Shenzhen breaks out with a super IPO: Annual revenue of 900 million yuan, ranking first in China
![]() 09/19 2024
09/19 2024
![]() 613
613

Written by Pencil Road | Xin Xin
The broken phone you discarded may be lying in some corner collecting dust. But in fact, used phones also have great potential for trading. Recently, a super IPO emerged in this field - Shanhui Technology.
Its core business is mobile phone recycling. According to Frost & Sullivan data, based on the total transaction value of consumer-end recycling in 2022, Shanhui Technology is China's largest mobile phone recycling service provider focused on offline trade-ins, with a market share of approximately 8.4%, and is also China's third-largest mobile phone recycling service provider, with a market share of approximately 1.5%.
Therefore, this is undoubtedly a solid super hidden champion.
- 01 -
Founded in 2016, Shanhui Technology is located in China's Silicon Valley - Shenzhen Bao'an District. The company specializes in aftermarket trading services for consumer electronics products, particularly mobile phone recycling.
Its core business can be roughly divided into four main areas:
1. Trade-ins. Consumers can trade in their old phones and receive a certain amount of cash or discount for purchasing a new phone.
2. Recycling without replacement. Consumers sell their old phones to Aihuishou without purchasing a new one.
3. Used phone sales: After inspection, grading, and pricing, recycled phones are sold through online platforms (Shanhui Youpin) and offline channels.
4. Corporate recycling and offline sales: For example, providing bulk processing services for old phones to corporate customers and offering offline sales solutions.
Shanhui Technology has a natural predisposition for the used goods business.
Its founder is Liu Jianyi. In 2003, he worked at Tianyin Holding, China's largest mobile phone distributor, where he was responsible for expanding and managing business relationships with mobile network operators in the telecommunications sector, which helped him accumulate deep industry resources and connections. Later, Liu Jianyi also served as a supervisor at a company engaged in the buying and selling of used mobile digital products.
These experiences cultivated Liu Jianyi's industry knowledge.
In 2016, the needs of the times made him a darling of the industry. That year, Liu Jianyi founded Shenzhen Shanhui, which coincided with a critical period in the mobile phone industry. China's smartphone shipments were high, and the market was gradually shifting from an incremental to a stock market, with the disposal of a large number of "retired" smartphones becoming an industry issue.
Doing what the times require you to do immediately is going with the flow. Liu Jianyi caught the wave.
- 02 -
Of course, competition in this field is fierce, with competitors roughly divided into three categories:
1. Other mobile phone recycling service providers: Such as Huishoubao, Aihuishou, etc., which also offer trade-in and idle recycling services and sell used phones through online platforms and offline stores.
2. Official recycling channels of mobile phone brands: For example, Huawei, Xiaomi, and other brands also offer trade-in services, but mainly for their own brand of phones.
3. Used phone trading platforms on e-commerce platforms: Such as Zhuanzhuan, Xianyu, etc., which also provide used phone trading services but primarily rely on the C2C model, lacking professional inspection and pricing services.
Compared to its competitors, Shanhui's business scope differs.
1. Shanhui focuses primarily on mobile phones, while Huishoubao, Aihuishou, and others have a broader focus (electronics).
2. Shanhui focuses on recycling phones from various brands, while Xiaomi, Huawei, and others only accept their own brand phones.
3. Compared to C2C platforms like Xianyu, Shanhui operates on an S2B2C model: an ecological platform that integrates suppliers, channel partners, and consumers.
- 03 -
Since its inception, Shanhui has successively received investments from renowned institutions such as Xiaomi Group, Shunwei Capital, and Qingtong Capital, with a total financing amount exceeding hundreds of millions of yuan.
However, the company still faces severe profitability pressures in its business operations.
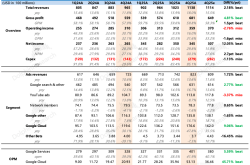
For the year ended December 31, 2021, the company's revenue was approximately RMB 749.7 million, with a net loss of approximately RMB 48.7 million.
For the year ended December 31, 2022, the company's revenue was approximately RMB 919.1 million, with a net loss of approximately RMB 99.1 million.
For the year ended December 31, 2023, the company's revenue was approximately RMB 1,158.4 million, with a net loss of approximately RMB 98.3 million.
There are several core reasons for this.
One is the decline in gross profit margin. The rapid increase in procurement costs for used phones outpaced the growth in sales, leading to a decrease in gross profit and gross profit margin. For example, its gross profit margin was approximately 8.2% in 2021, 6.1% in 2022, 6.8% in 2023, and projected to be around 4.5% in 2024.
Another factor is the rise in sales costs: As business grows and competition intensifies, sales costs (primarily procurement costs and commissions) continue to rise. Procurement costs are closely related to gross profit margin, while commissions are paid to store sales staff. Together, these costs usually account for over 90% of Shanhui's revenue for the year.
Moreover, it is difficult to see an effective way to reduce sales costs in the short term, given the relative maturity of the industry. This poses a challenge for Shanhui Technology.
This article does not constitute any investment advice.