Laplace IPO: Five Major Customers' Performance 'Wiped Out', Is the 1.8 Billion Fundraising Project Still Necessary?
![]() 09/04 2024
09/04 2024
![]() 622
622

On December 27, 2023, the photovoltaic company Laplace successfully passed the listing review, and the Shanghai Stock Exchange announced in April 2024 that Laplace had obtained approval for its initial public offering registration. However, to date, the company has not yet successfully listed, raising questions about the reasons behind this delay.
According to Laplace's prospectus, the company plans to list on the STAR Market, proposing to issue no more than 40,532,600 new shares publicly, raising a total of 1.8 billion yuan. The funds will be used for the research and production base of high-end photovoltaic equipment, the research and manufacturing base of high-end semiconductor and photovoltaic equipment, and for working capital.
Financial News reviewed the prospectus and found that during the reporting period, Laplace, as a specialized supplier of photovoltaic cell equipment, seized the opportunity of TOPCon mass production, transitioning from insolvency to over 100 million yuan in net profit in just over three years, showcasing impressive performance. However, despite its strong financial performance, it remains uncertain whether Laplace will successfully list, as the photovoltaic market has undergone significant changes, and the performance of its five major customers, on which the company heavily relies, has plummeted, raising questions about Laplace's ability to sustain its high growth. Furthermore, Financial News identified issues with the rationality of Laplace's fundraising amount and the interconnected shareholding structure between shareholders and customers, which have attracted regulatory inquiries. Successful listing will require further efforts.
Major Customers Struggling, Sustained Growth in Question
Public information indicates that Laplace is a provider of core process equipment and solutions for high-efficiency photovoltaic cells, specializing in the research, development, production, and sales of high-performance thermal processing, coating, and supporting automation equipment for photovoltaic cell manufacturing. It also offers equipment and supporting products and services for semiconductor discrete devices.
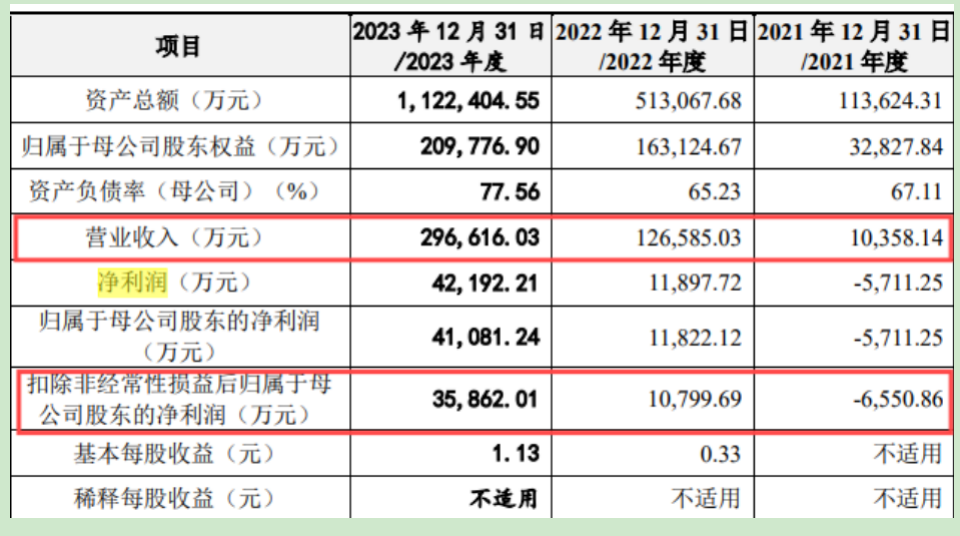
According to the prospectus, from 2021 to 2023 (the reporting period), Laplace's operating revenue was 104 million yuan, 1.266 billion yuan, and 2.966 billion yuan, respectively, with net profit attributable to shareholders after deducting non-recurring gains and losses of -66 million yuan, 108 million yuan, and 359 million yuan.
Financial News observed that Laplace's performance has been experiencing explosive growth over the past two years, with some indicators even doubling. This growth is primarily attributed to the booming photovoltaic industry during that period, which significantly boosted Laplace's overall performance. Moreover, by successfully capitalizing on the trend, Laplace demonstrated remarkable competitiveness during the N-type battery boom in 2022.
Global photovoltaic equipment development has gone through multiple stages. Since 2022, new-generation N-type batteries such as TOPCon and HJT have entered the industrialization process, ushering in a golden age for companies with N-type equipment production capabilities. During this period, Laplace successfully introduced its LPCVD and boron diffusion equipment to major customers, leading to a surge in performance.
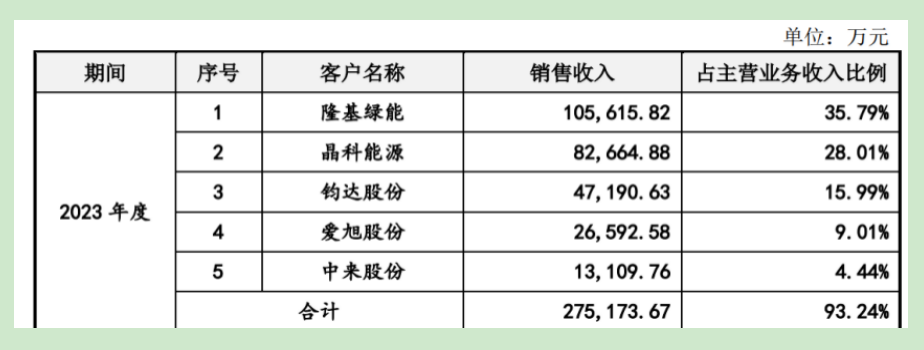
Laplace's recent growth has primarily relied on these major customers, including Longi Green Energy, JinkoSolar, Junda, Aikosolar, Zhonglai, Tongwei, and BYD, gradually leading to an over-reliance on these clients.
According to the prospectus, from 2021 to 2023, the sales revenue from the company's top five customers accounted for 99.99%, 98.67%, and 93.24% of its main business revenue, respectively, indicating a high concentration of major customers. In particular, sales to JinkoSolar accounted for 54.21%, 48.55%, and 28.01% of total revenue during this period, exceeding 50% in 2021.
Unfortunately, due to the supply-demand imbalance in the photovoltaic industry over the past two years, Laplace's major customers have struggled, with their performance plummeting.
Based on the latest statistics from Financial News, Laplace's top five customers—Longi Green Energy, JinkoSolar, Junda, Aikosolar, and Zhonglai (for 2023)—recorded negative net profit attributable to shareholders for the first half of 2024, plunging into losses (except for JinkoSolar, which recorded a profit of 217 million yuan). Furthermore, these companies saw year-over-year declines exceeding 100% (with JinkoSolar's decline at 93.85%), and Aikosolar's decline approaching 300%.
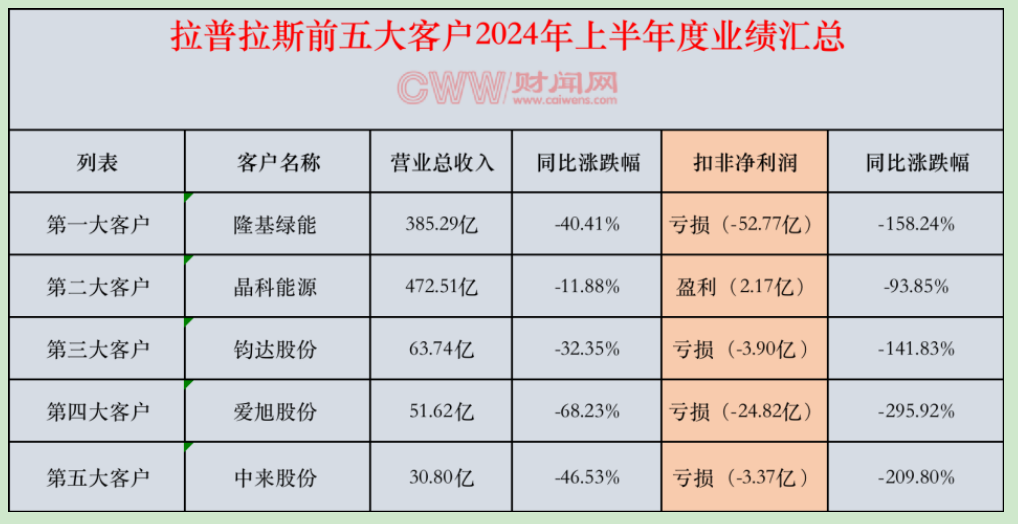
In this context, it remains uncertain how these major customers can continue to contribute to Laplace's growth. Sustaining Laplace's high growth trajectory amidst such challenges poses a significant hurdle for the company.
Moreover, the high concentration of major customers (exceeding 90% during the reporting period) poses significant risks for Laplace. Through horizontal comparison, Financial News found that while peer companies such as Jiejiaweichuang, Weidaonanomi, and Maiwei also face customer concentration issues, their customer structures are not as concentrated as Laplace's. Failure to address Laplace's highly concentrated customer base could present a major risk.
Global Photovoltaic Overcapacity Raises Questions About the Rationality of the 1.8 Billion Fundraising Plan
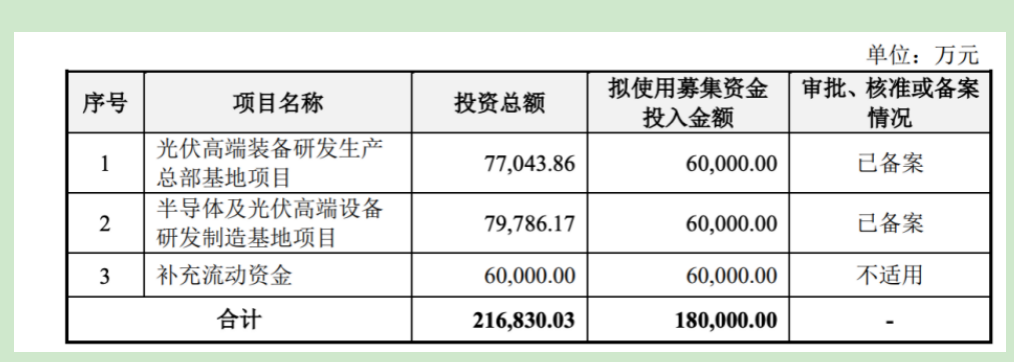
Apart from the sustainability of performance, concerns also arise regarding Laplace's fundraising plan. According to the prospectus, Laplace plans to issue no more than 40,532,600 new shares publicly, raising a total of 1.8 billion yuan. These funds will be allocated to the research and production base of high-end photovoltaic equipment, the research and manufacturing base of high-end semiconductor and photovoltaic equipment, and for working capital.
However, Financial News observes that with the issue of photovoltaic industry overcapacity becoming a focal point of public discourse and a reality over the past two years, the photovoltaic sector has faced challenges, casting doubt on the preconditions for Laplace's continued large-scale fundraising and expansion.
Public data shows that China's photovoltaic raw material exports (silicon wafers, cells, and modules) totaled 18.979 billion US dollars in the first half of 2024, a decrease of 35.07% year-on-year from the previous year, falling short of the 20 billion US dollar mark. Meanwhile, photovoltaic cell production by enterprises above designated size increased by 17.80% year-on-year to 286.9 GW. Although China's newly installed photovoltaic capacity grew by 30.68% year-on-year in the first half of this year, the total reached only 102.48 GW, significantly lower than actual output.
Industry insiders suggest that the domestic photovoltaic industry is already plagued by severe overcapacity, and over the next two to three years, more than half of China's photovoltaic manufacturers may be forced out of the market.
According to the prospectus, 600 million yuan of Laplace's 1.8 billion fundraising will be used for the research and production base of high-end photovoltaic equipment. However, given the apparent overcapacity in the photovoltaic industry and the substantial downturn in major customer performance, there are concerns about the absorbability of newly expanded capacity.
Perhaps anticipating the pressures in the photovoltaic industry, Laplace has gradually ventured into the semiconductor equipment sector. However, Financial News notes that based on sales data during the reporting period, photovoltaic equipment remains Laplace's primary product, accounting for 96.58%, 98.65%, and 92.64% of main business revenue in each period, respectively, exceeding 90% despite a slight decline. In contrast, revenue from semiconductor equipment accounted for less than 10%.
Out of the 1.8 billion yuan raised, 600 million yuan is earmarked for the research and production base of high-end semiconductor and photovoltaic equipment. However, given the minimal revenue from the semiconductor sector, questions arise about the allocation of these funds. Are they solely for the purpose of fundraising?
Furthermore, Financial News believes that as Laplace's photovoltaic products enter a downward adjustment cycle, and its semiconductor equipment business has yet to gain momentum, there is significant uncertainty regarding whether the company's performance will further grow or remain stable even if it successfully lists.
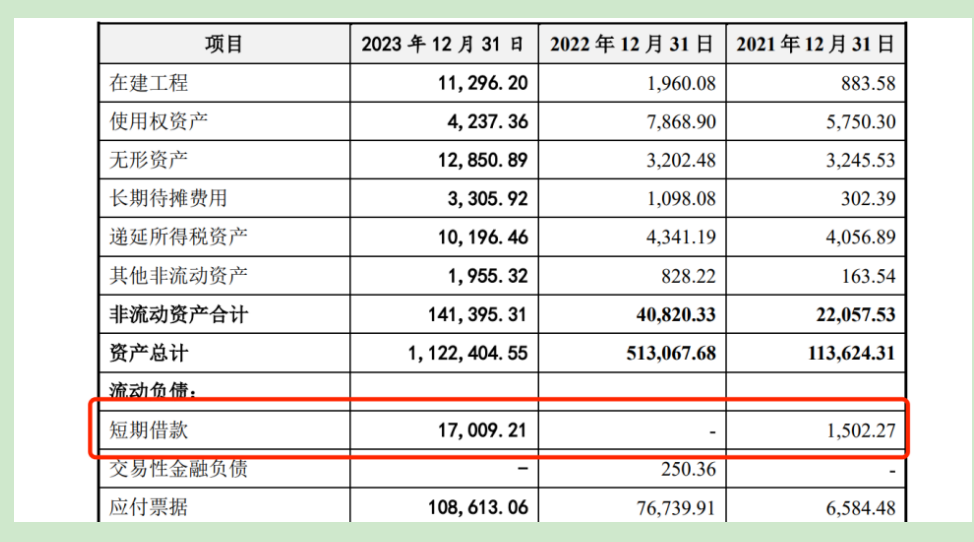
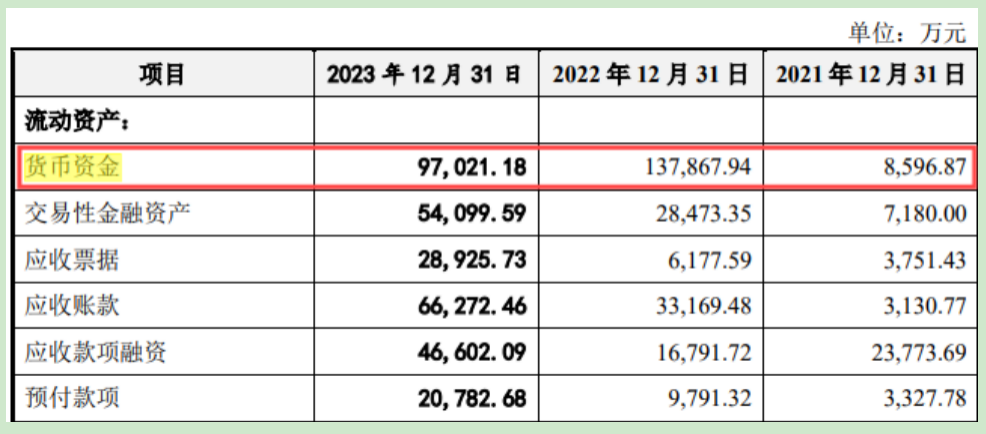
Apart from raising substantial funds for project construction, Laplace's fundraising plan also includes a provision for 600 million yuan in working capital. However, Financial News notes that as of the end of 2023, Laplace held 970 million yuan in monetary funds and 170 million yuan in short-term borrowings. On paper, the company does not appear to lack liquidity, raising questions about the rationale behind raising an additional 600 million yuan for working capital.
Major Customers Also Major Shareholders, Related-Party Transactions Under Regulatory Scrutiny
In addition to the aforementioned issues, Laplace's related-party transactions with major customers have also attracted the attention of regulators, particularly those involving Longi Green Energy and JinkoSolar. These companies are not only Laplace's major customers but also its shareholders, potentially raising concerns about Fictional transaction and pricing fairness.
These interconnected relationships between shareholders and customers have led to multiple inquiries during Laplace's IPO process, adding an intriguing layer to the situation. Financial News' research reveals that Liancheng Precision Machinery, Laplace's largest direct shareholder, invested in Laplace and signed a performance-based agreement in January 2019. In April 2020, Liancheng Precision Machinery acquired an additional 284,690 shares of Laplace's registered capital for 50 million yuan. To date, Liancheng Precision Machinery holds 16.87% of Laplace's shares, making it the company's largest shareholder.
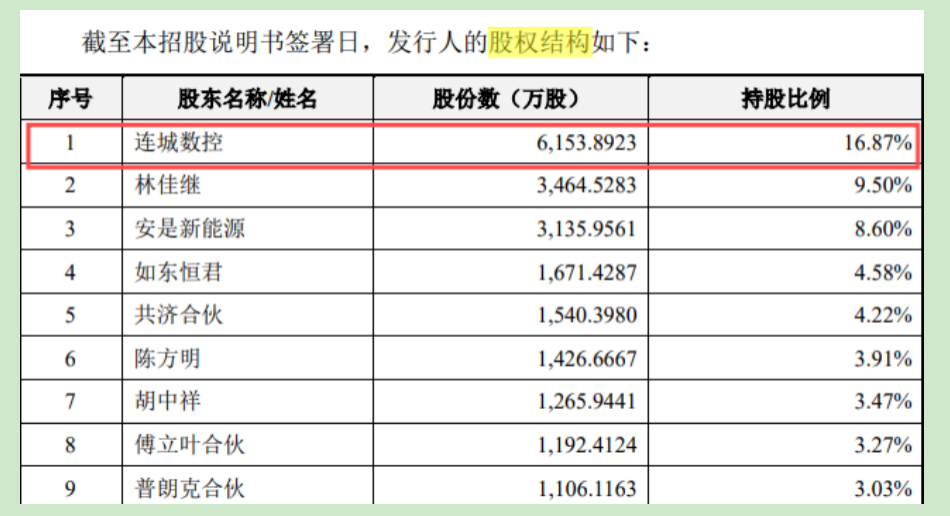
Upon closer examination, Financial News discovered that Zhong Baoshen, one of the actual controllers of Liancheng Precision Machinery, serves as the chairman of Longi Green Energy. Li Chun'an, the chairman of Liancheng Precision Machinery, also served at Longi Green Energy for many years. In 2020, Longi Green Energy contributed 31.12 million yuan to Laplace's revenue, accounting for 76% of its total revenue that year. In 2023, Longi Green Energy remained Laplace's largest customer, contributing an astonishing 1.056 billion yuan, although its share decreased to 35.79%. The relationship between Longi Green Energy and Laplace is particularly intriguing.
Apart from Longi Green Energy, JinkoSolar's relationship with Laplace is also noteworthy. After Longi Green Energy's contribution declined, JinkoSolar took over as Laplace's top customer in 2021. From 2021 to 2023, JinkoSolar purchased 55.5112 million yuan, 613 million yuan, and 827 million yuan worth of products from Laplace, respectively, accounting for 54.21%, 48.55%, and 28.01% of Laplace's main business revenue during these years.
What is the relationship between JinkoSolar and Laplace? Financial News' research revealed that in December 2021, Shangrao Hongxin and Dexing Chuanhong respectively invested 32 million yuan and 33 million yuan in Laplace. In April 2022, these two companies transferred their shares in Laplace to Shangrao Changxin, which shares the same controlling shareholder as JinkoSolar.
Relying on the support of these 'complexly' related photovoltaic listed companies, Laplace managed to turn a profit starting in 2022. However, behind this explosive growth fueled by customers who are also shareholders lies hidden risks. Apart from inquiries into related-party transactions, risks also stem from the influence of actual controllers on the company.
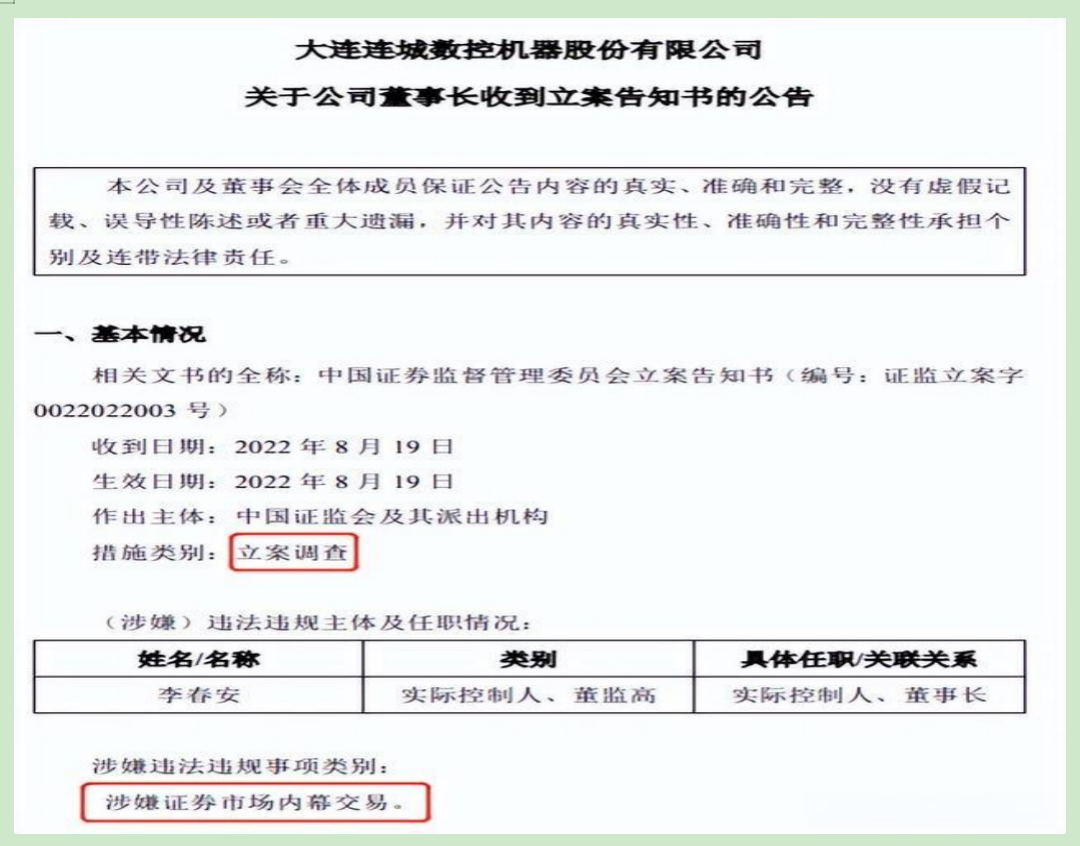
For instance, Li Chun'an, one of the actual controllers of Liancheng Precision Machinery, was investigated by the China Securities Regulatory Commission for suspected insider trading in the securities market in 2022. He received both an Advance Notice of Administrative Penalty and an Administrative Penalty Decision this year. Since Li Chun'an is also a concerted action person of Longi Green Energy, this incident impacted Longi Green Energy's share price, causing it to decline and its market value to shrink.
Although Longi Green Energy previously stated that the investigation into Li Chun'an had nothing to do with the company and that he did not hold any positions or participate in daily operations, the incident's impact on the company cannot be entirely disregarded.
Given Laplace's close relationship with Longi Green Energy and the fact that the chairman of its largest shareholder is under investigation, it would be inaccurate to claim that Laplace has been unaffected. Financial News noted that in Laplace's registration draft disclosed in April 2024, no mention was made of Li Chun'an's receipt of the Advance Notice of Administrative Penalty from Liancheng Precision Machinery. This raises questions about the quality of Laplace's information disclosure.
In summary, Laplace faces numerous challenges during its IPO process, particularly concerning the sustainability of its growth, fundraising amount, information disclosure, and related-party transactions. Additionally, the insider trading incident involving Li Chun'an, the actual controller of Liancheng Precision Machinery, Laplace's largest shareholder, has garnered widespread attention. These events highlight the current regulatory scrutiny on companies seeking to list and their related parties. Financial News will continue to closely monitor Laplace's listing journey.