Commercial Space Industry Sees Ongoing "Limit-Up Surge": SSE Unveils Listing Standards for Commercial Rocket Firms
![]() 12/29 2025
12/29 2025
![]() 450
450

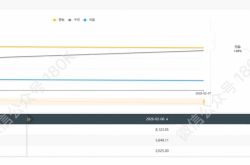
Recently, the A-share commercial space sector has been riding a wave of "limit-up surges," emerging as one of the hottest investment areas in the capital market. By the day's trading close, China Satellite had achieved limit-up for three consecutive days, with its total market capitalization nearing RMB 100 billion and trading volume approaching RMB 13 billion. Over a dozen stocks, including Aerospace Development and Guanglian Aviation, soared by more than 10%. The Commercial Space Index has accumulated an 80% gain year-to-date, reaching an all-time high.
Behind this surge lies a convergence of policy incentives, rapid technological advancements, soaring market demand, and increased capital inflows. This marks a pivotal turning point as China's commercial space industry transitions from technological demonstration to large-scale commercialization.
Commercial Space Industry Elevated to National Strategic Priority
In November, the China National Space Administration (CNSA) established a dedicated Commercial Space Bureau and unveiled the "Action Plan for Promoting High-Quality and Safe Development of the Commercial Space Industry (2025-2027)." The plan explicitly aims to "cultivate 4-5 leading enterprises with a scale of RMB 4-5 trillion by 2027 and establish a RMB 20 billion national commercial space development fund."
This dual approach of policy liberalization and financial support has removed institutional barriers for the industry. For instance, restrictions on weapons research and production licenses for commercial satellite development were lifted, enabling enterprises to freely pursue technological innovation. The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) initiated commercial trials for satellite-based IoT, facilitating the penetration of direct-to-satellite terminal technology into consumer markets.
Local governments have also responded proactively. Beijing, Shanghai, and Hainan have introduced specialized policies, creating a synergistic "national-local" policy framework. Hainan's commercial space launch site set a new record by completing a launch just three days after site transition, advancing toward high-density launch capabilities. The STAR Market reinstated its fifth set of listing criteria, opening financing channels for companies like Landspace and CAS Space to accelerate capitalization.
Technological Breakthroughs Drive Industry Momentum
Technological maturity is the core driver behind the commercial space boom. In December 2025, the Long March 12A carrier rocket completed its inaugural orbital-level liquid oxygen/methane rocket flight test at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center. Although the first-stage recovery fell short of expectations, key engineering data was validated.
Landspace's "Zhuque-3" Yao-1 rocket successfully reached orbit, marking the first time a private rocket company has demonstrated genuine launch capacity. According to Soochow Securities, China is projected to master rocket recovery technologies by 2026, reducing launch costs by 70-90% and potentially lowering single-launch costs to below RMB 100 million, ushering in an era of "scheduled satellite launches."
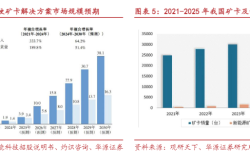
In satellite manufacturing, batch production capabilities have significantly improved. The Hainan Wenchang Satellite Super Factory is designed to produce 1,000 low-Earth orbit (LEO) satellites annually, while production lines in Tianjin and Beijing have achieved modular design and automated testing, shortening single-satellite development cycles from years to months. Major projects like China Starnet and the G60 Qianfan Constellation are accelerating network deployment, with over 200 satellites already in orbit as of December and a projected total exceeding 1,000 by 2026, forming a globally leading LEO satellite internet infrastructure.
LEO Constellations Fuel Industry Growth
The construction of LEO satellite constellations has created massive launch demand, becoming the core engine of industry growth. It is estimated that China's commercial launches will exceed 90 in 2025, a 46% year-on-year increase, with LEO satellite internet launches accounting for over 60% of the total. Satellite internet not only supports foundational services like broadband communication and IoT but also enables innovative applications such as 5G NTN smartphone direct-to-satellite connectivity, autonomous driving, and telemedicine. Galaxy Space is accelerating R&D of core technologies like phased-array antennas and onboard high-power systems to drive the proliferation of satellite communication terminals in consumer markets.
Space-Based Computing: The Next Frontier
Space-based computing power has emerged as the next frontier. With soaring global AI computing demand, ground-based data centers face energy consumption and cooling bottlenecks. In contrast, space-based data centers offer low energy costs and near-zero cooling expenses, making them a high-value application scenario for commercial space. Domestic institutions like Orbital Dawn and Zhejiang Lab have launched relevant initiatives, with plans to establish a gigawatt-scale centralized computing system in dawn-dusk orbits by 2026, heralding a new era of "space-based AI infrastructure."
2026: A Pivotal Year for Industry Transition
Market institutions widely believe that 2026 will be a pivotal year for the commercial space industry's transition from a "policy incubation phase" to a "regulated development phase." With the maturation of reusable rocket technologies, satellite constellation completion, and space-based computing deployment, the industry will enter a phase of normalized high-frequency launches, with 4-6 missions per month, and concentrated performance realization among chain enterprises.
SSE Unveils Listing Standards for Commercial Rocket Enterprises
On December 26, the Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE) officially released the "Guidelines for Applying the Fifth Set of STAR Market Listing Criteria to Commercial Rocket Enterprises," opening listing channels for commercial rocket companies during a critical phase of large-scale commercialization.
The Guidelines, for the first time, clarify detailed requirements for commercial rocket enterprises to apply the fifth set of STAR Market listing criteria. Replacing traditional profitability metrics, the fifth criteria emphasize "market capitalization + R&D," requiring a minimum market cap of RMB 4 billion and possession of core technological breakthroughs with interim achievements. The Guidelines further refine four core thresholds tailored to the commercial rocket industry:
- Core Business Scope: The Guidelines mandate that a company's core business must encompass "independent R&D, manufacturing, and launch services for commercial rockets," with core technology demonstrating significant advantages or breakthroughs. Key evaluation metrics include payload capacity, multi-satellite launch capabilities, and independent R&D of critical components. Enterprises undertaking national space programs will receive preferential support.
- Technological Milestones: Additionally, the Guidelines stipulate that applicants must have achieved "the first successful orbital insertion of a medium-to-large launch vehicle employing reusable technologies" and demonstrate no material risks compromising subsequent launch missions. This milestone is regarded as a critical validator of a rocket's commercial viability.
- Regulatory Compliance: Enterprises must hold commercial rocket R&D and manufacturing qualifications, with national approval secured prior to launch to ensure technical safety and regulatory compliance. They are required to occupy a significant position in the industrial chain, with a clear target market and a feasible plan transitioning from technical validation to scaled operations.
Commercial rocket development and launch services, positioned midstream in the commercial space value chain, play a pivotal "bridging" role. By 2025, China's commercial launches are projected to exceed 90, a 46% year-on-year increase. However, the industry still faces challenges such as high R&D investment, long development cycles, and incomplete scaled commercialization. The timing of these Guidelines could not be more opportune.
Policy and Technological Tailwinds Support Industry Growth
In June of this year, the China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC) issued the "Opinions on Establishing a Growth Tier on the STAR Market to Enhance Institutional Inclusivity and Adaptability," explicitly expanding the fifth criteria to encompass commercial space and other sectors. In November, the CNSA's "Action Plan for Promoting High-Quality and Safe Development of the Commercial Space Industry (2025-2027)" prioritized support for reusable rocket development, providing strategic direction for the industry.
In December 2025, Landspace's Zhuque-3 and CASIC's Long March 12A reusable rockets achieved successful orbital insertions, marking a critical advancement in China's reusable technology capabilities. According to public disclosures, domestic in-development reusable models generally exceed medium-lift rocket thresholds, approaching international heavy-lift standards.
Capital Market Sprint Accelerates
China's commercial rocket sector comprises over 20 enterprises, most still in the R&D phase and urgently requiring capital market support to overcome core technological hurdles such as rocket recovery and high-thrust engines. As of December 26's market close, the commercial space sector index surged 1.74% to a record high, with 20 constituent stocks hitting limit-up or surging over 10%, accumulating an 80% year-to-date gain.
Currently, multiple enterprises are accelerating capital operations: Landspace has completed STAR Market IPO counseling and may become the "first commercial space listing." Its Zhuque-3 rocket achieved orbital insertion in December, meeting the Guidelines' interim achievement requirements. Space Pioneer's reusable rocket, Tianlong-3, is undergoing pre-launch preparations in Jiuquan, targeting a STAR Market listing. Six enterprises, including Galactic Energy and CAS Space, completed IPO counseling filings in the second half of 2025, forming a collective sprint momentum.
SSE to Expedite Listings for Qualified Enterprises
The SSE stated it will leverage the Guidelines' release to expedite listings for qualified enterprises on the STAR Market, intensifying support for tech-driven enterprises breaking through core technologies. With precise capital allocation, enterprises will accelerate R&D in rocket recovery, high-thrust engines, and other critical areas, driving medium-to-large reusable rockets from R&D to scaled applications and gradually narrowing the gap with international leaders.
A Trillion-Yuan Industry Accelerates
As a trillion-yuan-scale emerging sector encompassing rocket launches, satellite manufacturing/operations, and space tourism, the commercial space industry is accelerating onto a fast track of development through capital empowerment. The Guidelines' release not only provides critical financing channels for commercial rocket enterprises but also aligns institutional innovation with China's national strategy of becoming a space power, securing a competitive edge in the global space race.