The Swift Progression of AI Large Models Fuels the Expansion of the Switch Market
![]() 12/23 2025
12/23 2025
![]() 588
588
A switch serves as a pivotal network device tasked with forwarding electrical (or optical) signals, thereby furnishing dedicated electrical signal pathways for any pair of network nodes it connects. Its fundamental role revolves around data forwarding based on MAC addresses. By assimilating the correlation between device MAC addresses and ports, it constructs a MAC address table, thereby facilitating efficient data transmission. Switches constitute one of the cornerstone devices within computer networks.
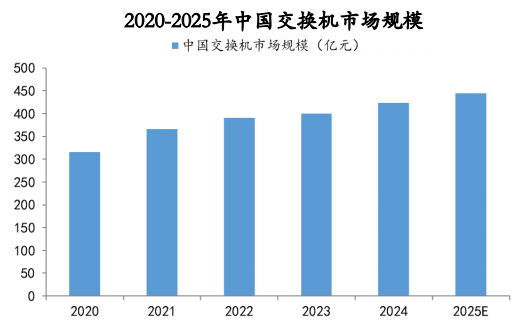
Propelled by policy initiatives, Chinese switches exhibit substantial potential for growth, with the market size demonstrating a steady upward trajectory. Forecasts indicate that the Chinese switch market is poised for a 5.9% year-on-year expansion in 2024, reaching an estimated value of approximately 42.36 billion yuan. By 2025, the market size is projected to escalate to 44.48 billion yuan.
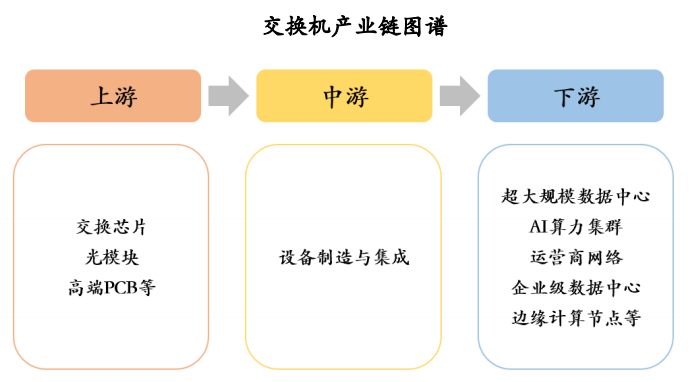
The switch industry has established a relatively comprehensive ecosystem. The upstream sector is underpinned by core components and software, with Ethernet switching chips, optical modules, and PCBs constituting the hardware backbone. The midstream sector encompasses equipment manufacturing, while downstream applications span hyperscale data centers (such as Alibaba Cloud and Tencent Cloud), AI computing clusters, operator networks (including China Mobile and China Telecom), and the enterprise market. Initiatives like the East Data West Computing project and the AI boom are driving the large-scale deployment of 400G/800G high-speed switches. The entire industry chain is accelerating towards high-end and sustainable development, propelled by the dual forces of policy support and technological innovation.
From the perspective of switch cost composition, switches are primarily constructed from chips, optical components, connectors, passive components, housings, PCBs, and other parts. Chips account for the highest cost share at 32%, followed by optical components (14%), connectors (10%), passive components (10%), housings (8%), and PCBs (7%).
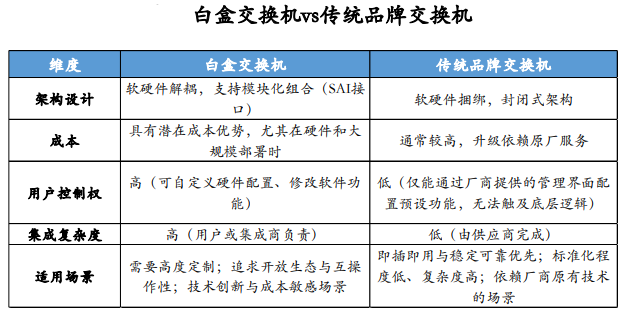
Traditional brand switches are characterized by closed hardware and software systems, leading to suboptimal device interoperability, complex operation and maintenance management, and challenging fault localization. Furthermore, the closed architecture imposes restrictions on subsequent upgrades and expansions. In contrast, white box switches represent open network devices with decoupled hardware and software, adopting an open architecture of "commercial hardware + open operating system" that supports flexible configuration management. The core essence lies in dismantling the traditional "hardware-software bundling" model, empowering users to customize network functions as per their requirements. They offer advantages in terms of flexibility, efficiency, and programmability, while simultaneously reducing network deployment costs.
The fundamental disparities between the two types of switches lie in the transparency of their internal structure, user control rights, and hardware-software decoupling. White box switches afford users a high degree of control over the underlying layer, rendering them suitable for technological innovation and cost-sensitive scenarios. Conversely, traditional brand switches (often referred to as black boxes) excel in providing out-of-the-box convenience, making them ideal for standardized needs and rapid deployment.
White Box Switches:
① Hardware Level: Comprises components such as switching chips, CPUs, and network cards, adhering to OCP standardization norms to ensure versatility.
② Software Level: Centered around network operating systems and applications, providing support for functional expansion.

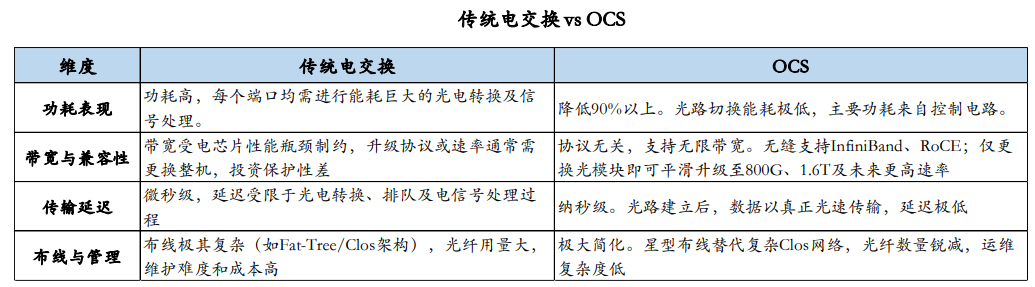
As AI large model training enters the era of "ten-thousand-card clusters," traditional electrical switching-based network architectures are encountering bottlenecks characterized by high network power consumption and elevated bandwidth requirements. OCS, or optical circuit switch, represents a network device that directly exchanges and reconstructs optical signal paths within the optical domain. Its core advantage lies in establishing end-to-end pure optical physical channels without the need for optical-electrical-optical (O-E-O) conversion. The "all-optical switching" mechanism renders it completely transparent to signal rates, protocols, and modulation formats, enabling seamless support for services ranging from 400G to future rates of 1.6T and beyond, thereby fundamentally ensuring ultimate network bandwidth and forward compatibility.
OCS has broad application prospects:
① Hyperscale AI training: Serves as the primary driving force, providing critical support for next-generation AI clusters constructed by industry leaders such as Microsoft and Meta.
② Dynamic task scheduling: Highlights its unique advantages by enabling on-demand network reconstruction (e.g., All-to-All, Ring) to significantly optimize GPU utilization.
③ Heterogeneous computing interconnection: Defines future architectures by providing an ideal interconnection solution for the pooling and flexible scheduling of CPU, GPU, and storage resources.
Advances in AI large models drive the application of high-bandwidth switching chips.
The bandwidth requirements for switching chips vary across different application scenarios. Switching chips for home switching devices typically operate at the 100-megabit level, those for small enterprise switching devices usually function at the gigabit level, those for large enterprise switching devices generally range from the gigabit to 10-gigabit level, and those for data centers and operators typically boast bandwidths spanning from 25G to 400G.
Recent frequent news releases indicate the successive launch of AI large models with ten-thousand-card scales, with models featuring 100,000 cards and even larger scales on the horizon. Smart computing center networks have undoubtedly emerged as a focal point, with network bandwidth and low latency emerging as key bottlenecks for large-scale networking.
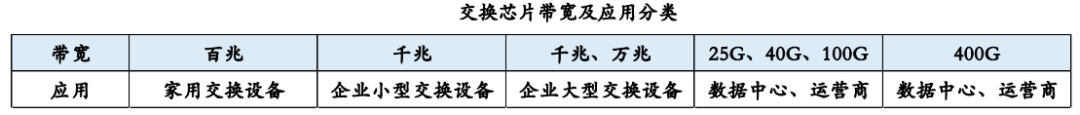
The production and manufacturing of switching chips face new challenges.
The semiconductor and integrated circuit industry primarily operates under two models: the Integrated Device Manufacturer (IDM) model and the vertical division of labor model. Under the IDM model, a company independently undertakes all stages of chip design, wafer fabrication, and packaging and testing, necessitating substantial technical reserves and financial strength. The vertical division of labor model encompasses Fabless companies, Foundry companies, and packaging and testing foundries. Under this model, different companies specialize in various links of the industry chain. Fabless companies concentrate on product R&D and design, outsourcing wafer fabrication, packaging, and testing to Foundry companies and packaging and testing foundries to achieve a precise allocation of technical and financial resources.
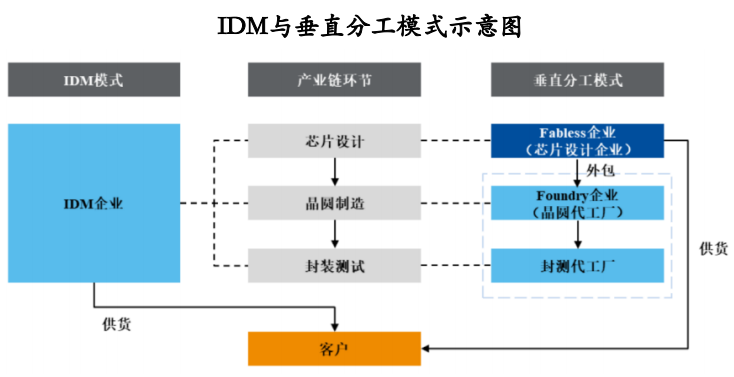
Prior to the 1980s, the global semiconductor industry was predominantly governed by the IDM model. However, factors such as high industry barriers and lengthy product cycles somewhat constrained industry development. In the late 1980s, with the emergence of Foundry companies in Taiwan, China, various links of the semiconductor industry chain began to differentiate. The Fabless and Foundry models gradually gained industry recognition, with their market shares increasing annually.
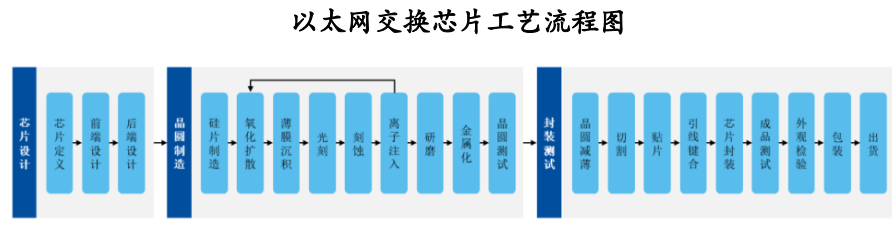
It is advisable to pay attention to domestic-related listed companies such as Shengke Communication, ZTE Corporation, Ruijie Networks, and Unisplendour Corporation.

Disclaimer: The individual stocks or companies mentioned in this article are solely representative of their association with the industry chain or hot topics. The information, data, and viewpoints cited are for personal research records only. The mention of individual stocks or companies is for case study purposes and does not constitute any buying or selling recommendations.
Shengke Communication (688702): A leading domestic designer of Ethernet switching chips.
ZTE Corporation (000063): A provider of ICT products and solutions.
Ruijie Networks (002396): An industry-leading provider of ICT infrastructure and solutions.
Unisplendour Corporation (000938): Ranked among the top in the domestic switch market share.






