High-Definition Analysis: Exploring the 'Big Three' and 'Small Three' Electrics in New Energy Electric Vehicles
![]() 07/04 2025
07/04 2025
![]() 730
730
This collection meticulously curates a series of high-definition images, offering a comprehensive and multi-faceted view of new energy vehicles, ranging from their overall structure to the intricate internal composition of battery packs, and from motor types to the advanced functionalities of smart cabins. These intuitive illustrations demystify the core technologies of new energy vehicles, eliminating the confusion caused by complex professional terminology.
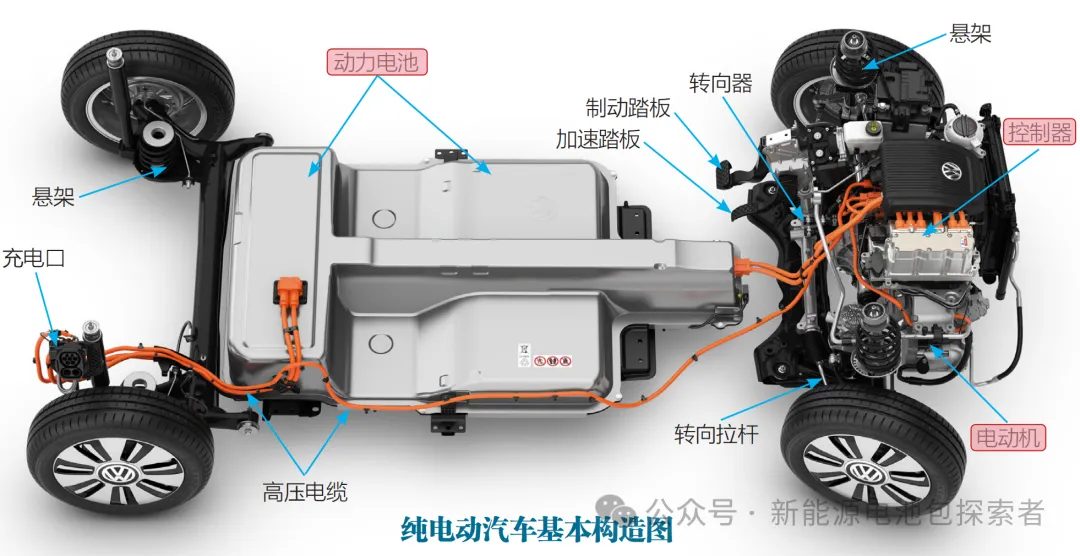
New energy vehicles, primarily electric vehicles, revolve around their electric system, which can be broadly categorized into 'Big Three Electrics' and 'Small Three Electrics'.
Big Three Electrics — power batteries, drive motors, and electric control systems, collectively determining range, power performance, and intelligence levels.
Small Three Electrics — high-voltage power distribution units (PDU), on-board chargers (OBC), and DC/DC converters, essential for power distribution, conversion, and transmission.
This article spans approximately 1400 words, accompanied by 9 images, offering an estimated reading time of 1-2 minutes.
01 Big Three Electrics: The Heart of the Power System
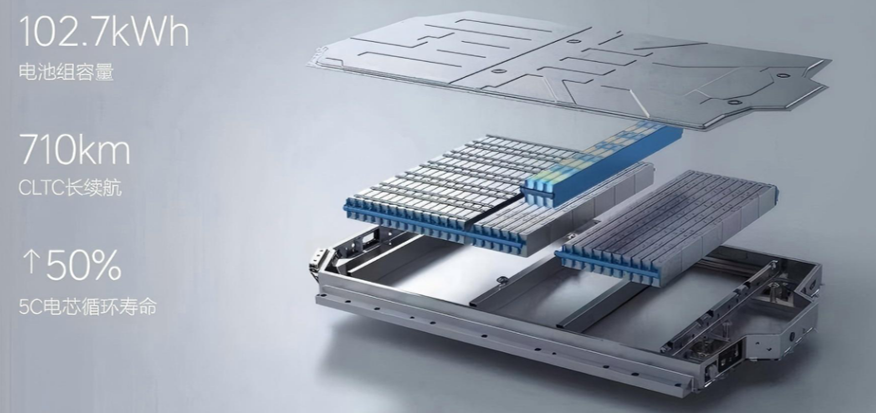
(1) Power Batteries
Function: Captures and stores high-voltage DC power from on-board chargers, generators, brake energy recovery systems, or external charging stations, and supplies this power to new energy vehicles.
Types: Ternary (NCM811, 622, 523, etc.), Lithium Iron Phosphate.
Ternary batteries, known for their high energy density, are commonly found in top-tier long-range models like the Xiaomi YU7 Max, but they come with safety concerns. Lithium Iron Phosphate batteries, on the other hand, offer superior safety and long cycle life, making them ideal for mid-to-low-end models.
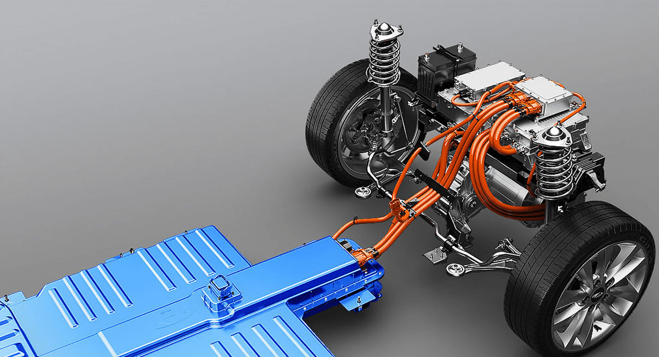
(2) Drive Motors
Role: Converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to propel the vehicle, often supporting kinetic energy recovery.
Types: Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (efficient, low noise), AC Asynchronous Motors (cost-effective, easy to maintain).
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors are used in models like BYD and Tesla Model 3/Y, while AC Asynchronous Motors are predominantly found in commercial vehicles or dual-motor four-wheel drive models.
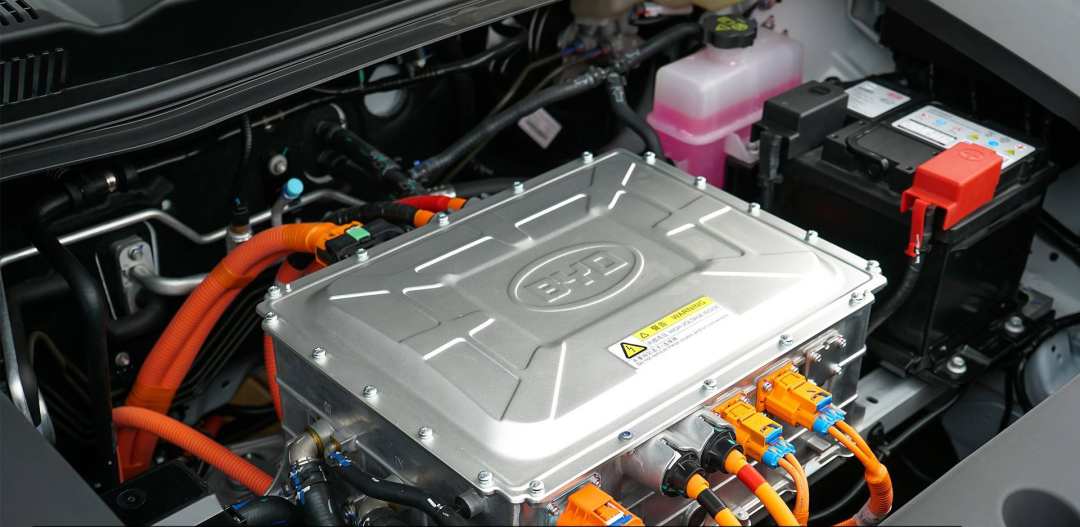
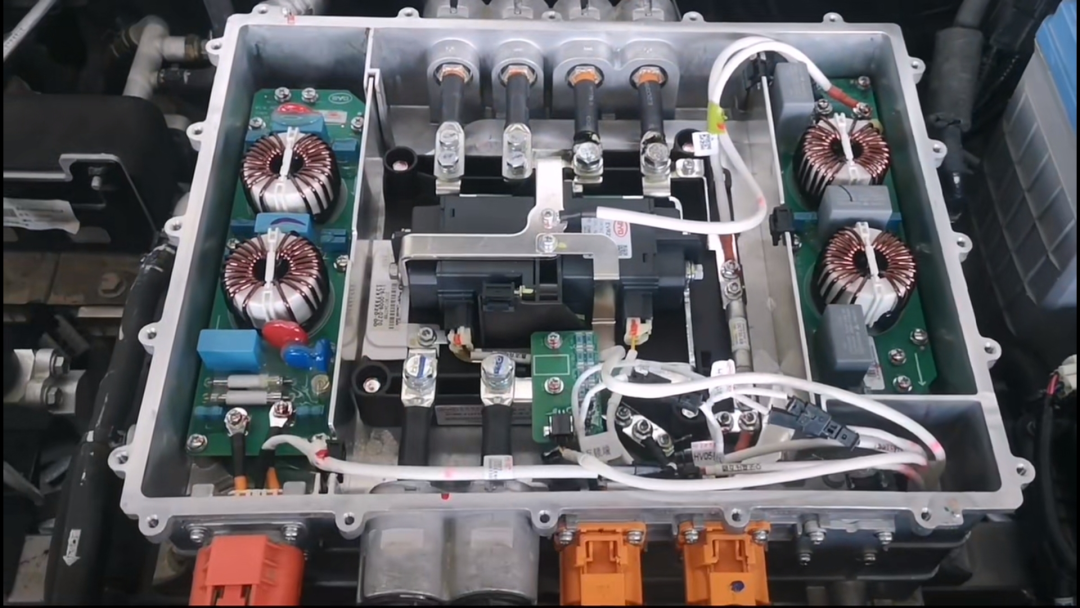
(3) Motor Controller Unit (MCU)
The electric control system serves as the nerve center of new energy vehicles, tasked with receiving operation commands from the driver, diagnosing and analyzing the status of the vehicle and its components, making informed decisions, and issuing control commands to various component controllers to ensure safe, intentional travel.
Key functions include:
- Operating condition identification
- Vehicle energy management
- Braking energy recovery control
- Motor torque control
- Electric auxiliary component control (e.g., electric power steering, electric air conditioning, electric heating, electric vacuum pump)
- Fault diagnosis
- System safety monitoring

02 Small Three Electrics: Power Distribution and Conversion Systems
Small Three Electrics encompass High-Voltage Power Distribution Units (PDU), On-Board Chargers (OBC), and DC/DC Converters.
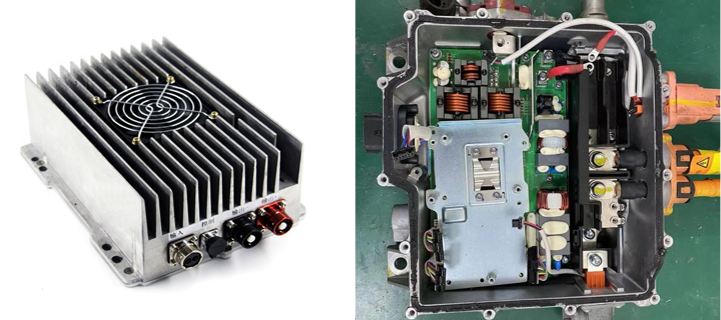
(1) High-Voltage Power Distribution Unit (PDU)
The PDU serves as a critical link between the power battery and other high-voltage vehicle components, responsible for distributing and controlling high-voltage power flow. Due to the unique electrical layout of each vehicle model, PDU products are often non-standardized.

Function: Connects high-voltage components such as power batteries, motor controllers, inverters, DC power supplies, electric air conditioning, electric defrosters, and charging sockets.
Composition: Includes copper bars, circuit breakers, air switches, contactors, soft starters, inverters, transformers, high-voltage relays, fuses, surge protectors, ammeters, voltmeters, transfer switches, etc. Currently, most PDUs are integrated within the power battery pack.
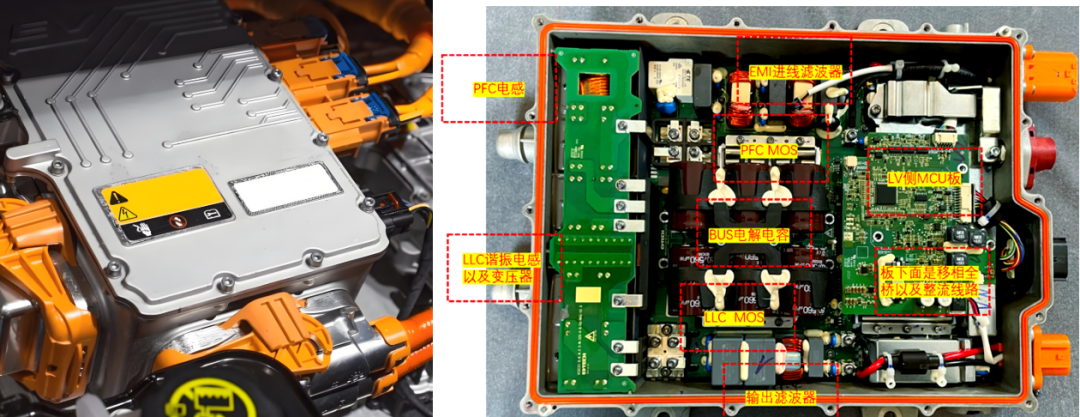
(2) On-Board Charger (OBC)
The OBC is pivotal for AC slow charging, converting AC power into DC power to recharge the power battery. It comprises power circuits and control circuits and can be unidirectional or bidirectional.
Unidirectional OBC: Simply charges the power battery with a straightforward structure.
Bidirectional OBC: Can invert the DC power of the power battery into household 220V AC power, enabling vehicle-to-grid (V2G) functionality.
(3) DC/DC Converter
The DC/DC converter transforms the high-voltage DC power from the power battery into low-voltage DC power for the vehicle's low-voltage systems. Control methods include high-voltage wakeup, hardwire activation, CAN wakeup, etc.
Function: Converts the vehicle's 336VDC or 540VDC power battery voltage to 12VDC or 24VDC, powering low-voltage electrical appliances like lights and the central console.
Composition: The mainstream electrical architecture of the DC/DC converter is phase-shifted full-bridge, employing MOS tubes for high-frequency control at 100KHz.