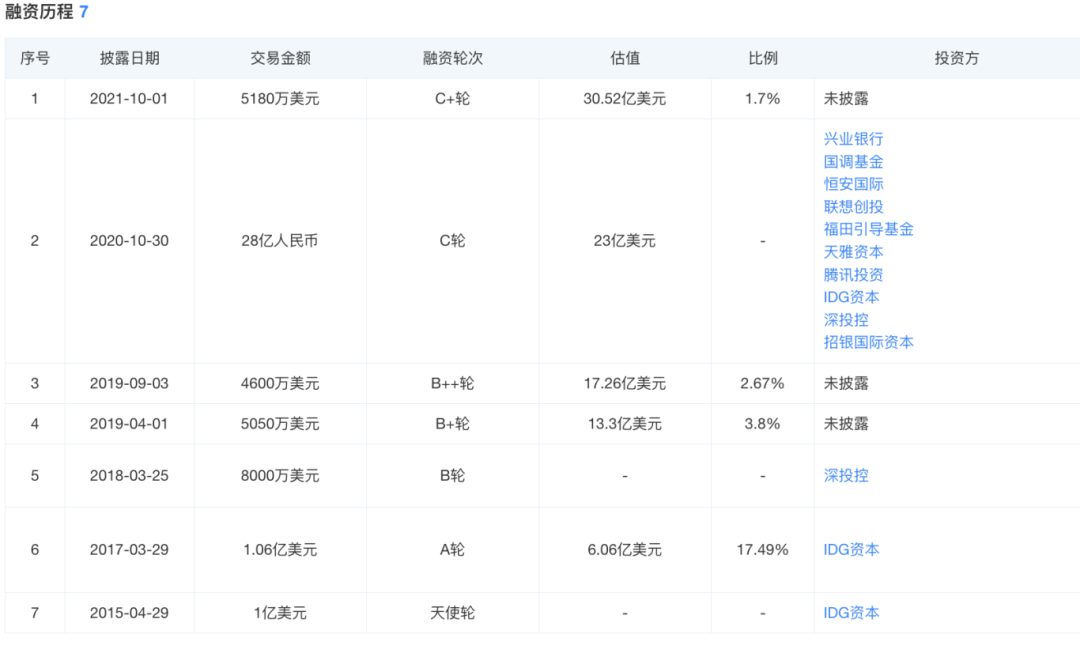
In April 2015, the company launched its Series A funding round of US$106 million. Since then, it has completed seven funding rounds, raising a cumulative amount exceeding US$700 million, attracting investors including IDG Capital, Tencent, Kingdee, Lenovo, and other institutions. As losses intensify, DMALL's funds are also rapidly decreasing. As of the first half of 2024, its cash and cash equivalents were only RMB 470 million. This may be one of the main reasons why DMALL made four consecutive attempts to list on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange.
Persistence pays off. Finally, DMALL passed the Hong Kong Stock Exchange's hearing and launched its share offering on November 28, planning to issue 25.774 million shares globally at a price of HK$30.21 per share, raising up to approximately HK$779 million.
IDC data predicts that China's overall digital transformation market will reach US$730 billion by 2028. In Hong Kong, DMALL already has a certain user base. In 2019, DMALL partnered with Hong Kong retail giant Dairy Farm International Holdings to launch the "yuu" app, gaining 5 million users in Hong Kong. Especially during the pandemic, yuu's delivery service gained recognition from a large number of Hong Kong users. This time, DMALL introduced one cornerstone investor during the IPO process. DFI Retail Group subscribed to 10.065 million offer shares for a total of US$39.06 million, accounting for approximately 39.05% of the total offer shares.
Undoubtedly, DMALL still has a halo in the capital market regarding its IPO. However, based on DMALL's development trajectory, HK$779 million will not sustain DMALL for long.
Fierce competition leads to a decline in DMALL's net customer revenue retention rate
The digital retail market is huge, and DMALL is not the only player in this market. Many enterprises have invested significant resources to gain a foothold in this field. As a result, the retail digitalization sector where DMALL operates is highly competitive.
Traditional supermarkets such as Walmart, Jingkelong, and Chaoshifa are also competitors. Walmart assists traditional retailers in digital transformation through the UID&SEE project, utilizing digital traffic and data analysis. Chaoshifa uses big data analysis and face recognition technology for precise marketing to electronic members.
The biggest impact on DMALL comes from technology companies. For example, Alibaba Cloud helps customers in various fields such as catering, home textiles, scenic spots, and supermarkets achieve digital transformation through excellent technical solutions, enhancing operational efficiency and market competitiveness. In the retail industry, Tencent Cloud provides personalized marketing solutions for enterprises by accurately understanding customer needs through data analysis. JD.com assists physical retailers in digital transformation through the "Natural Selection" project.
There are also competitors to DMALL on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, such as Youzan and Weimob. In terms of revenue scale, Youzan is comparable to DMALL, while Weimob's annual revenue is around RMB 2 billion, superior to DMALL's. As enterprises relying on retail digitalization, these companies have extensive offline partners and substantial offline supermarket resources, posing significant challenges to DMALL in acquiring new customers and exploring new businesses.
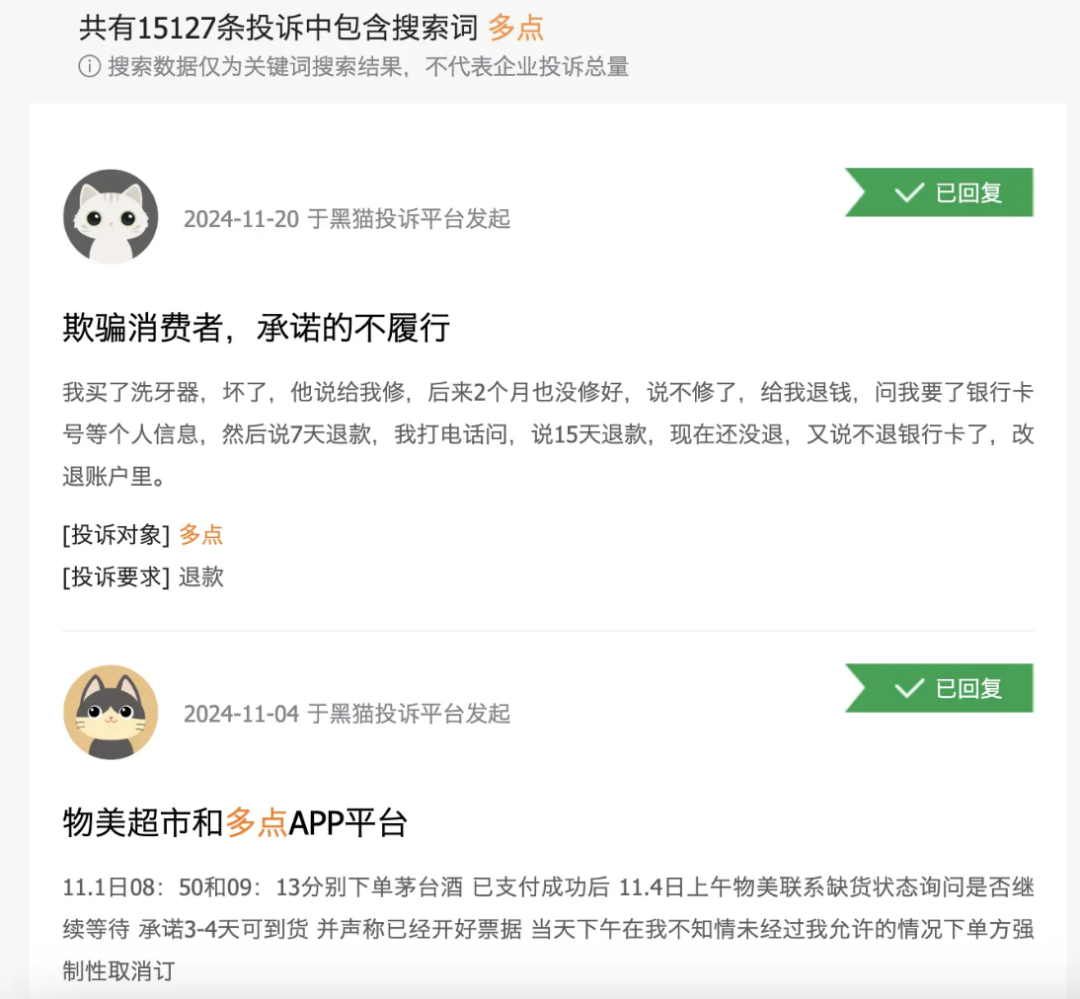
On HeiMao Complaints, there are 15,127 complaints about DMALL. The complaints involve product quality, customer service, and after-sales service. DMALL, which is highly tied to Wumart, is also being backlashed by Wumart users.
Amidst fierce market competition, DMALL needs to increase its competitiveness by increasing R&D investment. DMALL stated in its prospectus that it will continue to increase investment in technology research and development to enhance product intelligence and user experience. From 2021 to 2023, DMALL's R&D expenses decreased from RMB 614 million to RMB 551 million. By significantly reducing R&D expenses while still talking about R&D investment, where does DMALL's confidence come from?
Some netizens said that to avoid errors during peak hours with self-checkout, cashiers still need to allocate attention to self-payment areas, failing to achieve efficiency improvements and workload reduction.
Meanwhile, DMALL's net customer revenue retention rate is also declining. It fell from 208% in 2021 to 114% in 2023. This means that DMALL's ability to retain and expand its existing customer base has declined, with reduced customer loyalty and willingness to pay, casting a shadow over future performance.
Is going overseas the right solution?
Data shows that the market sizes of the retail industry in China and Asia were RMB 13.3 trillion and RMB 30.4 trillion, respectively, in 2021. However, the overall digitalization level remains low at 2.7% and 4.1%, far below the 12.4% in the United States. It is evident that while DMALL still has enormous growth potential in China, it has set its sights on the international market.
The prospectus reveals that DMALL has been deeply rooted in overseas markets for years. In 2023, overseas revenue reached RMB 123 million, accounting for 7% of total revenue. DMALL seems to have found a way to break through domestic competition, but is going overseas really the right solution?
The prospectus shows that DMALL's overseas operations span nine countries and regions, including Hong Kong, Cambodia, Singapore, Malaysia, Poland, Macau, Indonesia, the Philippines, and Brunei, with Hong Kong being the largest contributor. In the first half of 2024, Hong Kong contributed 6.4% of total revenue, while the Philippines contributed the highest revenue among other regions at RMB 5.627 million.
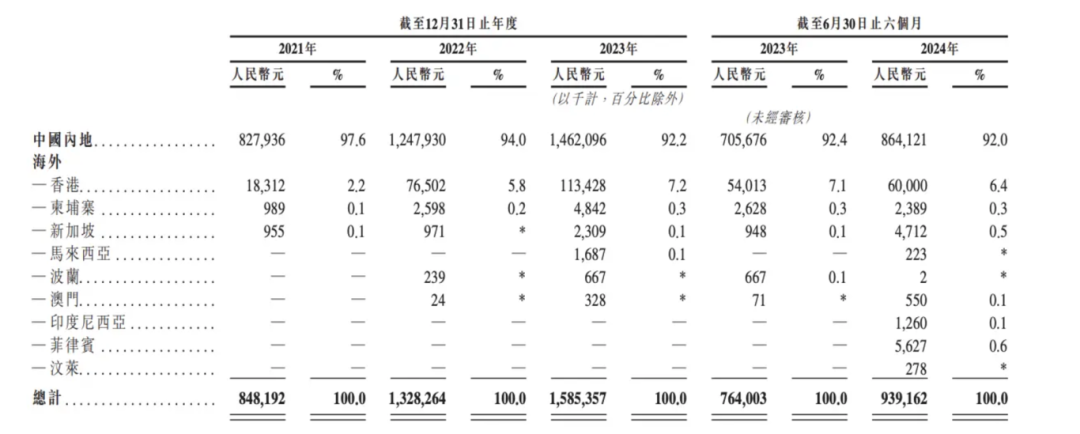
What's more noteworthy is that after overseas contributions reached 7.2% in 2023, they began to decline in 2024. Additionally, DMALL's overseas business is still in its infancy, requiring significant financial and material investments to address challenges such as cultural differences, legal and policy risks, market competition, operational and management challenges, and brand recognition.
DMALL needs to fully understand the characteristics of different markets, formulate feasible market entry and operation plans, and continuously optimize and adjust strategies to adapt to market changes. Currently, DMALL is still deeply mired in losses and may not be able to afford the large-scale expenses required for overseas expansion.
DMALL, which is difficult to shake off its reliance on Wumart, may have been destined for its eventual outcome from the moment of its birth.