Betting on Generative AI, SenseTime has begun to step into the limelight to compete fiercely?
![]() 09/09 2024
09/09 2024
![]() 442
442

[Abstract] SenseTime's financial performance has been unsatisfactory in recent years, with revenue declining by 10.57% in 2023 and a net profit loss of RMB 6.44 billion. Gross margin also plummeted from 66.75% in 2022 to 44.07% in 2023. Facing tight cash flows and accounts receivable impairments of up to 53%, SenseTime faces immense pressure in cost control and business expansion.
Amidst the need for change, SenseTime is shifting its focus to the generative AI field through business restructuring.
In 2023, its generative AI business revenue surged by 199% to RMB 1.184 billion, accounting for 34.8% of the company's total revenue. The rapid iteration and launch of its 'SenseNova 5.5' large model further consolidated its leading position in China's generative AI field.
As generative AI evolves, competition based on performance and applications has become the norm. The next stage should involve competition in scenarios. However, given the current landscape, price competition may emerge as the initial benchmark. Leading players, including those in the internet sector, continue to leverage their established brands to enhance market penetration.
SenseTime is stepping into an unfamiliar territory with this front-stage competition, which will now become its norm. How it navigates this role transformation is crucial to gaining an advantage.
Who Will Save SenseTime?
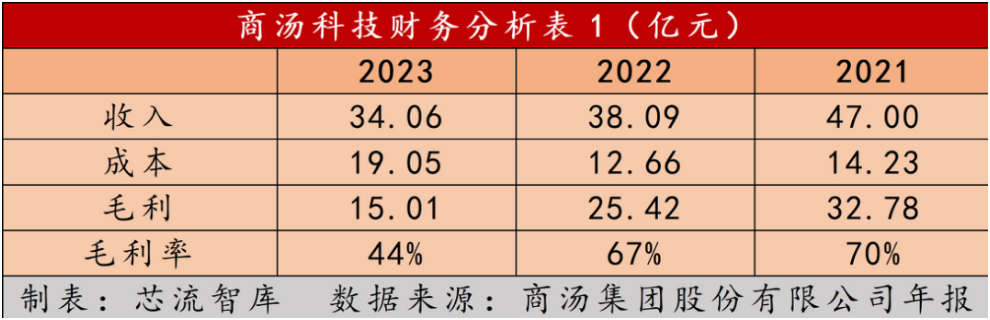
On March 26, 2024, SenseTime released its annual financial data. Core performance highlights include a 10.57% year-on-year decline in revenue to RMB 3.406 billion in 2023 and a net profit loss of RMB 6.44 billion, down 6.54% YoY, marking a double-digit decline in both revenue and profit.
Since its pre-IPO period in 2018, SenseTime has incurred consecutive losses for six years, totaling RMB 50.174 billion.
Alongside declining revenue, gross margin has also trended downwards. In 2023, SenseTime's gross margin plunged from 66.75% in 2022 to 44.07%.
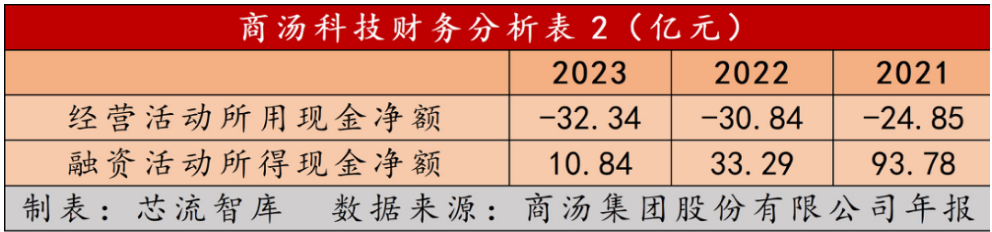
Cash flow is also a concern. Data shows that from 2021 to 2023, net cash flow from operating activities was negative at RMB -2.485 billion, -3.084 billion, and -3.234 billion, respectively. Meanwhile, net cash flow from financing activities was RMB 9.378 billion, 3.329 billion, and 1.084 billion, respectively. The company's cash on hand remains relatively abundant at RMB 16.53 billion, 7.963 billion, and 9.423 billion, respectively.
A notable trend is the increasing outflow of cash from operating activities and tightening cash flow from financing activities. While SenseTime previously relied on external funding for aggressive expansion, future decisions may require greater caution.
Especially now, as most capital markets have cooled down, the demand for funding for advanced AI technologies is exploding. For SenseTime, which needs to continuously iterate its technologies, the challenges are self-evident.
Additionally, the cumulative impairment loss on accounts receivable reached RMB 4.19 billion, with an additional RMB 1.6 billion in 2023 alone, representing a 53% impairment loss rate. This implies that over half of the company's accounts receivable are at risk of bad debt.
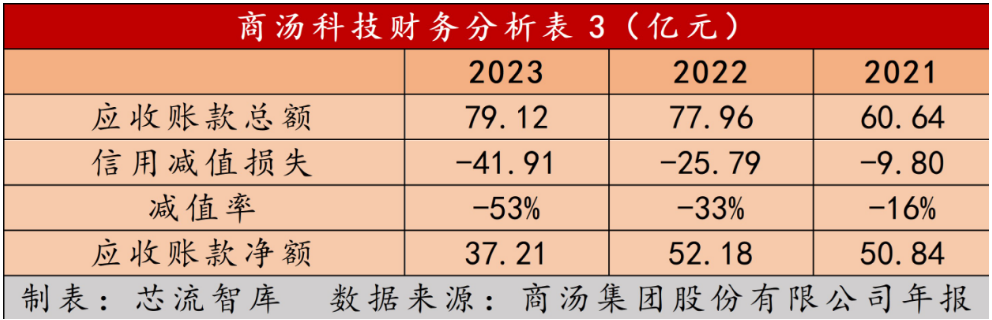
In response, SenseTime stated, "Most of our past revenue came from smart cities, which typically have long payment cycles due to their internal financial management and approval processes. Some customers, especially those in smart cities, face temporary budget constraints and an uncertain macroeconomic environment."
Amidst setbacks in its main business, SenseTime's commercialization has sparked more controversy and uncertainty.
Betting on Generative AI, SenseTime Starts Calculating its Business Moves
In 2023, SenseTime implemented a business restructuring, clarifying its three new business segments: Generative AI, Traditional AI, and Smart Automobile, gradually shifting its focus to Generative AI.
Currently, Generative AI is still in its early commercialization stage. Companies tend to launch products as soon as they're ready and iterate gradually, balancing revenue generation with long-term planning. This strategy contrasts sharply with SenseTime's past research-oriented approach, indicating a significant shift in its market positioning.
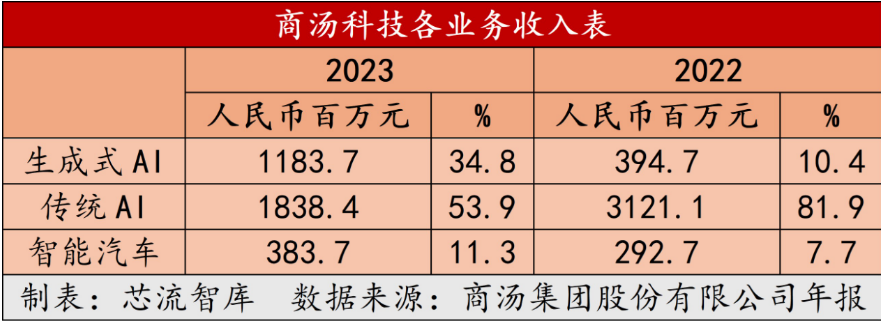
Data shows that SenseTime's Generative AI revenue surged 199% YoY to RMB 1.184 billion in 2023, accounting for 34.8% of total revenue.
This growth was facilitated by a strategic restructuring of the business structure in 2023. While traditional smart city and smart commerce segments still play important roles, their growth momentum has weakened. In contrast, the Generative AI business has been elevated to an unprecedented level, becoming a cornerstone of the company's future development.
In other words, SenseTime aims to prioritize its most promising businesses, leveraging their growth potential to secure market share and attract capital market attention.
While SenseTime's roots lie in visual technology, seemingly unrelated to large models, its computing power is formidable.
As early as 2021, SenseTime launched SenseCore, comprising computing power, platform, and algorithm layers, with substantial investments in computing power. Although initially criticized for its significant funding requirements, the strategic value of computing power has become evident in the era of large models.
Notably, SenseTime, which previously operated quietly behind the scenes, has become increasingly visible this year.
Especially in the early stages of Generative AI iteration, SenseTime's momentum has been overwhelming, even surpassing some established players with earlier layouts.
Meanwhile, despite downsizing in smart cities and smart commerce, the smart automobile segment remains significant.
In 2023, the Jueying Smart Automobile business generated RMB 383.7 million in revenue, up 31.1% YoY. Both intelligent driving and smart cockpits achieved sustained growth. In terms of mass production delivery, the smart automobile segment added 1.29 million vehicles YoY, a significant increase of 163%. Economically, the gross margin per smart cockpit vehicle increased by 30%.
Can SenseTime Turn Things Around?
Historically, Generative AI is not SenseTime's first foray into trending technologies. In 2021, SenseTime capitalized on the 'metaverse' concept to make a splash in its IPO, briefly becoming a focal point.
However, as the metaverse hype faded, SenseTime faced criticism for being more concept than substance.
Now, with the 'large model' opportunity back in hand, avoiding the pitfalls of commercialization is SenseTime's top priority.
Cost, efficiency, and scale are crucial issues to address on the path forward.
Currently, SenseTime's 'SenseNova' large model ranks among the top in China's AI field, with a strategic goal of building 'China's OpenAI.'
However, large models still grapple with the challenge of homogeneity. Many utilize similar datasets and training methods, producing similar outputs.
A clear solution to precisely match industry-specific scenarios in healthcare, transportation, education, finance, etc., remains elusive.
Another significant challenge stems from price wars ignited by domestic internet giants' large models.
ByteDance announced significant price cuts for its 'Doubao pro-128k' version in May, reducing inference costs by 95.8% to around 1% of industry prices. Alibaba's 'Tongyi,' Baidu's 'Wenxin,' and iFLYTEK's 'Spark' have followed suit, offering lightweight models at single-digit prices per million tokens or even for free.
With prices dropping before market penetration, companies are racing to grab market share and iterate based on user scale. In this race, brand perception and even slight price differences can significantly influence consumer decisions.
In this undifferentiated 'attack' phase, SenseTime must either match price cuts or pay an even higher cost unless it can offer revolutionary product scenarios. Facing years of losses, the pressure may just be beginning.
Moreover, while Generative AI holds promise, its maturity and widespread adoption require time. Even OpenAI, a pioneer in the field, is still on the path to commercialization. Public records show that OpenAI incurred losses of USD 540 million in 2022. While 2023 figures are yet to be released, profitability remains distant.
Epilogue
As Generative AI evolves, competition based on performance and applications has become the norm. The next stage should involve competition in scenarios. However, given the current landscape, price competition may emerge as the initial benchmark.
Leading players, including those in the internet sector, continue to leverage their established brands to enhance market penetration, driving incremental growth.
Against this backdrop, it remains uncertain whether SenseTime can swiftly translate its technological layout into sustained profit growth. This front-stage competition, previously unfamiliar territory for SenseTime, will now become the norm.
Navigating this role transformation is crucial to gaining a competitive edge.