["Long Article of 10,000 Words"] Domestic and International RPA Products Upgrade to AI Agent, Where are the Future Opportunities for the Continuous Evolution of RPA Agent?
![]() 09/18 2024
09/18 2024
![]() 638
638

["Long Article of 10,000 Words"] The Evolution of RPA's AI Agent: What Advantages and Opportunities Does It Bring to RPA Vendors?
A Comprehensive Overview of Global RPA Agent Products: New Opportunities for the Hybrid Automation of RPA and AI Agent
Domestic and International RPA Products Upgrade to AI Agent, Where are the Future Opportunities for the Continuous Evolution of RPA Agent?
What Are the Products and Solutions that Integrate RPA and AI Agent, and What Are Their Advantages? A Comprehensive Guide
What are the Integrated Products of RPA and AI Agent? What Are Their Advantages, Opportunities, and Future Development?
How Does the Collective Evolution of RPA Products to AI Agent Impact Enterprise Automation? Read This Article to Find Out, with 9 Related Papers Attached
Total Word Count: Approximately 13,000, Reading Time: 20 Minutes
Written by Wang Jiwei
Even the tech community might not have anticipated that the popularity of AI Agent would reignite interest in RPA.
Since the advent of ChatGPT and the global popularity of large language models, many have predicted the demise of RPA. However, upon closer inspection, RPA is not only alive and well but has evolved with the latest technologies, giving rise to RPA Agent and autonomous digital workers.
Traditional RPA is indeed a thing of the past, but RPA integrated with LLM and AI Agent is thriving.
Extended Reading: How Long Will Contemporary RPA Built on AI Survive Under the Influence of Generative AI?
Shortly after the popularity of LLM, attention shifted to AI Agent. Due to issues such as insufficient API quantity and stability, researchers found that the current stage favors a significant enhancement of AI Agent's execution capabilities through "UI+API Automation."
Gartner has already written about "providing automation through API+UI integration" in its 2022 Magic Quadrant for RPA report, predicting that by 2024, 95% of RPA vendors will offer automation through API and UI integration.

Extended Reading: RPA in the New Trend of API and UI Integration: Overseas Vendors Take the Lead, Where Do Domestic Vendors Stand?
RPA's UI automation capabilities alone make it a super tool for "Tool Use" among the four design patterns of AI Agent outlined by Professor Andrew Ng. Furthermore, the integration of numerous enterprise-grade APIs and connectors allows RPA to facilitate various business processes based on enterprise management software that may be out of reach for AI Agent alone.
By invoking RPA through APIs and then participating in more complex business processes in the real world with APIs+UI, this model enables AI Agent to be implemented in any business scenario.
The insufficient execution capabilities of AI Agent have also piqued the academic community's interest in RPA, making the integration of LLM, AI Agent, and RPA a focal point. For those interested, please refer to the following papers:
1. PromptRPA: Generating Robotic Process Automation on Smartphones from Textual Prompts PromptRPA: Generating Robotic Process Automation on Smartphones from Textual Prompts Paper Link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.02475
2. ProAgent: From Robotic Process Automation to Agentic Process Automation ProAgent: From Robotic Process Automation to Agentic Process Automation Paper Link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2311.10751 Project Link: https://github.com/OpenBMB/ProAgent
3. AUTONODE: A Neuro-Graphic Self-Learnable Engine for Cognitive GUI Automation AUTONODE: A Neuro-Graphic Self-Learnable Engine for Cognitive GUI Automation Paper Link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.10171
4. SmartFlow: Robotic Process Automation using LLMs SmartFlow: Robotic Process Automation using LLMs Paper Link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.12842
5. FlowMind: Automatic Workflow Generation with LLMs FlowMind: Automatic Workflow Generation with LLMs Paper Link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.13050
6. Automating the Enterprise with Foundation Models Paper Link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.03710 Project Link: https://github.com/HazyResearch/eclair-agents
7. CAAP: Context-Aware Action Planning Prompting to Solve Computer Tasks with Front-End UI Only Paper Link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.06947
8. Human-Centered Automation Paper Link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.15960
9. GUIDE: Graphical User Interface Data for Execution Paper Link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.16048
With the popularity of AI Agent construction platforms like Coze and Dify, RPA enthusiasts have exclaimed, "Isn't this just an upgraded version of RPA?" This sentiment arises partly because the AI Agent construction page resembles RPA. To substantiate this claim, consider the comparison between the Coze workflow construction interface and the RPA construction interface below.
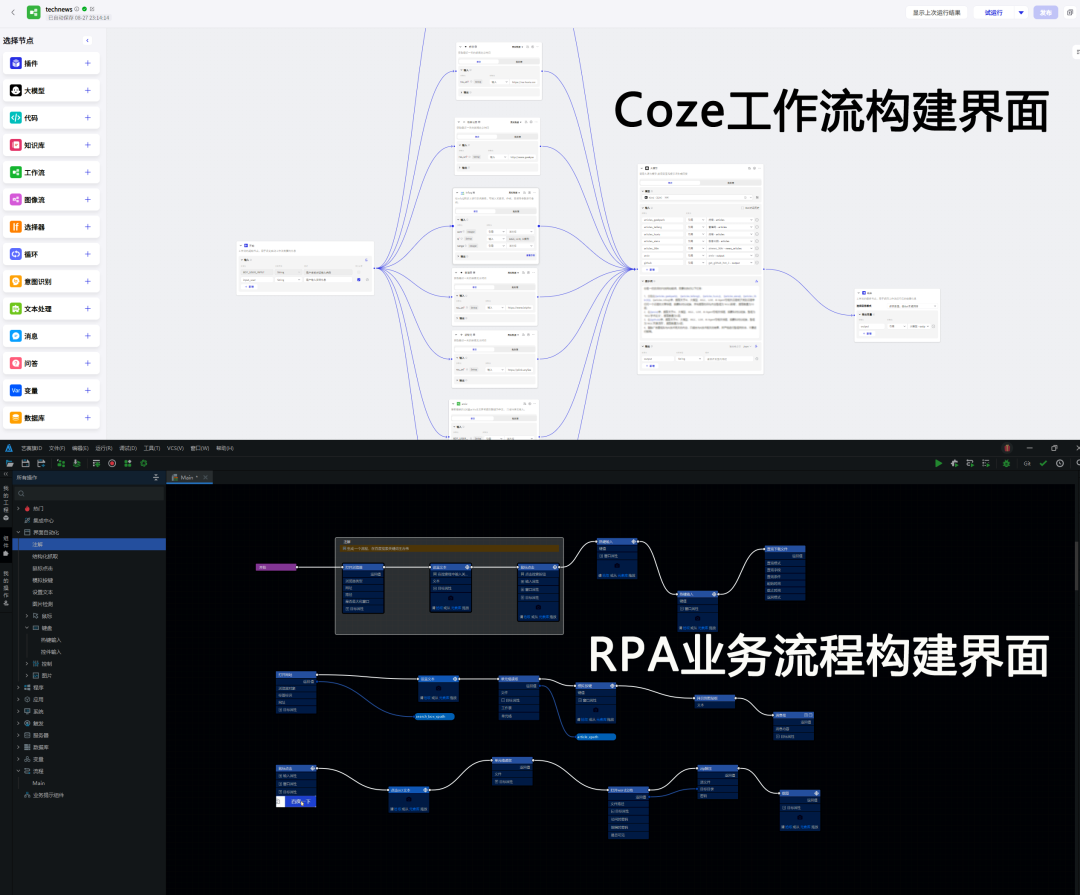
Coze Workflow Construction Interface vs. RPA Business Process Construction Interface
Some may wonder why AI Agent and RPA are compared when they are fundamentally different products. This confusion likely stems from a lack of understanding of AI Agent's "Tool Use" concept or the integration of RPA and AI Agent. For a clearer distinction and connection between RPA and AI Agent, refer to the image below. For more detailed information, feel free to search or consult large language models; there is an abundance of relevant material online.
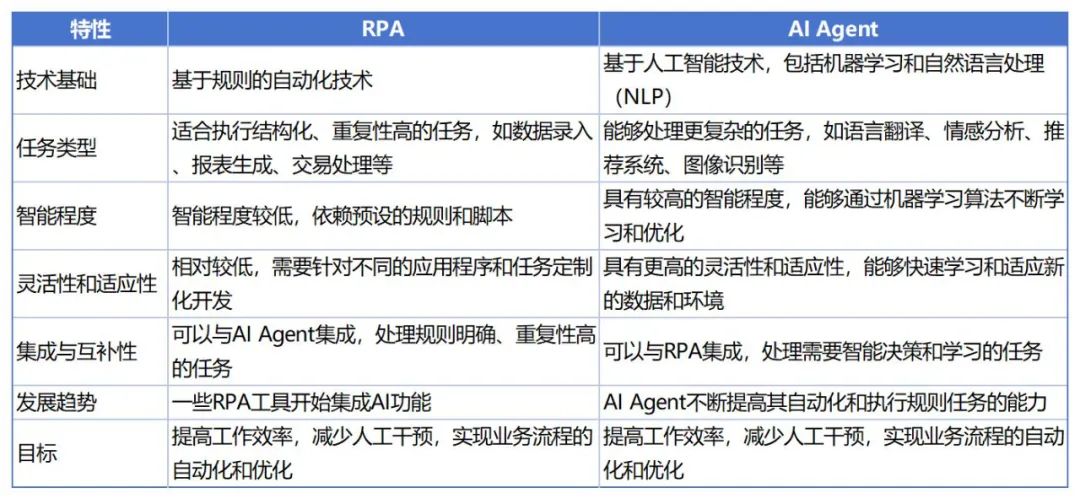
In fact, RPA Agent has become a significant category within the AI Agent family and is gaining popularity in enterprise applications. In enterprise-level applications, discussions about the integration of RPA, AI Agent, and LLM far exceed those solely focused on AI Agent.
Firstly, many organizations have already deployed RPA, relying on it for automation of various business processes. Gartner has predicted in two separate reports that: - By the end of 2023, 90% of large and very large organizations will have deployed some form of Robotic Process Automation (RPA). - By 2024, 75% of governments will have initiated or implemented at least three hyperautomation initiatives, with RPA serving as a crucial component for digital modernization. Therefore, organizations must leverage their investments in RPA by integrating it with AI Agent technology, aligning with the trend of enterprise automation. Secondly, RPA significantly enhances AI Agent's execution capabilities in complex enterprise business processes with minimal investment, making it an ideal tool for expanding AI Agent's capabilities. One of the most frequently asked questions among enterprises that have adopted RPA is how to integrate RPA and AI Agent to improve operational efficiency.
Another crucial aspect is that RPA Agent can proactively think about how to accomplish tasks. Imagine: traditional RPA followed predefined rules, akin to a wooden puppet that merely claps to welcome guests. In contrast, RPA integrated with Agent not only claps to welcome but also inquires about your purpose and guides you to a restaurant to assist with ordering. This expands the potential of RPA's future capabilities exponentially.
Furthermore, digital workers powered by RPA integrated with AI Agent are a primary research direction for AI Agent. The digital workers introduced by RPA vendors have evolved into more capable intelligent digital workers.
Extended Reading: [Long Article of 10,000 Words] Ten Major Research Directions for the Future Development of AI Agent: Digital Workers, Super Individuals, and Embodied Intelligence
To meet the growing demand for upgrading RPA to Agent, RPA vendors must stay abreast of the times and leverage all means to integrate LLM and AI Agent with RPA, driving technological iteration. As a result of increasing market demand and the efforts of technology providers, RPA products and solutions have collectively evolved to include Agent capabilities.
So far, which vendors have launched AI Agent products or solutions? What forms do they take? What are the advantages and opportunities of RPA Agent? What is the future trend? In this article, Wang Jiwei Channel delves into these questions with 13,000 words. Note: All research reports and papers mentioned in this article have been packaged. Reply with 'RPA Agent' to access them.
Evolution of AI Agent in Overseas RPA
In August, Gartner, a global consulting and research firm, released the "Magic Quadrant for Robotic Process Automation (RPA), 2024" report. The report predicts that by 2025, 90% of RPA vendors will integrate generative AI technology to further enhance automation intelligence. After further market consolidation and strategic shifts by vendors, only 13 vendors were selected for this year's report. Four vendors remain in the Leaders quadrant, with Microsoft overtaking SS&C-acquired Blue Prism to become one of the top three global RPA vendors, SAP entering the Challengers quadrant, and ServiceNow newly entering the Visionaries quadrant. In the Niche Players quadrant, four vendors remain, with only Laiye Technology representing domestic vendors, demonstrating improved execution capabilities and vision completeness.
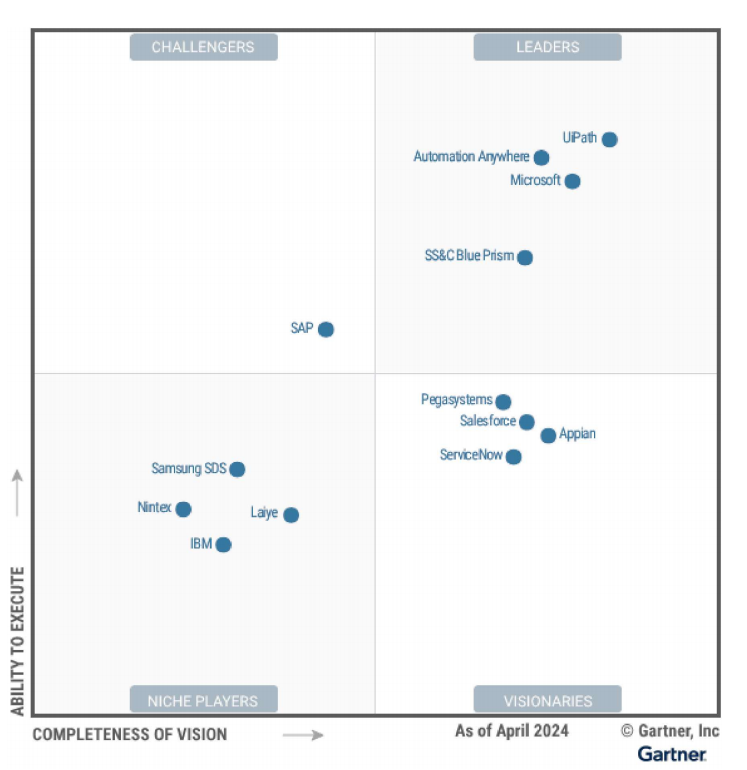 Changes across quadrants have been significant in just one year.
We'll briefly introduce the report here, as it primarily serves as a foundation for the content that follows.
Tracing the report's leads, Wang Jiwei Channel found that at least four vendors have launched or focused on the AI Agent model. Below is an overview of these vendors and their products. Incidentally, Laiye Technology's AI Agent product will be introduced in the domestic section.
Automation Anywhere: AI Agent Studio
In July, Automation Anywhere introduced AI + Automation Enterprise System, integrating GenAI process models with its traditional automation platform to enhance customers' workflow automation.
A groundbreaking new feature of this system is the ability to build custom AI Agents using AI Agent Studio. AI Agent Studio provides low-code tools for developers of all levels to easily build, manage, and govern custom AI Agents. Developers can start with a base model of their choice, including models from AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure OpenAI Service, and will support Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) services by the end of October.
Changes across quadrants have been significant in just one year.
We'll briefly introduce the report here, as it primarily serves as a foundation for the content that follows.
Tracing the report's leads, Wang Jiwei Channel found that at least four vendors have launched or focused on the AI Agent model. Below is an overview of these vendors and their products. Incidentally, Laiye Technology's AI Agent product will be introduced in the domestic section.
Automation Anywhere: AI Agent Studio
In July, Automation Anywhere introduced AI + Automation Enterprise System, integrating GenAI process models with its traditional automation platform to enhance customers' workflow automation.
A groundbreaking new feature of this system is the ability to build custom AI Agents using AI Agent Studio. AI Agent Studio provides low-code tools for developers of all levels to easily build, manage, and govern custom AI Agents. Developers can start with a base model of their choice, including models from AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure OpenAI Service, and will support Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) services by the end of October.
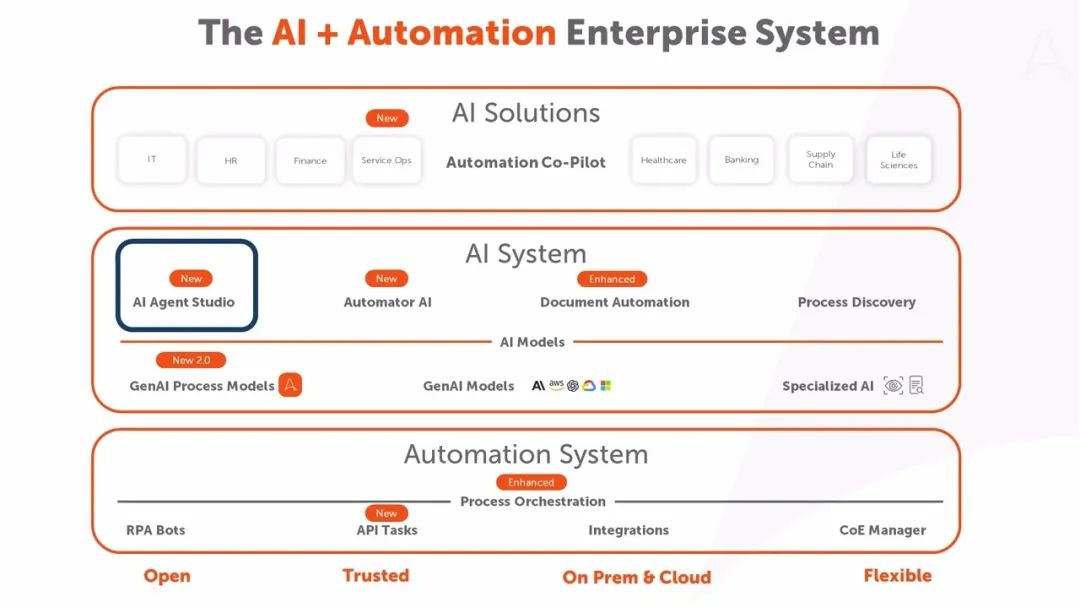
The underlying engine supporting the AI + Automation Enterprise System is Automation Anywhere's unique GenAI process model. GenAI Process Model 2.0 is designed to facilitate faster process discovery, increase automation creation speed by 30%, enhance document processing accuracy to 90%, and improve automation flexibility by 50%, surpassing what LLMs can offer independently. These models are optimized using rich metadata from over 300 million process automations running on Automation Anywhere's cloud-native platform.
Automation Anywhere has also introduced Automation Co-Pilot, an embedded enterprise assistant tailored for organizations and integrated with Amazon Q Service. Business users can now complete tasks in any application more efficiently, obtain on-demand assistance through chat interactions, inquire about knowledge base issues, invoke AI Agents, or initiate automations. The enterprise-grade Automation Co-Pilot can be embedded into any application users work with and operate across systems within the organization.
Salesforce: Einstein Service Agent
Salesforce has been active in AI Agent developments recently.
First, in July, they introduced Einstein Service Agent, the company's first fully autonomous AI Agent. Einstein Service Agent understands and acts on various service issues without pre-programmed scenarios, enhancing customer service efficiency.
Built on the Einstein 1 platform, Einstein Service Agent analyzes the entire context of customer messages before autonomously determining the next action to take, utilizing large language models (LLMs) for interactions. It employs generative AI to create conversational responses based on the company's trusted business data, including Salesforce CRM data, which can be customized to match the company's voice, tone, and branding guidelines with just a few clicks.

Then, in August, Salesforce launched two new autonomous AI Sales Agents: Einstein Sales Development Rep (SDR) Agent and Einstein Sales Coach Agent. The former is designed to autonomously manage inbound leads and engage potential customers through natural language, providing 24/7 support, while the latter focuses on enhancing sales team skills through realistic role-playing scenarios.
Salesforce plans to introduce Agentforce during the September Dreamforce conference. Based on the Einstein1 low-code platform, Agentforce enables the creation, testing, and scaling of custom AI Agents. Agentforce allows customers' custom AI agents to securely leverage Data Cloud to integrate all enterprise data, seamlessly execute tasks through Flow automation, and easily access enterprise APIs through MuleSoft.
Before official deployment, extensive testing can be conducted in a sandbox environment to ensure smooth operation. After deployment, these agents can function within customers' applications, websites, social media, and Slack.
Salesforce aims to deploy millions of AI-driven agents and expects to reach a billion-scale commercial impact.
ServiceNow: Now Assist Series AI Agents
Since last year, ServiceNow has actively promoted generative AI, integrating various powerful AI capabilities into its workflow platform. These efforts have primarily focused on the Now Assist series of AI Agents, which are integrated with the company's Service Management, Customer Service Management, Human Resources Service Delivery, and Workflow Creator modules.
In September 2023, ServiceNow released Now Assist, an AI-powered solution designed to enhance productivity and experience for its customers across IT, Customer Service, Human Resources, and Development. Driven by ServiceNow's proprietary generative AI engine, Now Assist introduces a domain-specific 'Now LLM' aimed at improving enterprise-level productivity and data privacy.
In November, all customers gained access to new Now Assist products, including Now Assist in Virtual Agent, Process Generation, and Now Assist for Field Service Management, through the ServiceNow Store.

In March 2024, Now Assist for IT Operations Management AIOps was launched, applying generative AI to accelerate issue resolution by analyzing alerts and providing useful context to operations teams. Additionally, a series of Impact AI Accelerators were introduced in ServiceNow Impact, designed to help companies expedite the time-to-value for ServiceNow investments.
In May, ServiceNow introduced the BYO GenAI model capability for Now Assist, further empowering its agents. Customers can choose any large language model as the core of Now Assist agents, whether proprietary LLMs like GPT-4 or Gemini Pro, or custom-developed LLMs, to optimize the Now Assist experience.
Now Assist for Strategic Portfolio Management was also released, aiming to assist product managers in integrating unique customer needs through customer feedback.

Among overseas RPA vendors, apart from the ones mentioned above that have introduced AI Agents, most others primarily focus on Copilot. For instance, UiPath has launched UiPath Autopilot for developers and testers, which can also integrate with Microsoft 365 Copilot plugins. Appian's latest business process platform has added more support for Appian AI Copilot.
Even Microsoft, which has launched open-source agent architectures like Autogen and Taskweaver, has enhanced its Copilot offerings by integrating Power Automate plugins to improve execution capabilities.
Currently, the LLM application model embodied in Copilot better aligns with market demands and has almost become a standard feature in enterprise applications. However, according to Forrester's forecast on the automation tool market trends, by 2028, vendors will incorporate AI Agent orchestration capabilities into their platforms, so AI Agent solutions will eventually emerge.
This can be seen in UiPath founder Daniel Dines' recent interviews, where he extensively discussed AI Agents.
Evolution of AI Agents in Domestic RPA
While foreign RPA vendors primarily focus on Copilot, domestic RPA vendors have mostly concentrated on AI Agents. Since the second half of last year, several vendors have successively launched integrated Agent and RPA products. Below is a brief introduction to the AI Agent products and solutions already introduced by vendors.
Laiye Technology: AI Agent Digital Employees
On June 20, Laiye Technology held its Laiye Lead annual product launch event themed 'Digital Employees Enter the AI Agent Era', where it unveiled three high-value, implementable AI Agent digital employee products based on its digital labor platform: Digital Employee Development Assistant, Knowledge Management and Q&A Assistant, and Document Review and Risk Control Assistant.
Digital Employee Development Assistant: Utilizes multi-modal large model technology to improve code generation efficiency and accuracy. It automatically parses complex Excel files, generates automation processes on demand, simplifies development, and reduces costs. The extended command library quickly produces Python code, seamlessly integrates with RPA products, and enhances code reuse and development speed. The 'self-healing' feature automatically adapts to UI changes, reducing interruptions and maintenance costs, enhancing process stability, and ensuring business continuity and efficiency.
Knowledge Management and Q&A Assistant: Integrates large models, RAG, RPA, and IDP technologies to automate document understanding and knowledge generation, providing enterprises with an intelligent solution.
Document Review and Risk Control Assistant: Enhances enterprise document processing efficiency and accuracy, safeguarding cash flow management and business operational risk control.
Zhidezhi AI: RPA Agent
In August 2023, Zhidezhi AI released its proprietary vertical 'TARS' large language model and the industry's first product-level Agent implementation, RPA Agent (TARS-RPA-Agent). Through 'natural conversational interaction and hyper-automation execution,' it significantly lowers the threshold for creating 'digital employees,' making them truly accessible to everyone. In December, Zhidezhi AI completed its Series C funding round, led by Jintaifu Capital and Anji Smart Valley, raising nearly 200 million yuan.
In February 2024, Zhidezhi Mobile Agent launched, and the first public beta of the new version of Zhidezhi Agent was opened at the end of March. In August, Zhidezhi Agent 7.0 was officially released, featuring:
Natural conversational interaction: 'All-in-One' assistant work experience;
Intent understanding and process planning: Enhanced intent understanding and precise process breakdown and planning capabilities;
Multi-generation product capabilities integration: Integrates all capabilities of first-generation RPA and second-generation IPA digital employee element capture, components, and process orchestration;
Precise software interface operation: Multi-modal screen semantic understanding, screen scanning and recognition, and precise interface operation by Agent;
Simultaneously, Zhidezhi AI's underlying TARS large model, trained with hundreds of billions of parameters, has evolved again, supporting larger training parameters and enabling natural language communication, scientific knowledge, and efficient task execution, balancing dialogue and work seamlessly.
In terms of intelligent Q&A, based on Zhidezhi AI's document system (IDP), it can provide precise Q&A and processing of files.
Jinzhiwei: K-Agent
In March, Jinzhiwei unveiled its AI Agent product, K-Agent, and built Jinzhiwei Kopilot based on the K-Agent platform. Jinzhiwei Kopilot is an intelligent assistant (Copilot) application cluster targeting various industries, embodying large model capabilities and directly addressing enterprises' practical needs.
The K-Agent platform boasts capabilities in intelligent interaction, reasoning, analysis, and self-training, enabling continuous learning and self-optimization. Users can rapidly develop and deploy various intelligent assistant (Copilot) digital employees on the K-Agent platform to address diverse business scenario needs.
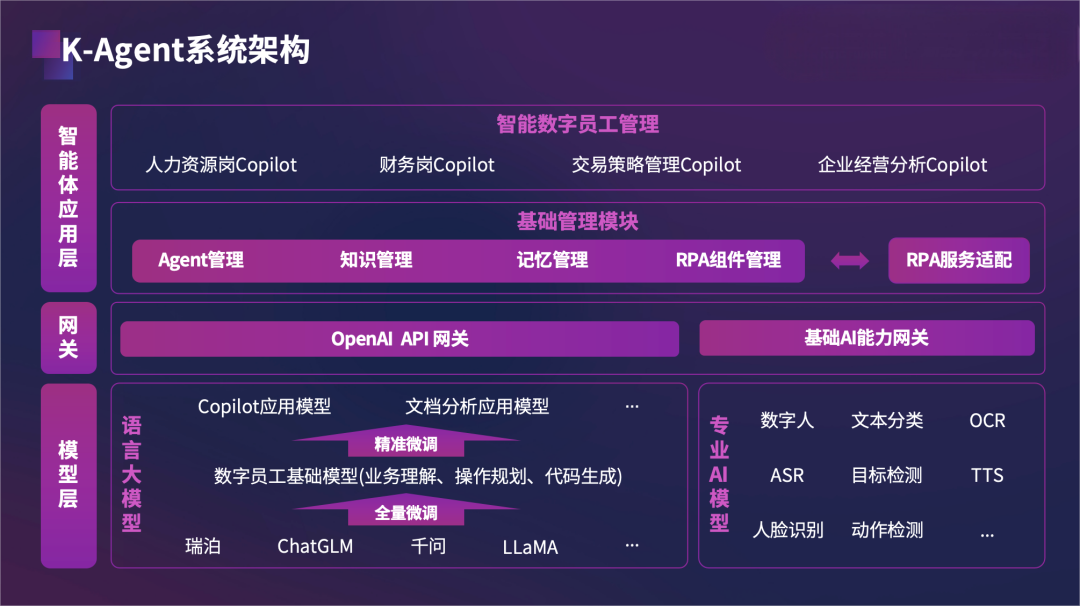
Intelligent assistants developed on the K-Agent platform rely on fine-tuned domain models to autonomously analyze task instructions, plan operational processes, generate RPA scripts to invoke corresponding platforms or applications, and efficiently complete business requirements, providing execution results feedback or answering user questions, transforming complex business decisions into executable business capabilities.
Technologically, K-Agent leverages combinatorial AI technology, drawing on the strengths of various technologies to enhance the learning mechanism of intelligent assistants, making the models smarter with each use. In terms of scenarios, K-Agent incorporates industry-specific knowledge bases to ensure knowledge coverage, professionalism, compliance, and accuracy as required by the industry, reducing the cost of personalized services.
Yidatai Technology: Yunxiaoda - Cuber Digital Employee 3.0
In November 2023, Yidatai Technology launched 'Yunxiaoda - Digital Employee Platform,' a large model-based digital employee aggregation and training platform tailored for the supply chain industry.
This platform provides supply chain enterprises with a virtual digital employee expert team for high-frequency business scenarios such as experienced supply chain freight rate managers, logistics visibility tracking managers, and supply chain newcomer growth mentors. It equips employees with accurate and relevant knowledge in the supply chain domain, facilitating a human-machine collaboration model combining 'white-collar employees' and 'AI Agent Yunxiaoda Digital Employees.'
In July this year, Yunxiaoda-Cuber Digital Employee 3.0 was launched. This product is built on the Agent automation entry point of large models, enabling it to usher in a new era of human-machine collaboration in the supply chain through the guidance of CuberAgent.
As an ultra-automation solution for digital employees based on large supply chain models, Yunxiaoda Cuber revolves around upstream and downstream business scenarios in the supply chain, encompassing upstream manufacturing, intermediate logistics and distribution, and downstream wholesale and retail. It achieves end-to-end automation across marketing and customer acquisition, procurement and sales management, warehousing and logistics, trucking and customs clearance, contract fulfillment, and financial settlement.
Notably, on August 7th, Yida Technology announced the completion of its Series B+ funding round, led by CDH Investments (Venture Growth Capital) with follow-on investment from New Shang Capital.
Yisaiqi: Qiqi Assistant
Since the emergence of large models, Yisaiqi has focused on evolving its RPA products towards ease of learning, use, and stability, deeply integrating large models with RPA. In terms of ease of learning, the semantic understanding capabilities of large models are leveraged to intelligently recommend operational steps for completing tasks, facilitating users to quickly grasp RPA process development, enhancing learning efficiency and user experience.
In terms of ease of use, large models' generative AI capabilities are harnessed to convert natural language commands into code and integrate them into the RPA designer, improving developers' process development efficiency.
In April, Yisaiqi launched Qiqi Assistant (AI-agent), which, by integrating large model capabilities, converts users' natural language inputs into executable commands, automatically determines processing, executes automated processes, and returns processing results in a human-understandable language format.
Regarding stability, during process development, Yisaiqi utilizes the knowledge base of large models to assist developers in problem localization and error troubleshooting, thereby enhancing process stability.
Rongzhi Information: Hyper Agent
On March 29th, Rongzhi Information unveiled its 2024 product portfolio featuring 12 product matrices spanning the entire business lifecycle, including process discovery, analysis, design, automation, execution, monitoring, and reassessment. Among them are Wendo large model and Hpyper Agent, the super intelligent agent.
In late May, Rongzhi Hyper Agent was officially launched. This product primarily integrates the application development capabilities of the "Wendo" large model with the process automation capabilities of iBot digital employees, bridging human intentions with digital workforce commands. Leveraging large models, the Agent simplifies the driving of automation processes, transitioning from rule-based repetitive capability models to autonomous composite capability models encompassing logical reasoning, abstract summarization, and intent recognition, thereby shortening system development cycles and bridging the gap between humans and systems.
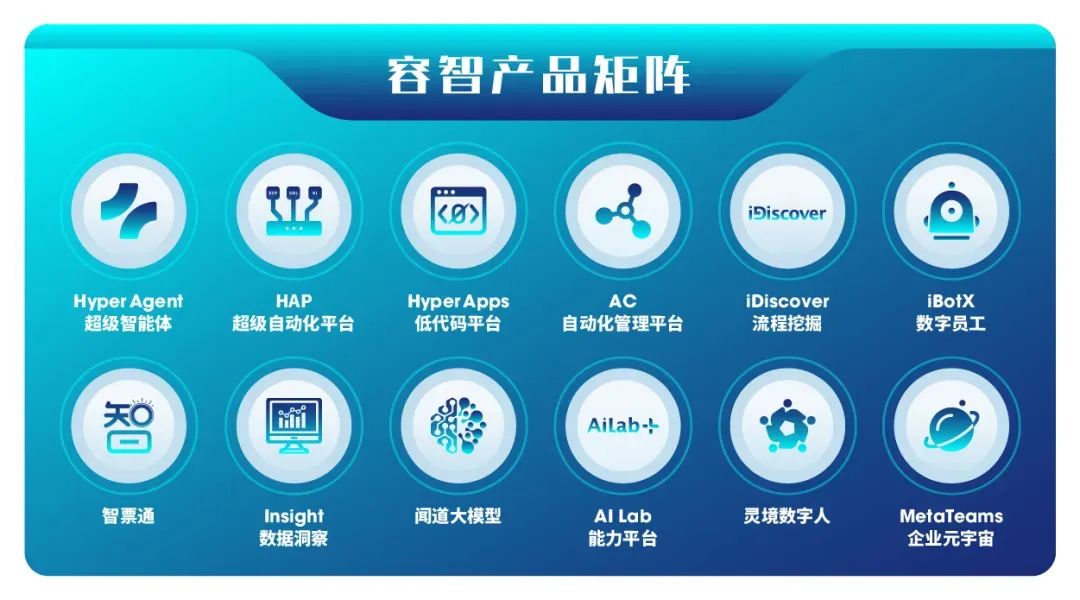
Through Hyper Agent, enterprises can easily and efficiently create enterprise-grade Agent applications, orchestrate workflows, and even switch large model backends with a single click to build Agents tailored to scenarios and individual needs. During natural language interactions, employees can leverage iBot digital employees to automatically complete tasks or execute specific services.
Daguan Data: Digital Employee Agent Platform
In May, Daguan Data launched its Digital Employee Agent Platform. Daguan Smart Digital Employee combines the efficient execution capabilities of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) with the advanced semantic understanding technology of the "Caozhi" large model, realizing enterprise applications that integrate knowledge bases with large models.
On the Daguan Smart Digital Employee Platform, RPA serves as the execution core of digital employees, automating repetitive tasks. The Caozhi large model endows them with the ability to comprehend complex languages and task planning, enabling digital employees to accurately capture and respond to user needs.
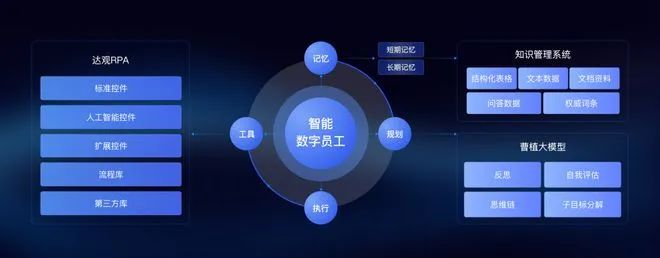
Furthermore, through a knowledge management system, digital employees can store and utilize historical data to optimize task execution strategies. This integration not only enhances enterprise operational efficiency but also drives business process intelligence and automation.
The new-generation intelligent knowledge management system, built upon the "Caozhi" large language model, offers capabilities such as knowledge production, knowledge organization, knowledge search, knowledge Q&A, knowledge graphs, and knowledge communities. It processes and refines massive structured and unstructured documents accumulated by enterprises through natural language techniques, establishing a more intelligent and user-friendly knowledge management system.
Zhongguancun Keking: AgentGraph Application Development Platform
On November 23, 2023, Zhongguancun Keking officially launched its Enterprise Knowledge Large Model, AgentGraph Application Development Platform, and "Super Employee" series of AIGC applications, providing enterprises with out-of-the-box, seamlessly integrated, and cost-effective domain-specific large model services.
Zhongguancun Keking has established a two-winged underlying technology architecture, forming a product system comprising four categories: the Enterprise Knowledge Large Model, its supporting platform of Domain Large Model Factory and Domain Knowledge Base Factory, and four product lines focused on intelligent marketing, intelligent service, intelligent operation, and super employees.
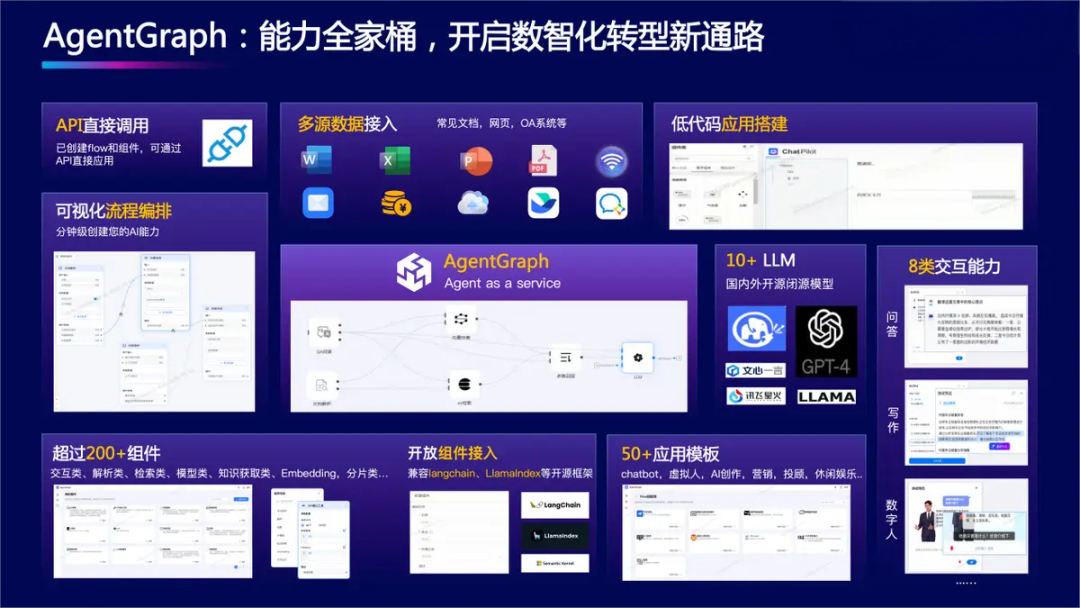
The AgentGraph Application Development Platform serves as an intermediate layer connecting the two-winged architecture and the four product categories, adapting to over a dozen open-source foundational large models, supporting one-click switching with strong compatibility. It boasts over 50 application templates and has modularized over 200 AI capabilities, enabling zero-code application creation in as little as three minutes, further reducing customer innovation costs and shortening development cycles.
AgentGraph integrates Zhongguancun Keking's Enterprise Knowledge Large Model, pre-installing multiple types of large models for domestic and international languages and images, offering a comprehensive range of functions. It is an enterprise-grade, one-stop, end-to-end large model application open platform, providing application development tools such as open large model invocation, visual task flow orchestration, AI and system tool components, data processing and storage, low-code application construction, and monitoring and operation.
Kingdee: AI Management Assistant Cosmic
In May, Kingdee introduced Cosmic, an AI management assistant for enterprise management, embodying super intelligence.
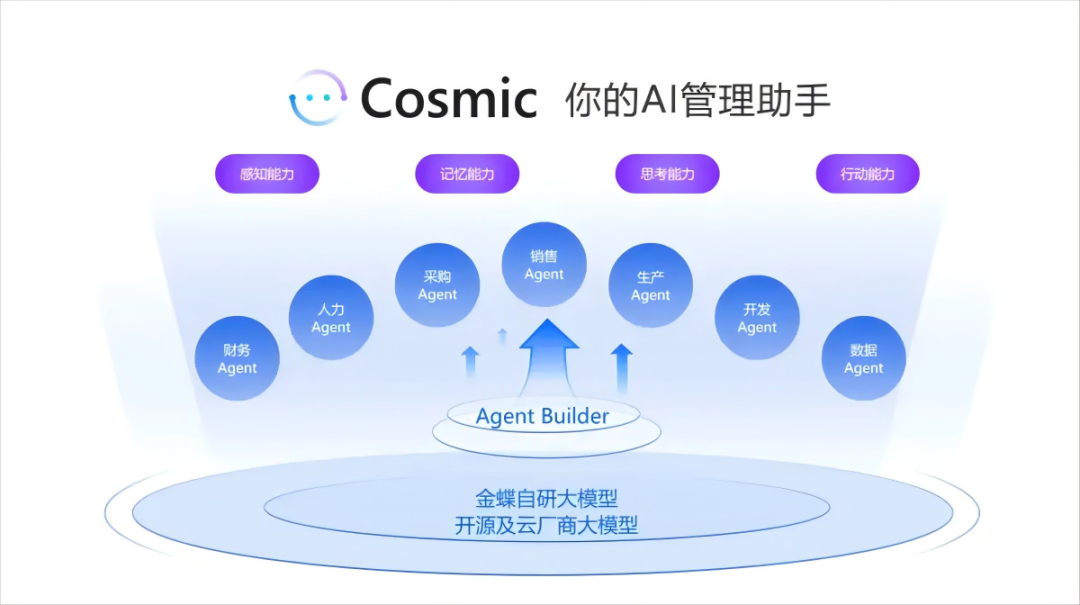
Drawing on Kingdee's practical experience across over 7.4 million enterprises and trillions of training data, Cosmic possesses perceptual abilities for listening, speaking, reading, and writing, as well as memory capabilities to accumulate and leverage management experience. It can comprehend and plan, mobilize systems, and execute actions. Through conversational interactions and collaborative, scalable AI applications, Cosmic empowers managers and employees to effortlessly tackle various management tasks such as financial management, data analysis, contract processing, and cadre selection, streamlining and enhancing enterprise operations.
Currently, Cosmic covers diverse business scenarios including finance, human resources, and supply chain, striving to "make every individual have an AI management assistant." Additionally, Cosmic empowers Kingdee's various SaaS products targeting large, medium, and small markets through AI capabilities.
Yonyou: Agent Based on YonGPT 2.0 Model
In August, Yonyou officially unveiled YonGPT 2.0, its enterprise service large model. Currently, based on YonGPT 2.0, Yonyou BIP boasts three key products: "ZhiYou" (Intelligent Agent), "Digital Intelligence Employee," and "Intelligent Search," each built upon Intelligent Agent (Agent), Human-Computer Interaction (HCI), and RAG application frameworks, respectively. It also offers over 100 scenario-specific enterprise intelligence services, including smart contracts, smart order generation, smart monthly closing, AI interviews, and smart talent discovery.

The YonGPT 2.0 large model serves as the platform layer, underpinned by generalized professional capabilities such as enhanced domain knowledge Q&A, PPT analysis report generation, and smart contract review, ensuring model support for business foundational capabilities. At the platform layer itself, various "experience data" are embedded to help the model fine-tune through several application frameworks based on professional data to ensure model effectiveness.
For instance, in case of business operational issues, the Agent application framework can be fine-tuned; for human-computer interaction problems, the HCI application framework can be adjusted; and for knowledge generation or application generation issues, the RAG business framework can be leveraged for fine-tuning. Based on these application frameworks, enterprises can also leverage the AI Agent (Intelligent Agent) builder to rapidly construct agents tailored to various scenario needs using applications and business knowledge from Yonyou BIP, realizing agile enterprise application innovation.
From the explorations, products, and solutions introduced by these vendors in the GenAI and AI Agent realms, it is evident that RPA technology vendors are adopting diverse approaches to evolve their platforms and meet evolving enterprise needs. Through continuous iteration and evolution, they aim to maintain sufficient market competitiveness in the AI Agent era, with strategic layouts in place.
Further Evolution of RPA
To remain relevant in the AI Agent era, RPA vendors are adopting various methods to develop their platforms and address evolving enterprise needs. Drawing from the products and solutions introduced by multiple vendors mentioned above, we can summarize the following directions for RPA evolution:
1. Enhancing RPA through AI Capabilities
One of the most adaptable approaches for RPA technology vendors is integrating AI capabilities into their platforms. By leveraging machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision, RPA bots can become smarter and more adaptable. This integration enables RPA bots to handle more complex tasks, make informed decisions, and learn from interactions with users and systems.

Integrating AI capabilities, especially GenAI, into RPA platforms opens up new possibilities for automation. AI-enhanced RPA bots do not simply follow predefined rules and workflows but can learn from data, identify patterns, and make informed decisions. This allows enterprises to automate more complex cognitive tasks such as fraud detection, sentiment analysis, or predictive maintenance.
AI-enhanced RPA bots can also continuously improve their performance over time through machine learning. By analyzing their operational results and receiving user feedback, these bots can fine-tune their algorithms and adapt to evolving business needs. This self-learning capability ensures that RPA solutions remain relevant and effective over the long term.
2. Focusing on End-to-End Automation
RPA technology vendors are shifting their focus from automating individual tasks to achieving end-to-end automation across entire processes. By integrating RPA with AI Agents and other automation technologies, vendors aim to provide seamless and intelligent automation experiences.
End-to-end automation encompasses integrating RPA with AI agents, Business Process Management (BPM) tools, and low-code platforms; orchestrating data and task flows across multiple systems and applications; and providing a unified platform for managing and monitoring automation initiatives.

The goal of end-to-end automation is to streamline and optimize entire business processes from end to end. Rather than automating isolated tasks, RPA vendors' solutions focus on creating holistic automation solutions that can handle complex workflows spanning multiple systems and departments.
For instance, an end-to-end automation solution integrating AI Agents and RPA for a typical procure-to-pay process in an organization would involve:
An AI Agent that interprets and extracts relevant information from purchase requisitions and invoices;
An RPA bot that validates extracted data against business rules and inputs it into appropriate systems;
A BPM tool that coordinates tasks and approval flows across different departments and stakeholders;
A low-code platform enabling business users to customize and extend automation solutions as needed.
By providing end-to-end automation solutions, RPA vendors can help enterprises achieve greater efficiency, accuracy, and agility in their operations. These solutions enable organizations to break down silos, eliminate manual handoffs, and gain real-time visibility into their processes.
3. Empowering Citizen Developers
Another strategy adopted by RPA vendors is empowering citizen developers to create and manage their own automation solutions. By providing user-friendly interfaces and low-code tools, vendors enable business users with minimal programming experience to build and deploy RPA bots and AI Agents.
Supporting citizen developers offers several benefits, including faster development and deployment of automation solutions; reduced reliance on IT departments and specialized skills; and improved agility and flexibility in adapting to evolving business needs.
RPA vendors' low-code platforms allow business users to create automation solutions using visual drag-and-drop interfaces and pre-built templates. These platforms abstract the complexity of programming, enabling citizen developers to focus on designing the logic and workflows of their automation solutions.
For example, a marketing manager can use a low-code RPA platform to automate the process of collecting and analyzing social media data. By dragging and dropping data connectors, data transformation AI models, and other components, they can create custom automation solutions without writing any code.
By democratizing automation, RPA vendors can tap into broader markets and expand their customer base beyond large enterprises to include specialized IT teams. Small and medium-sized enterprises can also benefit from the power of automation without significant upfront investments or technical expertise.
What are the advantages of RPA-based AI Agents?
After ChatGPT ignited the era of large language models at the end of 2022, RPA hyperautomation vendors emerged as one of the fastest to adopt GenAI technology. From then until now, most vendors have undergone at least two iterations, from integrating GenAI technology to applying AI Agent technology.
Beyond enhancing product capabilities and reducing resource consumption, the primary objective of this evolution is to compete in the market against OpenAI, Google, startups, and existing portfolio vendors.
As mentioned earlier, many RPA vendors have launched products and solutions integrating GenAI and AI Agents, showcasing how IT can build robots, create document extraction models, arrange complex business trips, and provide healthcare guidance. However, many organizations remain skeptical about RPA vendors' ability to sustain innovation in GenAI integration.
In this regard, Craig Le Clair, Vice President and Principal Analyst at Forrester, who is optimistic about RPA vendors, offers six compelling reasons. Here they are:
1. LLMs will initially be adopted for micro-automation, providing low-level cognitive support. Many such applications will occur in operational or backend processes, representing the sweet spot for GenAI integration with RPA. We're already seeing GenAI combined with RPA bots or digital process automation (DPA) workflows, which will become the mainstream for enterprise business process automation.
2. RPA platforms are well-suited for building advanced AI Agents that act on behalf of enterprises or individuals, without extensive programming rules. AI Agents are a crucial trend, making decisions and actions with varying degrees of autonomy to execute services. For example, RPA-based Agents (RPA Agents) receive alerts from banks' anti-money laundering systems, integrate public and private data archives, and complete Level 1 investigations, significantly reducing false positives – previously unachievable with rule-based AI+RPA.
3. Mature RPA platform architectures can manage thousands of automations, indicating a surge in centralized AI Agent management. RPA vendors have invested in process intelligence for "dynamic work management." Forrester predicts that by 2026, data mined from running processes will manage work between humans and AI Agents.
4. With widespread RPA deployment, organizations are eager to expand AI Agents based on RPA. Thousands of companies have established RPA platforms and are willing to inject LLM-based Agents to enhance technology investments and ROI.
5. RPA's rapid growth is partly due to its ease of integrating with existing work modes through UIs, valuable for smarter Agents in the future. RPA leaders are investing in AI-driven workflows for more robust end-to-end orchestration, expected to be widely adopted by 2027.
6. GenAI's biggest challenges are trust and data security. For over a decade, RPA platforms have addressed security management automation. One challenge is securing human credentials for robots accessing core systems, which current GenAI startups and hyperscalers struggle with.

Among these six reasons, the second is particularly crucial. To compete with large language model enterprises, tech giants, and AI Agent providers, RPA platforms must position themselves as the preferred solution for building, deploying, and managing these intelligent agents. This means providing robust tools and frameworks for enterprises to easily create, deploy, and maintain AI Agents.
Hyperscalers and startups may favor generic solutions over use-case-specific ones, potentially limiting buyers to specific platforms. RPA Agent solutions should cater to hyperscalers and startups alike, transcending use-case specificity.
To succeed in competition, RPA platforms must remain agnostic, not reliant on specific technologies or platforms. This ensures adaptability to evolving tech landscapes and meets diverse customer needs. RPA platforms and their service partners are more likely to succeed by offering domain-specific AI Agents, tailored for specific industries or business scenarios, thereby providing more precise and effective solutions.
Market Opportunities in RPA and AI Agent Integration
Enterprise automation has evolved over the past decade, primarily through UI and API automation iterations. Promoted by companies like UiPath in the mid-2010s, RPA's UI automation capabilities fueled the rise of low-code business applications.
Despite initial skepticism about RPA's stability and automation longevity, many enterprises have established Centers of Excellence for Automation and progressed to Intelligent Automation (IA), integrating RPA, API automation, OCR document processing, and more. This marks a shift from simple click automation to more complex process automation.
These tools combine coding and low-code, requiring specialized skills for deployment but remain rule-based, suitable for structured processes.
In contrast, AI Agents employ advanced planning and execution strategies, flexibly understanding unstructured data and processes. They excel in tasks not easily defined by rules, demonstrating greater adaptability and resilience than traditional RPA. They can self-correct errors or seek human assistance.
While AI Agents revolutionize enterprise automation, RPA is not obsolete. Rule-based automation remains optimal for tasks requiring massive repetitive data entry or migration, like entering 1,000 records daily into an ERP system or migrating 100,000 electronic health records. Tool selection depends on task nature.
AI Agents broaden enterprise automation boundaries. As a nascent category, extending Agent reasoning to existing automation routines offers the simplest path to expanding Agent use cases. Over time, AI Agents will penetrate strategic core business workflows.
Antti Karjalainen, co-founder of sema4.ai, divides AI Agent and enterprise automation structures into three tiers, as illustrated below:
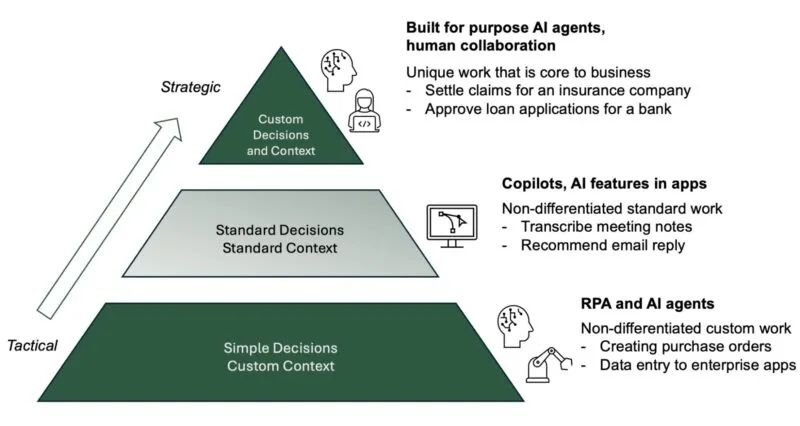
Tier 1: Involves tactical tasks requiring no complex decisions but specific contexts, handling enterprise-specific data, documents, and systems. RPA's strength and an ideal starting point for AI Agent projects. By identifying opportunities in RPA routines' workflows, Agents can expand automation scope, leveraging AI Agents to go beyond standard RPA reach.
Tier 2: Ascending the pyramid, this tier involves standard decisions in standard environments, embodied in Copilot products and workflows. Typically captured by platforms like ServiceNow or Salesforce, this tier thrives on users' ability to innovate with vendors' AI, automation solutions, data, and processes. Future enterprise automation will fully integrate AI Agents and RPA in Copilot forms, presenting significant RPA opportunities.
Tier 3: At the pyramid's peak, this strategic tier involves complex decisions and specific contexts, core to an enterprise's existence. Customized enterprise-grade AI Agents tailored for specific purposes will drive future enterprise development.
From these three tiers, enterprises should experiment and integrate within their existing RPA hyperautomation frameworks to maximize RPA-based AI Agents and hybrid intelligent workflows in business processes, supporting strategic and tactical applications alike.
This integration process presents opportunities for RPA and Agent vendors alike.
RPA Market Trends in the Agent Era
Gartner's Magic Quadrant for RPA reveals sustained high growth. In 2022, the RPA software market reached $2.8 billion, growing at 22.1%, double the global software market average. Even amidst the rise of generative AI and large language models in 2023, RPA maintained a 22% growth rate, reaching $3.2 billion.

Gartner's 2023 RPA Magic Quadrant highlights three key trends:
1. AI at the Core of RPA Vendor Strategies: To navigate AI and LLM hype, RPA vendors strategically position their platforms as AI-centric essentials for the future. Vendors design product roadmaps focusing on AI trust, risk, and security management (TRiSM), enhanced AI skills and studios, expanded access to general-purpose LLMs (from Amazon, Anthropic, OpenAI, etc.), and proprietary specialized LLMs. Short-term, customers can expect improved self-healing, script fixing, and IDP extraction accuracy in RPA platforms' AI development capabilities.
2. Substantial Investments in GenAI Automation Development: RPA vendors heavily invest in GenAI to aid automation development. Most focus on hint-based development, converting natural language requests into automated workflows, lowering technical barriers and broadening access for citizen developers. While useful for initiating larger automation efforts or designing simple workflows, hint-based development is limited for complex end-to-end automation. Customers should try hint-based automation if these emerging features are reasonably priced. Long-term, customers expect advanced AI-enhanced automation development, with GenAI potentially extracting recordings from task mining to autonomously build automations mimicking employees' routine tasks – a crucial step toward autonomous businesses.

3. Broader Orchestration and Automation Offerings: Most RPA vendors now provide platforms beyond RPA, supporting multiple automation technologies (IDP, BPA, conversational AI, LCAP, process mining, task mining, test automation, iPaaS). Integration into larger automation platforms necessitates robust orchestration across native and third-party solutions. Customers want creative packaging and pricing from RPA providers, recognizing customers' reluctance to pay for unneeded technologies. However, if bundled in low-cost, low-risk packages, customers may trial these technologies. To leverage bundled automation, customers should seek platforms with strong process modeling, governance, and unified user experiences.

These three trends essentially emphasize two points: AI, especially GenAI, is becoming RPA's core, facilitating simpler, deeper applications. Post-GenAI integration demands stronger native integration, third-party solutions, and orchestration capabilities. These factors determine RPA platforms' ability to integrate GenAI faster and better, forming enterprise-grade solutions for organizations. RPA vendors with years of experience and end-to-end automation platforms are best suited for this, an advantage lacking in generic AI Agent platforms.
RPA's Future in the AI Agent Era
As AI Agents evolve and become more complex, RPA's role will undoubtedly change, but it won't become obsolete. RPA vendors must adapt and integrate with AI Agents to provide more comprehensive, intelligent automation solutions. Here are possible futures for RPA in the AI Agent era:
RPA and AI Agent Integration: RPA's future lies in tight integration with AI Agents. This integration goes beyond technical combination; it's about workflow complementarity. RPA's precision and efficiency, combined with AI Agents' intelligent decision-making and learning capabilities, will propel automation to new heights.
Seamless integration and hybrid automation
The seamless integration between RPA robots and AI agents will make the automation process smoother and more efficient. For example, AI agents can handle complex tasks such as natural language understanding and image recognition, while RPA robots can perform rule-based repetitive operations. This hybrid automation solution can handle both structured and unstructured data, providing a more comprehensive automation service.
Intelligent orchestration and continuous learning
In the intelligent automation architecture, intelligent orchestration of tasks and workflows will be crucial. RPA and AI agents will be able to coordinate across multiple systems and technologies to achieve end-to-end automation. Furthermore, through continuous learning, automation solutions can self-optimize based on data and user feedback, adapting to ever-changing business needs.
Specialized and verticalized automation solutions
The future of RPA may also involve the development of more specialized and verticalized automation solutions. This means that RPA vendors will need to deeply understand the needs of specific industries and create customized templates, pre-built integrations, and AI models. For example, in healthcare, automation solutions may need to handle patient data and medical records, while in finance, they may need to process transaction data and risk assessments.
Rise of the 'as-a-service' model
With the development of cloud computing technology, the 'as-a-service' model for RPA and AI is becoming increasingly popular among enterprises. This model allows companies to access various RPA robots, AI agents, and automation tools by subscribing to cloud platforms, eliminating the need to purchase and deploy automation solutions locally. This approach not only reduces initial investment costs but also allows for flexible resource adjustments based on actual usage, enabling pay-as-you-go pricing.
A future of human-machine coexistence
As RPA and AI technologies continue to evolve and converge, future work scenarios may place greater emphasis on human-machine coexistence. In this model, humans, RPA robots, and AI agents will each leverage their strengths, complementing each other's capabilities. Humans will focus on creative and strategic tasks, while RPA robots and AI agents will handle repetitive and technical tasks. This symbiotic relationship will enhance work efficiency, unleash human potential, and provide broader application spaces for RPA and AI agents.
In summary, the integration of RPA and AI agents opens up endless possibilities in the field of automation. Through seamless integration, intelligent orchestration, specialized customization, and the 'as-a-service' model, enterprises can build smarter, more flexible, and efficient automation solutions to address increasingly complex business challenges.
The end of the text
Note: For RPA-related articles, please reply with the keyword 'RPA' in the background. [Wang Jiwei Channel, focusing on AIGC and IoT, specializing in digital transformation, business process automation, and AI agents, welcome to follow and communicate.]