Pixel 10 Unveiled: Has Google's Focus Shifted Beyond Mobile Phones?
![]() 08/22 2025
08/22 2025
![]() 632
632
Google's autumn 2025 conference arrived as anticipated.
Tech headlines were once again dominated by the Pixel 10 Pro's camera specifications, the Tensor G5 chip, and a suite of "AI innovations." However, if this were a conventional mobile phone event, the discussion would end here. 
But Google has never been a conventional mobile phone company.
For industry observers and secondary market investors who stay abreast of trends, the true value of this conference lies not in whether the Pixel 10 can disrupt iPhone sales, but in its clear indication of Google's core strategic path for the next decade: hardware serves as a means for Google to achieve AI dominance, not an end in itself.
While the public debates whether the Pixel 10 is worth buying, a professional perspective should inquire: What grand strategy is Google pursuing with its ongoing investment in hardware? And how will it reshape the competitive landscape of Apple, Qualcomm, and even the entire AI industry?
Silicon Rabbit interviewed a former Google engineer post-conference. This article presents the core viewpoints we discussed with the expert.

Unconventional Logic Behind Routine Upgrades
First, let's quickly recap the key conference highlights.
Tensor G5 chip: The performance improvement is as expected, but its true significance lies in providing dedicated computing power for the next-generation edge-side large model, Gemini Nano. 
Camera system: The Pixel 10 standard edition compensates for the lack of telephoto, while the Pro edition achieves 100x digital zoom with AI algorithms. Computational photography remains the core race.
Charging ecosystem: Full support for the Qi2 standard and the launch of its own magnetic snap solution, Pixelsnap, directly targeting Apple's MagSafe, filling in ecosystem gaps. 
These upgrades are "standard operating procedures" for flagship phones and are prerequisites for market competition. However, if one believes that Google's goal is to capture hardware gross margins, they have gravely misjudged its strategic intentions.
Google's hardware endeavors are essentially a long-term investment in AI. The Pixel's existence is not to become a sales leader but to serve three crucial roles: an AI model training platform, a hardware benchmark for the Android ecosystem, and a core entry point for Google services.

Decoding Google's Triple-Pronged Hardware Strategy
1. A Closed-Loop Experimental Field for AI Iteration
What truly warrants attention at this conference are the features driven by edge-side AI:
For instance, the new version of Gemini Live can now use the phone's camera to real-time identify and actively frame key information in the image. This interactive method, which integrates visual prompts, is distinctly forward-thinking, and its experience is already akin to the interactive HUD (Heads-Up Display) interface effects commonly seen in games. 
Based on Gemini's shooting assistance function, AI not only guides users in real-time for composition but also automatically extracts several representative poses during movement for users to choose from. Users first select the style, and AI then progressively guides the completion of the composition. 
Furthermore, Gemini is deeply integrated into the post-processing workflow of Google Photos. Users can now use natural language commands to have Gemini complete photo editing tasks, such as eliminating glare, defogging, enhancing saturation, etc., just as they would converse with AI for "text-to-image" generation. 
More interestingly, Apple outlined its AI vision at WWDC last year, and now Google has taken the lead in implementing it. At this conference, Google introduced the "Magic Cue" feature, whose implementation mechanism is akin to a combination of App Intents and smart suggestions on the iPhone.
It automatically displays information prompts based on user history data, schedules, and timelines in appropriate software scenarios, truly achieving "remembering things for you." 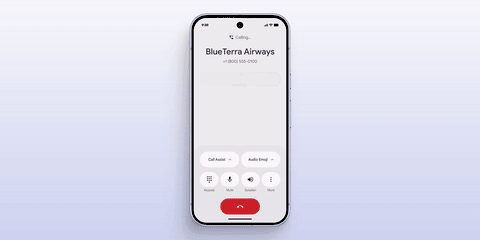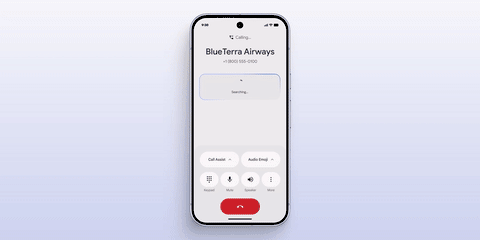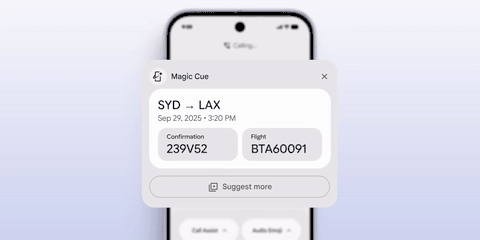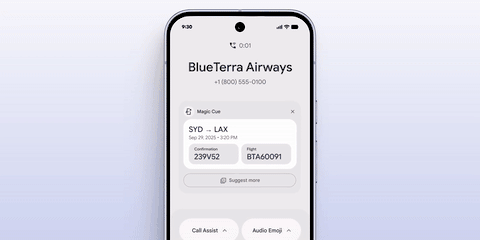
Automatic display of order rescheduling during a phone call|Google
Additionally, Gemini's voice capabilities have undergone significant enhancements. At the end of the conference, Jimmy Fallon demonstrated Gemini's real-time translation effect during calls: it not only completes semantic translation but also recognizes and mimics the speaker's timbre and tone, reproducing a voice that is "more like you than yourself" in another language. 
The significance of these features extends far beyond "showing off skills." They reveal a harsh reality: high-quality, scenario-based user interaction data has become a core asset for training the next generation of AI.
As a personal device with the most sensors and the most complex scenarios, mobile phones are the optimal terminal for collecting such data. By deploying these cutting-edge AI features among global users through Pixel, Google is essentially establishing a continuously evolving data flywheel: the more frequently the feature is used, the smarter the model becomes; the smarter the model, the more frequently the feature is used.
These AI capabilities proven successful on Pixel will swiftly feed back to Android Auto, Google Glass, Nest Hub, and other full-scenario hardware. Pixel is the "vanguard" of Google's AI strategy, and its mission is not to capture the market but to gather crucial "intelligence" for the larger AI model forces.
2. Defining the Hardware Standard for the Android Ecosystem
The self-developed Tensor chip and the introduction of the Pixelsnap ecosystem are pivotal steps for Google to strengthen its hardware discourse power.
The goal of the Tensor chip has never been to outperform Snapdragon in peak performance but to provide a deeply optimized computing power solution for Google's AI models. It clearly demonstrates to all Android manufacturers the software-hardware integrated form that future AI phones should embody – computing power must serve the user experience, not benchmarking.
The Pixelsnap magnetic snap ecosystem is an even more strategically significant move. It may appear to be imitating MagSafe, but it is actually the starting point for Google to construct a moat for its hardware ecosystem. A unified magnetic snap interface standard paves the way for future expansion of peripherals (such as external lenses, power banks, etc.), which will significantly enhance the stickiness and derivative value of the hardware ecosystem. Through Pixel, Google is showing the Android camp how to escape homogeneous hardware competition and build differentiated barriers through AI and ecosystems.
3. Safeguarding the Strategic Entry Point for Data and Services
Amidst the fragmentation of the global internet and geopolitical factors exacerbating the risk of technological decoupling, giants are all contemplating how to defend their "digital sovereignty."
For Google, the continuous growth of its core businesses (search, advertising, cloud, AI) heavily relies on seamless access to services and the free flow of data. The increasingly closed Apple ecosystem poses a potential threat to it.
The existence of Pixel provides Google with a fully autonomous and controllable hardware outlet. From chips to systems to hardware, Google has mastered full-chain control, ensuring that its core services can reach users with the best experience without relying on any third-party hardware vendors.
This strategic defensive value far surpasses the profits of hardware itself. Pixel is Google's strategic insurance against an uncertain future.

Returning to the original question: Is Google's ambition still in mobile phones?
The answer is undoubtedly no. Mobile phones are merely the vehicle, with AI and ecosystems being the core.
Through Pixel, Google demonstrates a new paradigm of technological competition: hardware becomes an extension of software and AI capabilities, data flow is more valuable than hardware sales, and ecosystem control is more crucial than market share.