ZTE Welcomes Its First Female Chairwoman at 40: Why Fang Rong?
![]() 04/03 2025
04/03 2025
![]() 646
646

In the post-5G era, ZTE embraces AI technology.
After four decades of establishment, ZTE has welcomed its first female chairwoman.
Following Li Zixue's resignation as chairman of ZTE due to age reasons three days ago, on March 31, ZTE (000063.SZ) announced the election of Fang Rong as the company's chairwoman. Notably, this marks the first time in ZTE's 40-year history that a woman has held this position.
On the same day, ZTE's 10th Board of Directors also appointed the company's new senior management team. Xu Ziyang continued to serve as president, while Wang Xiyu, Li Ying, and Xie Junshi were appointed executive vice presidents, responsible for R&D, finance, operations management, and marketing, respectively.

Source: Screenshot from ZTE's official website
On the same day, Fang Rong issued a letter to all ZTE employees, paying tribute to Li Zixue's contributions. The letter highlighted Li Zixue's leadership in guiding the company out of a difficult period, stabilizing operations, seizing opportunities like China's 5G construction, and setting a clear strategy for the AI era, laying a solid foundation for the company's steady development. The letter also noted that amidst the current complex and ever-changing external environment, the world has entered an AI-driven industrial revolution, presenting both opportunities and challenges. The company's transformation from full connectivity to 'connectivity + computing power' has become increasingly urgent.
Under Fang Rong's leadership, can ZTE further deepen its involvement in AI, computing power, and other sectors, accelerating its transformation?
01. Why Fang Rong?
From her public resume, it's evident that Fang Rong is not a traditional 'parachuted' executive.
According to available information, Fang Rong holds a degree in Communication Engineering from Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications and has extensive experience in the telecommunications industry, research and development, and management. She joined ZTE's controlling shareholder Zhongxingxin in 1995 and entered ZTE in 1997, serving as its senior vice president from 1998 to 2009. Since 2018, Fang Rong has been a member of ZTE's board of directors and served as a non-executive director.

Source: Screenshot from ZTE's official website
Much of Fang Rong's career has been intertwined with ZTE, with deep experience in technology research and development and years of governance as a board member. Fang Rong can be considered one of the key witnesses and drivers of ZTE's development trajectory in recent years.
Especially during ZTE's core development period from 1998 to 2009, when the company was expanding from the domestic market to overseas, Fang Rong was one of the few executives who could directly participate in top-level management discussions. Therefore, she witnessed ZTE's strategic layout and market offensive and defensive strategies during the 2G, 3G, and 4G cycles, gaining a profound understanding and grasp of ZTE's internal power structure, technology path, and corporate culture.
In 2018, after ZTE was sanctioned by the United States, the company faced a challenging period. Fang Rong, as a non-executive director, played a crucial role in rebuilding the compliance system, adjusting internal governance, and restoring market credibility. This experience as a 'crisis sharer' has given her a high degree of trust and cohesion within the organization.
Throughout her career, Fang Rong has led her team to achieve breakthroughs and large-scale commercialization in the development of communication products such as optical communications, videoconferencing, and power supplies. As an important promoter of ZTE's globalization strategy, she has successfully led her team to achieve significant breakthroughs in emerging markets like India and high-end markets like Europe.

Source: Canned image library
Fang Rong's female identity also gives this personnel change a symbolic meaning. In a technology-intensive industry like communications equipment, dominated by male engineers, promoting a woman to the highest decision-making level is a significant breakthrough in industry culture.
Looking back at Fang Rong's past activities, her public appearances and media statements are not numerous, giving the outside world an impression of rationality, restraint, and emphasis on collaboration. ZTE's choice of such a reserved chairwoman may imply the company's current core proposition: not radical expansion or passive defense, but finding the optimal solution between technical stability and strategic evolution.
From this perspective, Fang Rong, who is familiar with the company's guidelines and execution routes, appears to be the most suitable choice for ZTE at this moment.
02. ZTE's 'Stable Progress'
Fang Rong's appointment marks a significant transition for ZTE and the beginning of a new era. As a 40-year-old communications equipment enterprise, ZTE not only boasts deep technological accumulation and a global market foundation but also faces significant challenges brought about by industrial cycle changes and technological boundary reshaping.
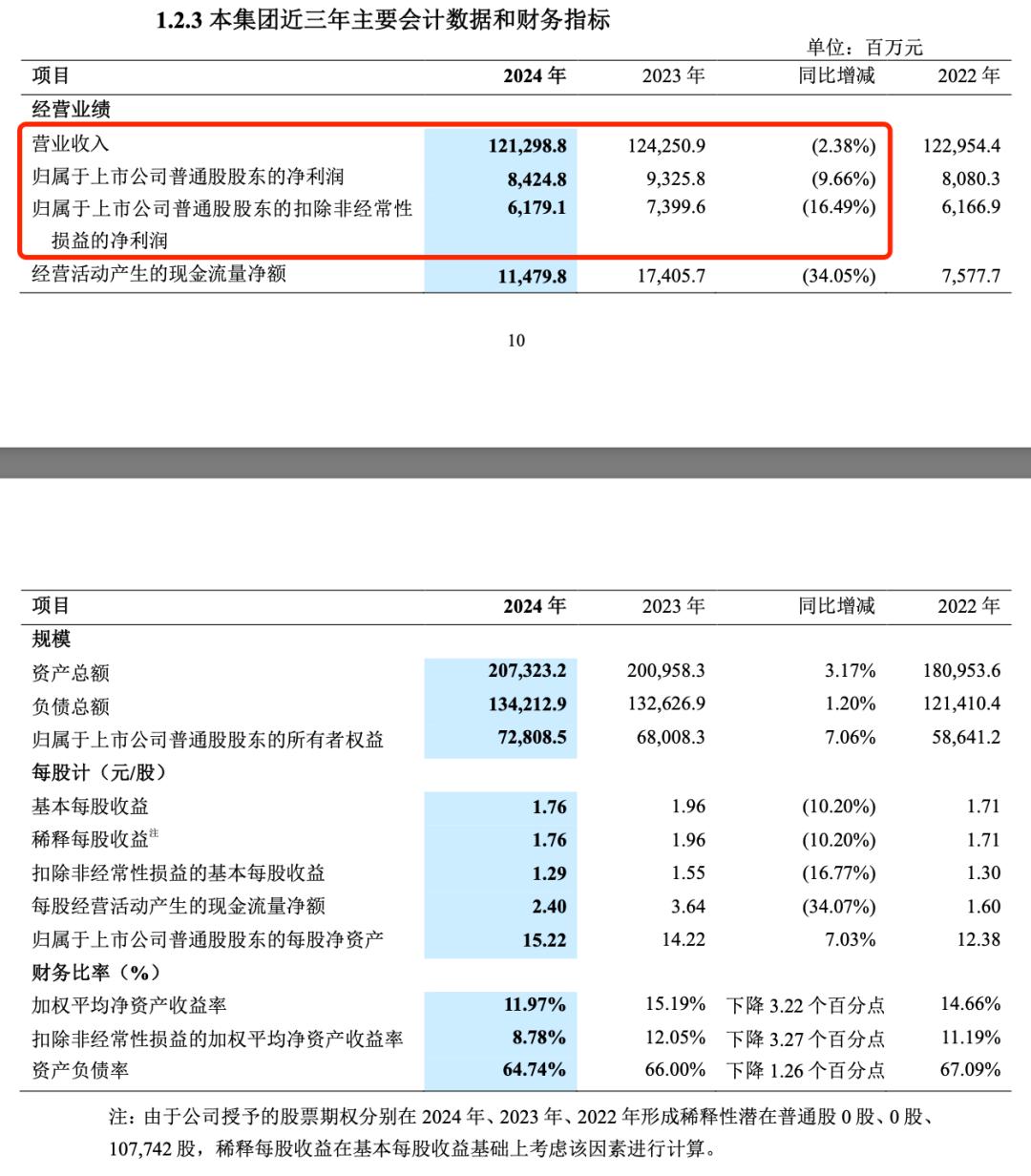
According to ZTE's financial report data, in 2024, the company faced performance pressure, with revenue of 121.299 billion yuan, a year-on-year decrease of 2.38%; net profit attributable to shareholders of listed companies was 8.425 billion yuan, a year-on-year decrease of 9.66%; and non-deductible net profit was 6.179 billion yuan, a year-on-year decrease of 16.49%. Notably, the company's non-deductible net profit loss in the fourth quarter of 2024 was 719 million yuan, marking a new low for the same period in the past six years.
Source: Screenshot from ZTE's financial report
In terms of revenue composition, ZTE's revenue primarily comes from three segments: operator networks, government and enterprise business, and consumer business. Among them, the operator network business is the core, contributing about 60% of revenue over the long term.
In 2024, the operator network business, which accounted for the largest proportion, 'lost speed,' contributing to the overall decline in ZTE's revenue. This business segment generated revenue of 70.33 billion yuan during the period, a year-on-year decrease of 15%, marking the first decline in six years. ZTE attributed this to the decline in overall investment by domestic operators.
Facing the 'cooling' of the operator market, ZTE has expanded new growth points and continued to increase its focus on government and enterprise business. In 2024, ZTE's government and enterprise business achieved revenue of 18.566 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 36.68%; however, due to market competition and price wars, the gross profit margin of this segment fell sharply from 34.94% to 15.33%. The gross profit margin of the international market also declined; in 2024, ZTE's international market revenue was 39.293 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 4.04%, while the gross profit margin of the international market fell from 36.91% to 26.91%.
To address the decline in performance, ZTE attempted to initiate a 'cost reduction and self-rescue' mode. In 2024, the company's R&D expenses, management expenses, and sales expenses fell by 4.97%, 12.05%, and 20.5%, respectively; however, these cost reduction measures have yet to reverse the decline in profitability.
Against this backdrop, Fang Rong's first priority after taking office was to stabilize the fundamentals. The communications equipment industry remains technology-intensive, with heavy asset and R&D investments and long-term returns. Therefore, deepening service capabilities within the operator network segment, expanding the international market, and compensating for the contraction of the incremental market have become the most critical short-term tasks.

Source: Canned image library
While stabilizing the fundamentals, ZTE will also prioritize AI. According to reports, networks and computing power, industry applications, and AI terminals are key directions for ZTE's AI layout. Fang Rong stated that ZTE will continue to collaborate with global partners to accelerate the deployment and upgrade of AI infrastructure, promote the integration of digital intelligent technology into various industries, and bring intelligent experiences to every consumer.
In its investor relations activity record, ZTE mentioned, 'The past three years have indeed been a plateau period for the company's revenue growth, but based on the ICT investment environment and the company's own preparations, we are confident that revenue will return to the growth track in 2025.'
It is foreseeable that as ZTE's first female chairwoman in 40 years, Fang Rong's appointment is not only symbolic but will also become a key variable in ZTE's transformation and upgrading process. Whether ZTE can seize new opportunities in this challenging industry environment will test the judgment of the new helmsman and management team on industry cycles, the mobilization of the organizational system, and the persistence in strategic direction.







